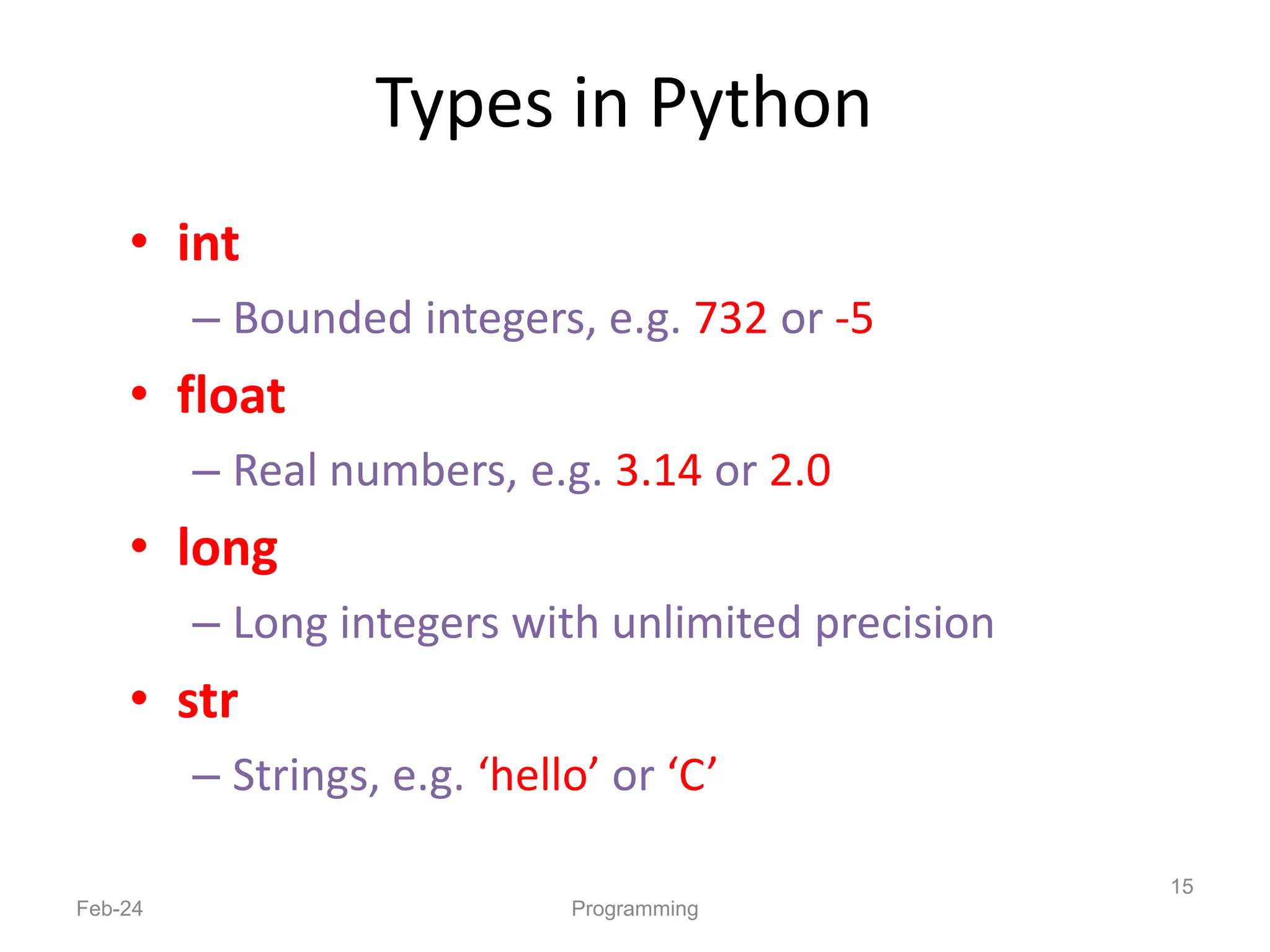
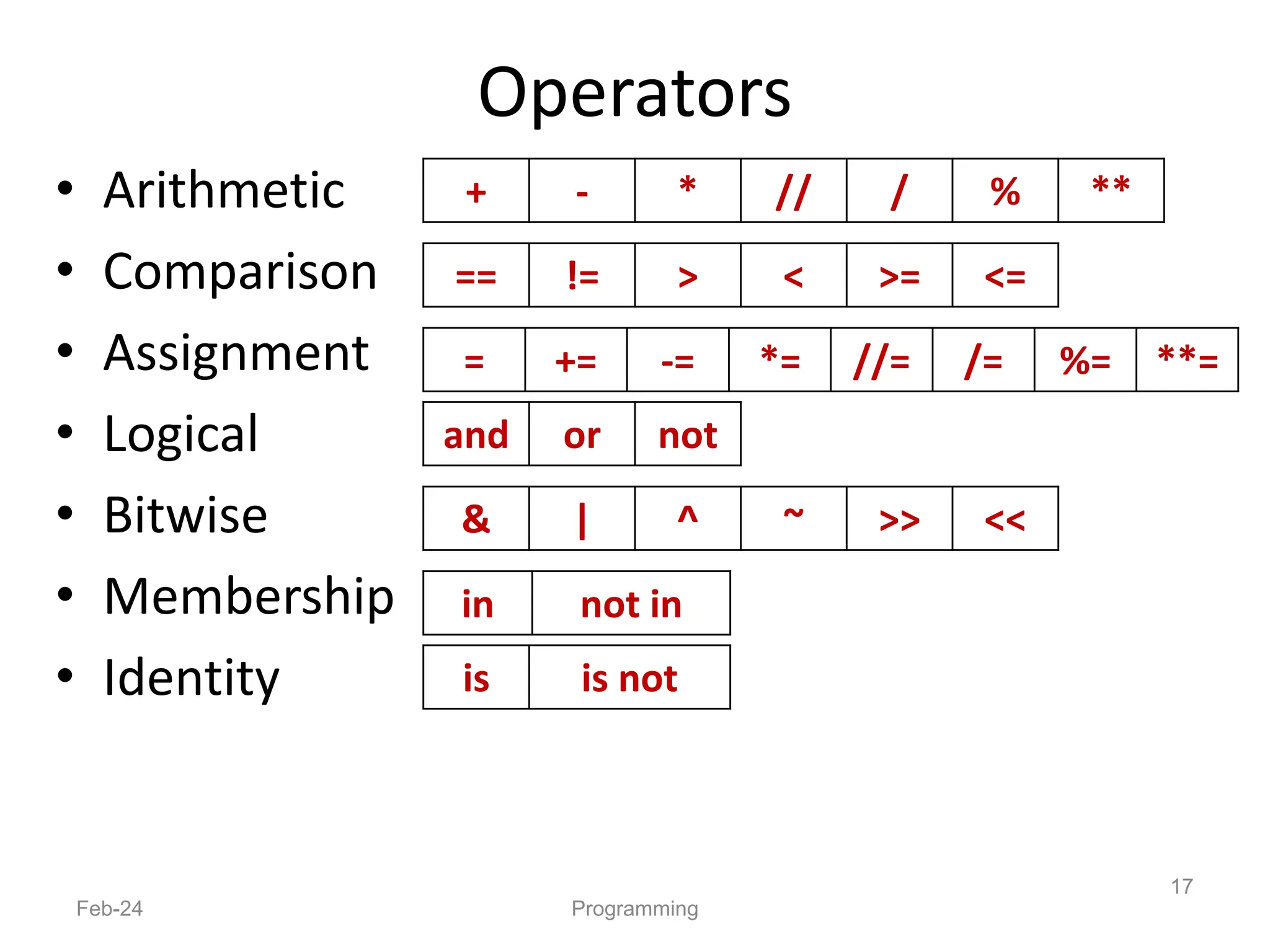
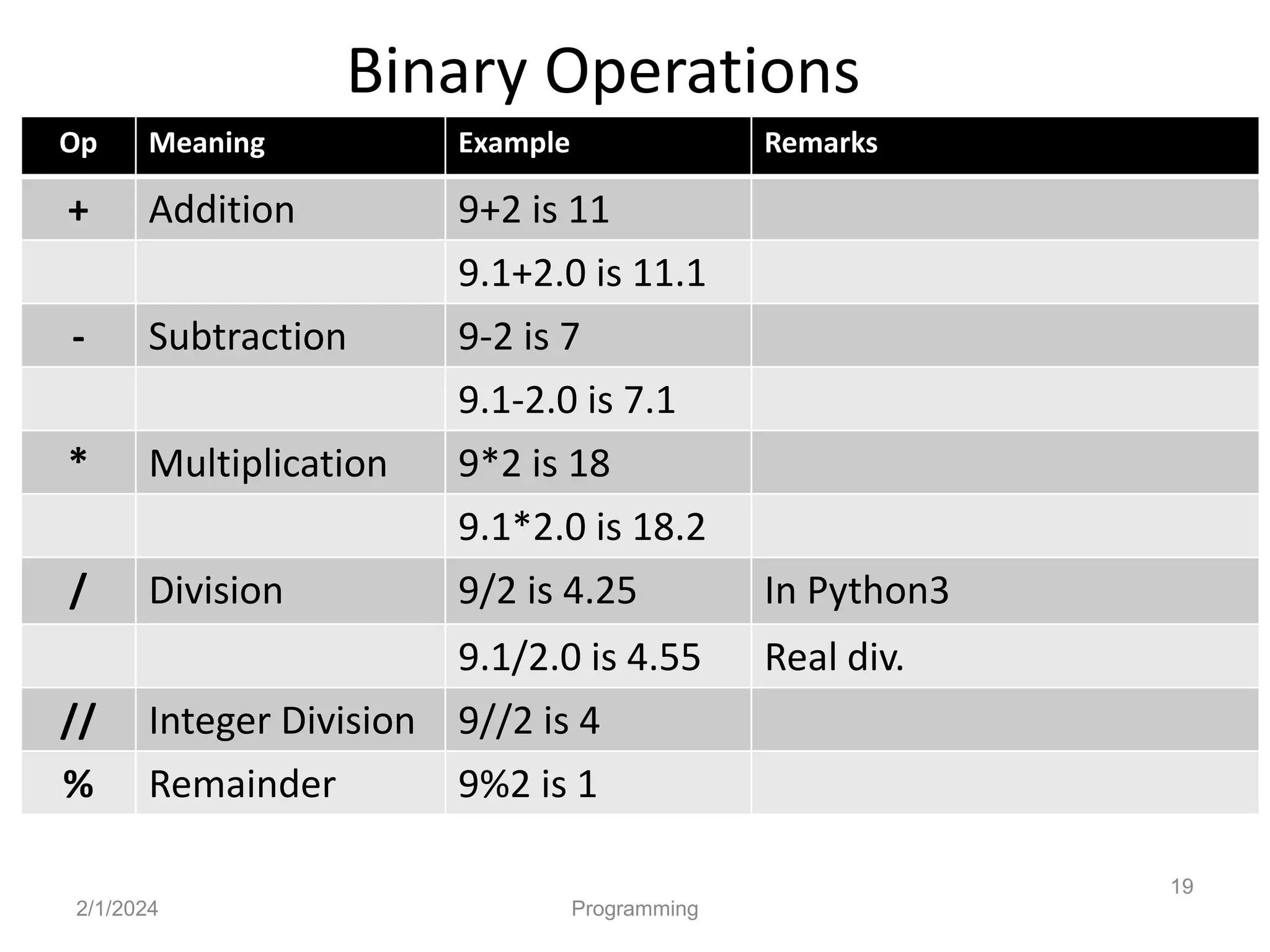
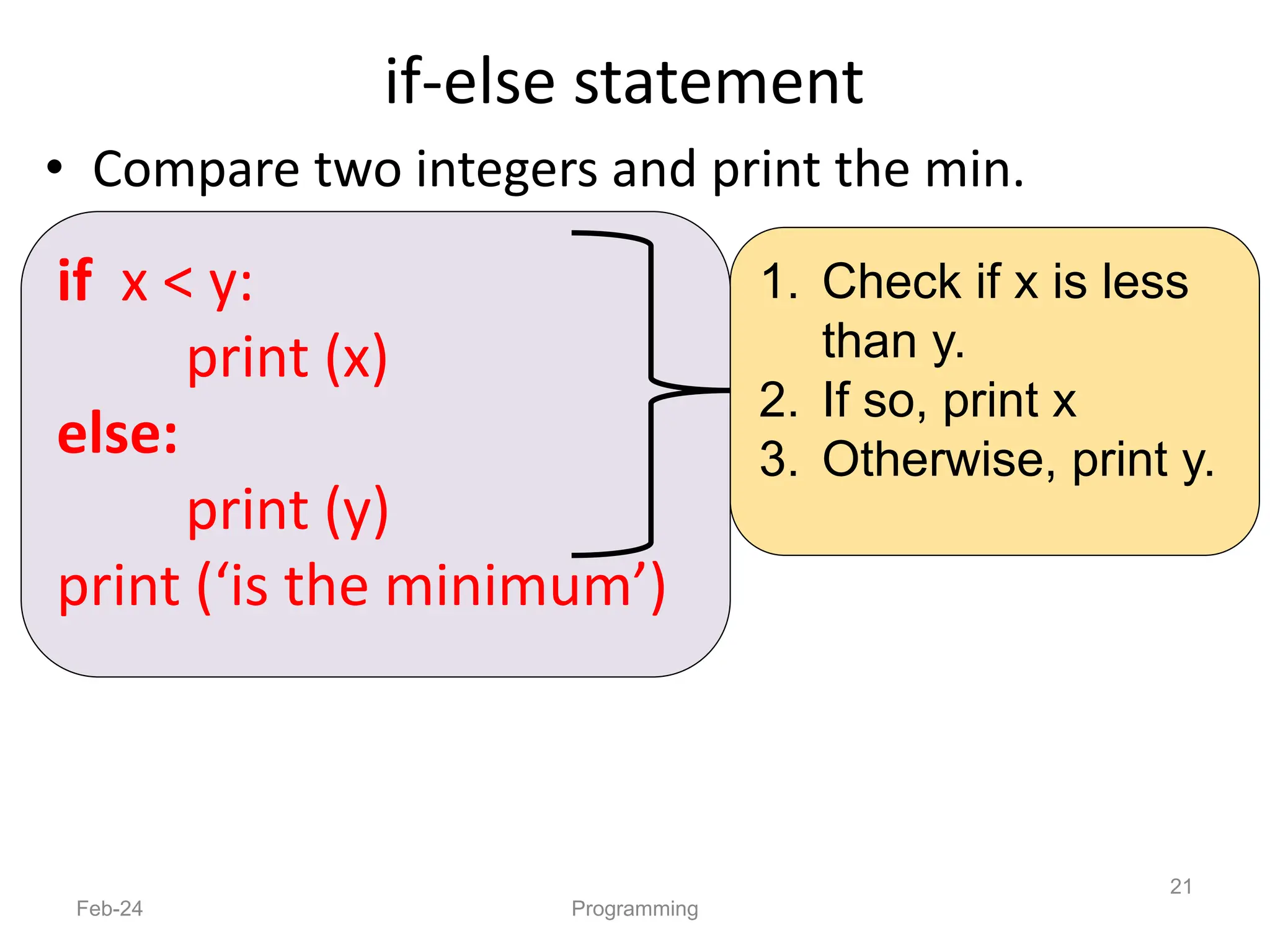
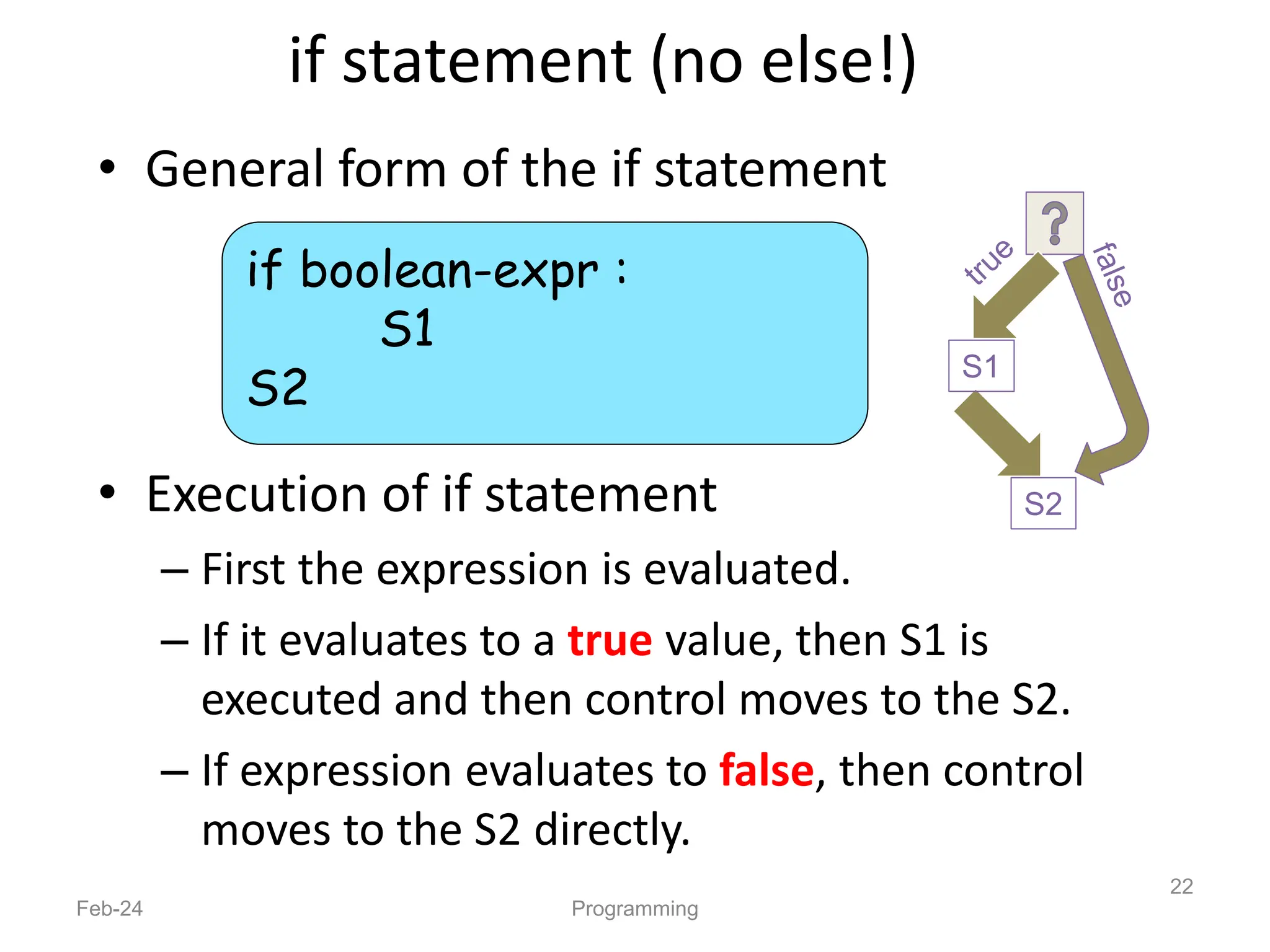
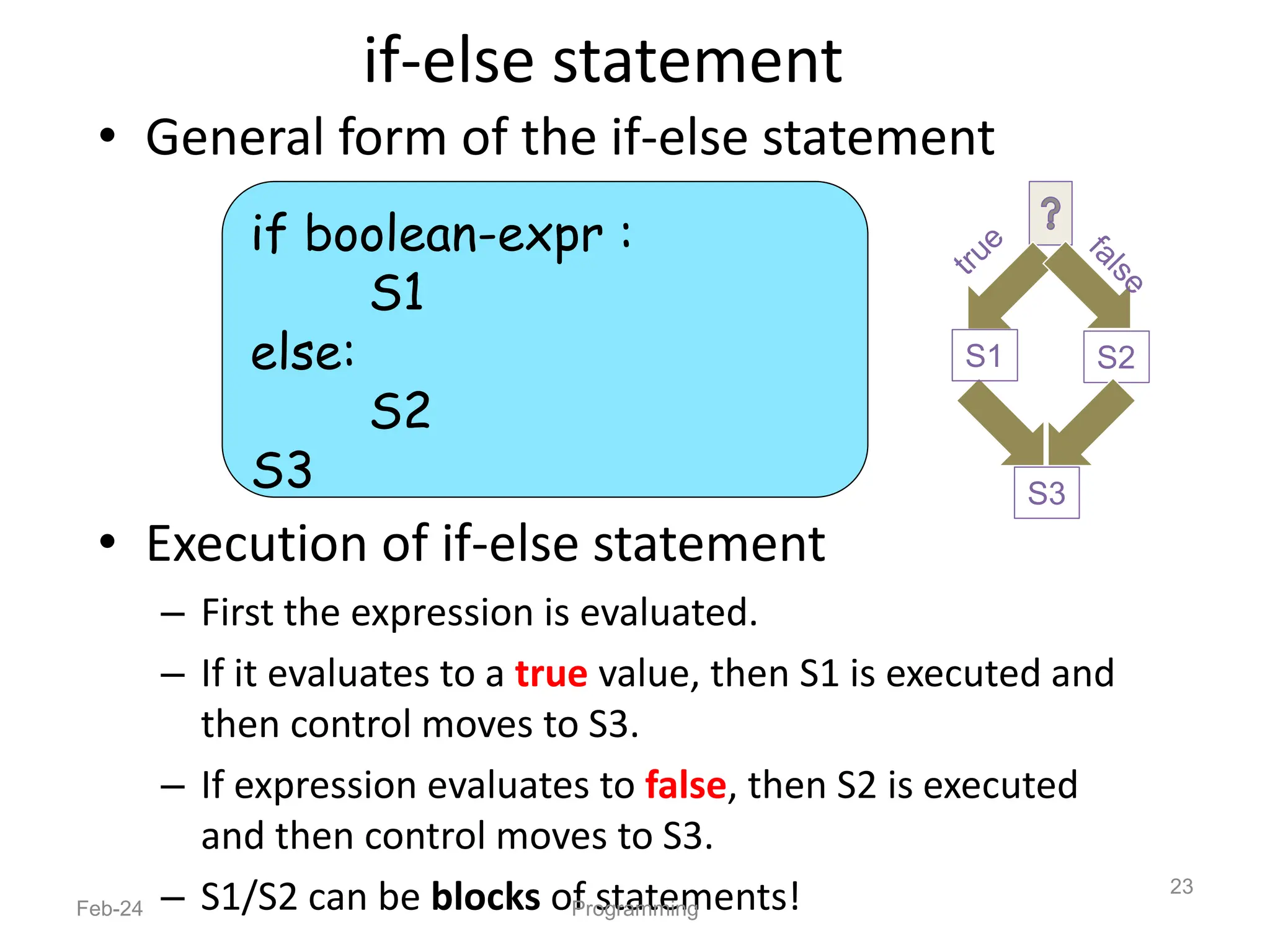
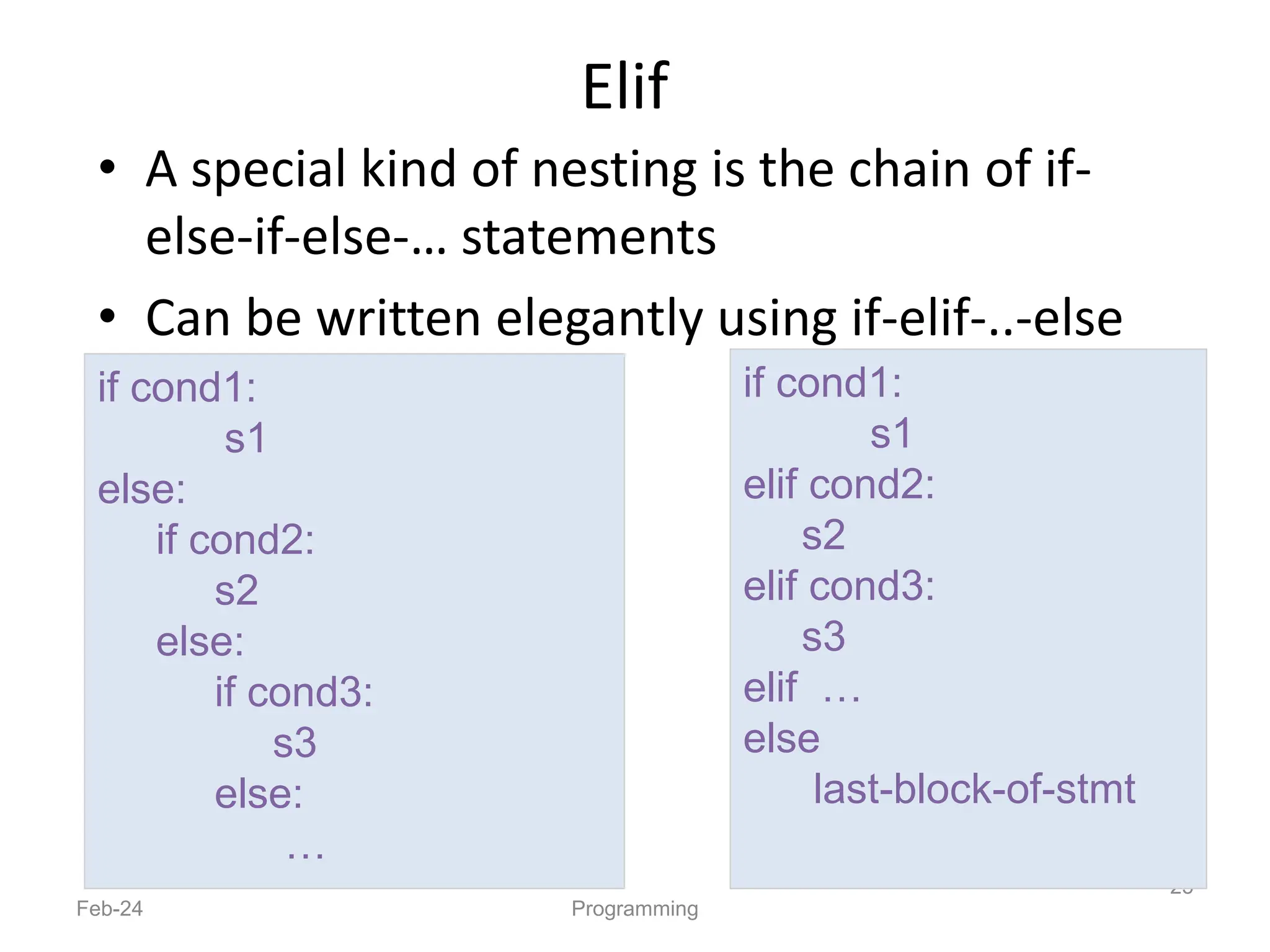
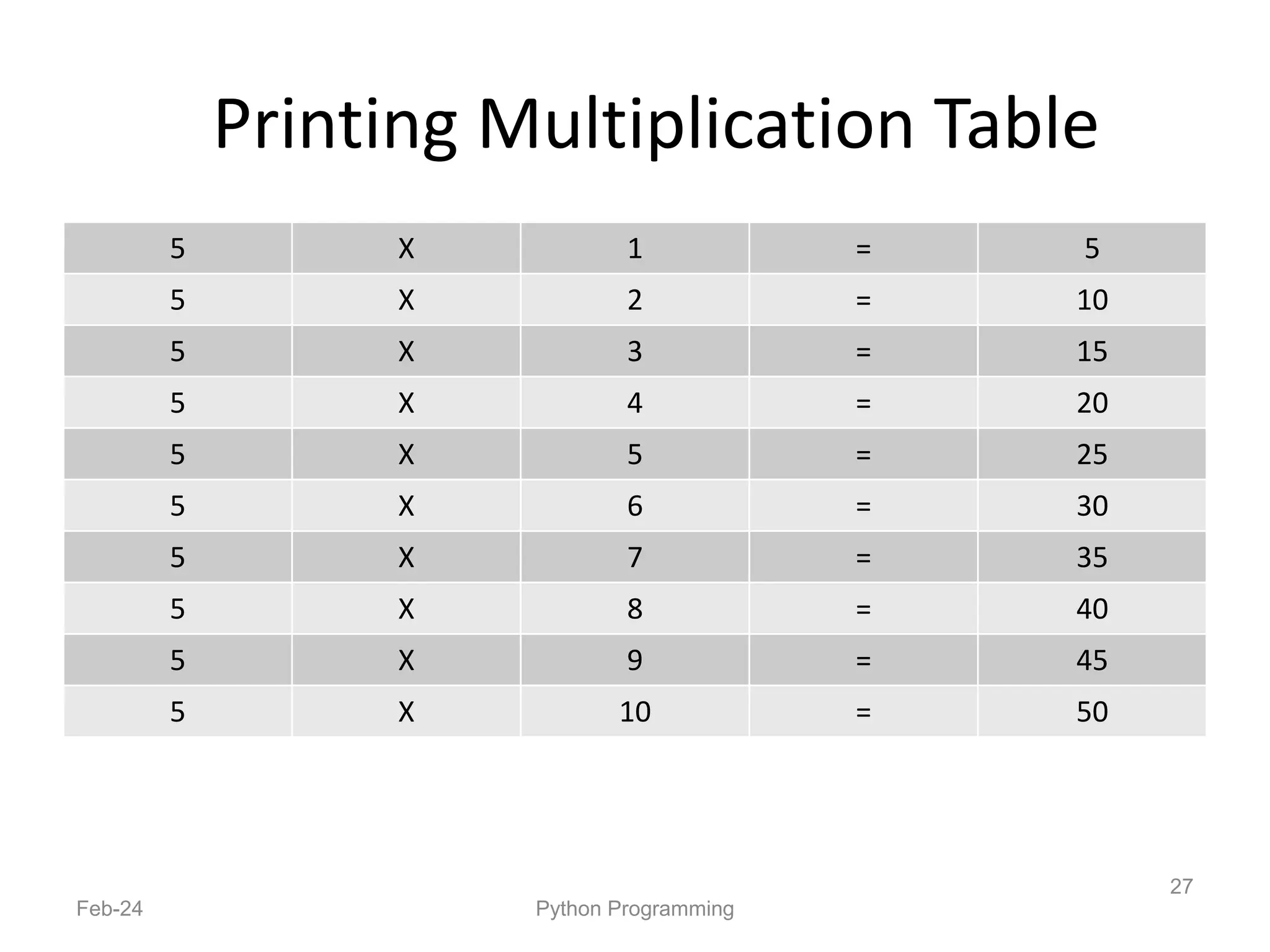
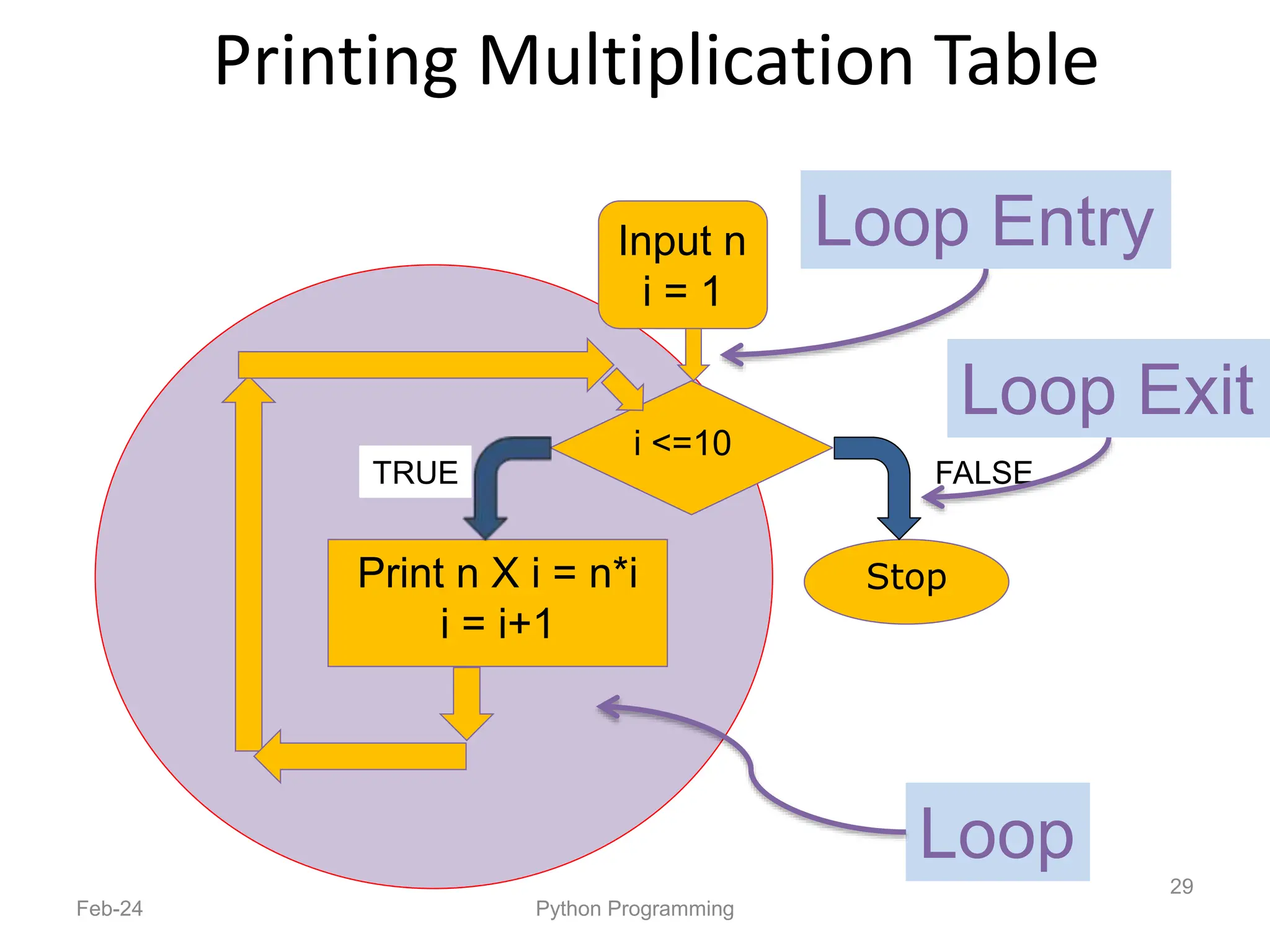
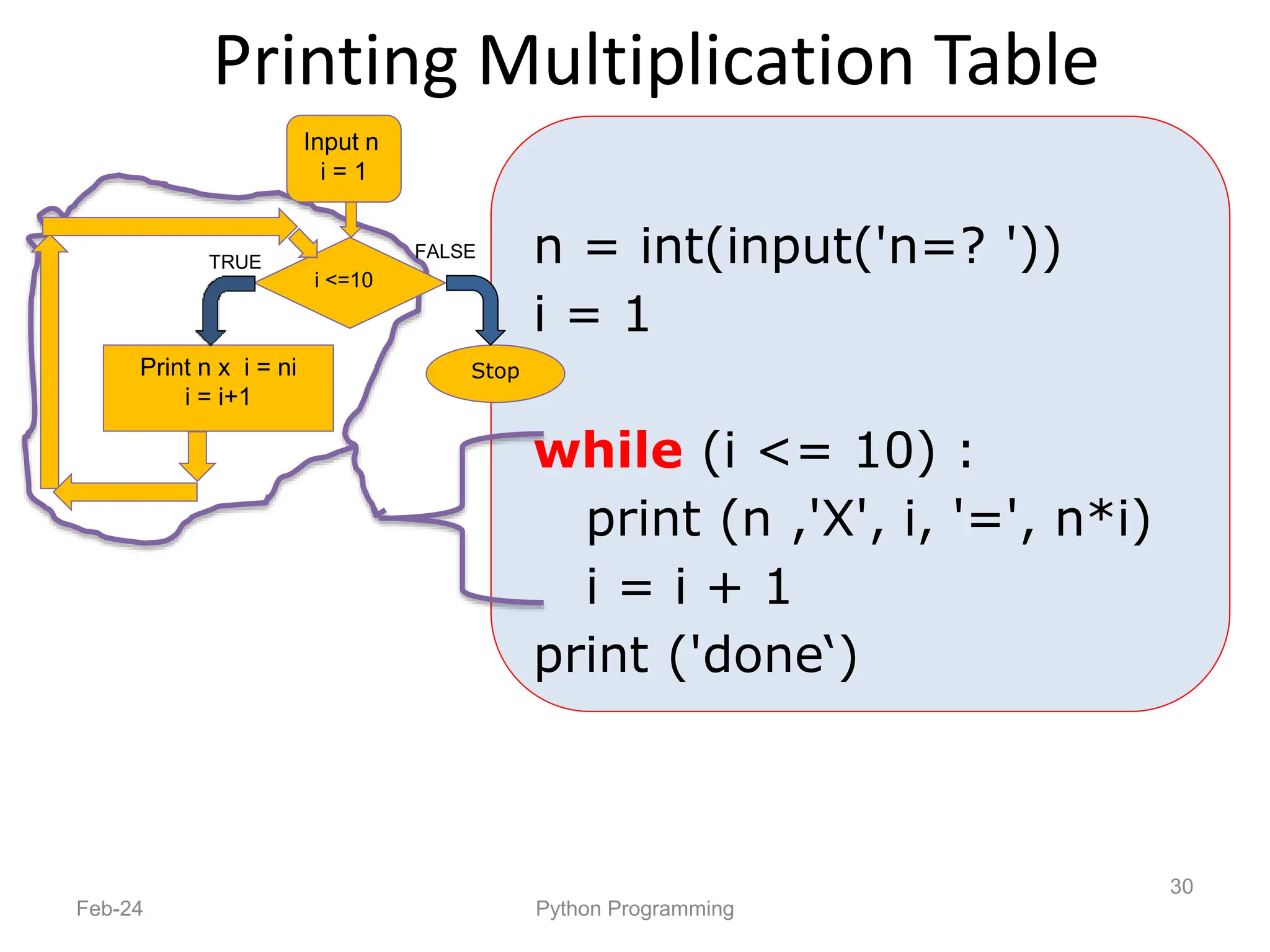
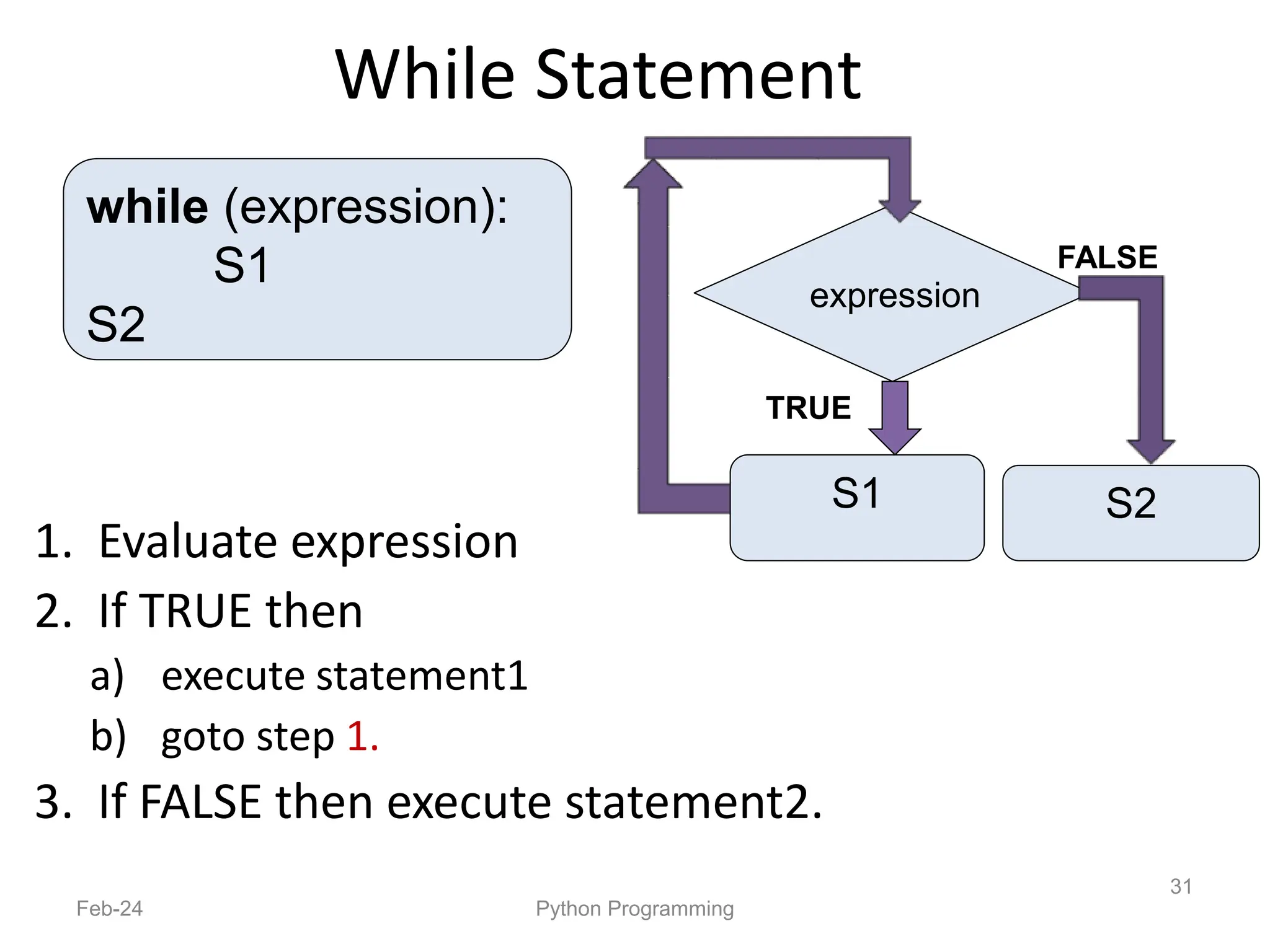
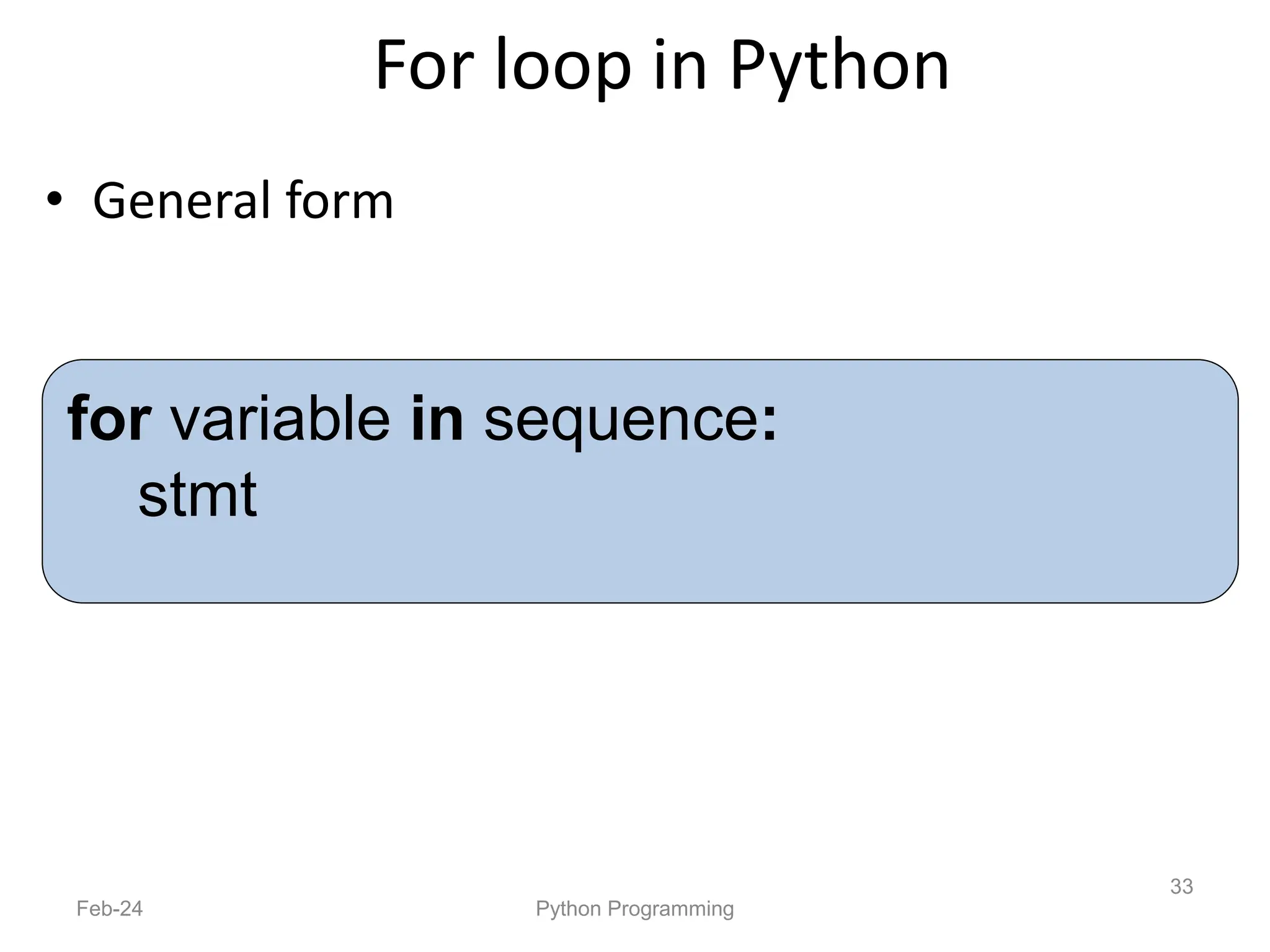
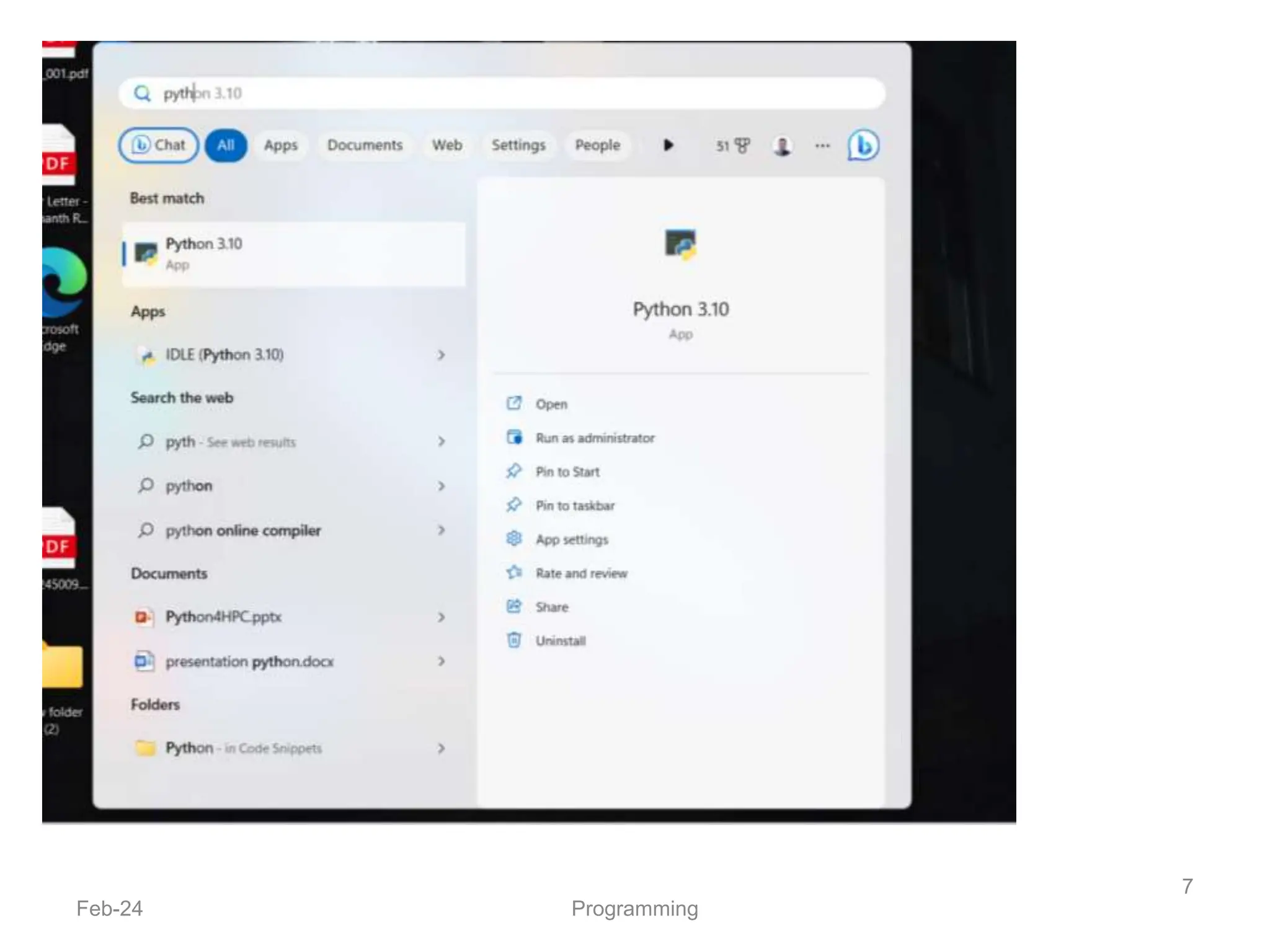
- Python is an interpreted, general-purpose programming language created in 1991 and named after Monty Python.
- It is used widely in applications like web development, data analysis, and scripting.
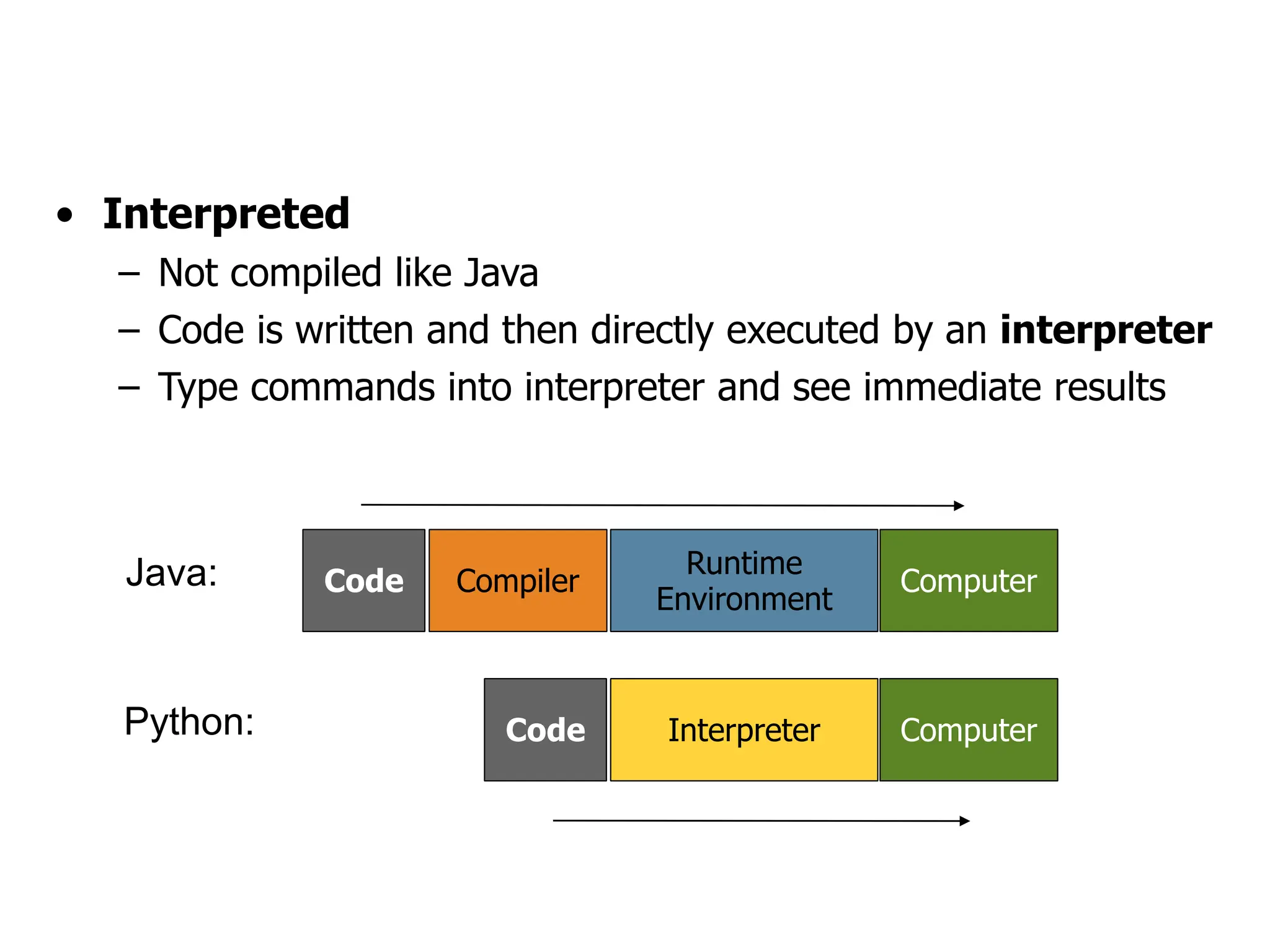
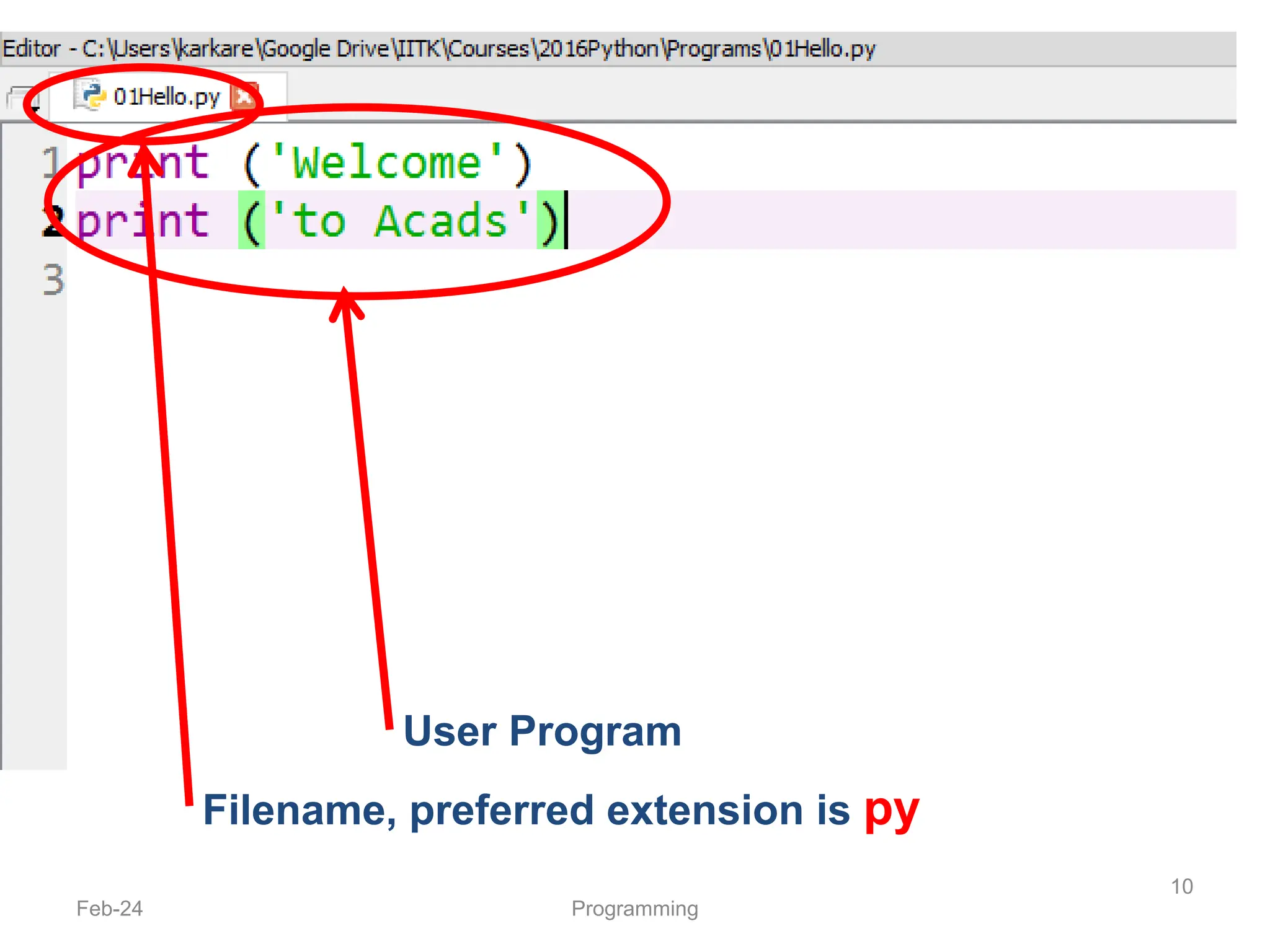
- Python code is written and executed directly by an interpreter rather than being compiled like languages like Java.
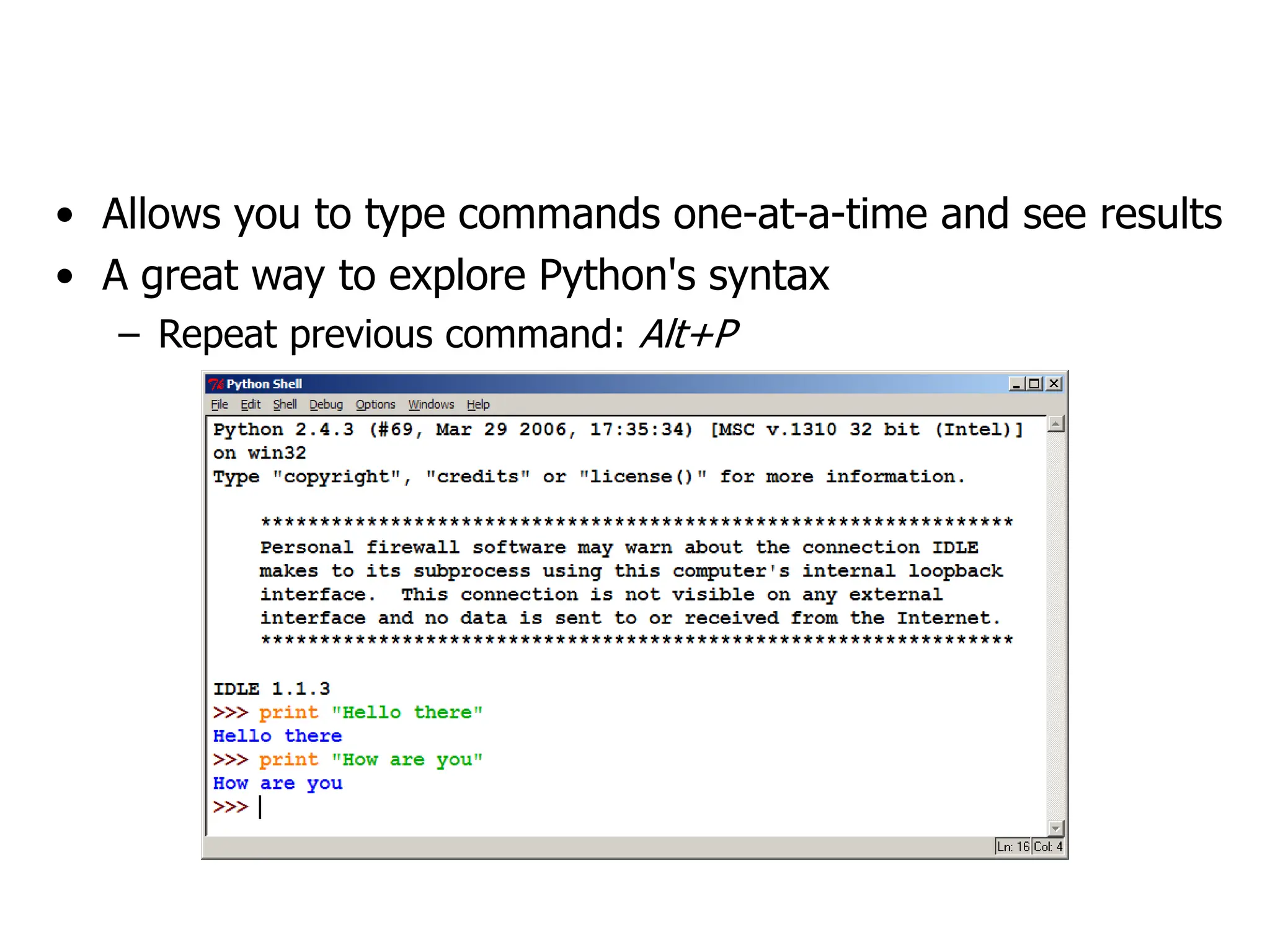
- The Python interpreter allows typing commands one at a time to see immediate results and explore syntax interactively.






![Python Shell is Interactive
Feb-24 Programming
12
IN[1]:
IN[2]:
IN[4]:
IN[3]:
Python Shell Prompt
User Commands
(Statements)
Outputs
( )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python4hpc-240201064801-b443537b/75/Python4HPC-pptx-12-2048.jpg)

![input
• Take as argument a string to print as a prompt
• Returns the user typed value as a string
– details of how to process user string later
Feb-24 Programming 14
IN[1]:
IN[2]:
IN[3]:
( )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python4hpc-240201064801-b443537b/75/Python4HPC-pptx-14-2048.jpg)