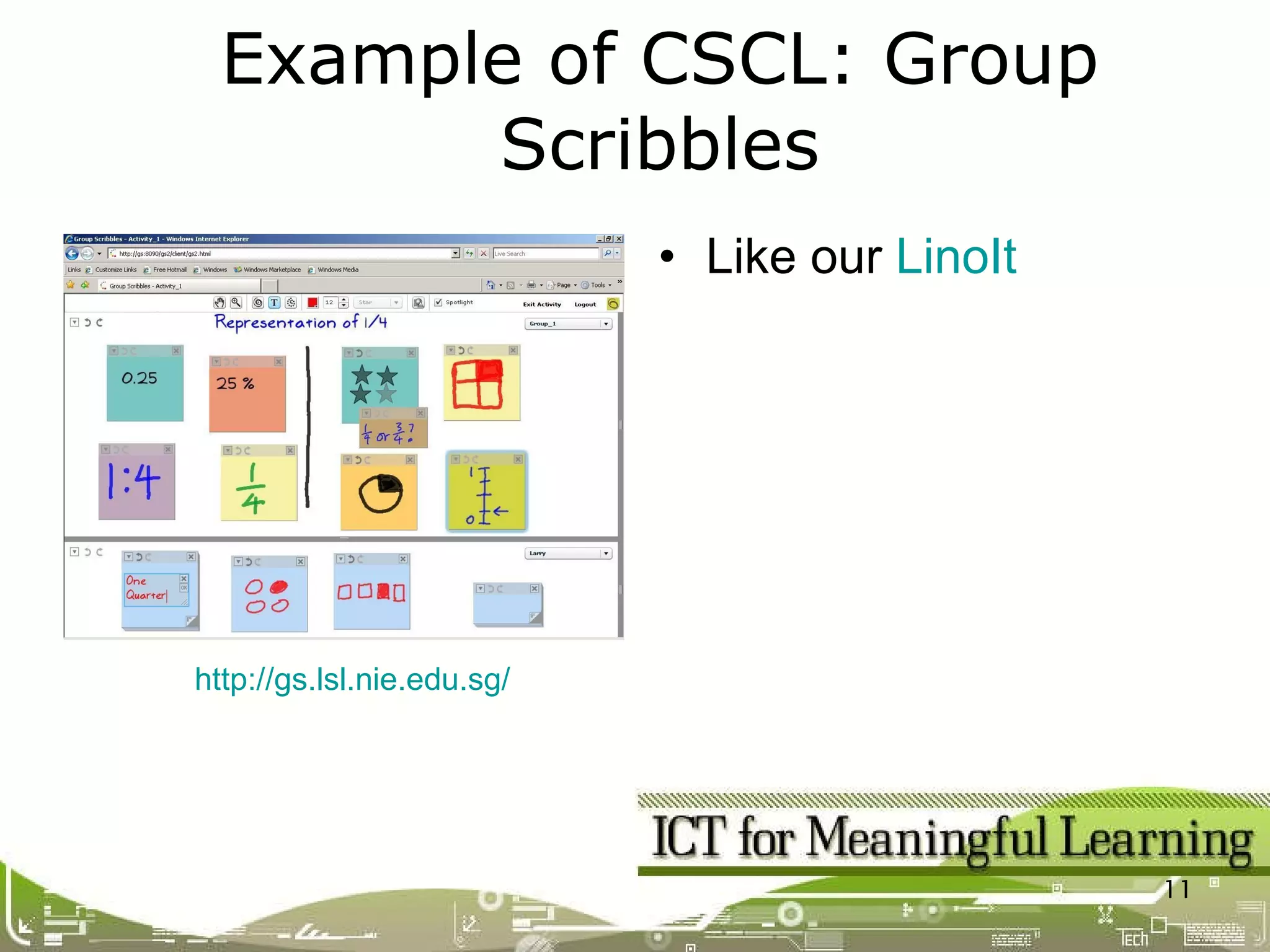
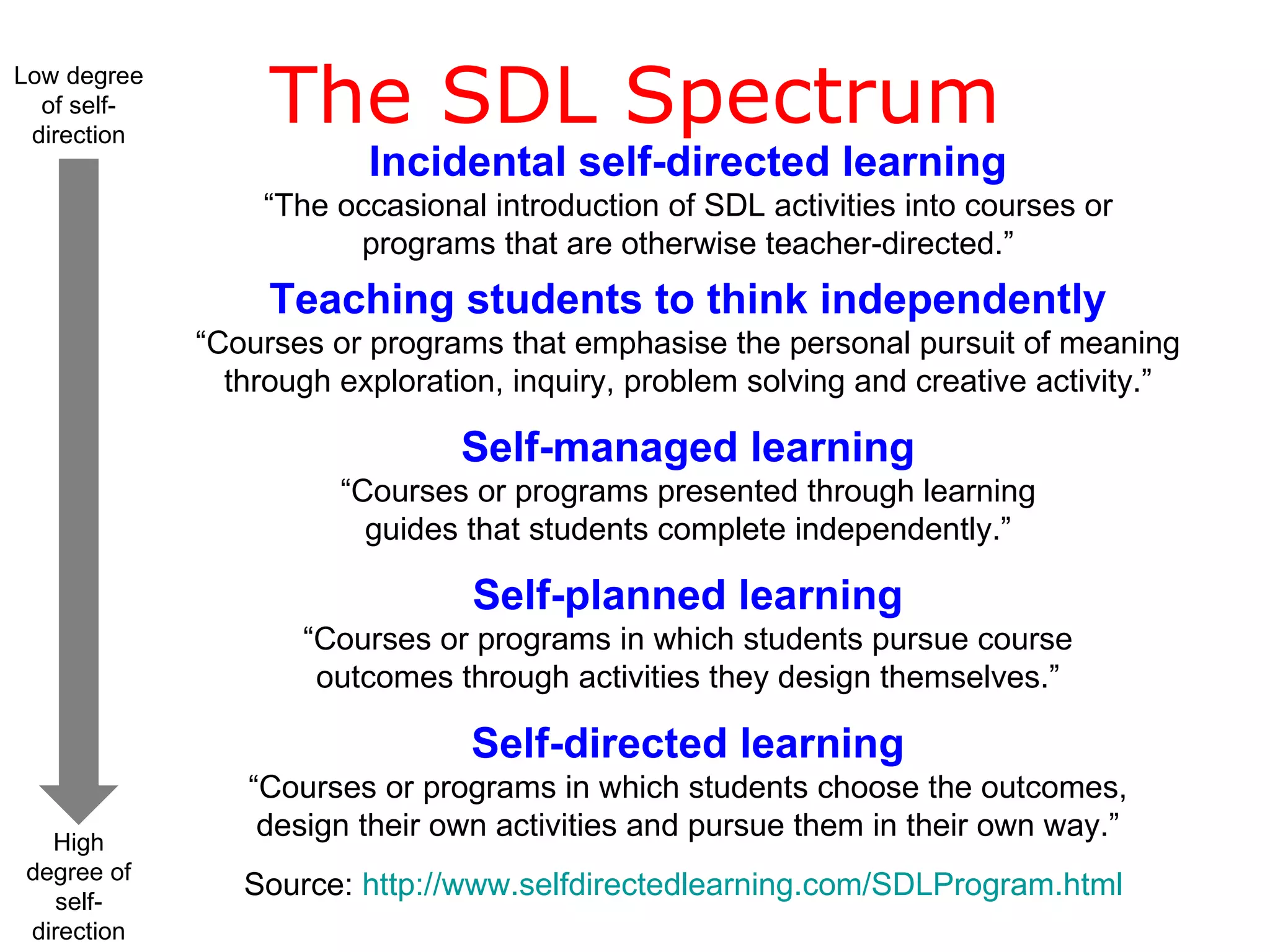
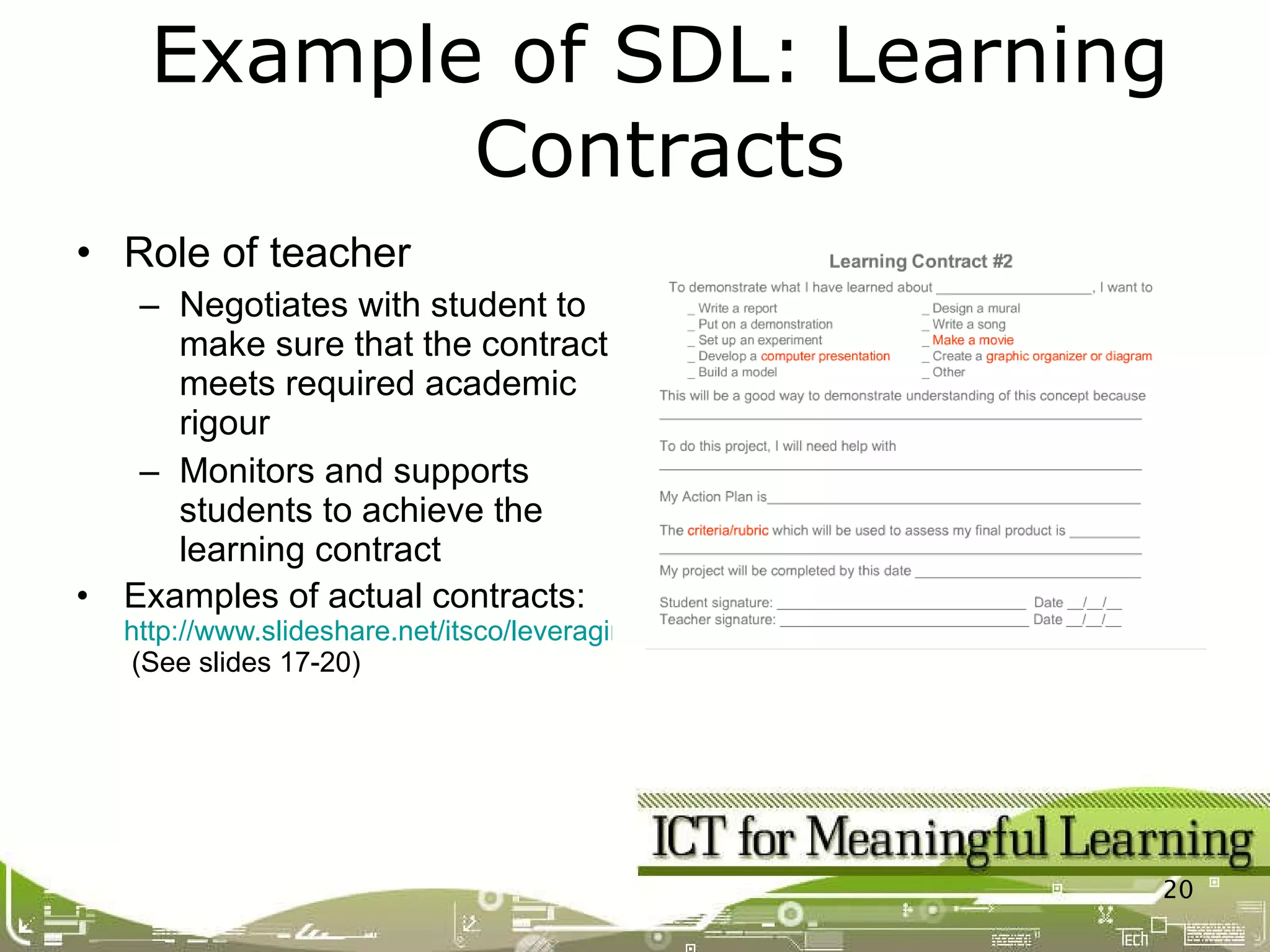
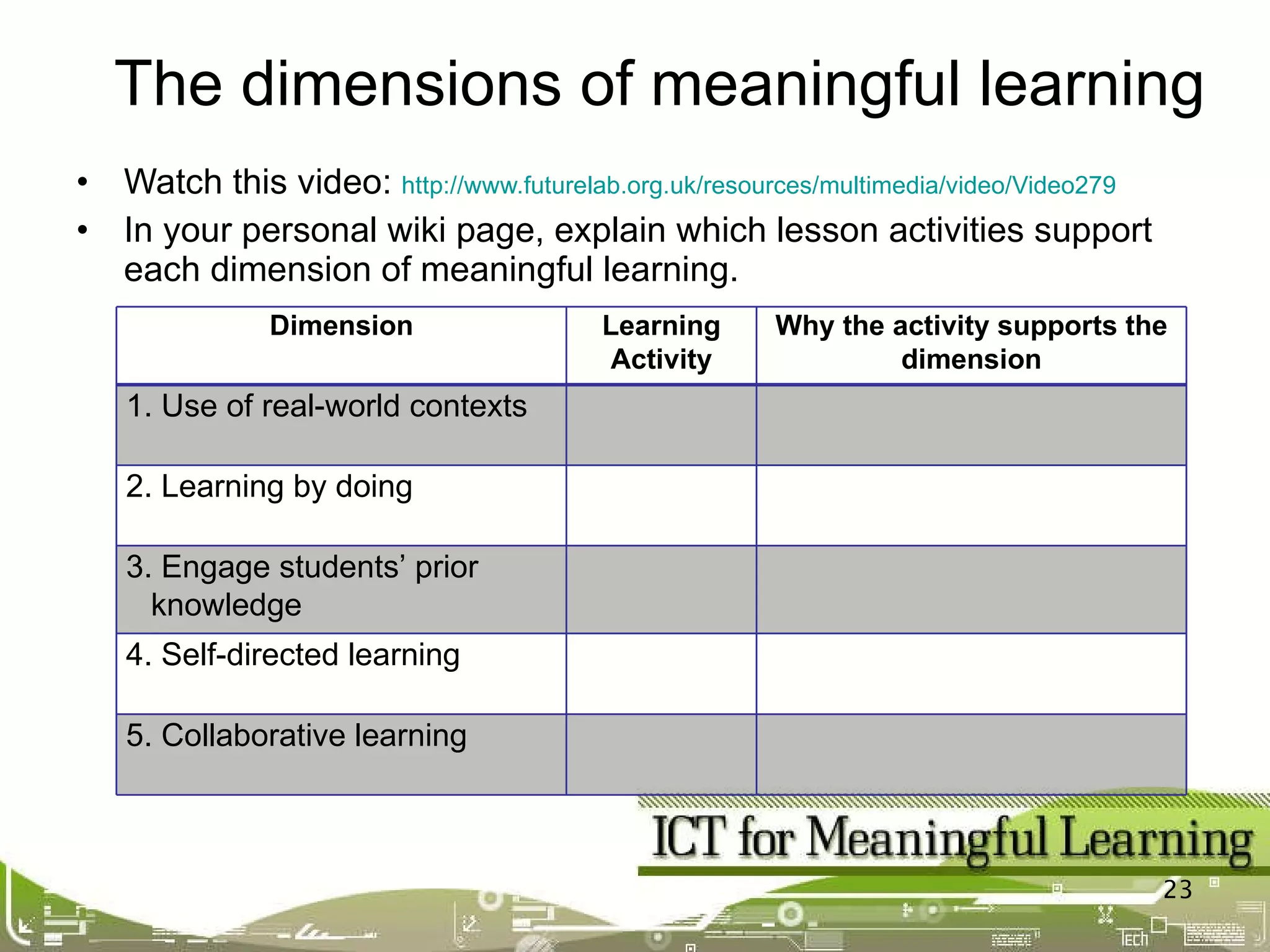
The document discusses dimensions of meaningful learning including collaborative learning, self-directed learning, and how teachers can support these approaches. It provides details on collaborative learning techniques like group roles and tasks. For self-directed learning, it defines SDL and discusses creating learning contracts and using blogs. It also shows how ICT tools can enable both collaborative and self-directed learning.