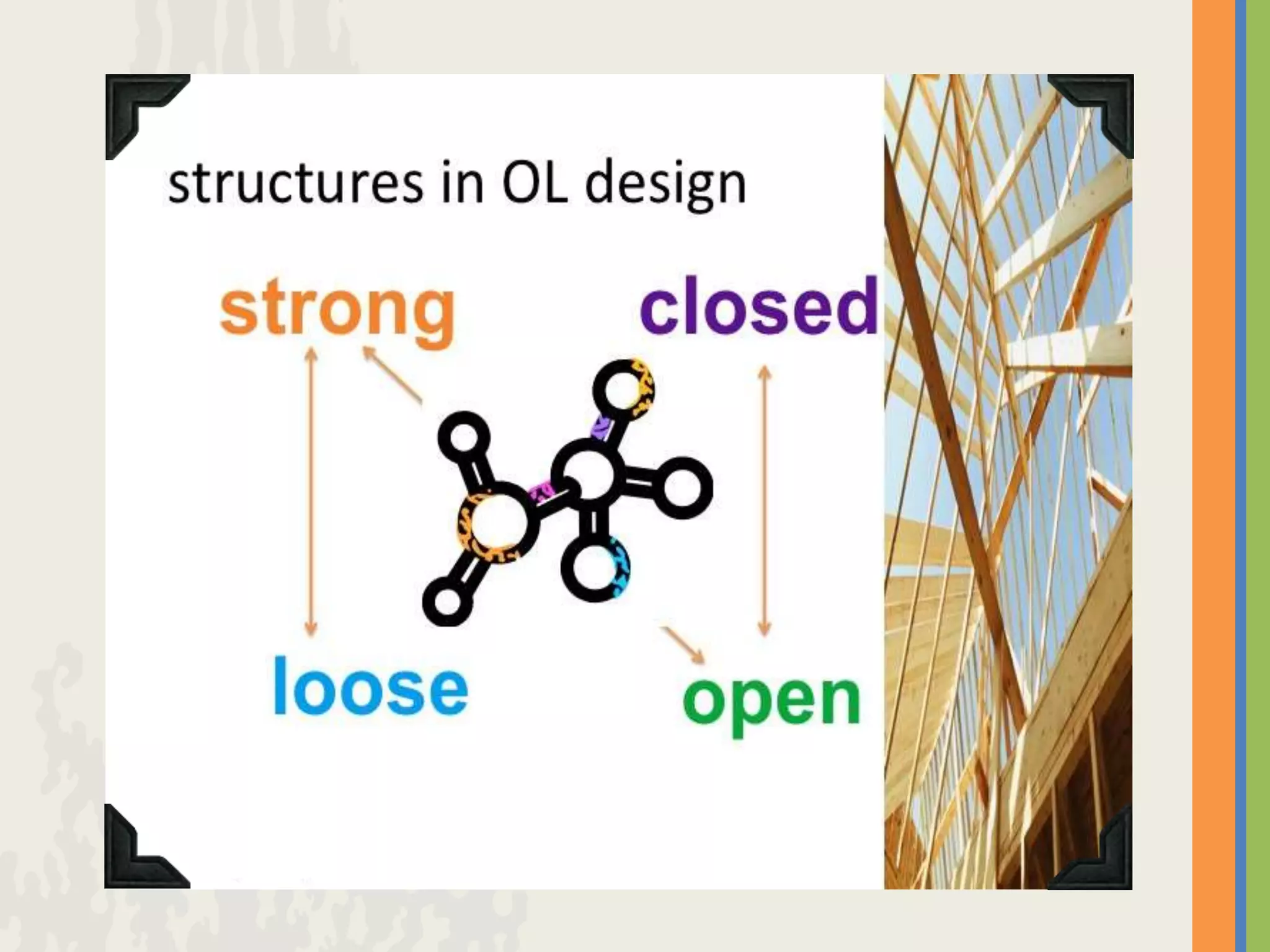
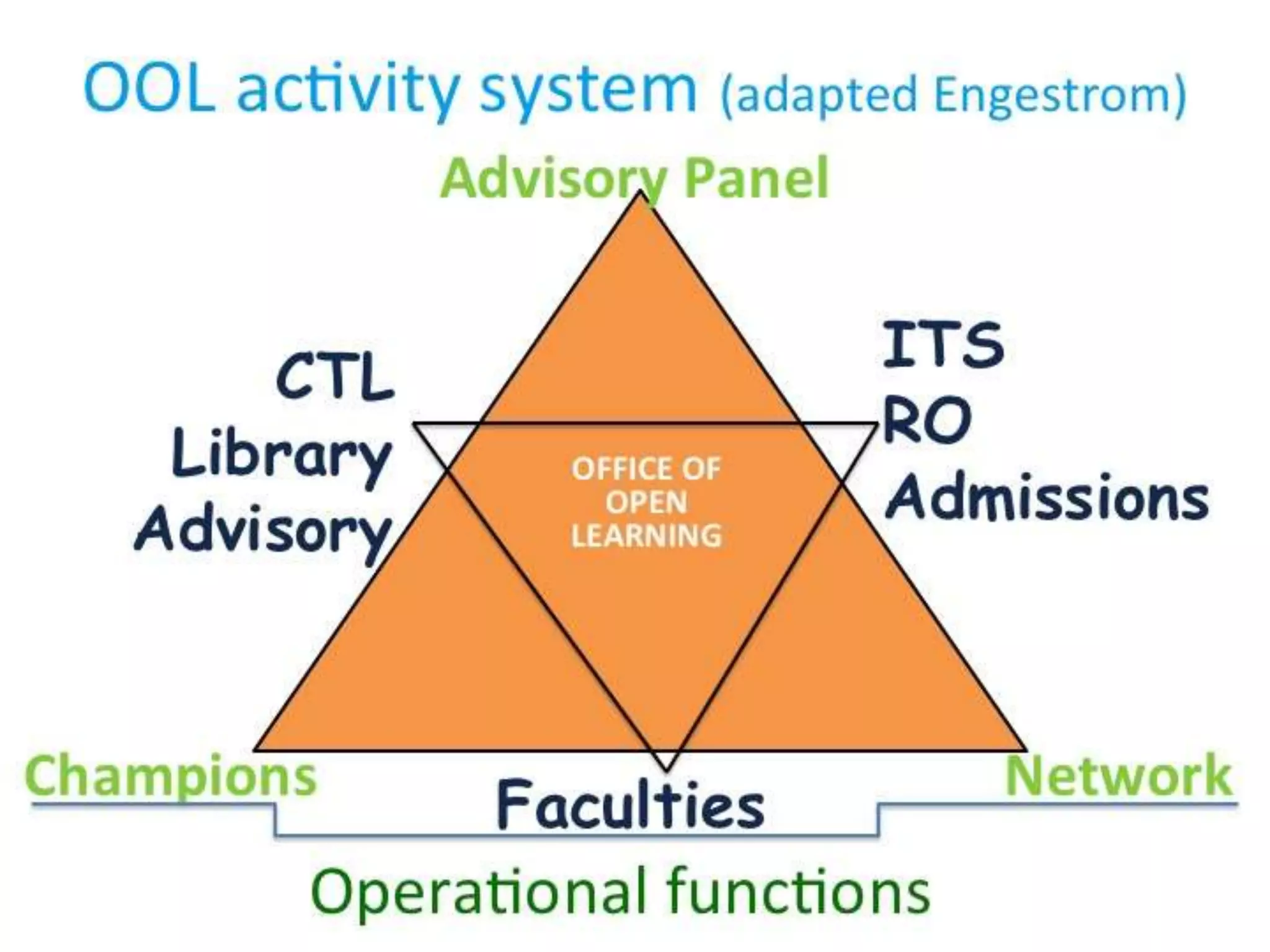
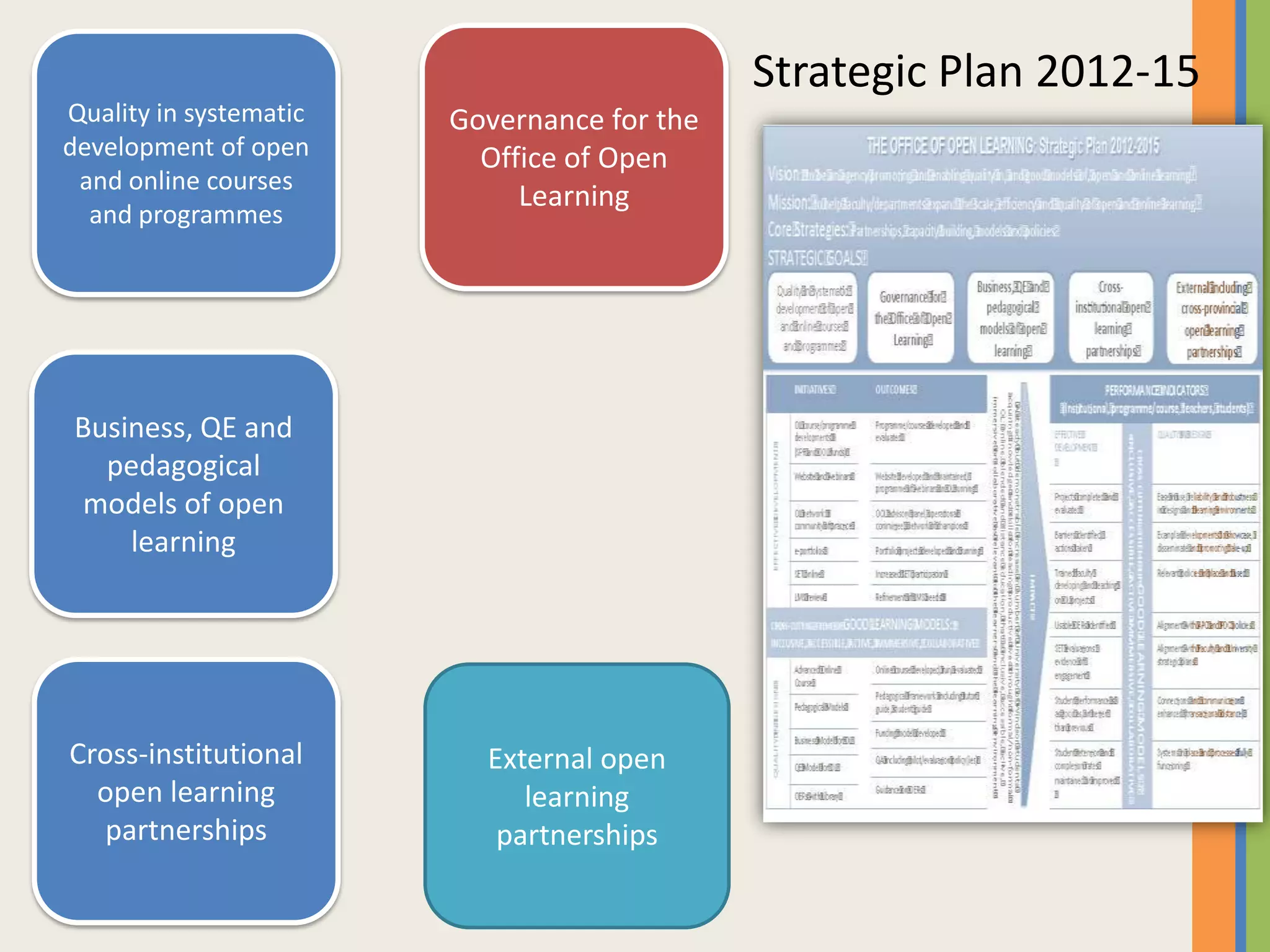
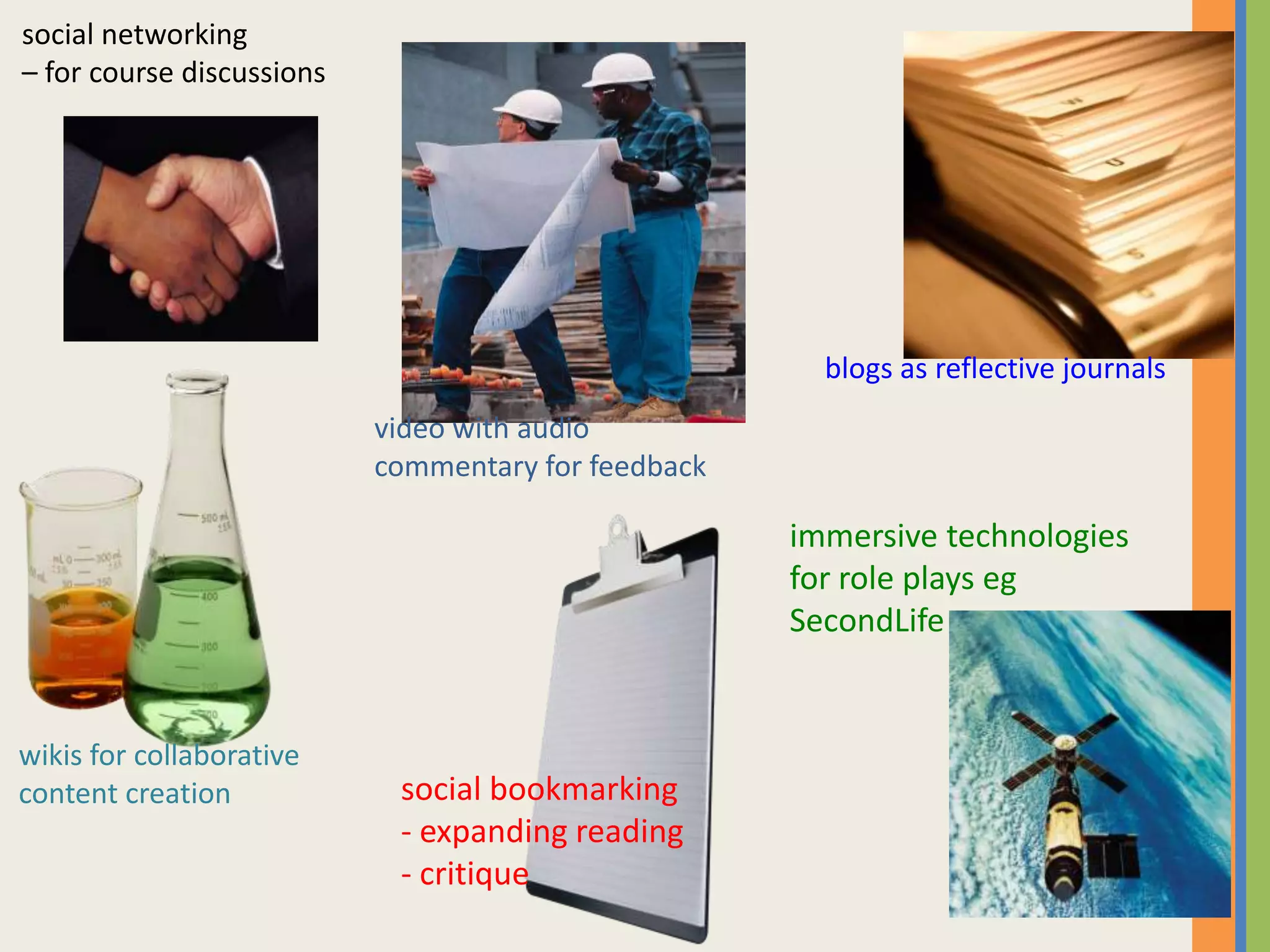
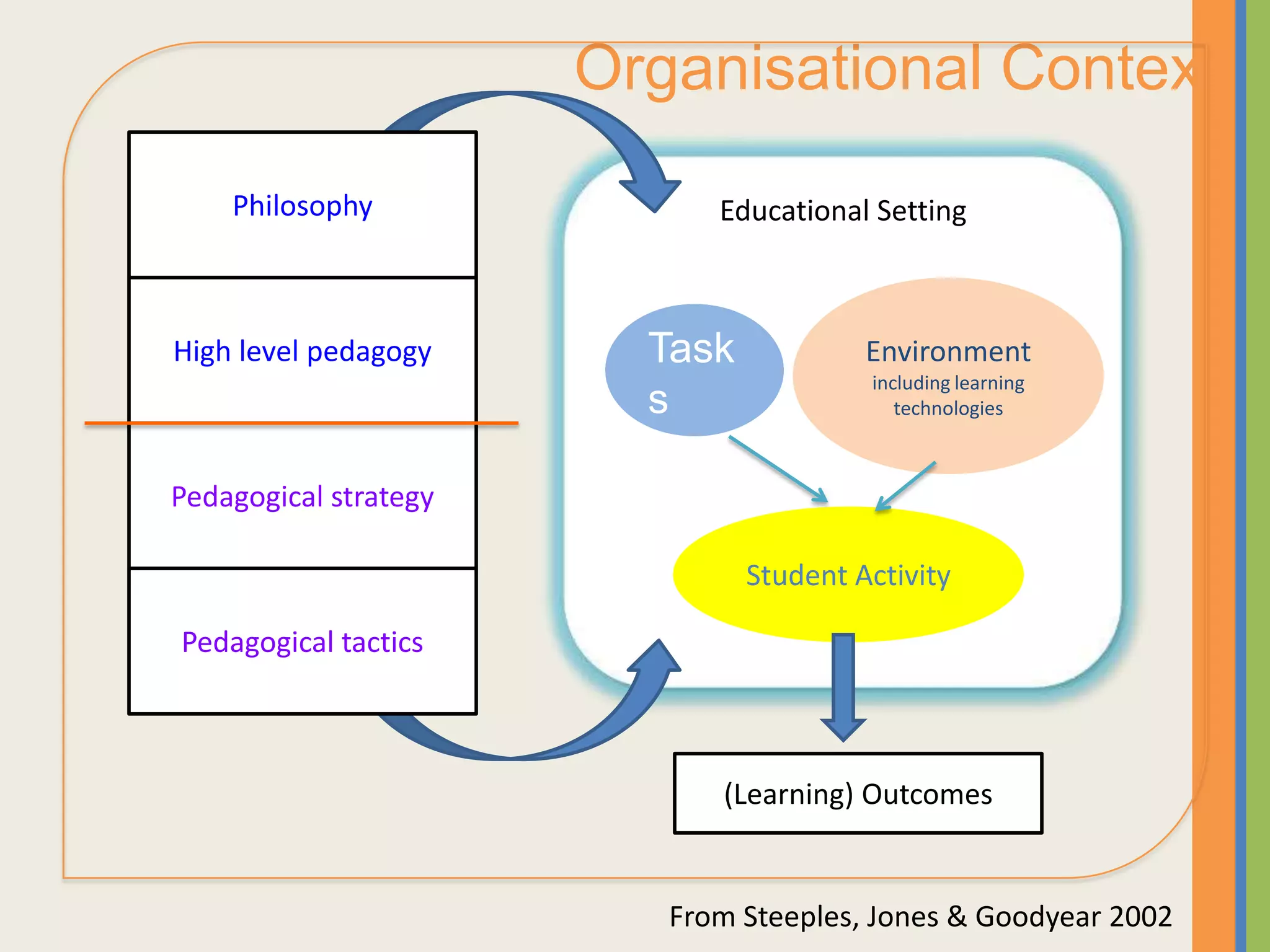
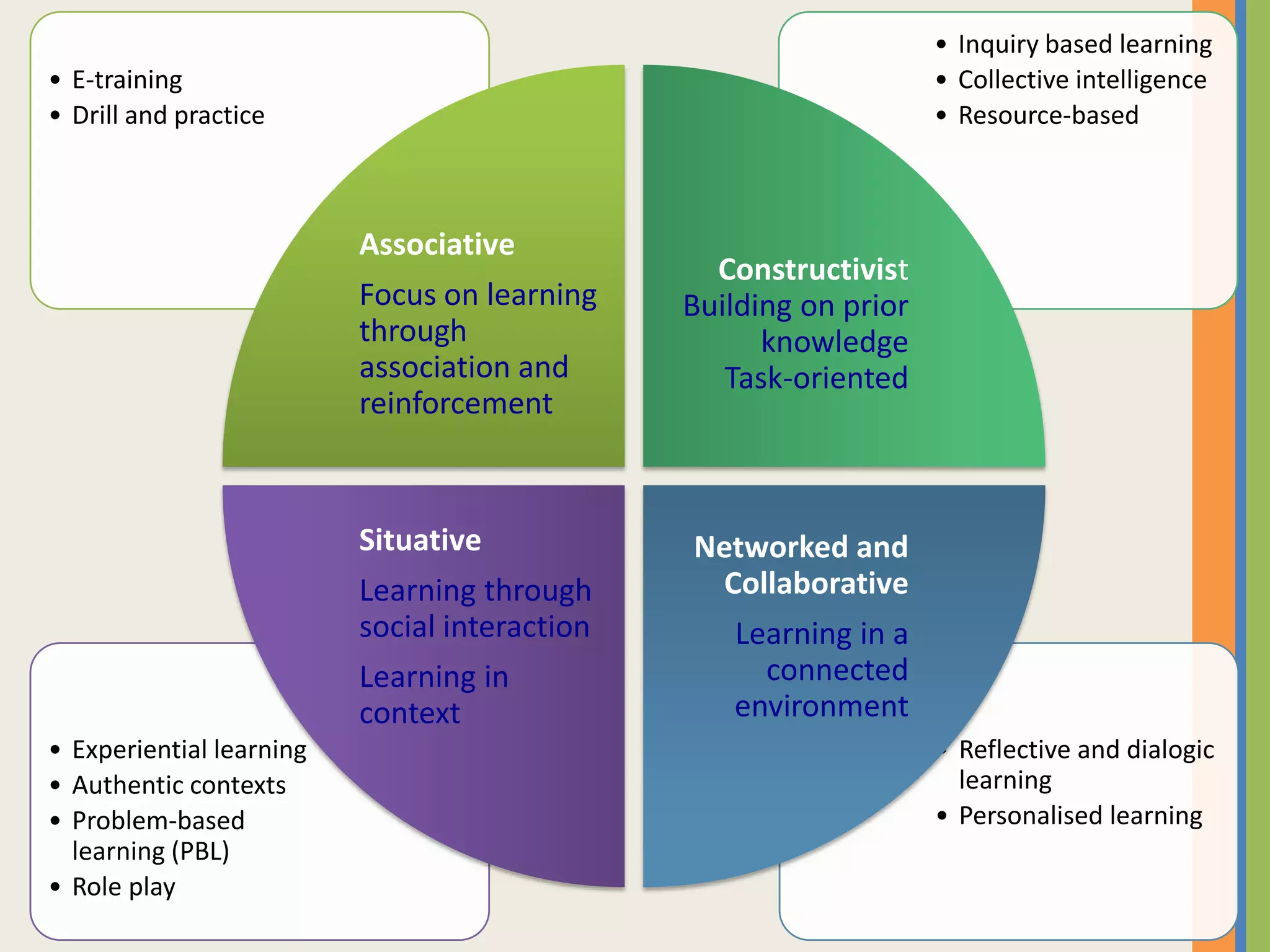
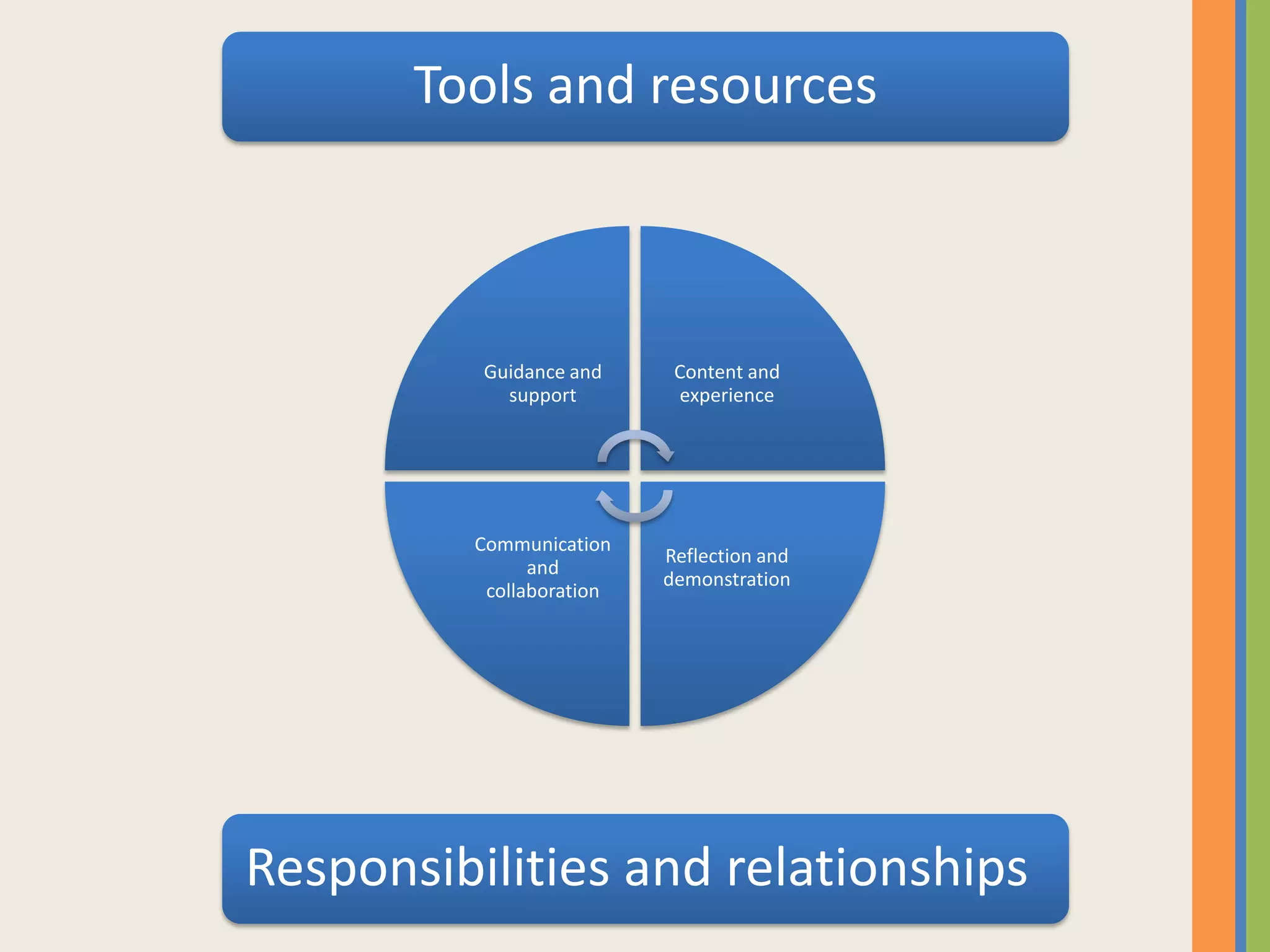
The document provides an overview of open and online learning, emphasizing its concepts, strategies, and the use of technology-enhanced tools to enhance learning experiences. It outlines the goals of open learning initiatives, the transformation in curriculum, and the roles of various technologies such as MOOCs, e-books, and mobile apps in education. Additionally, it discusses the support and resources available for transitioning to online learning and encourages participation in ongoing discussions and courses about open learning.