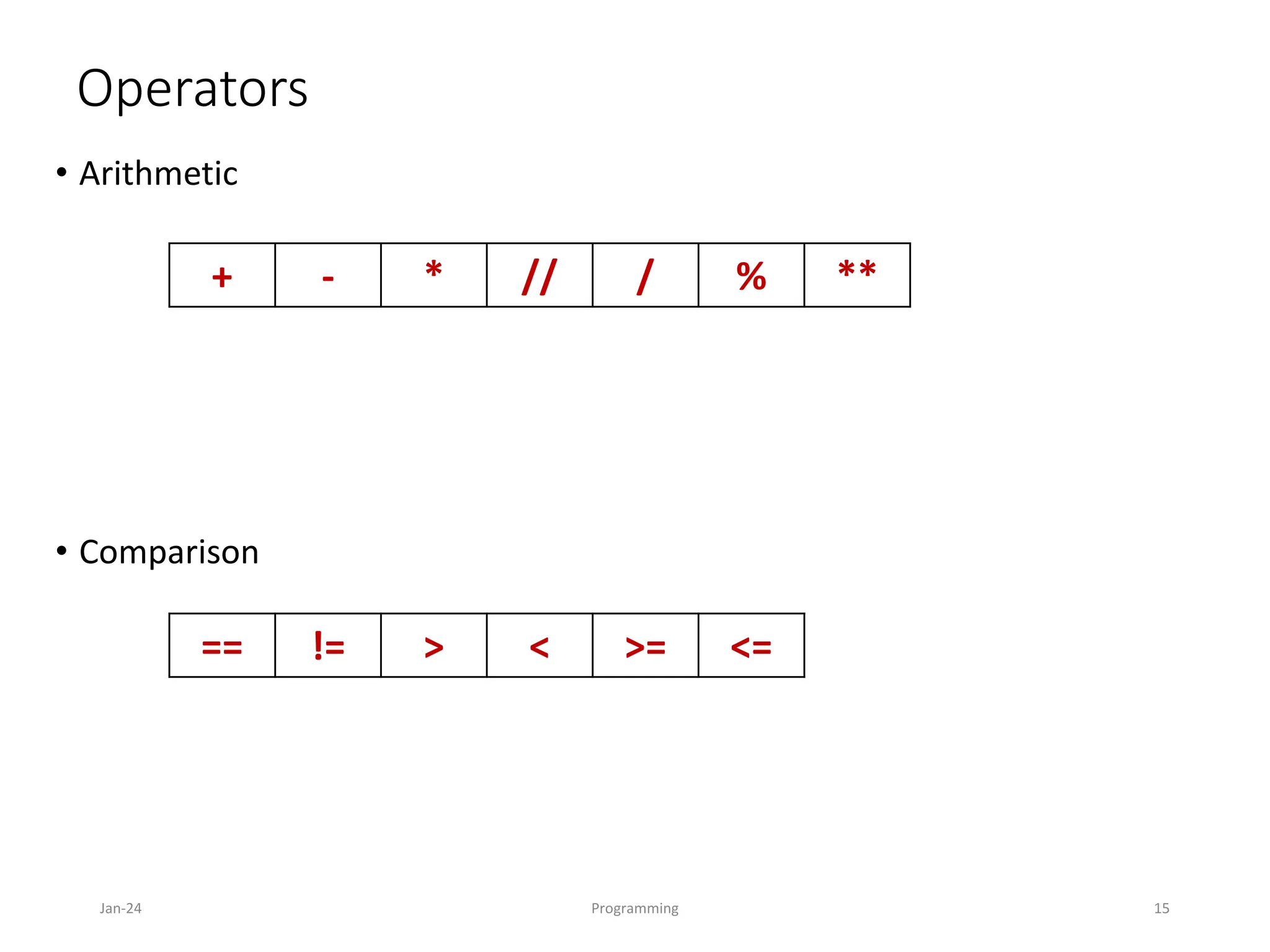
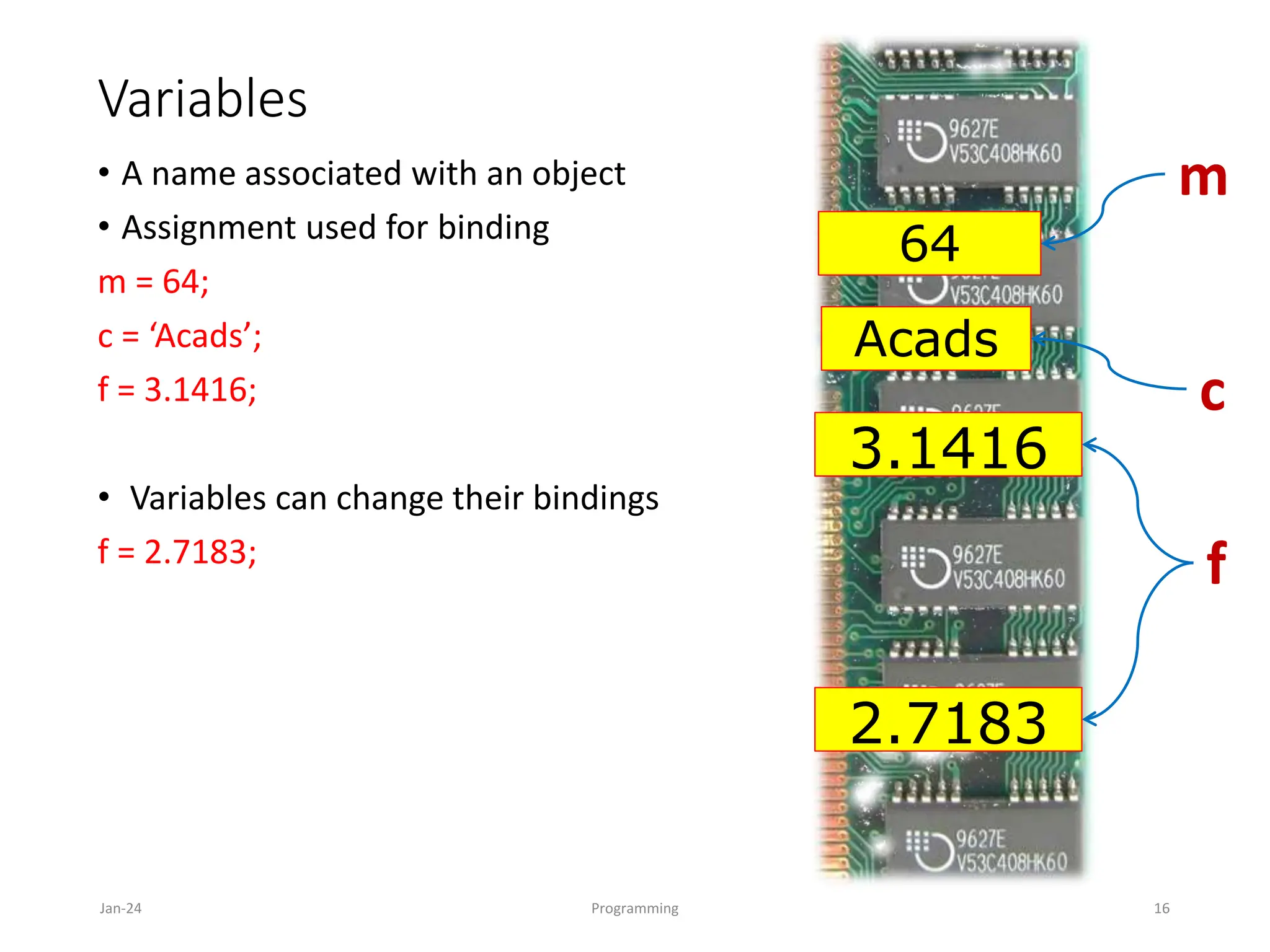
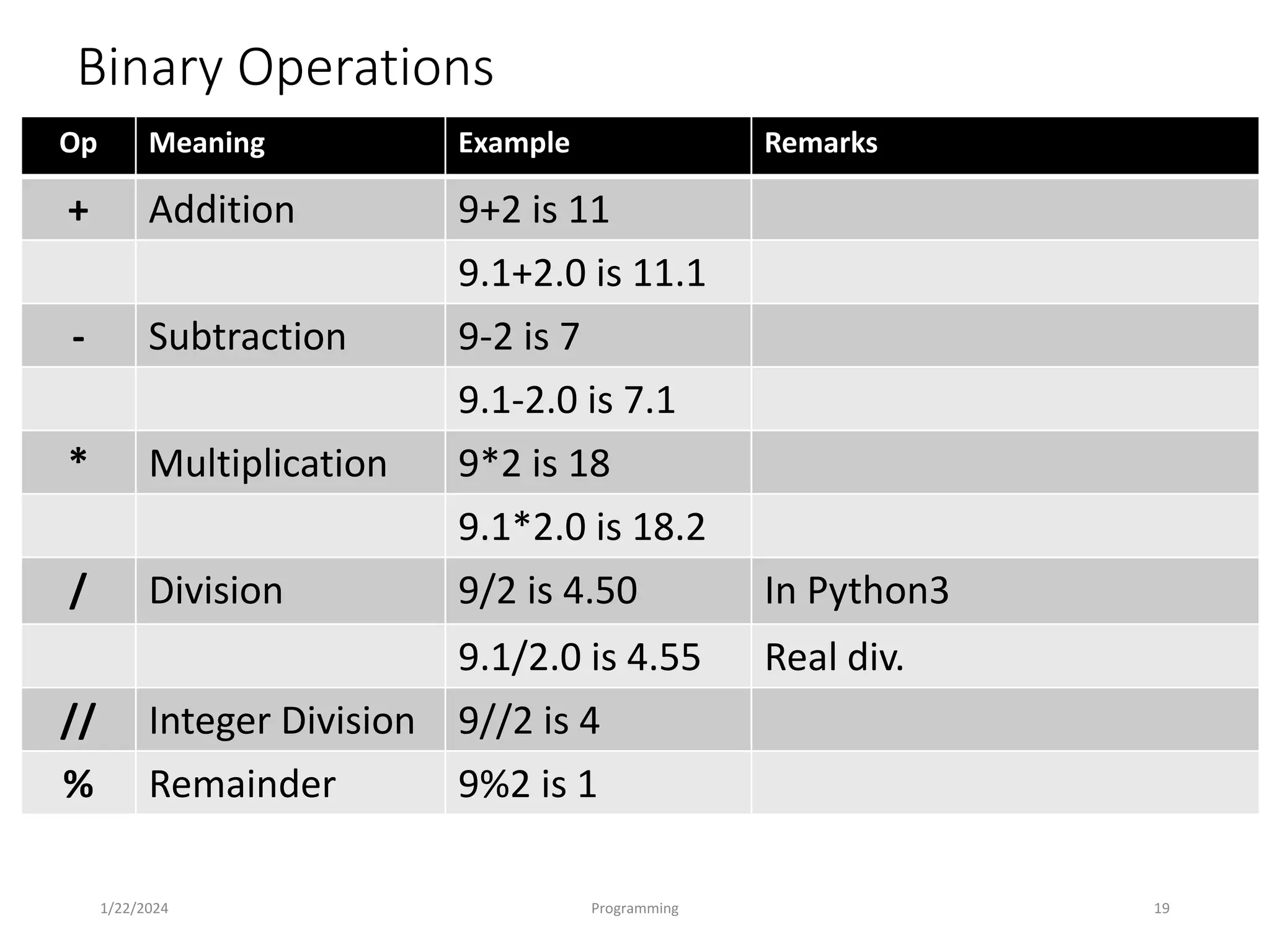
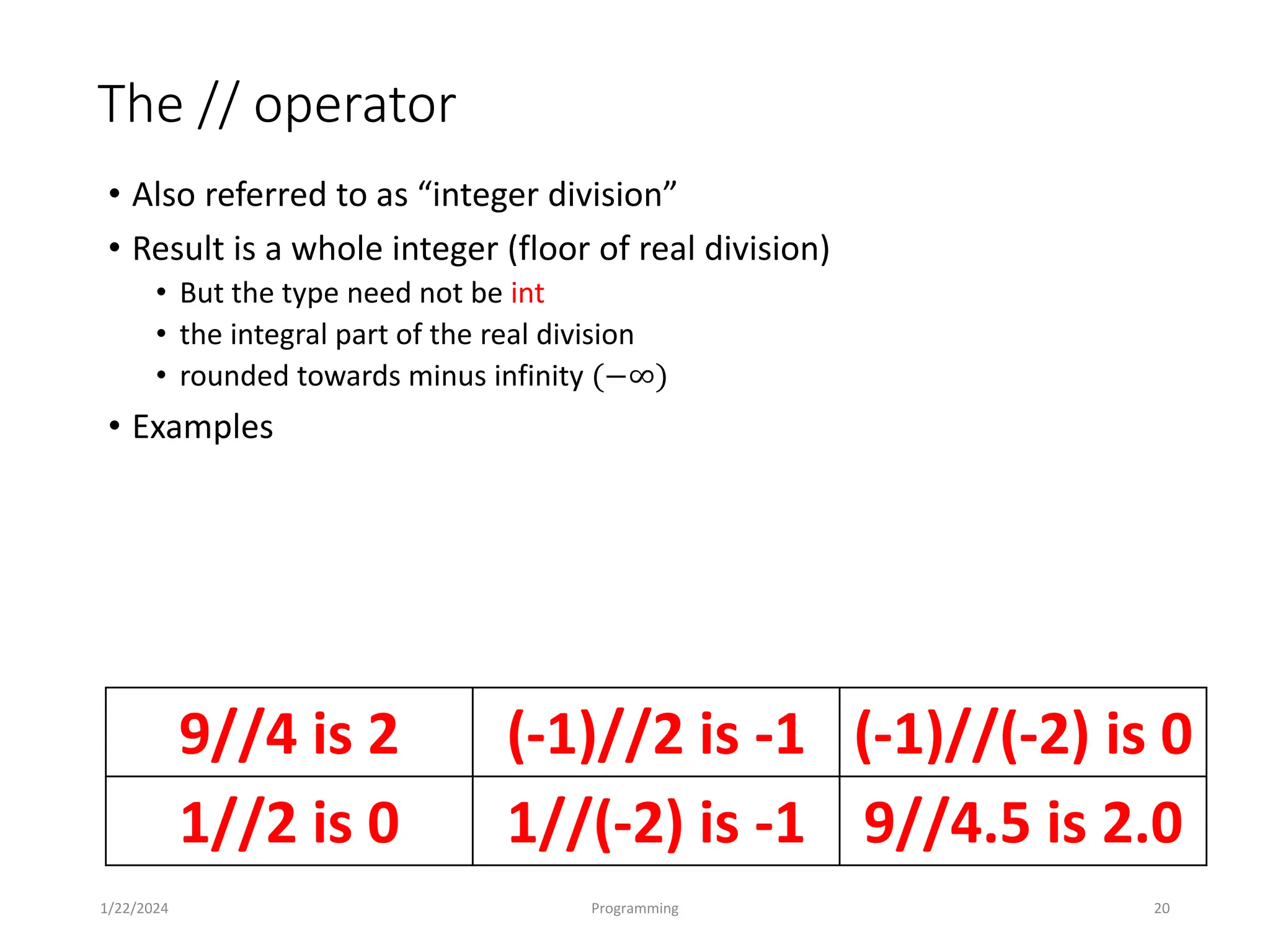
The document is an introduction to programming languages, specifically focusing on Python. It covers essential concepts such as types, operators, variables, conditional statements, and loops in Python, detailing how to write and manipulate programs using the language. Additionally, it outlines the programming cycle and various coding principles essential for beginners.




![Python Shell is Interactive
Jan-24 Programming 8
IN[1]:
IN[2]:
IN[4]:
IN[3]:
Python Shell Prompt
User Commands
(Statements)
Outputs
( )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/updatedpython-240122093202-d118b8e7/75/Updatedpython-pptxUpdatedpython-pptxUpdatedpython-pptx-8-2048.jpg)