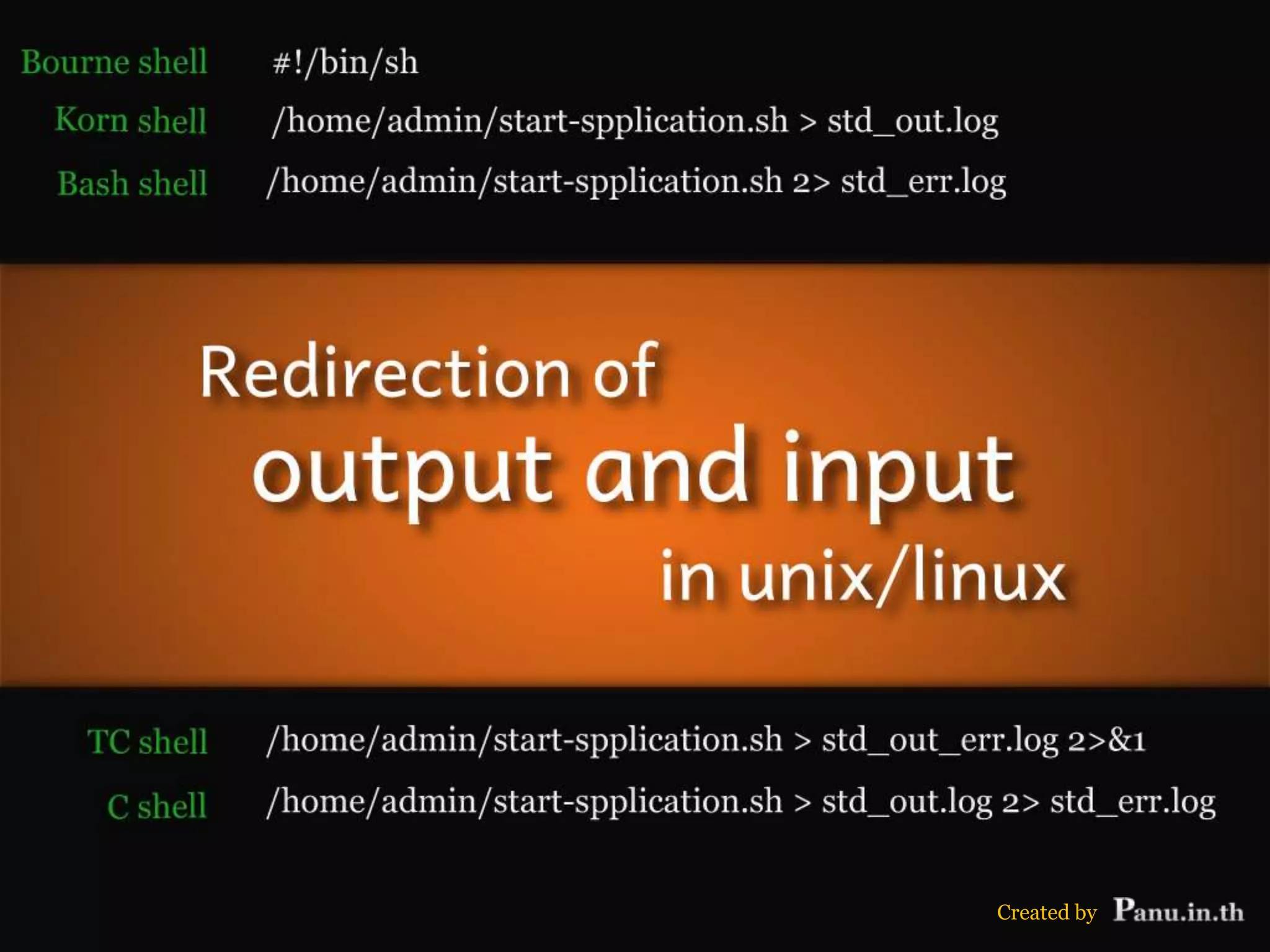
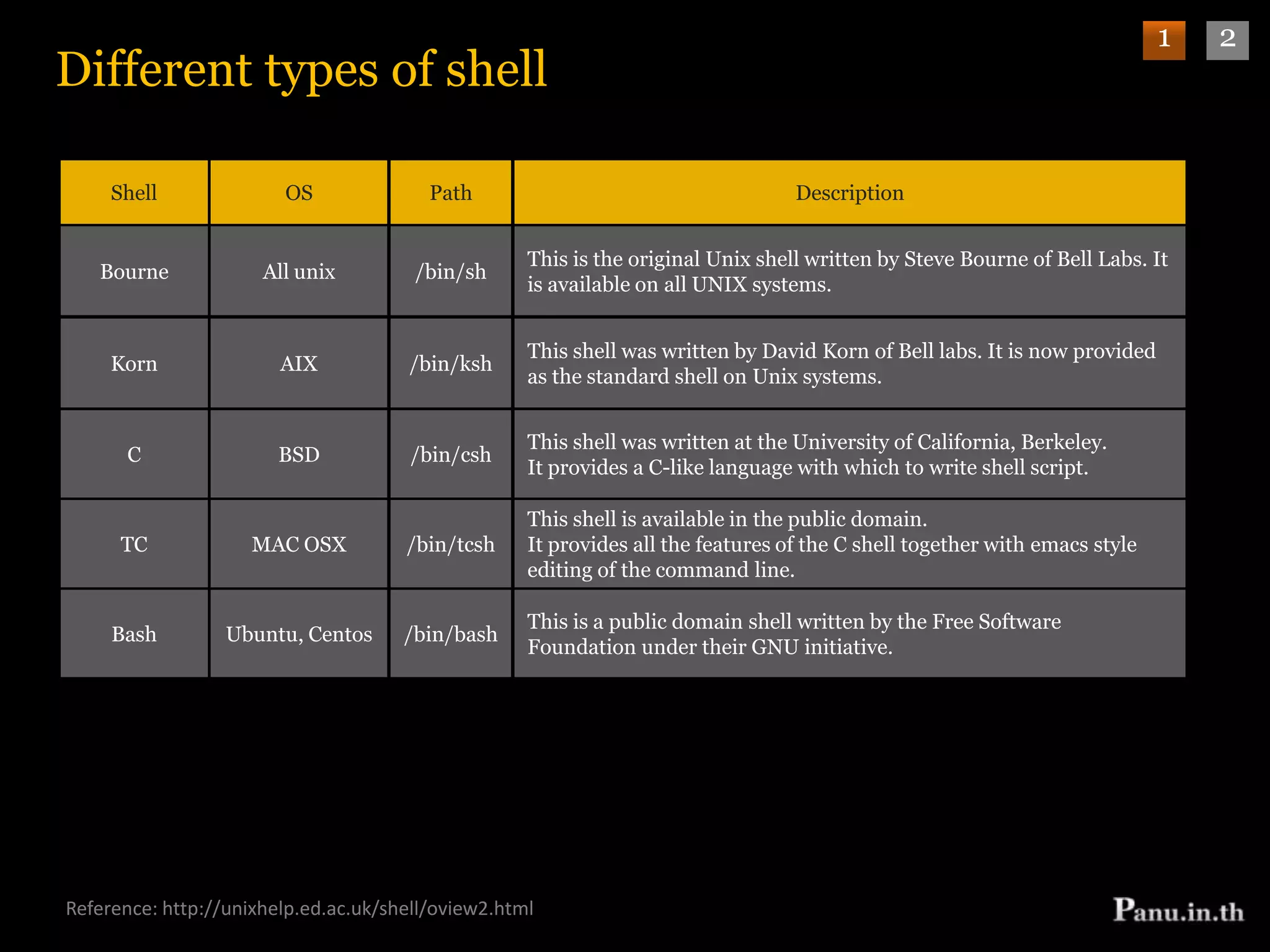
This document discusses different types of shells, their features, and configuration files. It also covers redirection of input/output in shells. There are several common shells like Bourne, C, TC, Korn, and Bash that vary in their features such as command history, aliases, scripting abilities. Configuration files configure shells and are read during login or interactively. Redirectors like >, >>, <, 2>, 2>&1 are used to control input/output streams and send them to files. Examples show how redirection is used for various purposes like logging output and errors separately.