Selenium 1000 Java: Mastering Web Automation
Dive into the world of web automation with "Selenium 1000 Java," your ultimate guide to mastering Selenium WebDriver using Java. This comprehensive resource is designed for both beginners and experienced testers, offering:
In-Depth Tutorials: Step-by-step instructions to set up and configure Selenium with Java.
Real-World Examples: Practical examples and projects to apply your knowledge.
Advanced Techniques: Explore advanced topics like handling dynamic web elements, integrating with CI/CD pipelines, and cross-browser testing.
Best Practices: Learn industry best practices for writing efficient and maintainable test scripts.
Troubleshooting Tips: Solutions to common issues and challenges faced during automation.
Whether you're aiming to enhance your testing skills or automate complex web applications, "Selenium 1000 Java" equips you with the tools and knowledge to succeed.
Feel free to customize this description further to suit your specific needs!
















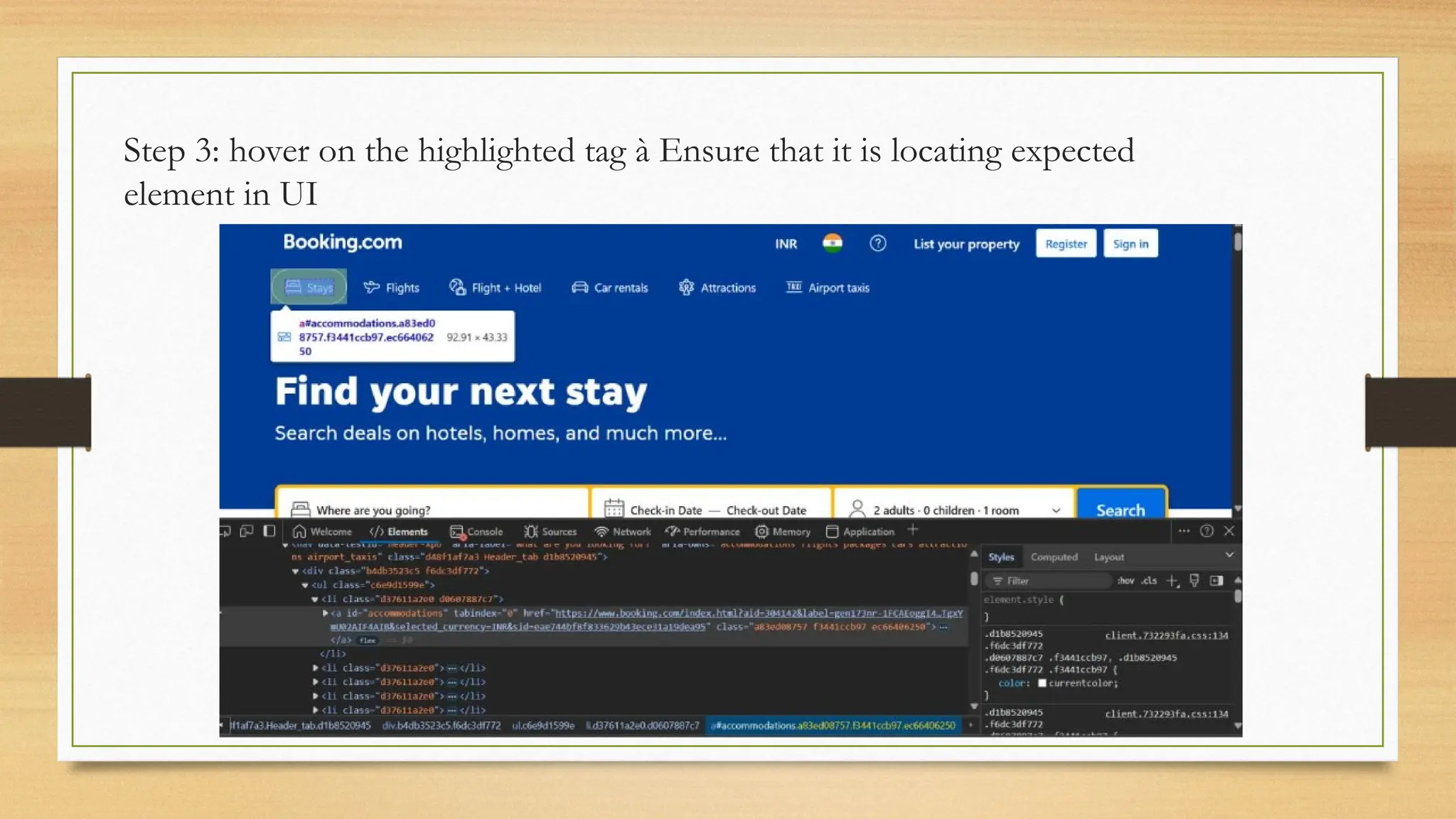





![Example
Example:
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[@id='flights']")).click();
Select objSelect = new
Select(driver.findElement(By.xpath("//select[@name='sr_cabin_class']")));
objSelect.selectByVisibleText("Business");
List<WebElement> options = objSelect.getOptions();
for(WebElement dropdown: options) {
System.out.println(dropdown.getText());
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumbasicsandoverview-250221064314-b7eb0b1e/75/Selenium-Basics-and-Overview-topics-pptx-28-2048.jpg)
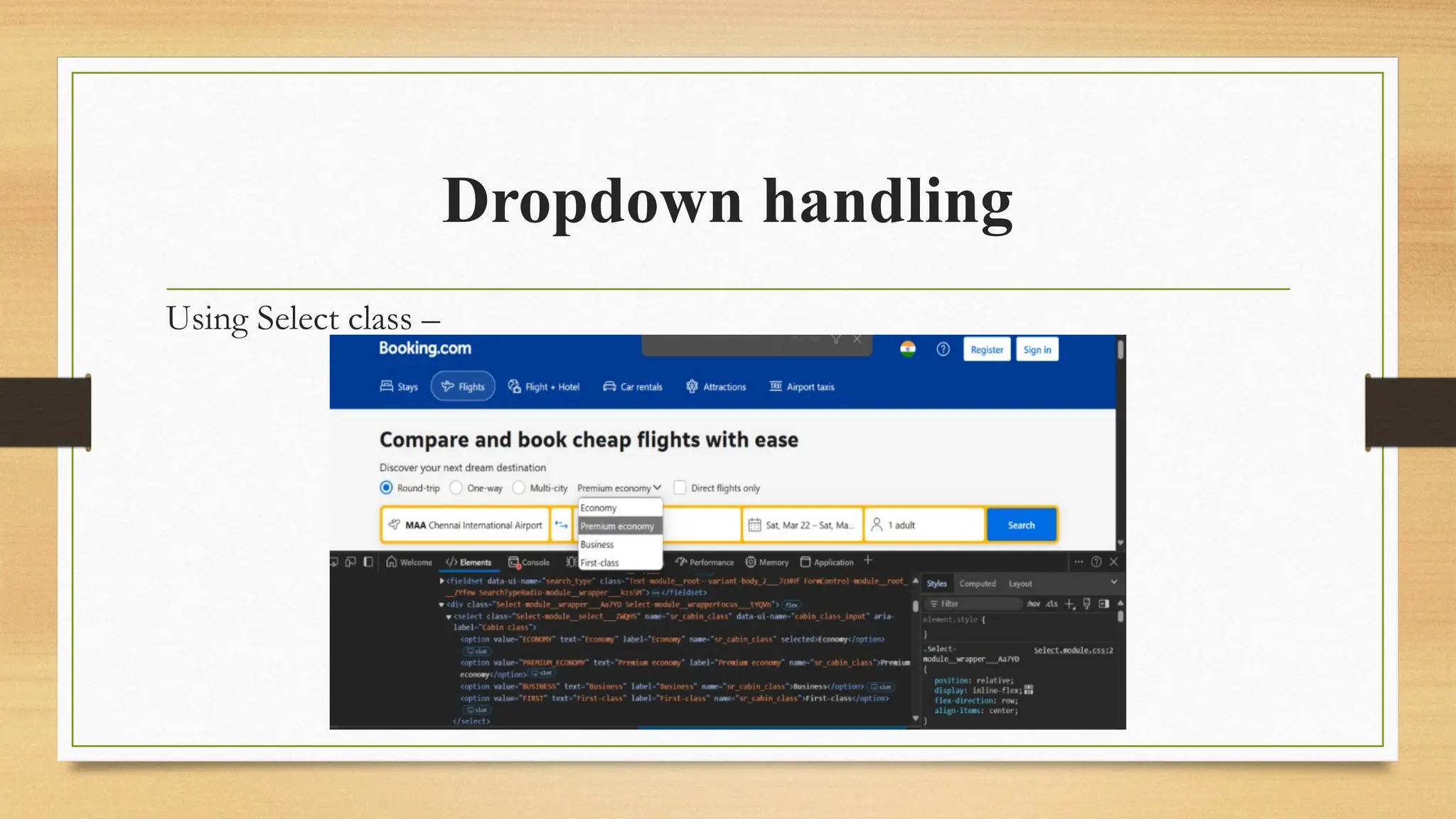
![Without using Select class –
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[@id='flights']")).click();
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//select[@name='sr_cabin_class']")).click();
List<WebElement> options = driver.findElements(By.xpath("//select[@name='sr_cabin_class']/option"));
for(int i=0; i<=options.size(); i++) {
String value = options.get(i).getText();
if(value.equals("Business")) {
options.get(i).click();
break;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumbasicsandoverview-250221064314-b7eb0b1e/75/Selenium-Basics-and-Overview-topics-pptx-29-2048.jpg)
![Find Radio Element
Select as text:
//
div[contains(@class,'Text
-module__root--variant')
and text ()='One-way']
Select as button:
//
div[contains(@class,'Text
-module__root--variant')
and text
()='One-way']/preceding::
span[contains(@class,'Inp
utRadio-module')][1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumbasicsandoverview-250221064314-b7eb0b1e/75/Selenium-Basics-and-Overview-topics-pptx-30-2048.jpg)



![• Text fields and buttons
driver.get("https://www.booking.com");
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//
input[@name='ss']")).sendKeys("Chennai");
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//li[contains(@id,'autocomplete-
result')]//div[text()='Chennai']")).click();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumbasicsandoverview-250221064314-b7eb0b1e/75/Selenium-Basics-and-Overview-topics-pptx-35-2048.jpg)
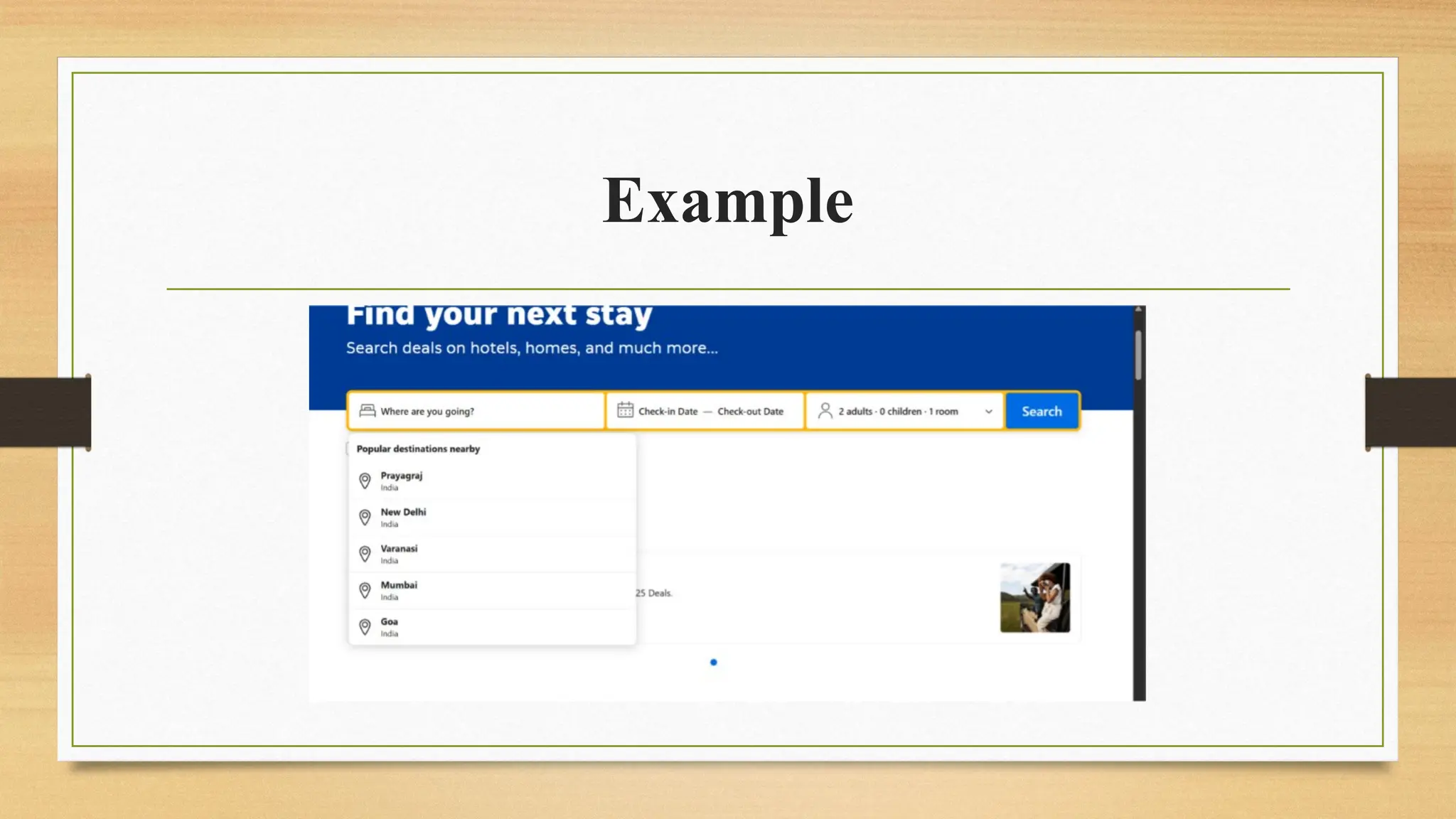
![driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@name='ss']")).click();
List<WebElement> options = driver.findElements(By.xpath("//div[text()='Popular
destinations nearby']/following-sibling::ul/li//span/following-sibling::div/div[1]"));
for(int i=0; i<=options.size(); i++) {
String value = options.get(i).getText();
if(value.startsWith("V")) {
options.get(i).click();
break;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumbasicsandoverview-250221064314-b7eb0b1e/75/Selenium-Basics-and-Overview-topics-pptx-38-2048.jpg)