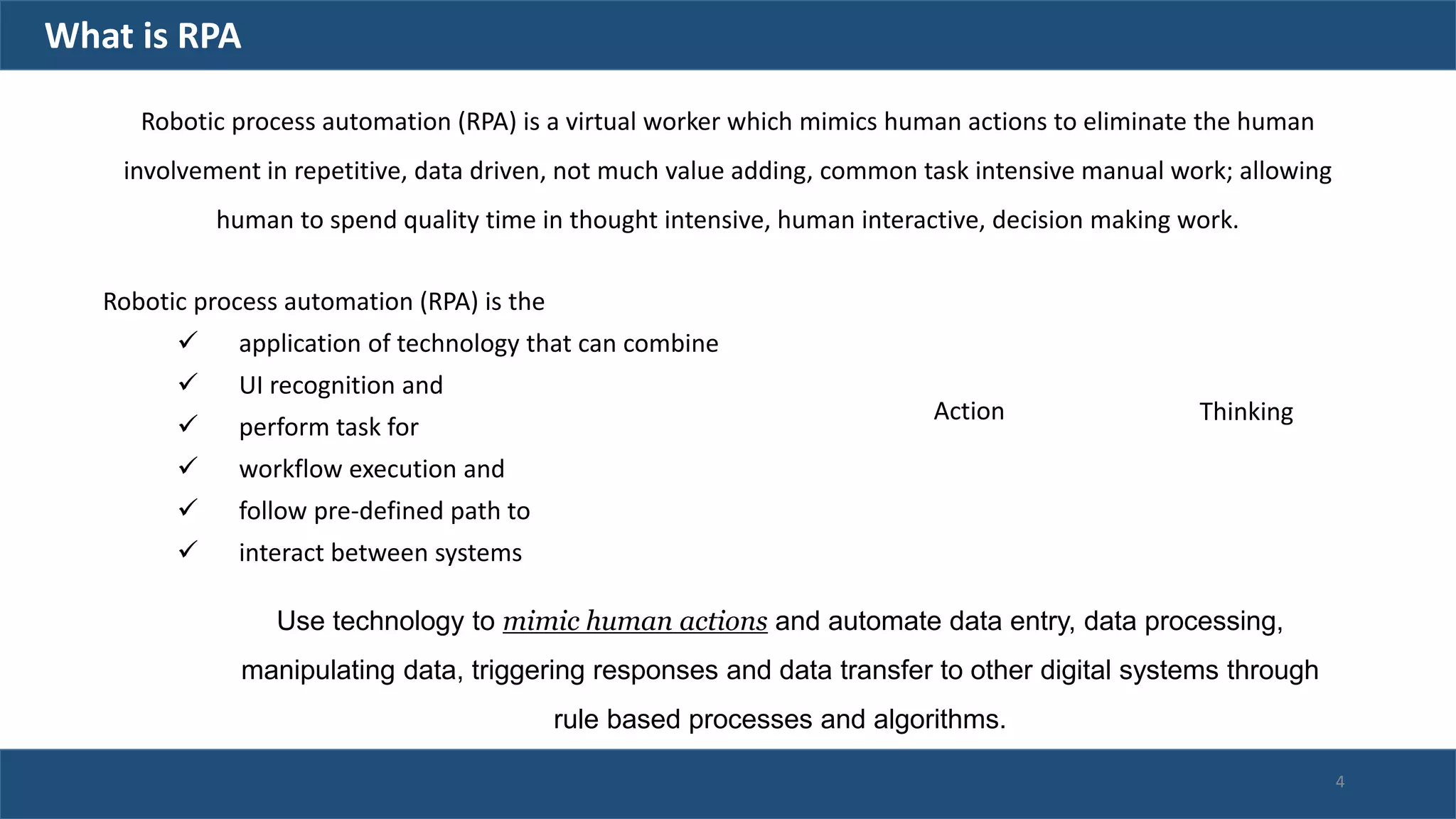
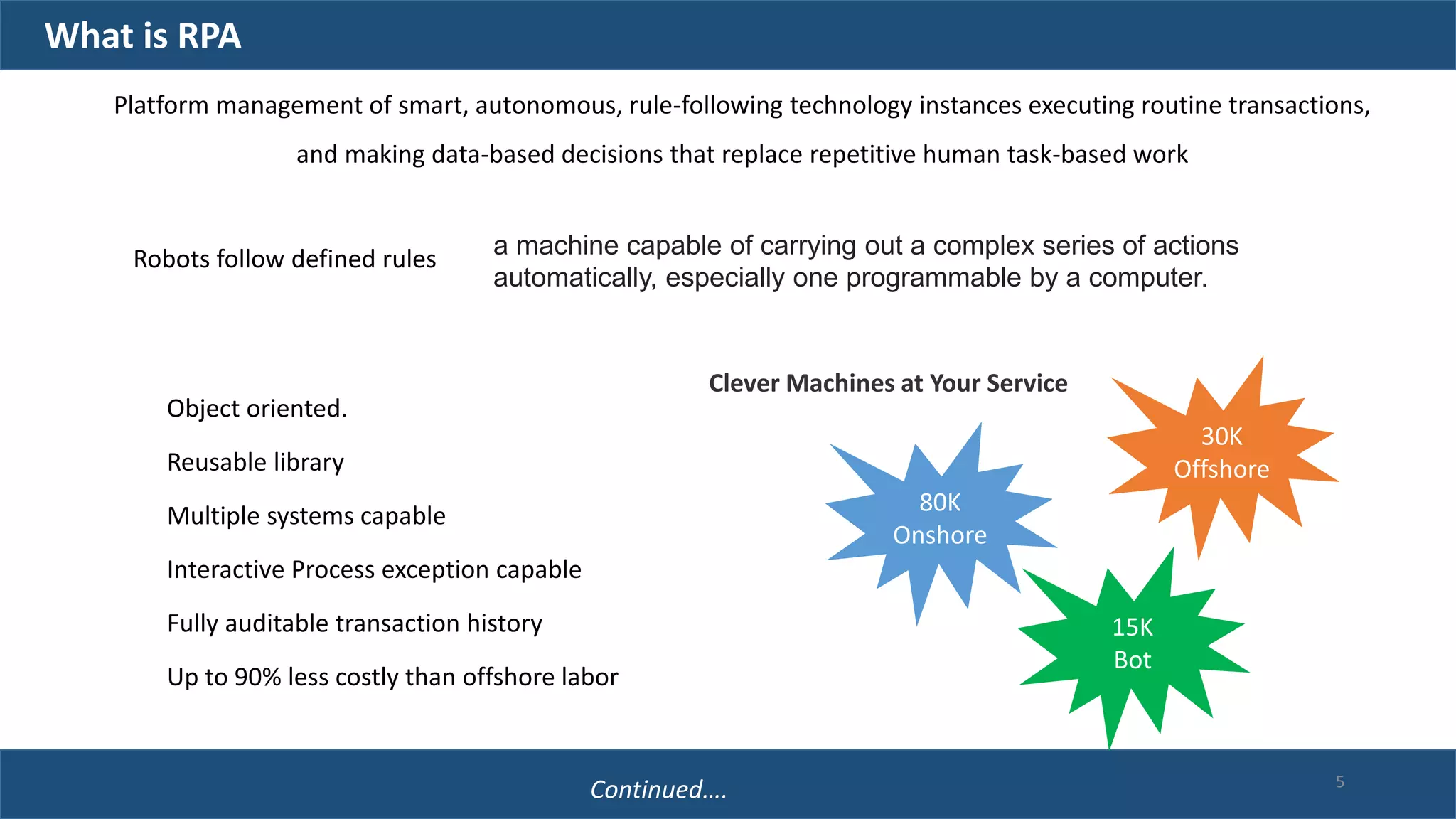
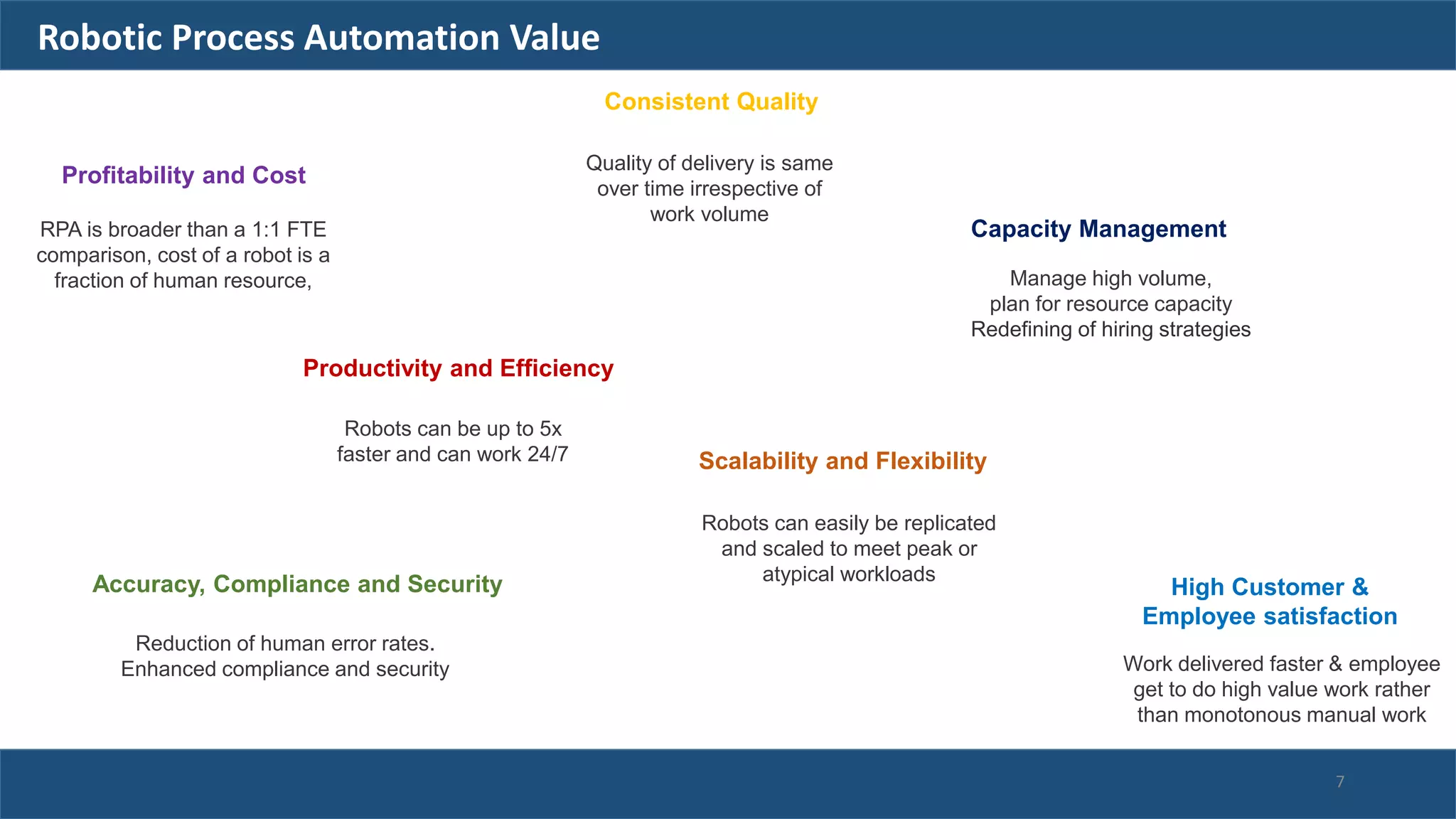
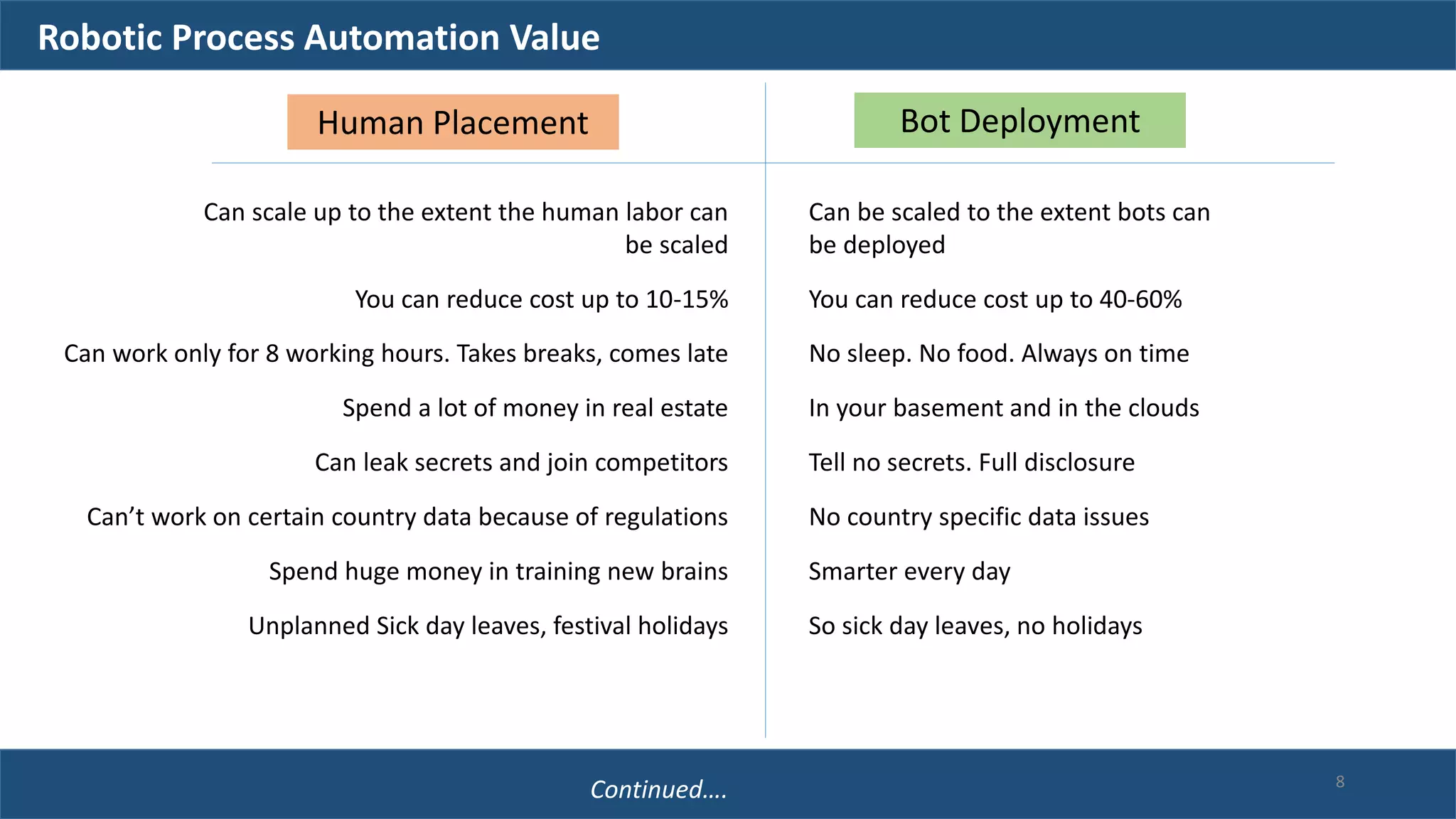
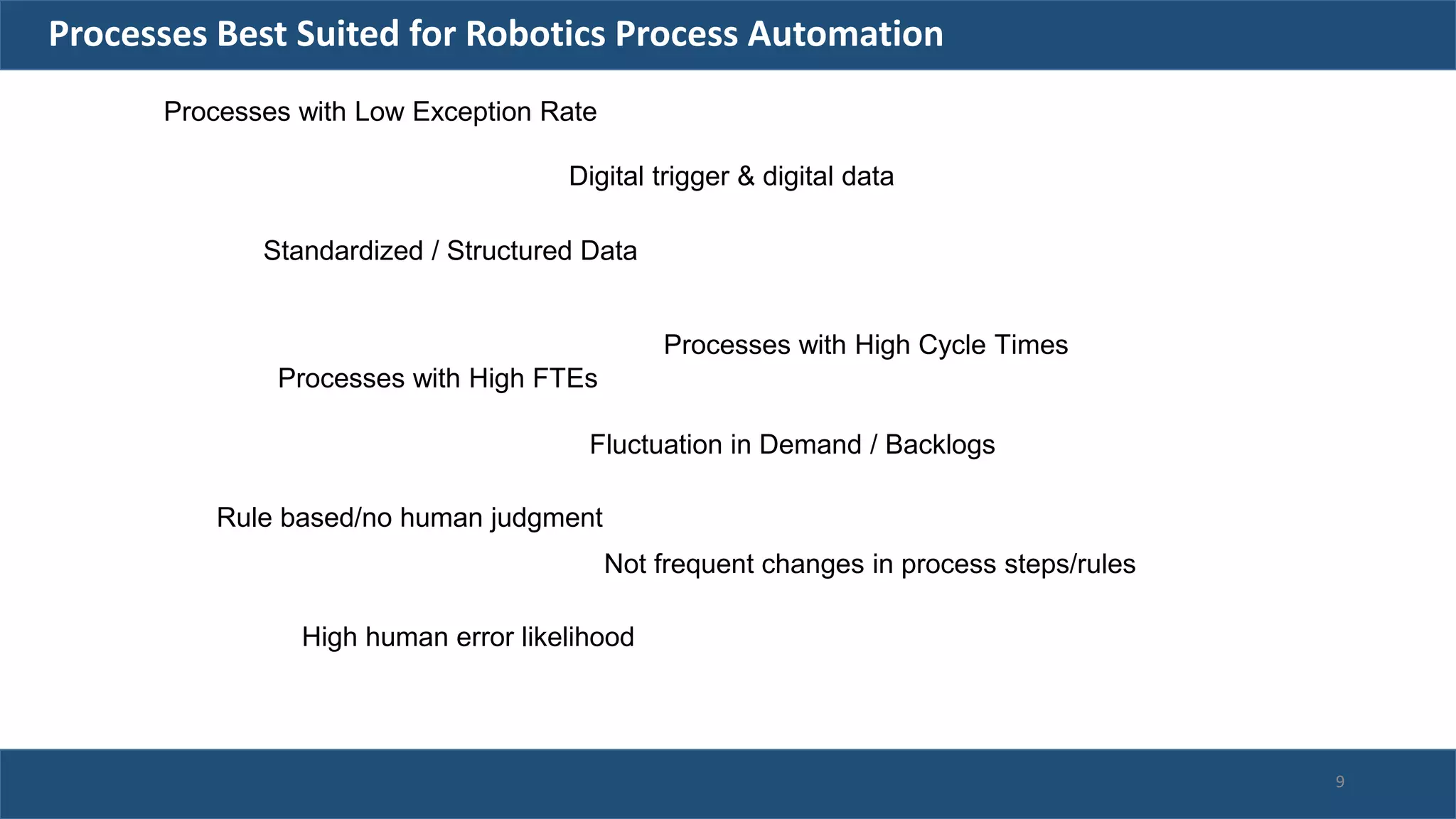
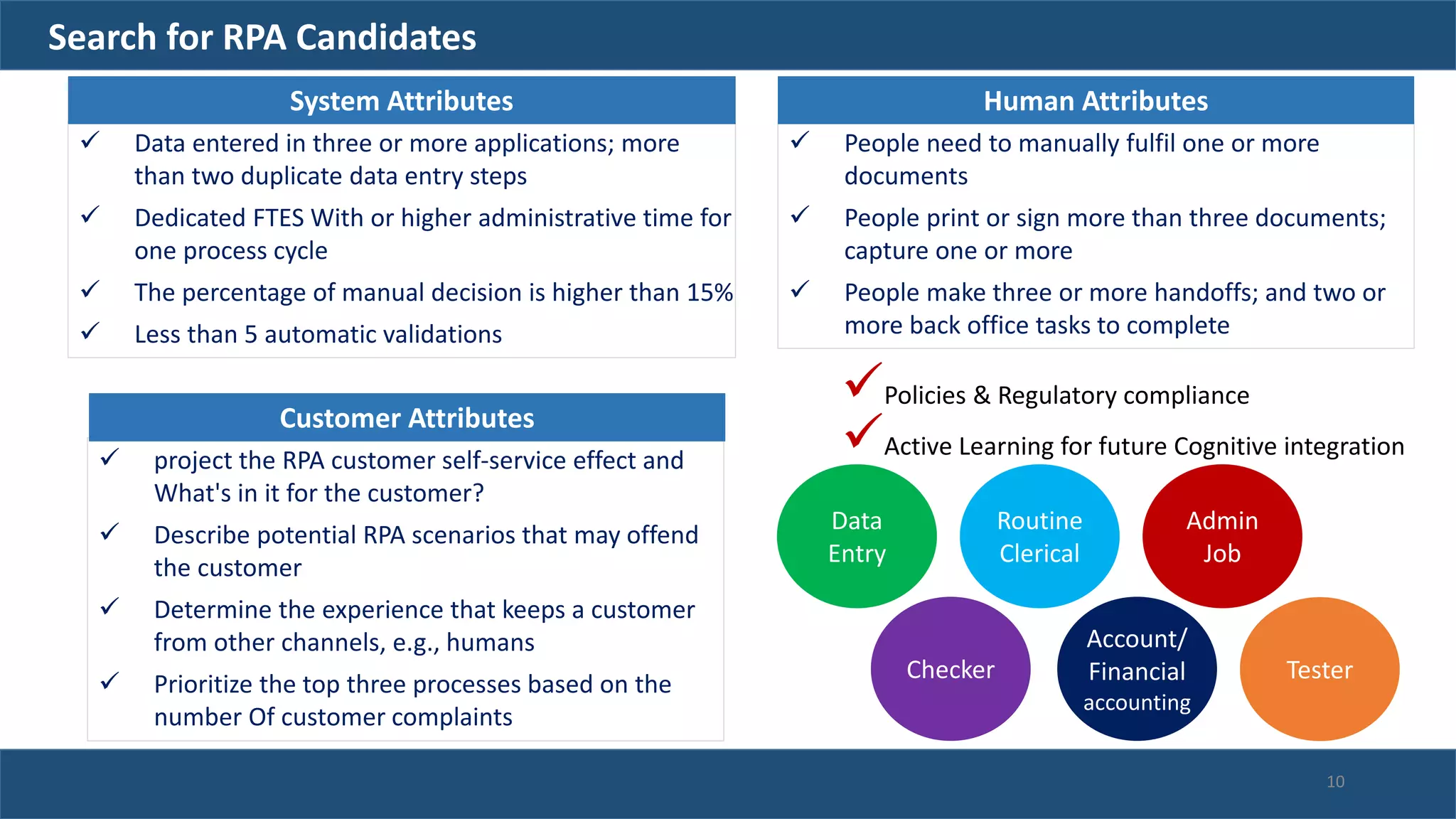
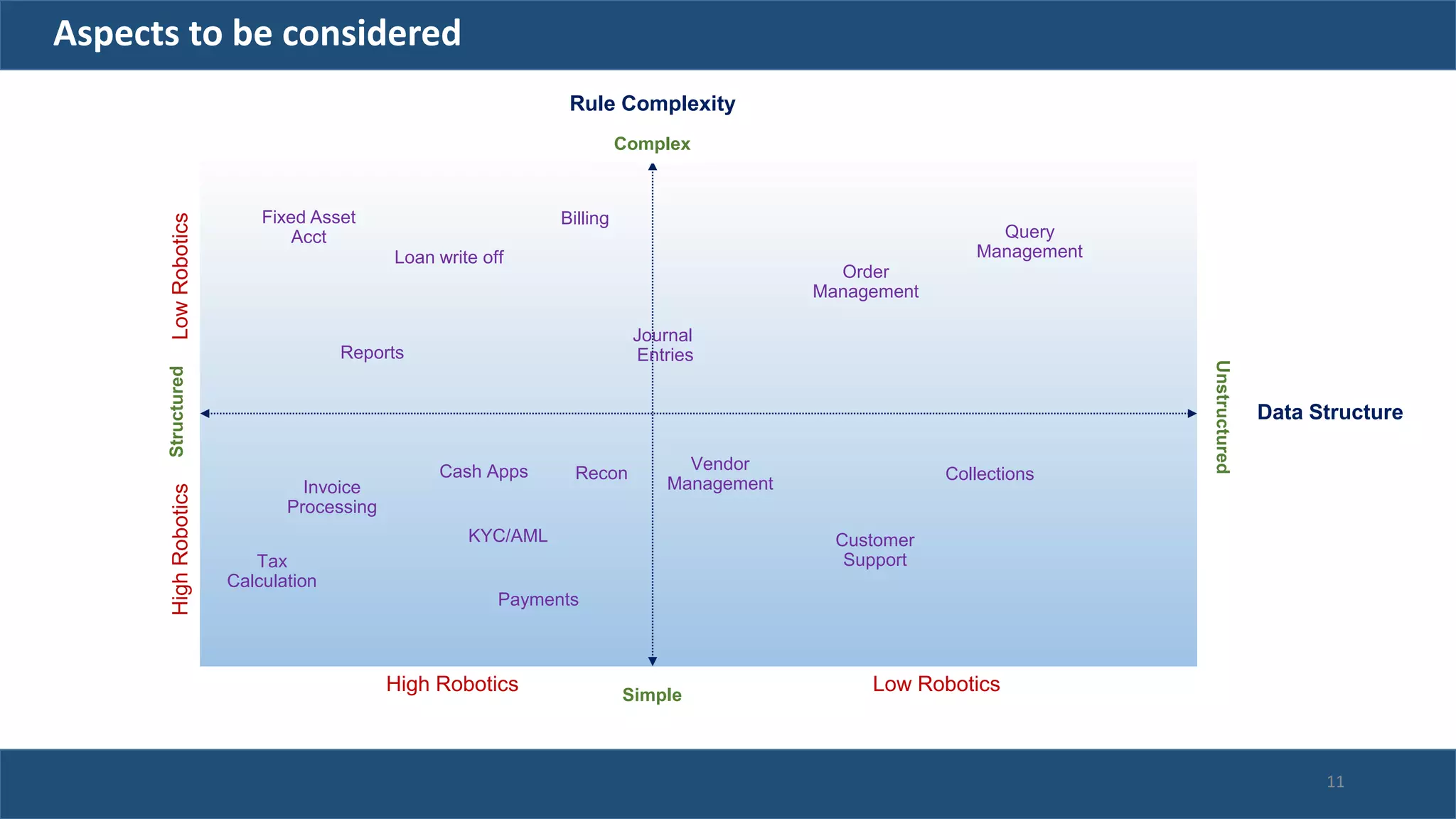
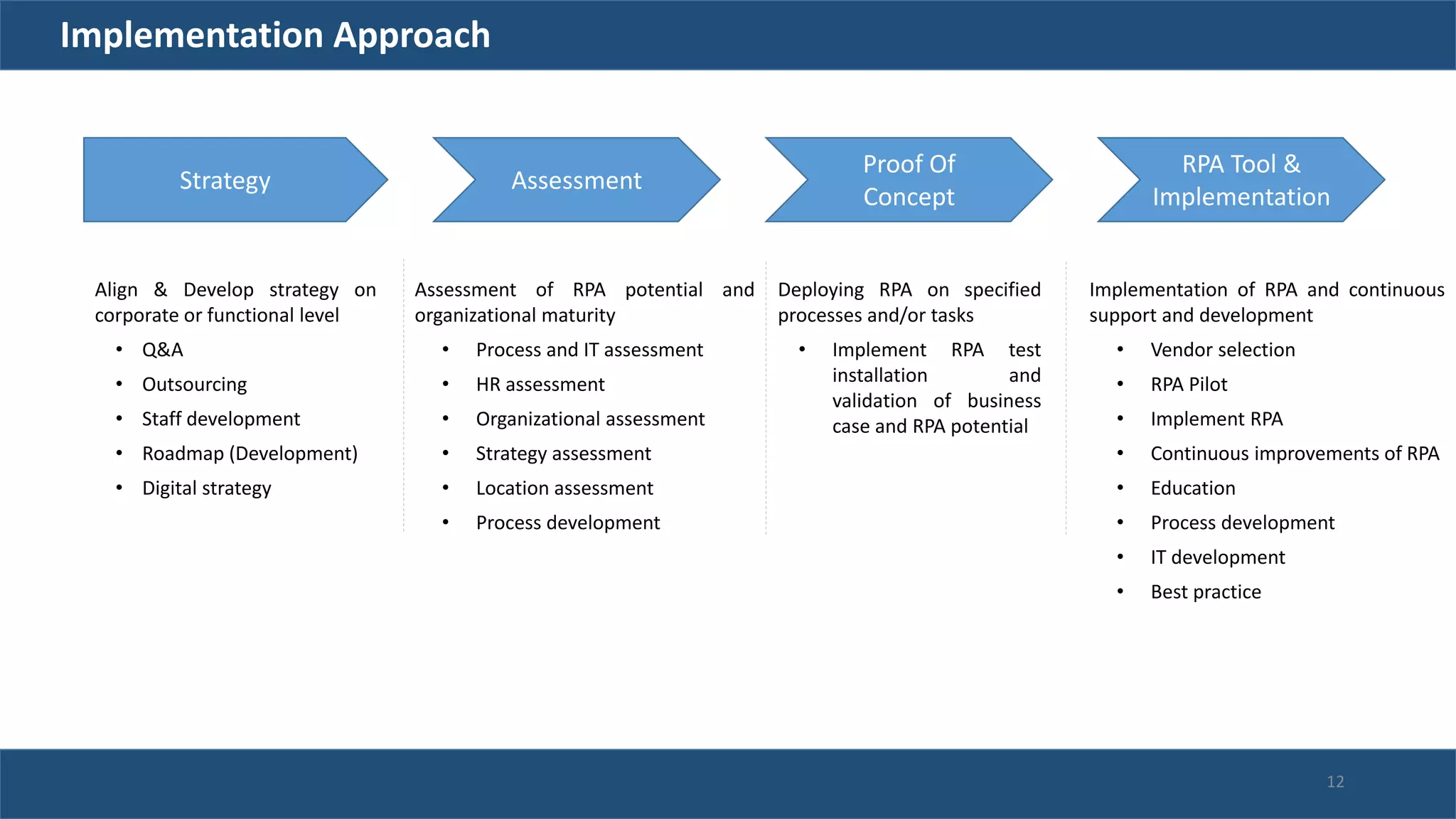
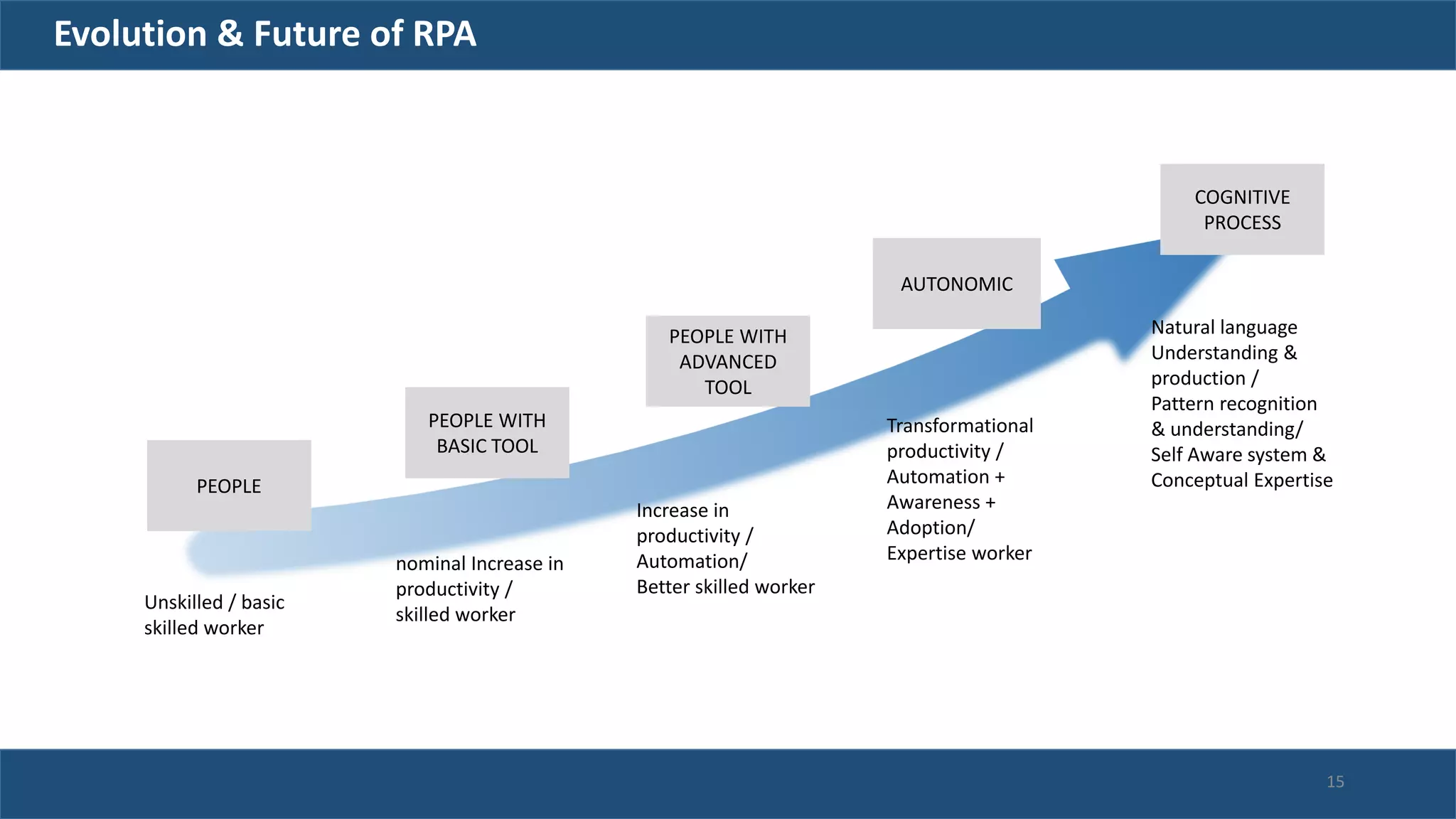
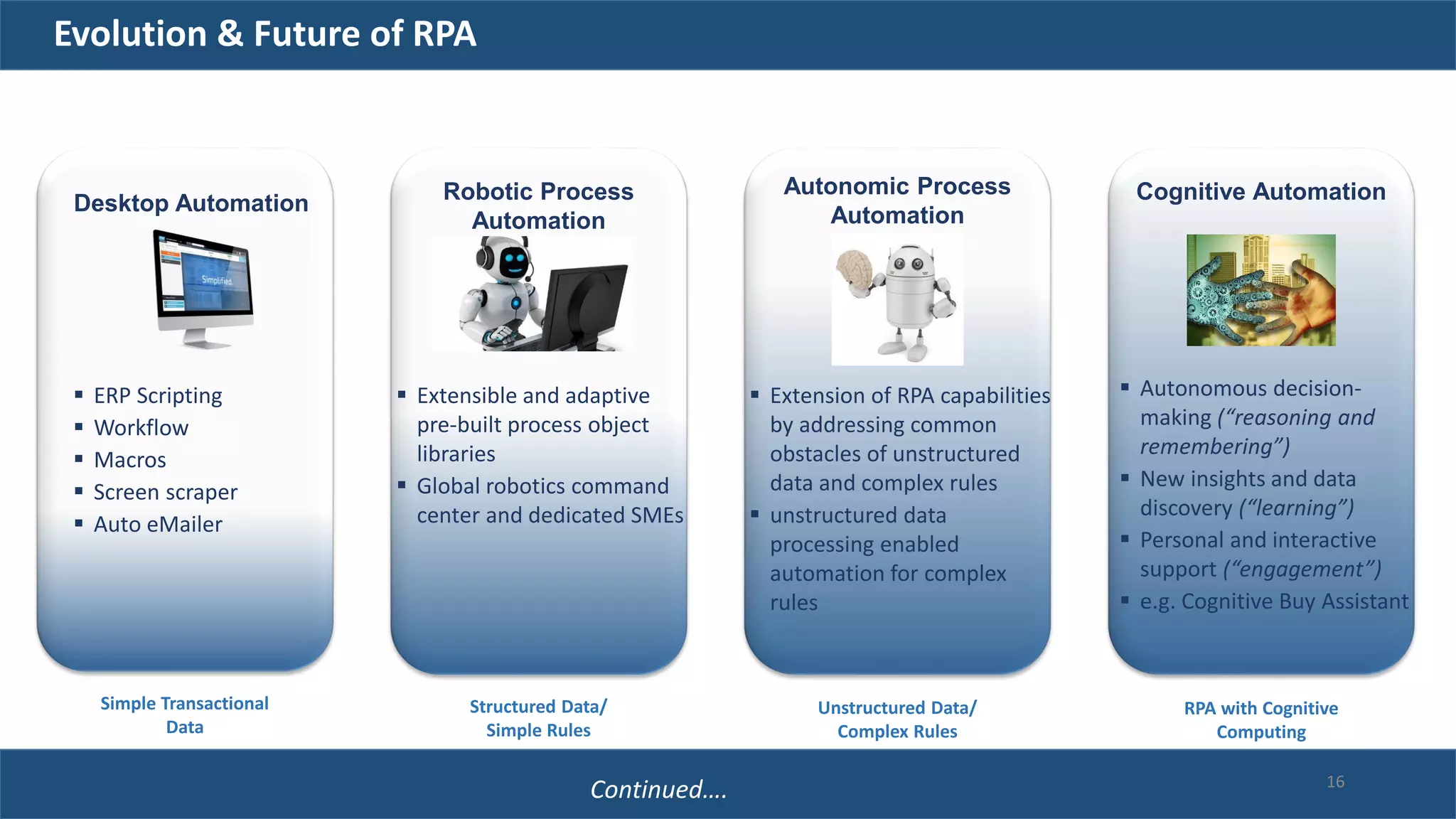
The document discusses robotic process automation (RPA). It begins with an overview of RPA, noting that RPA mimics human actions to automate repetitive tasks. It then discusses why RPA is used, identifying processes that are good candidates for automation. The document outlines best practices for RPA implementation and provides examples of real-life RPA uses. It concludes by examining why RPA implementations sometimes fail, such as due to unstructured data, frequent business changes, and lack of collaboration.