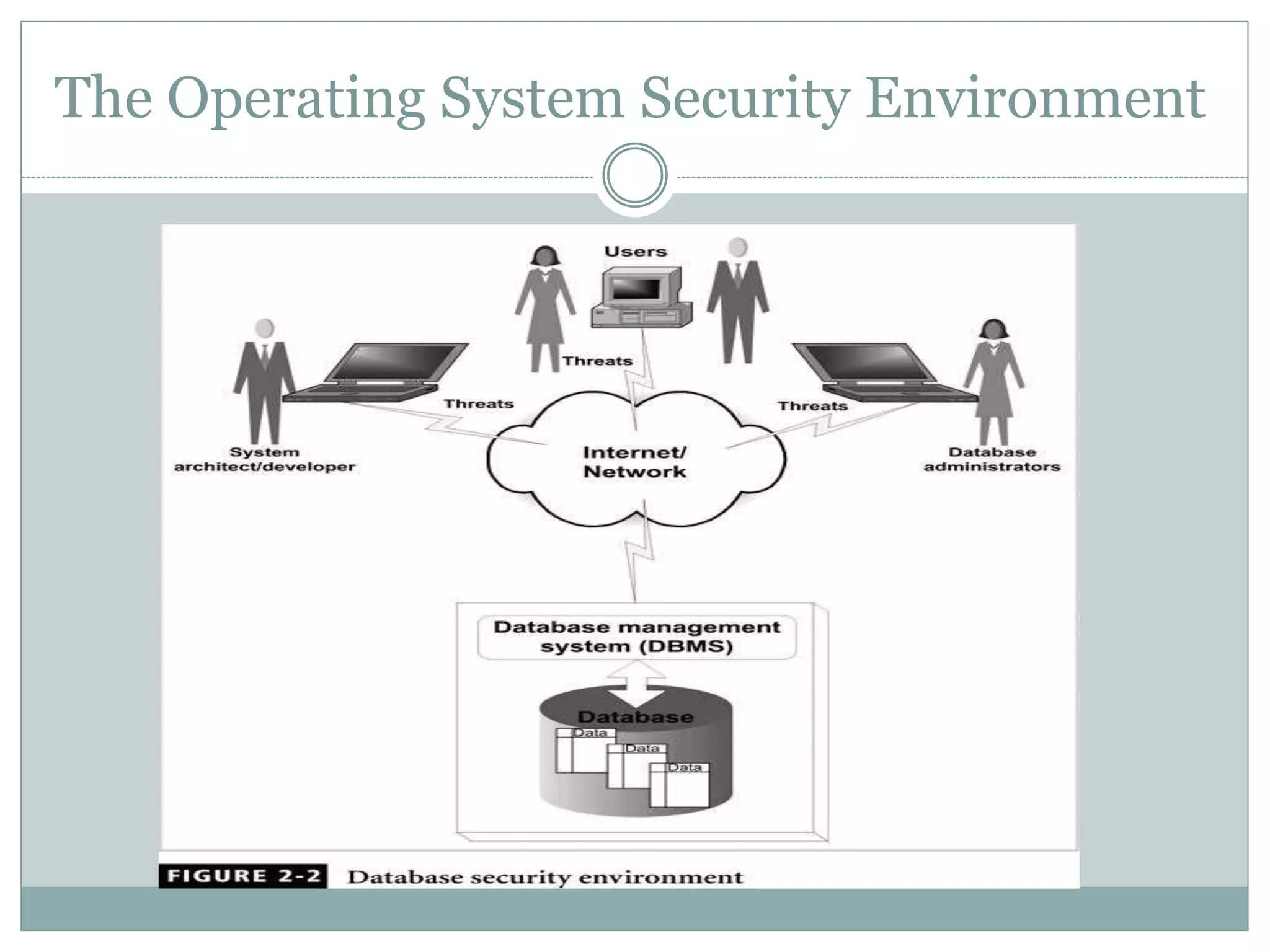
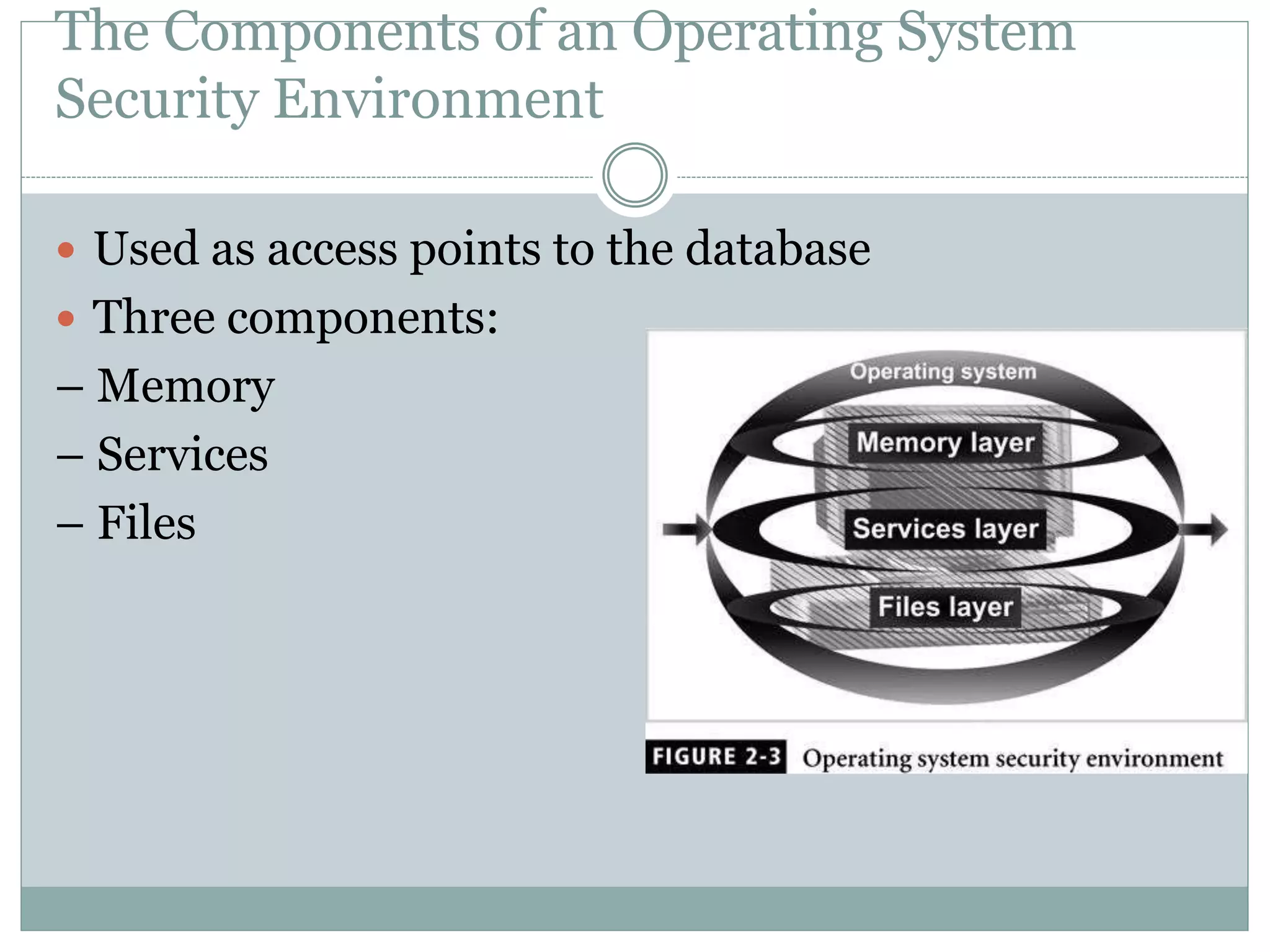
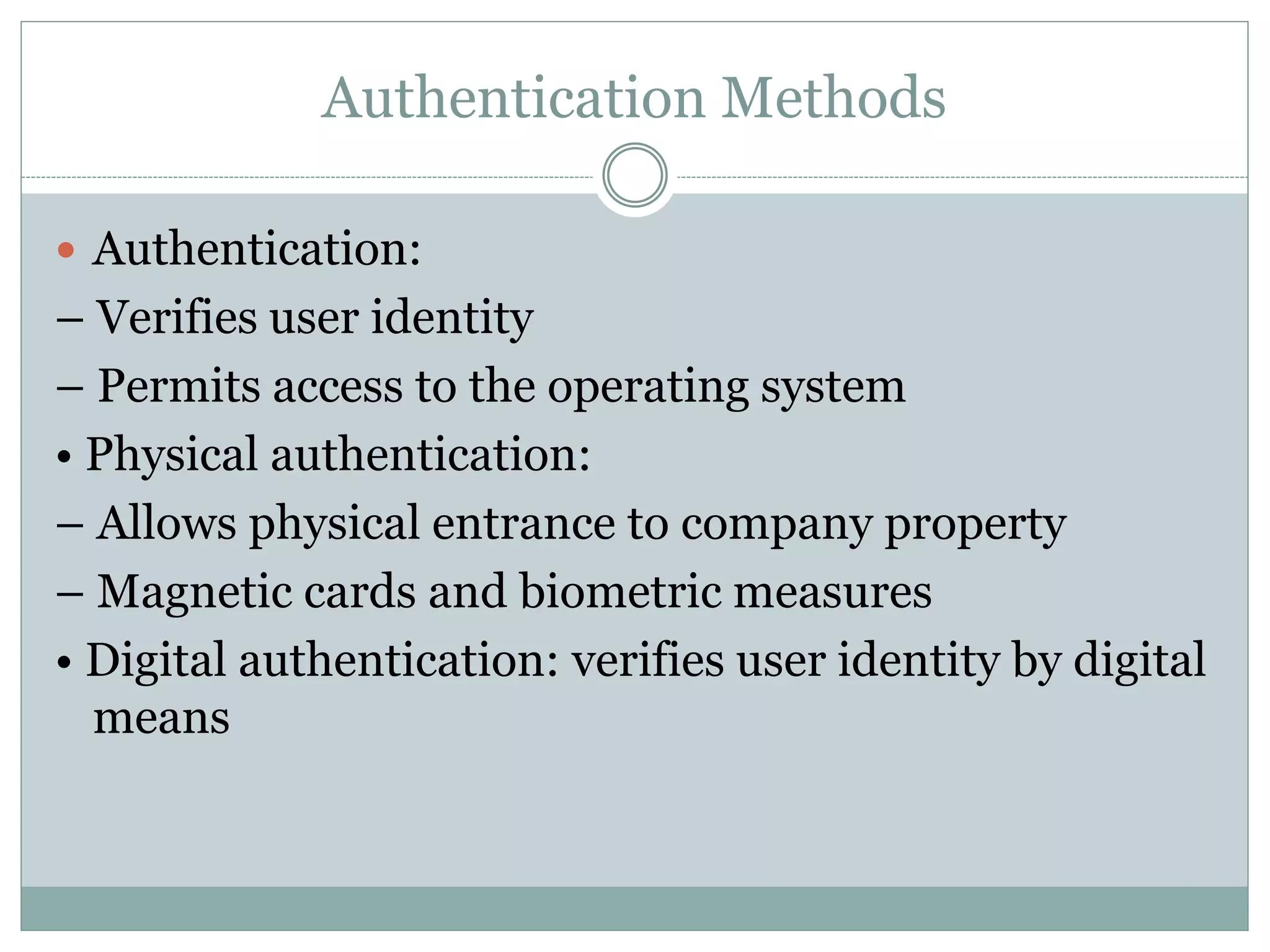
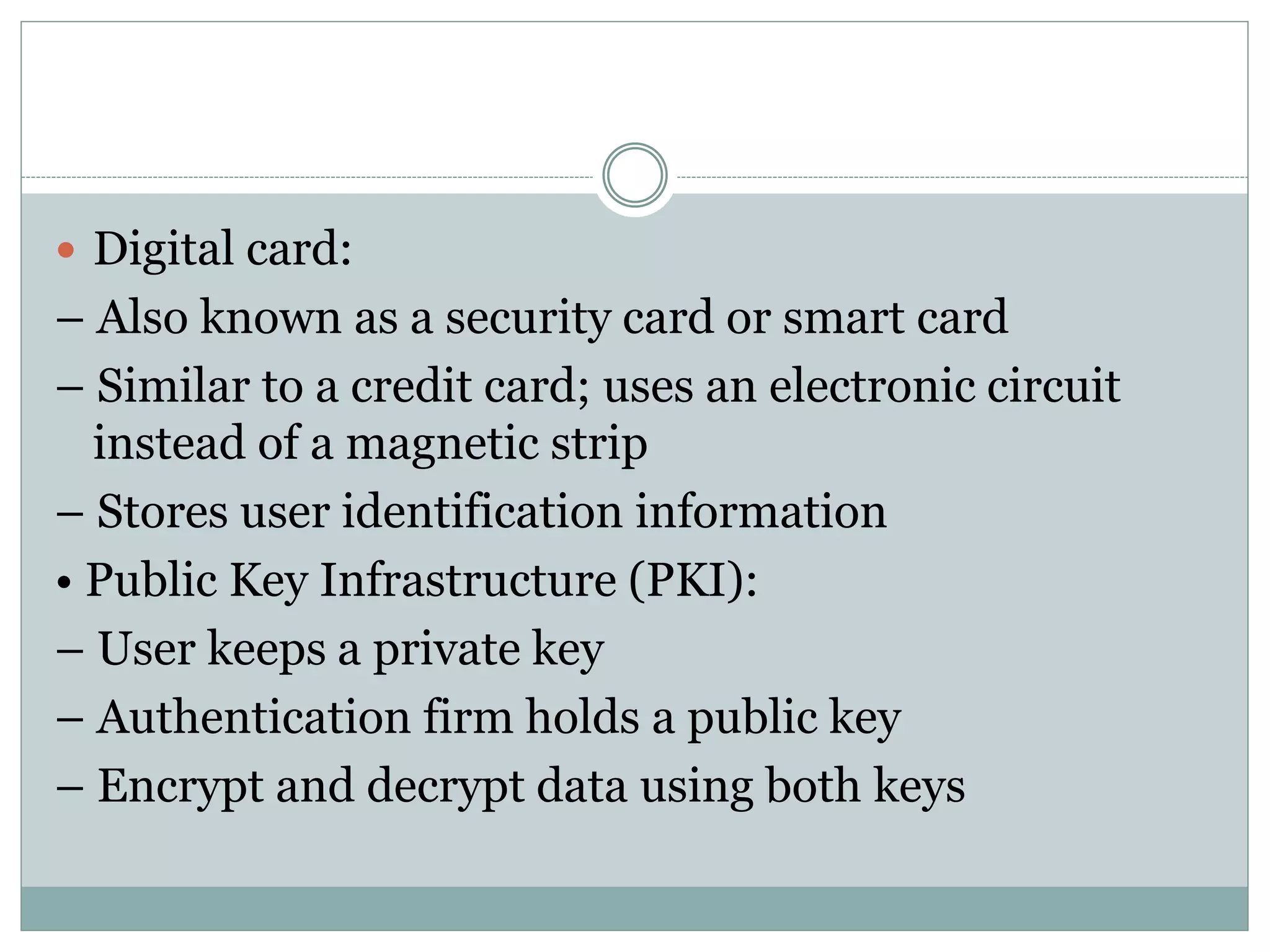
The document provides an overview of operating system security, outlining key functions, components, and threats associated with operating systems. It discusses various security measures like user authentication, password policies, and best practices for managing files and memory. Additionally, it highlights the importance of protecting users' data and preventing unauthorized access and malicious activities.