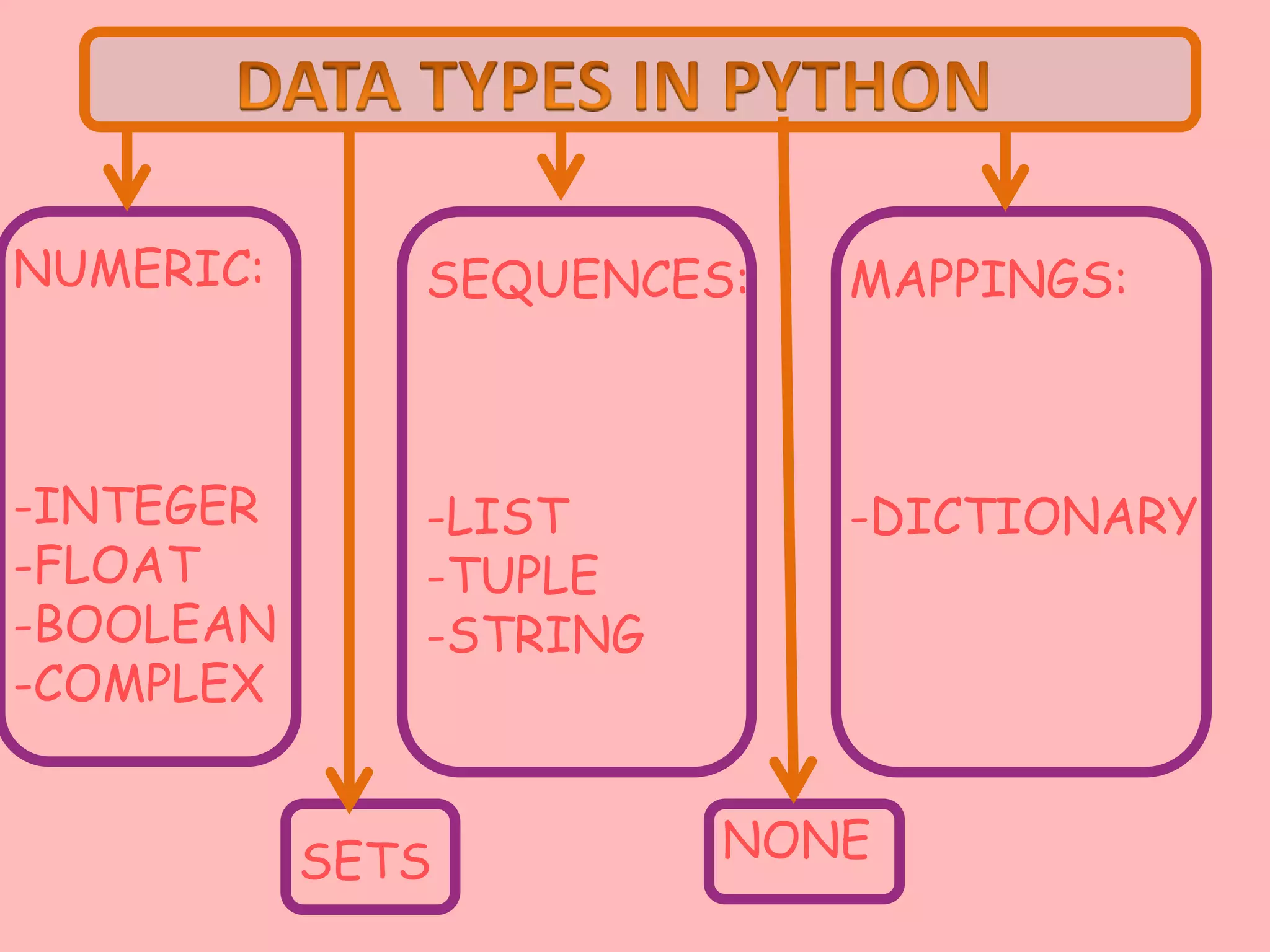
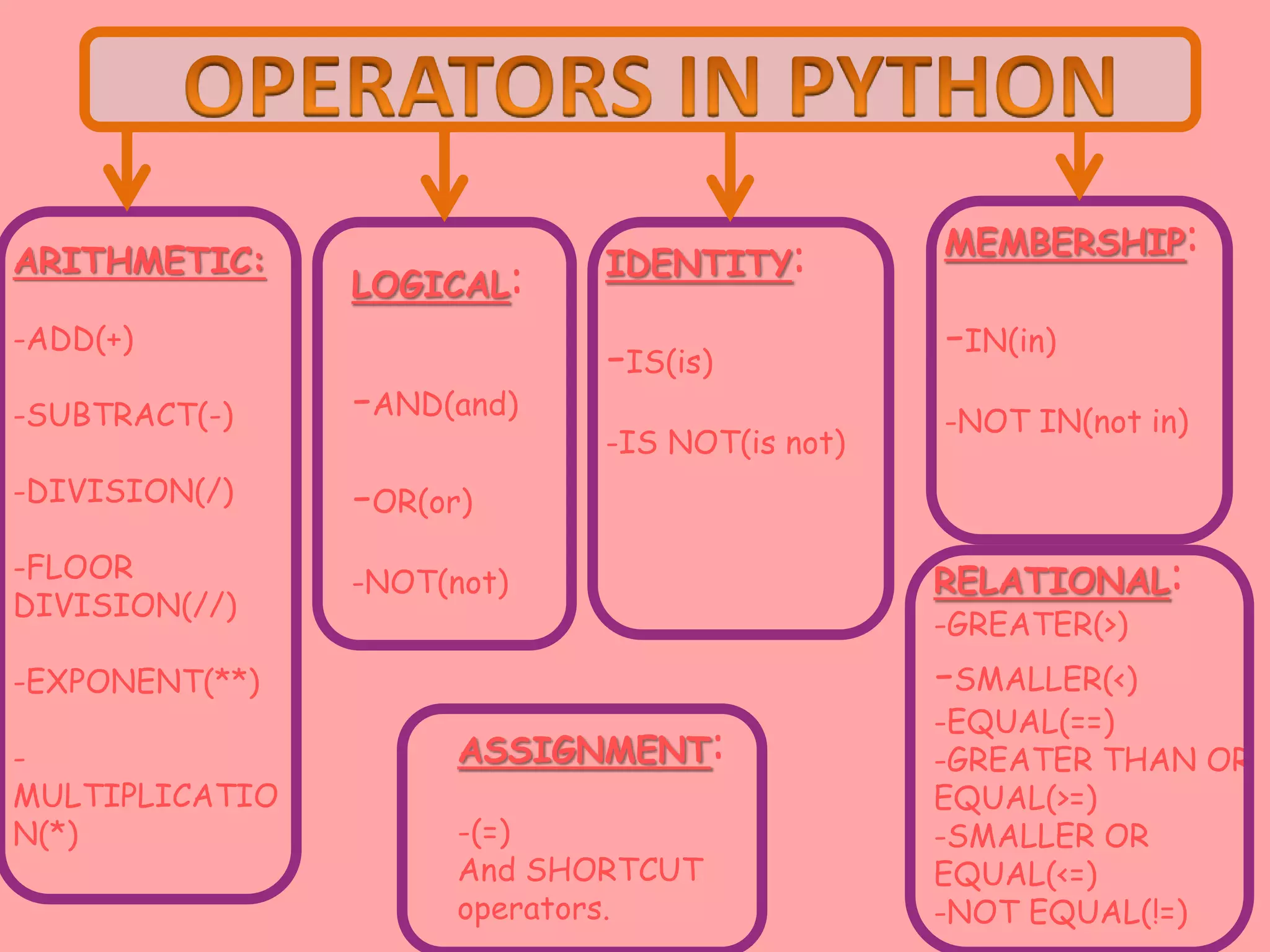
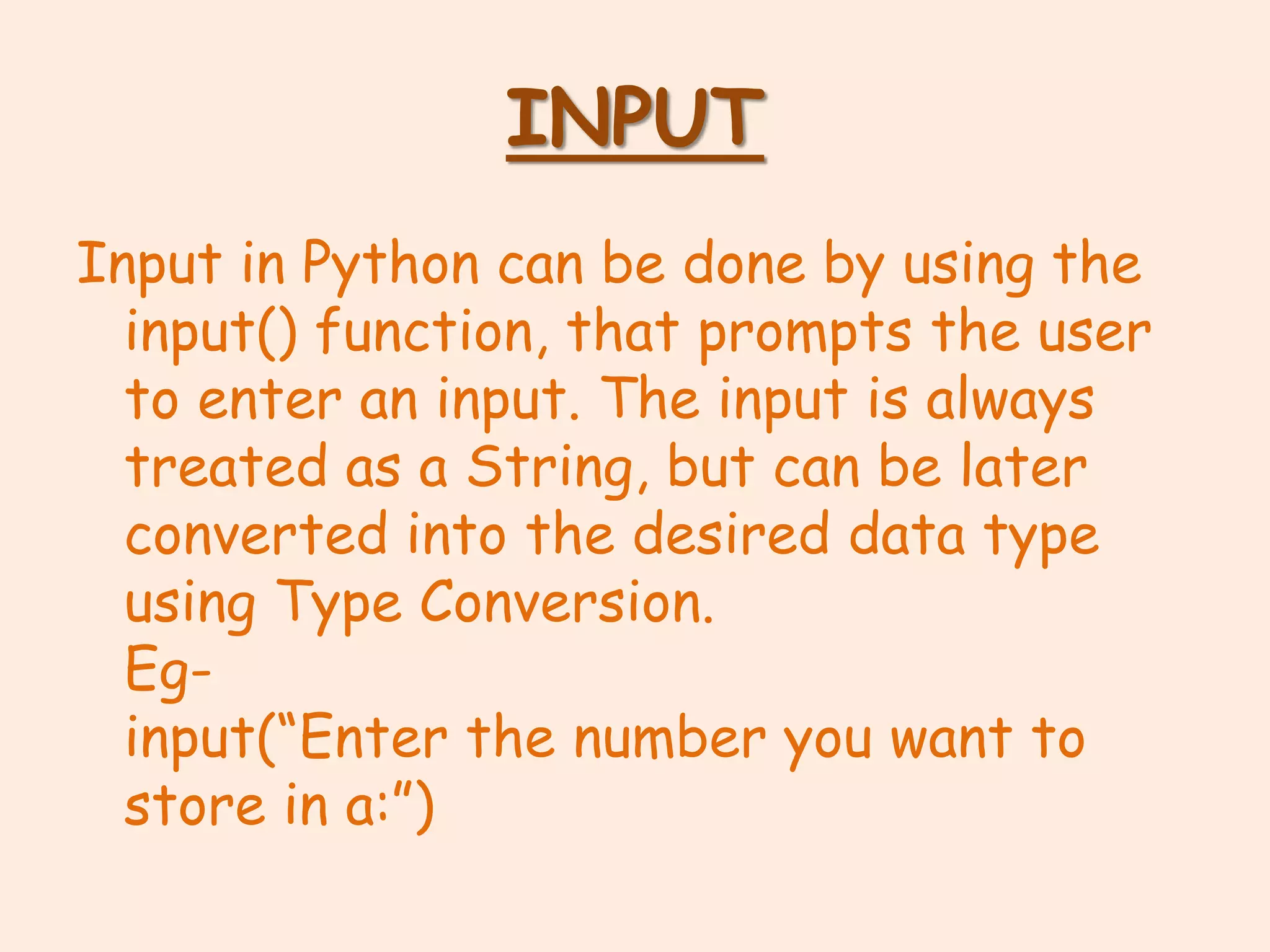
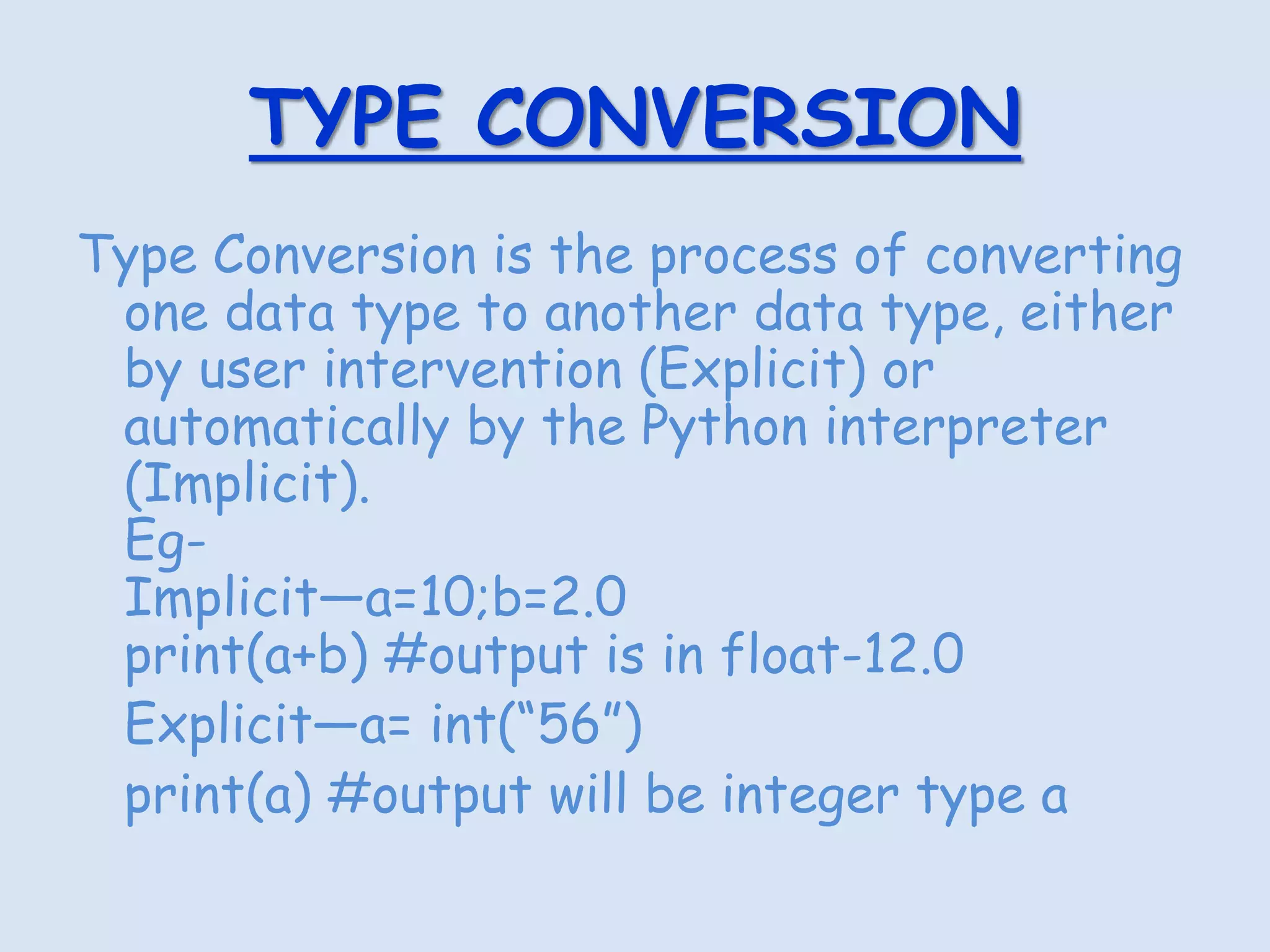
Python programming data types include numeric, sequences, mappings, and None. Numeric types include integer, float, boolean, and complex. Sequences include lists, tuples, and strings. Mappings include dictionaries. Operators like arithmetic, logical, identity, membership, assignment, and relational are used to perform operations. Expressions combine values and operators to evaluate to a value. Statements are units of code the interpreter can execute like assignments and prints. Input is via the input() function and output via print(). Debugging removes mistakes through syntax, logical, and runtime errors. Type conversion changes data types explicitly or implicitly.