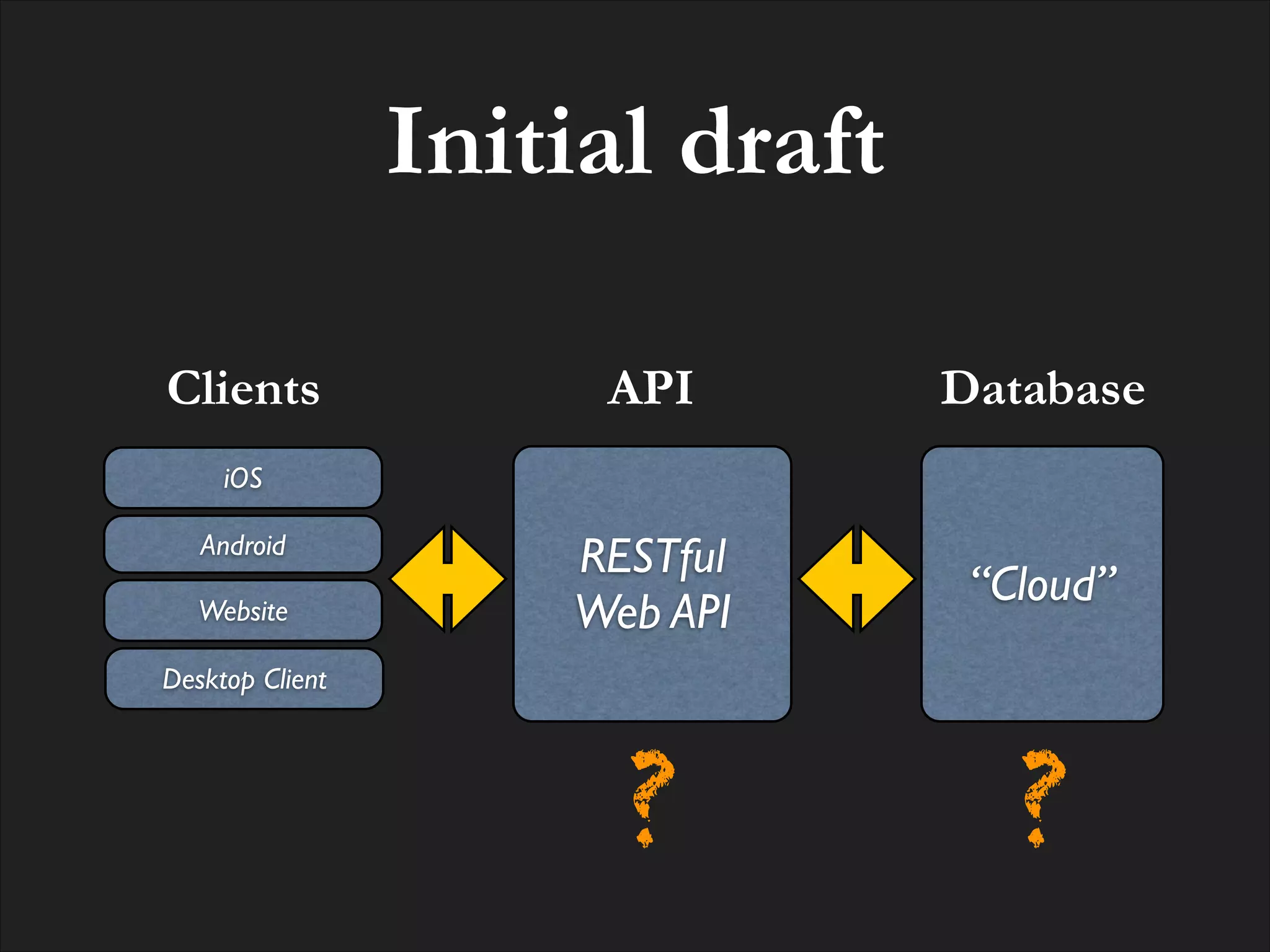
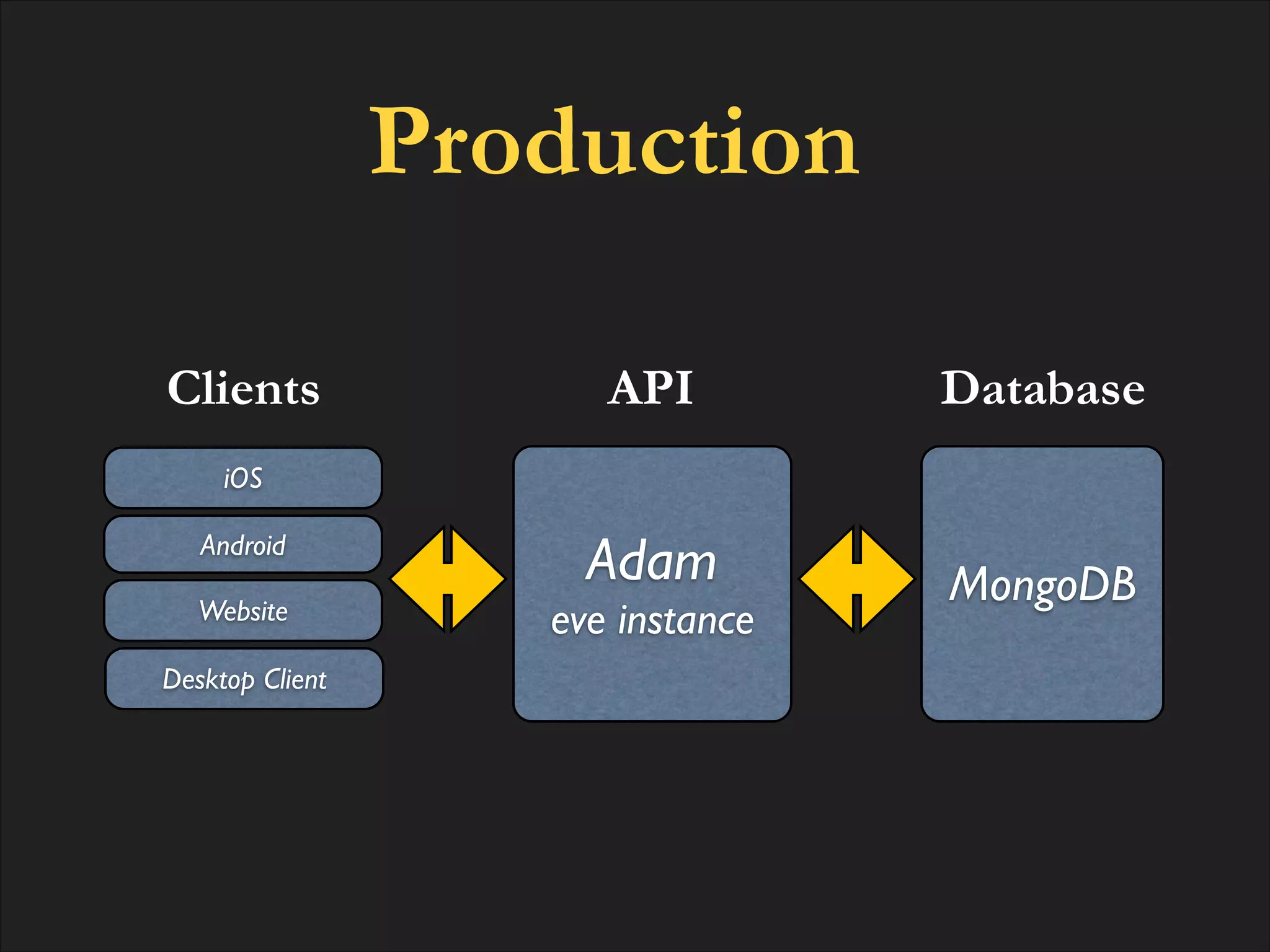
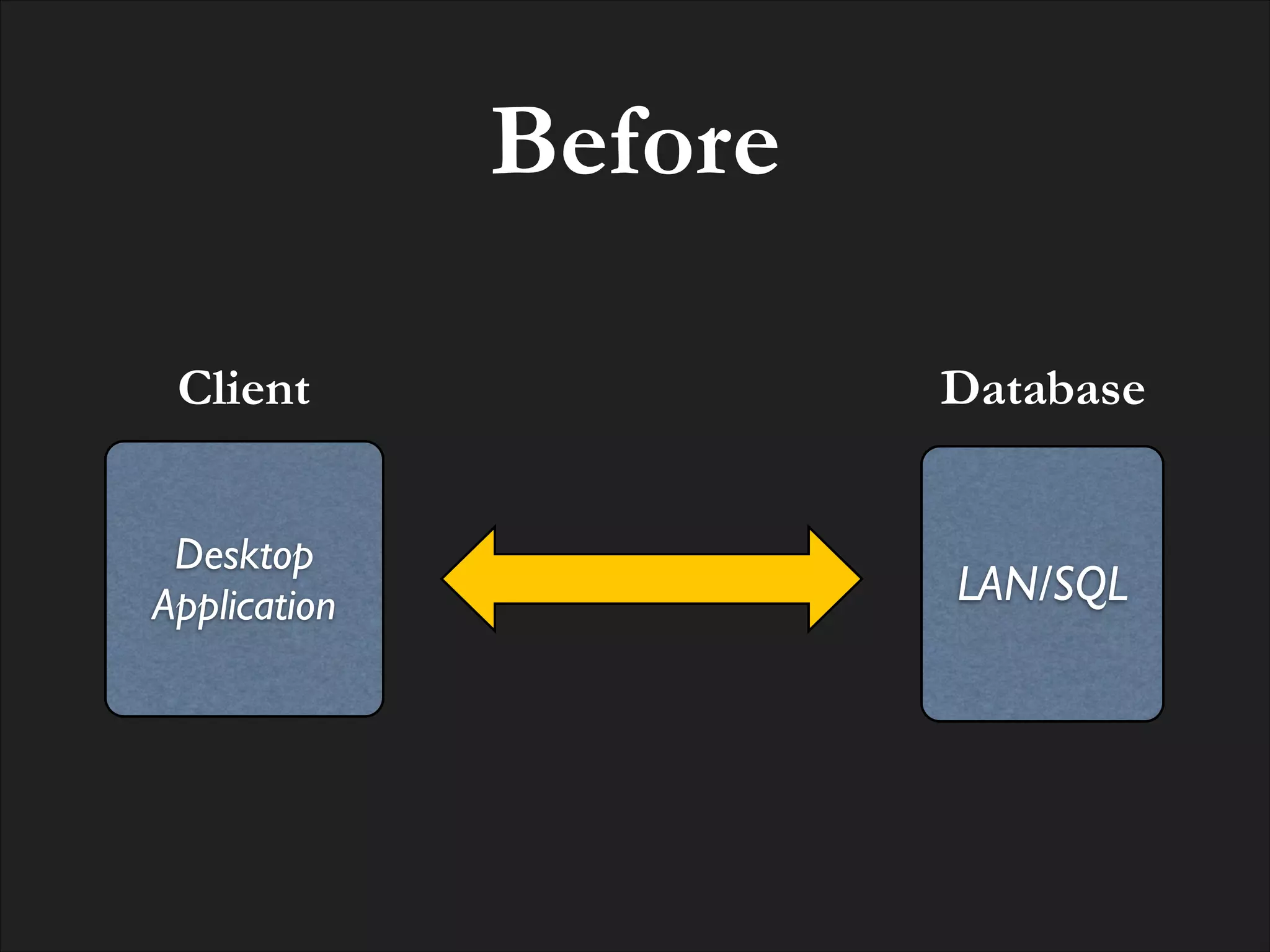
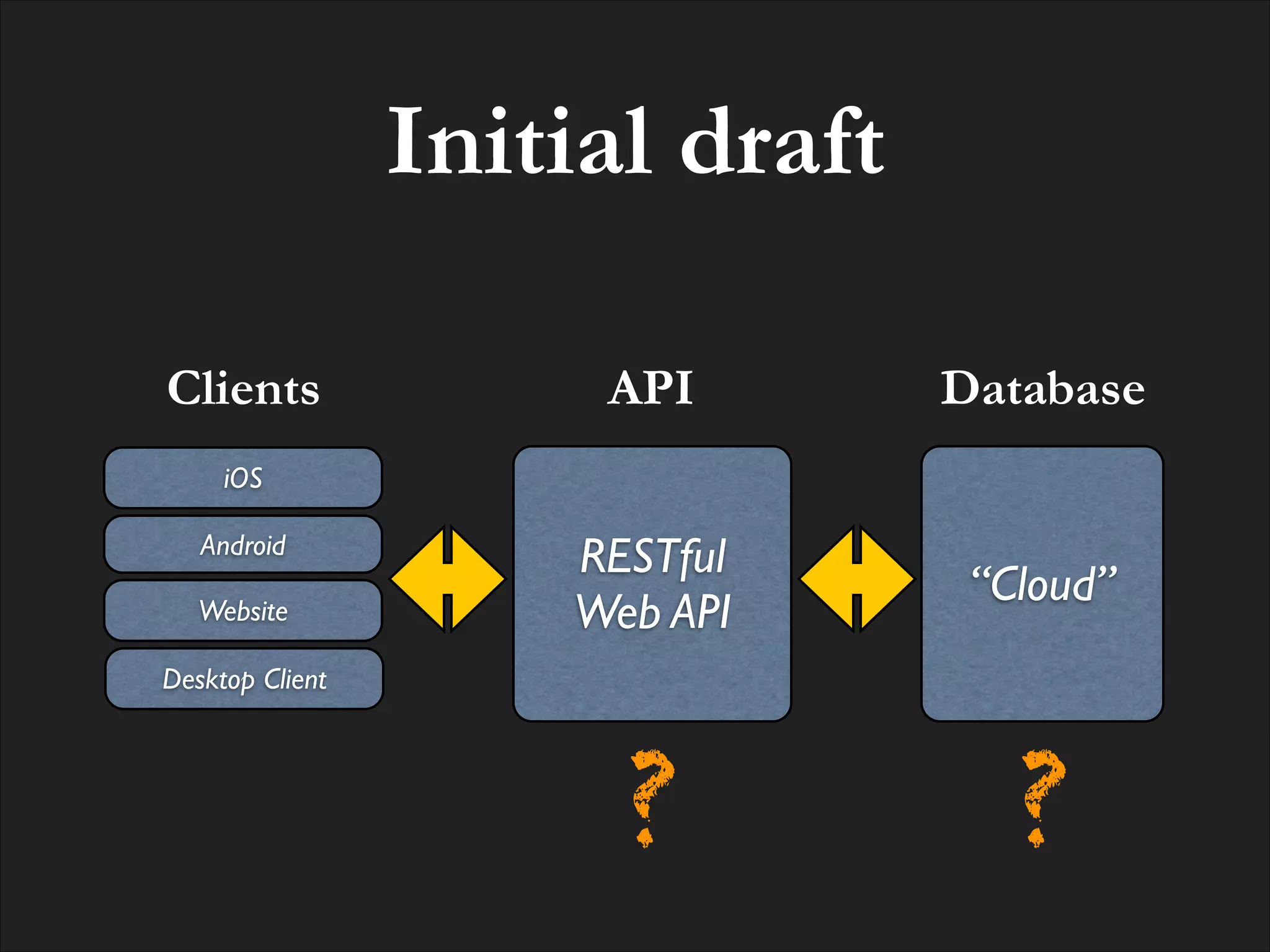
The document discusses the integration of MongoDB with RESTful web APIs, emphasizing its advantages for full stack development. It highlights MongoDB's JSON-style data storage, ease of setup, performance, and the natural mapping of Python dictionaries to MongoDB's data format. Additionally, it presents the development of the Eve REST API framework and its community contributions.













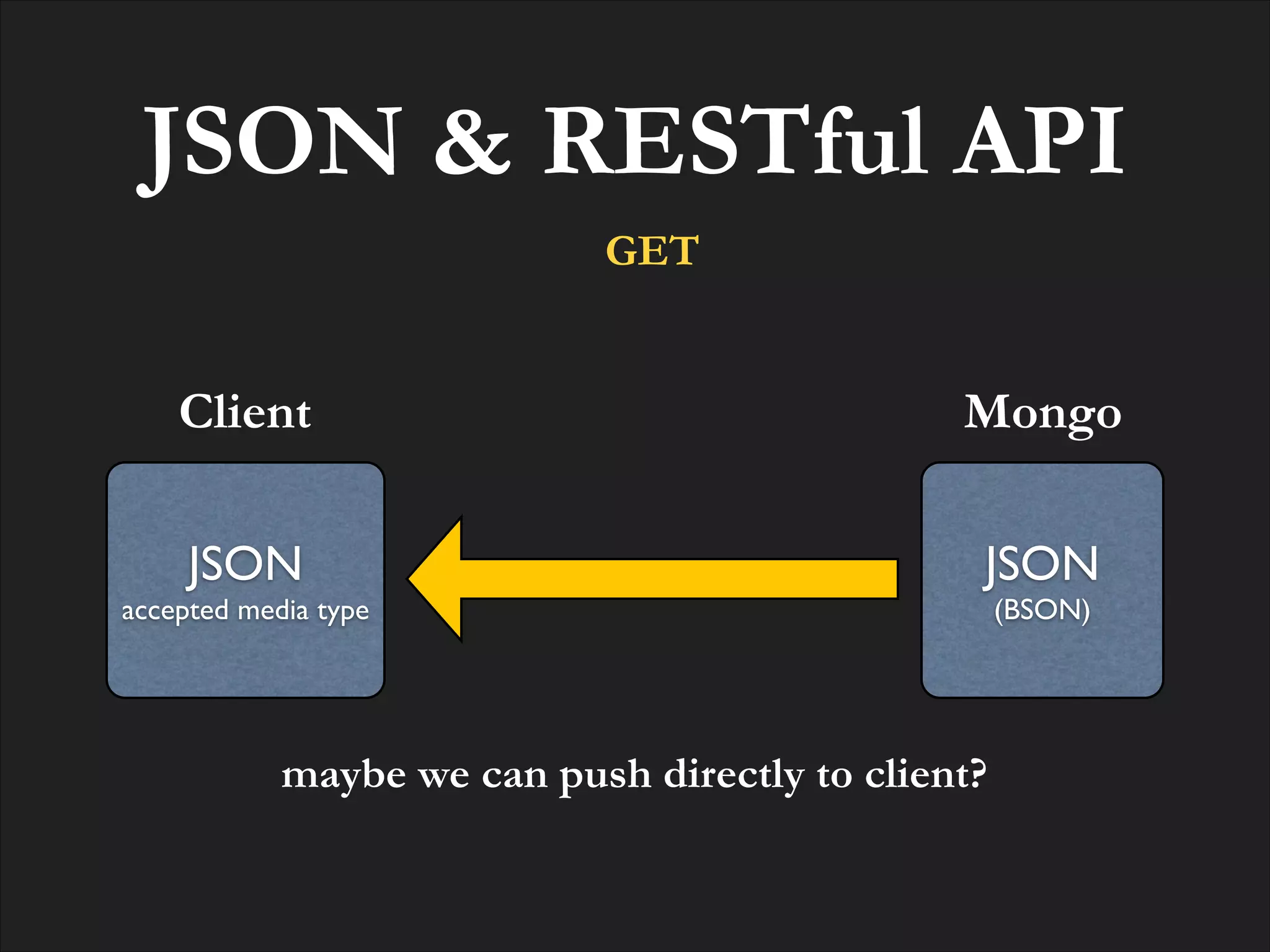
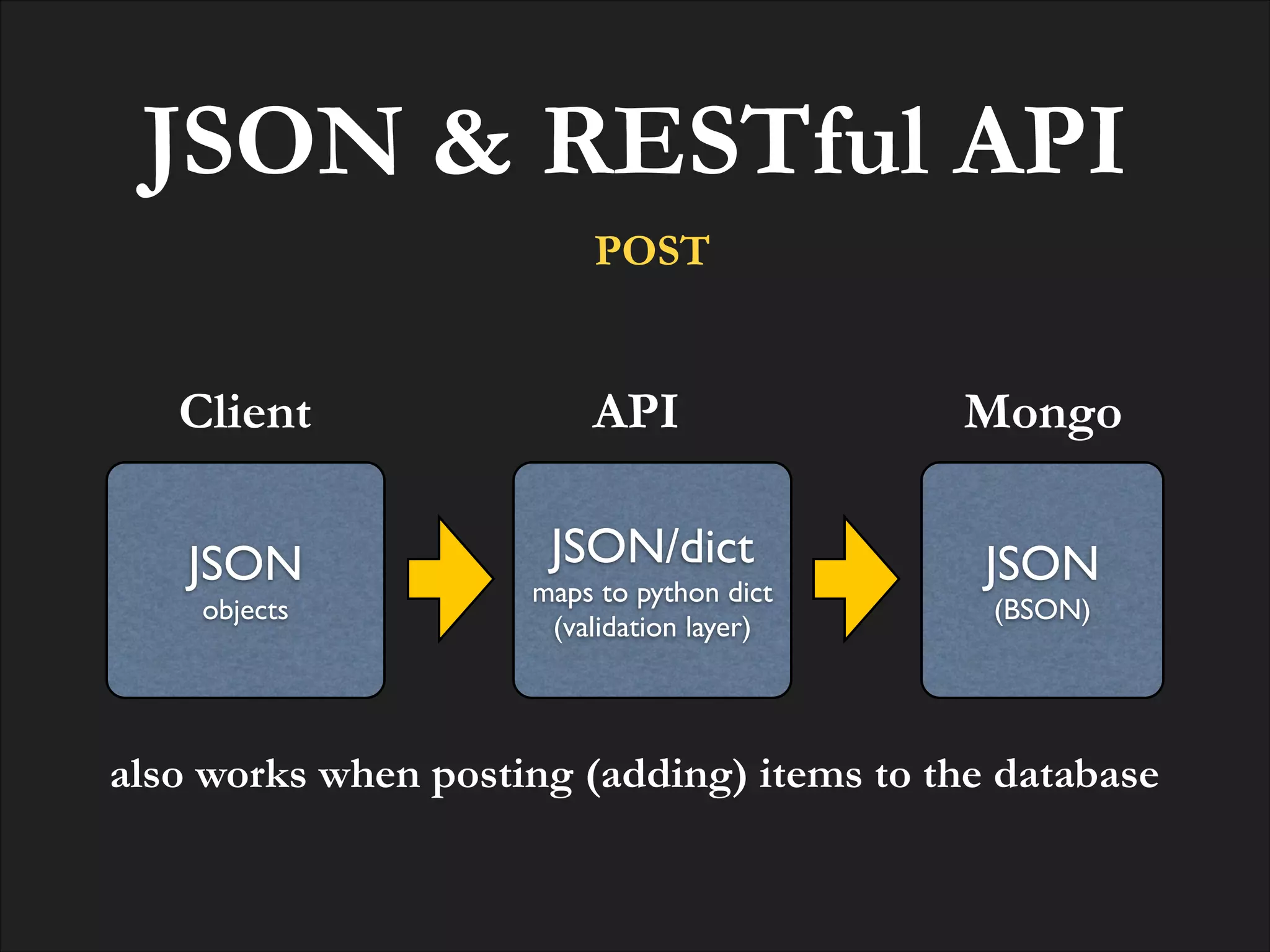


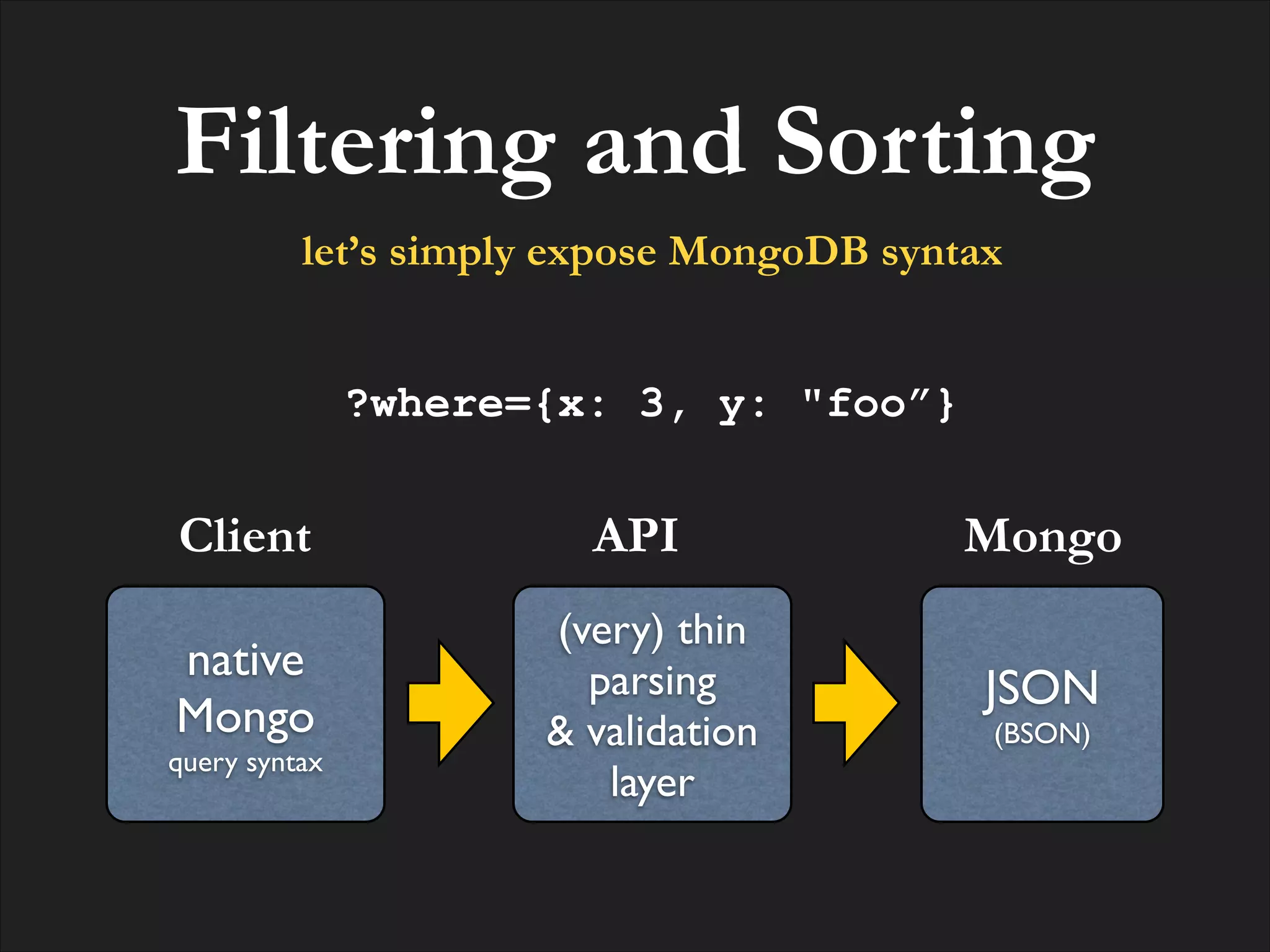









![Resource GET
/contacts?where={“age”: {“$gt”: 20}}&projection={“lastname”: 1}
def get_collection(collection):!
documents = []!
cursor = db(collection).find(where, projection)!
for document in cursor:!
documents.append(document)!
return documents
find() accepts a python dict
as query expression, and
returns a cursor we can
iterate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restwebapiwithmongodb-121026105422-phpapp01/75/RESTful-Web-API-and-MongoDB-go-for-a-pic-nic-33-2048.jpg)
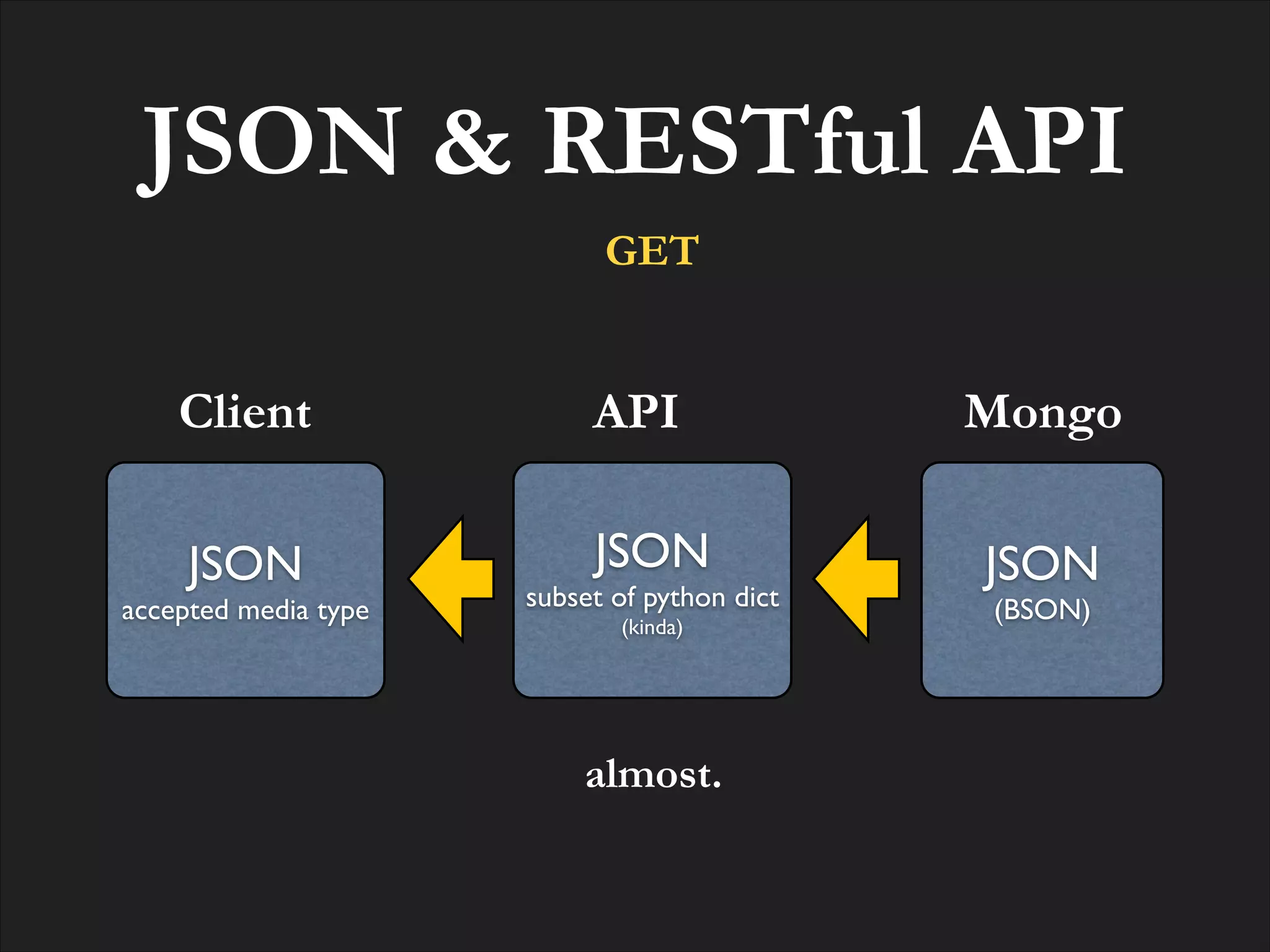
![Resource GET
/contacts?where={“age”: {“$gt”: 20}}&projection={“lastname”: 1}
def get_collection(collection):!
documents = []!
cursor = db(collection).find(where, projection)!
for document in cursor:!
documents.append(document)!
return documents
find() accepts a python dict
as query expression, and
returns a cursor we can
iterate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restwebapiwithmongodb-121026105422-phpapp01/75/RESTful-Web-API-and-MongoDB-go-for-a-pic-nic-34-2048.jpg)
![Resource GET
/contacts?where={“age”: {“$gt”: 20}}&projection={“lastname”: 1}
def get_collection(collection):!
documents = []!
cursor = db(collection).find(where, projection)!
for document in cursor:!
documents.append(document)!
return documents
find() accepts a python dict
as query expression, and
returns a cursor we can
iterate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restwebapiwithmongodb-121026105422-phpapp01/75/RESTful-Web-API-and-MongoDB-go-for-a-pic-nic-35-2048.jpg)
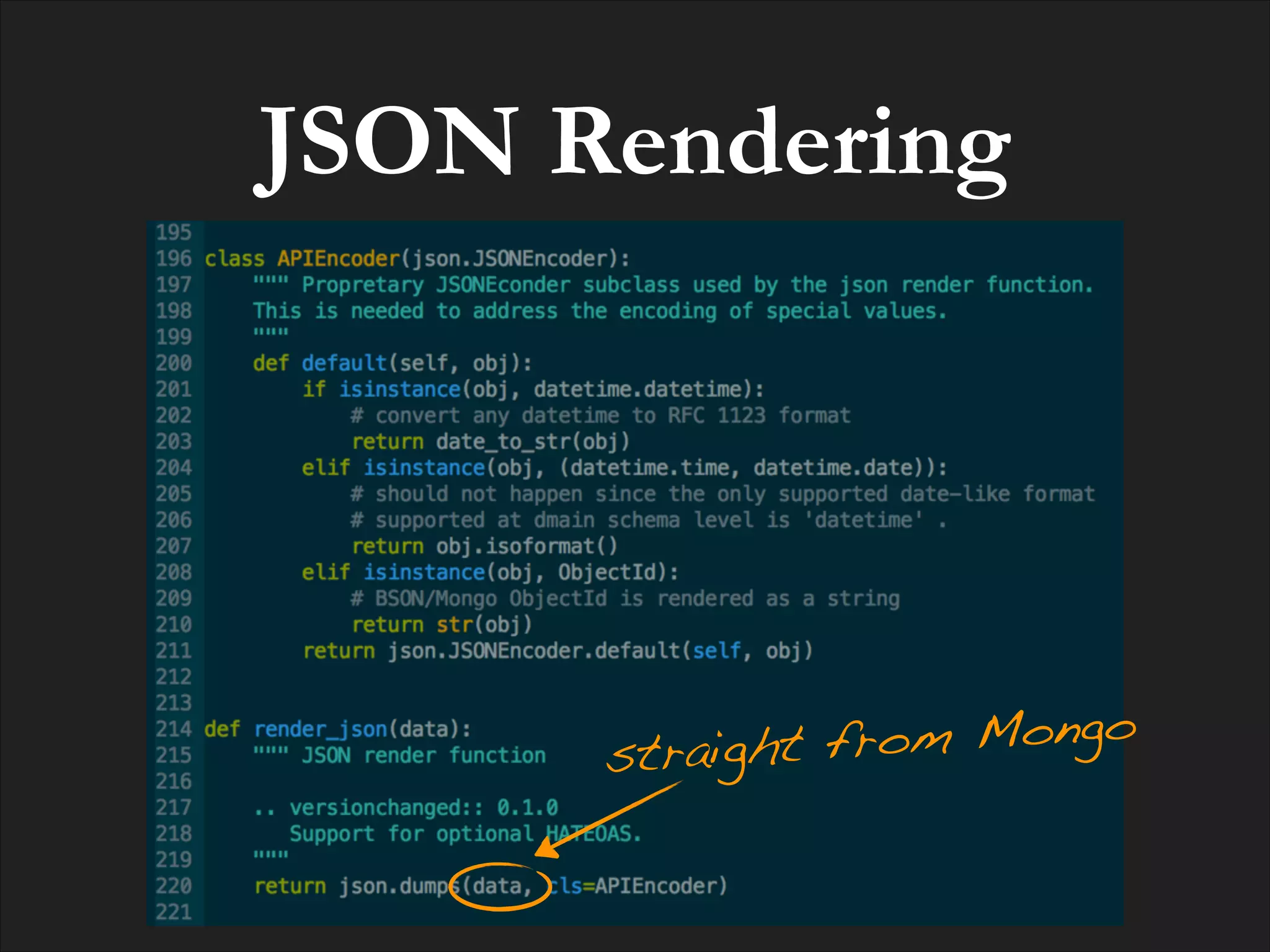
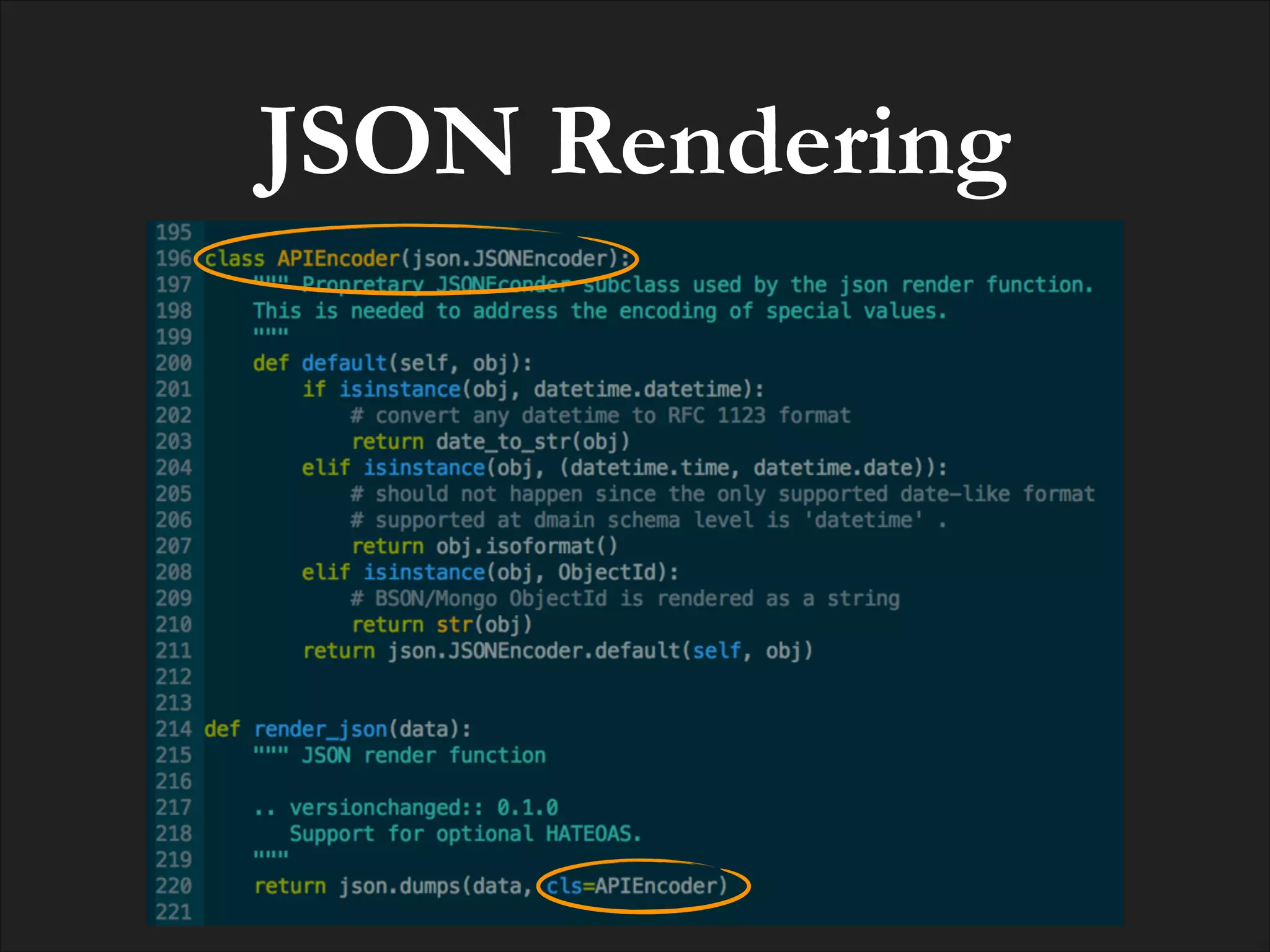

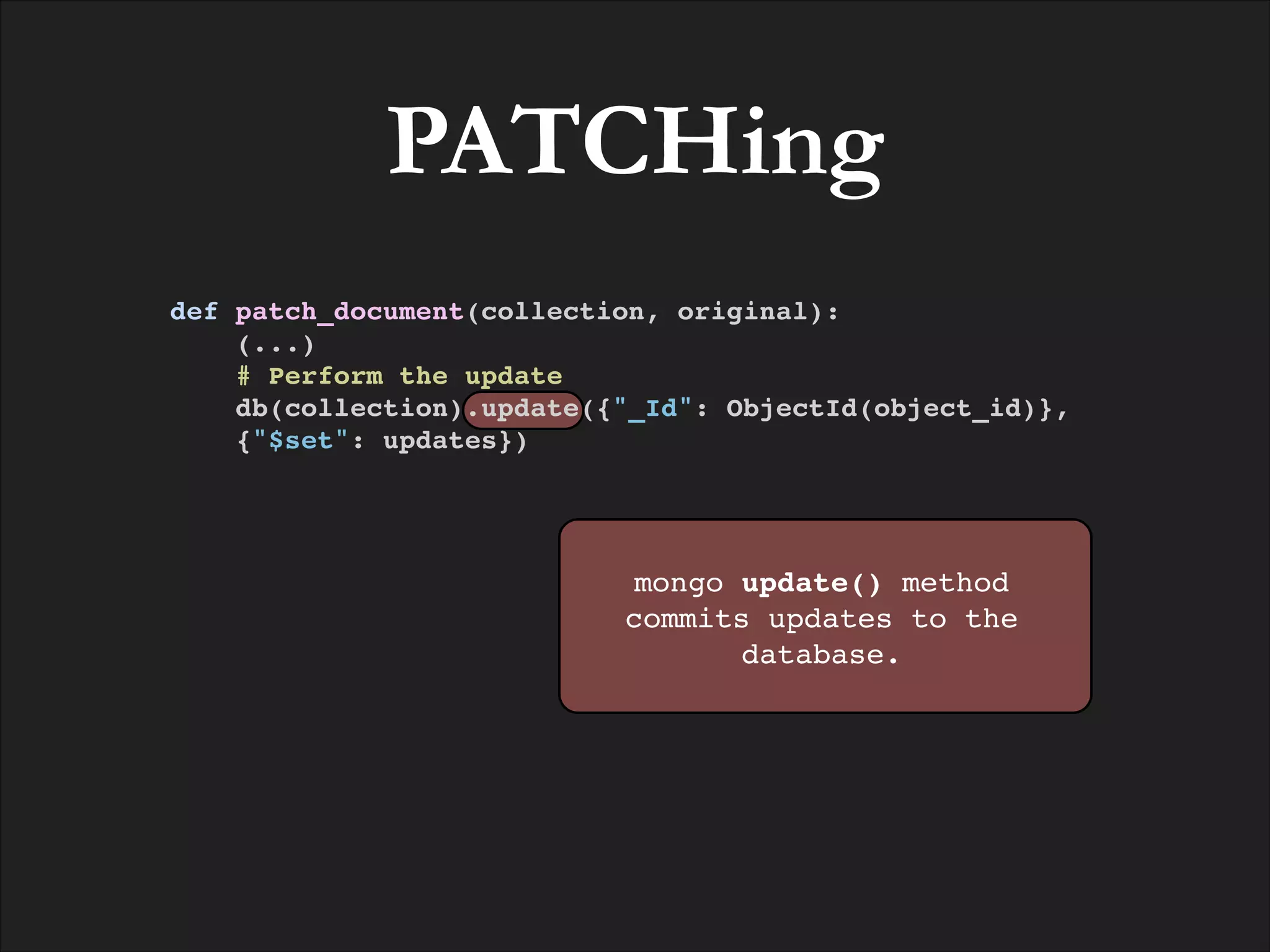

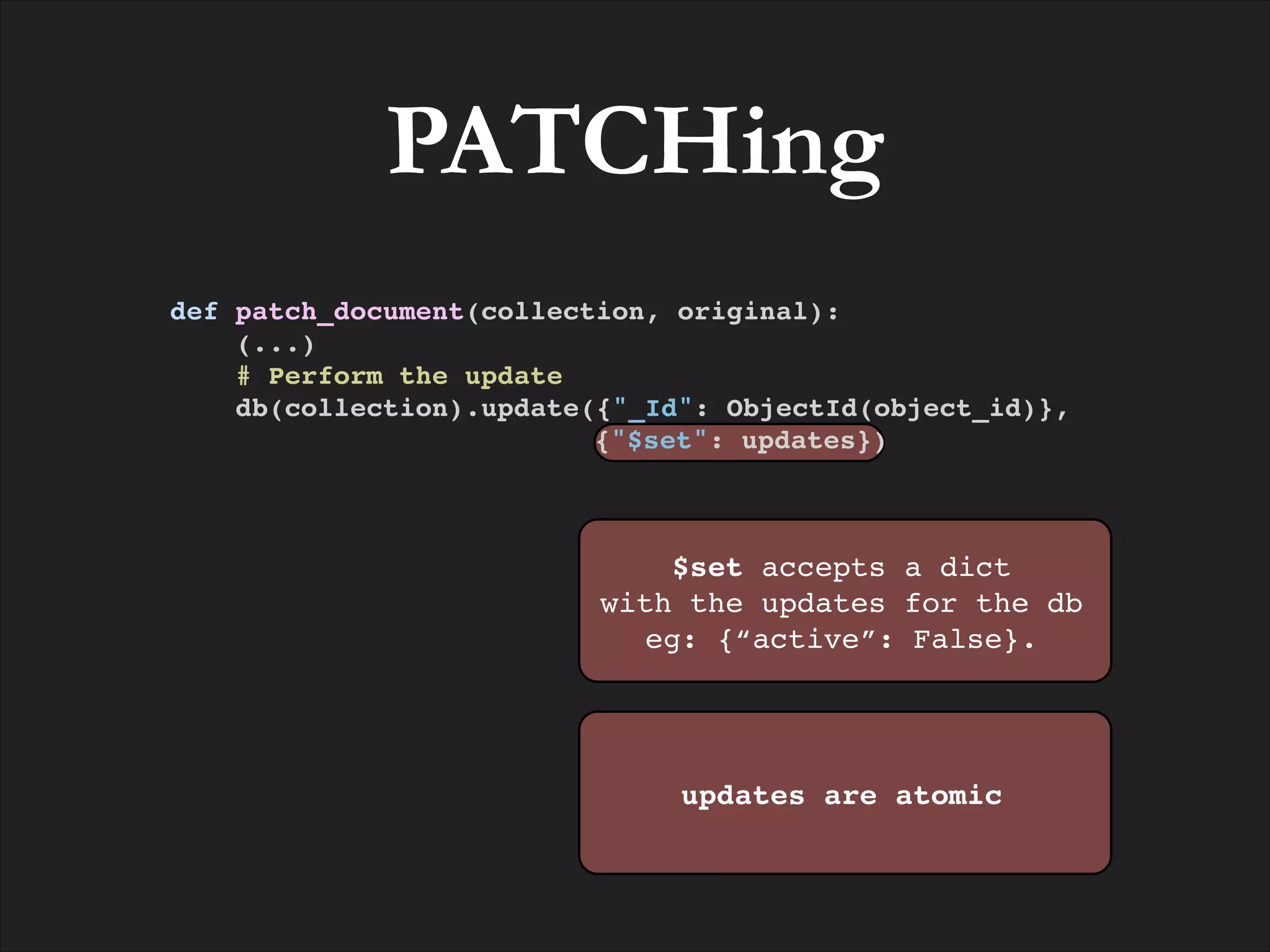

![POSTing
Take #1
def post(collection):!
(...)!
for key, item in docs.items():!
response[ID_FIELD] = db(collection).insert(item)
push document and get its
ObjectId back from Mongo.
like other CRUD operations,
inserting is trivial in
mongo.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restwebapiwithmongodb-121026105422-phpapp01/75/RESTful-Web-API-and-MongoDB-go-for-a-pic-nic-44-2048.jpg)