This document provides an overview of Linux topics including:
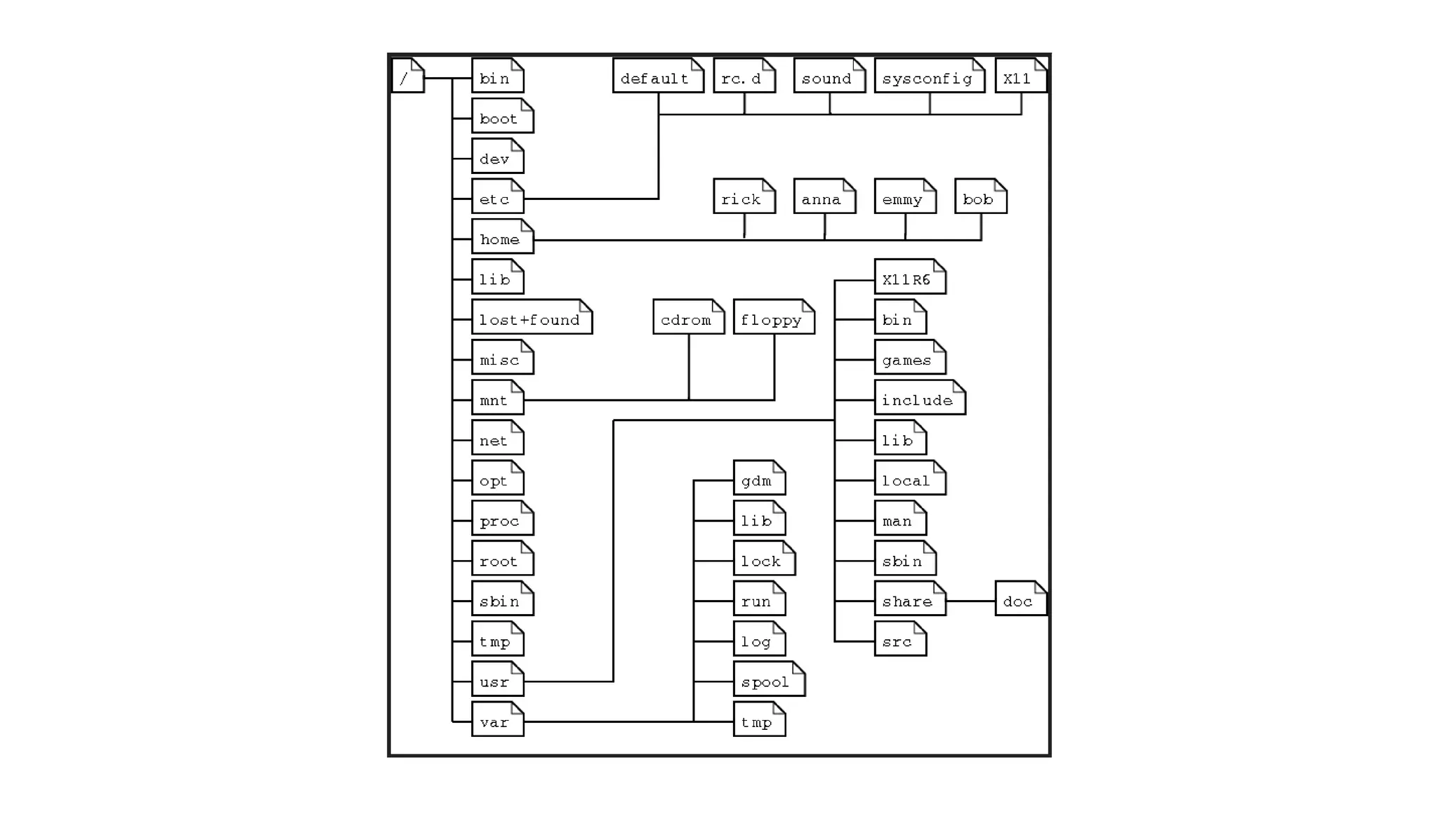
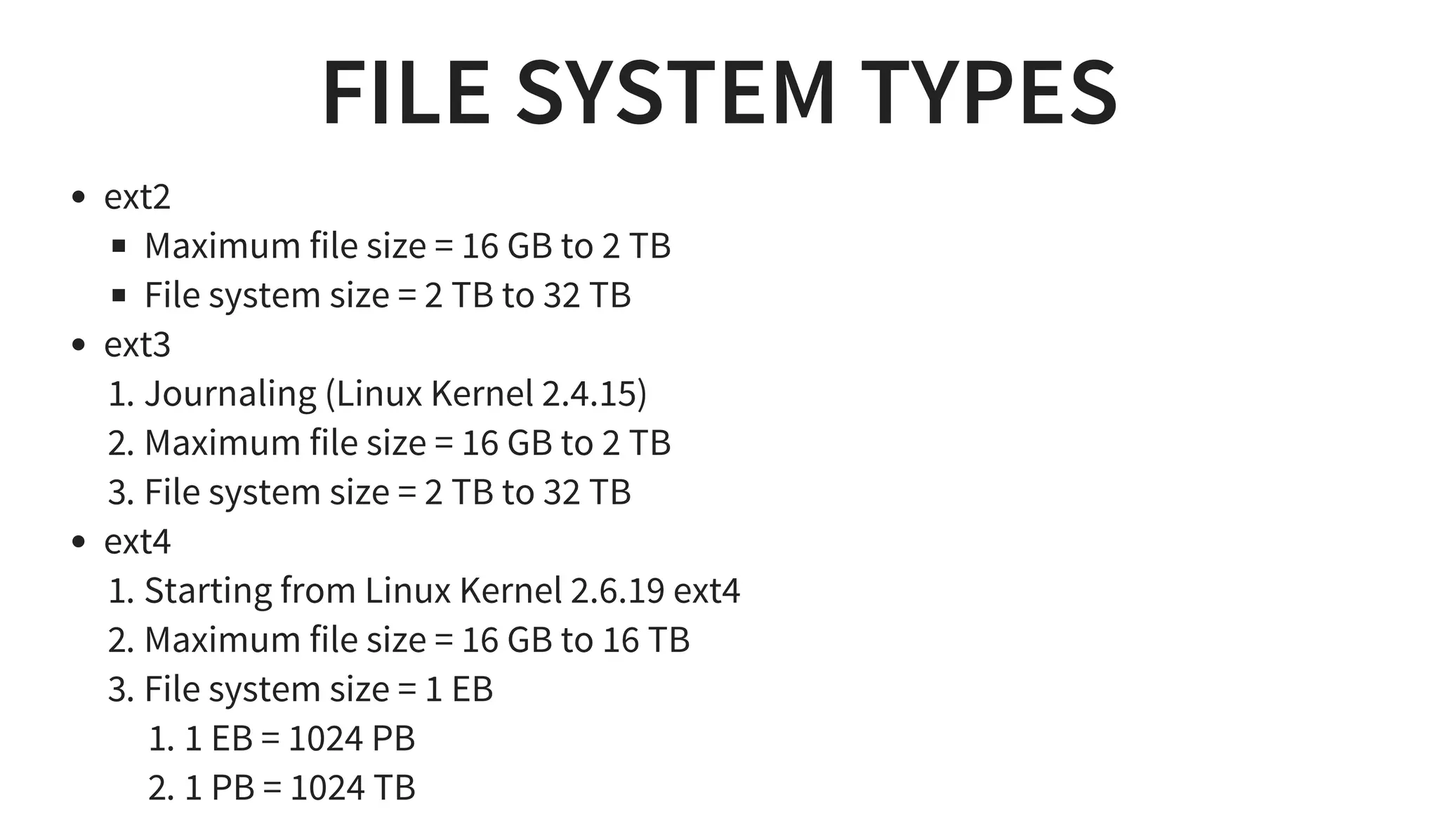
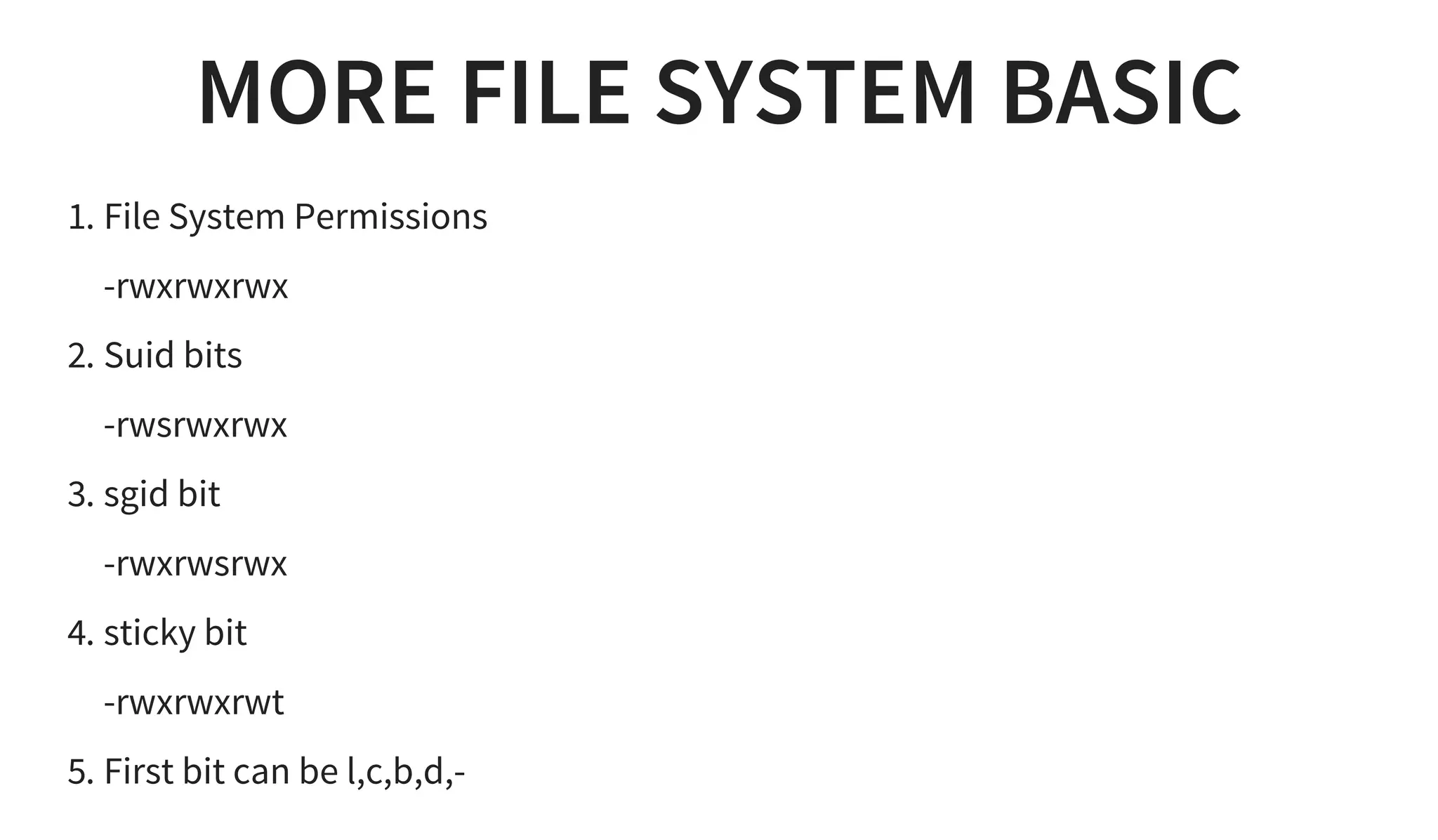
1. It discusses various Linux distributions like Debian, Redhat and file system basics like directories and permissions.
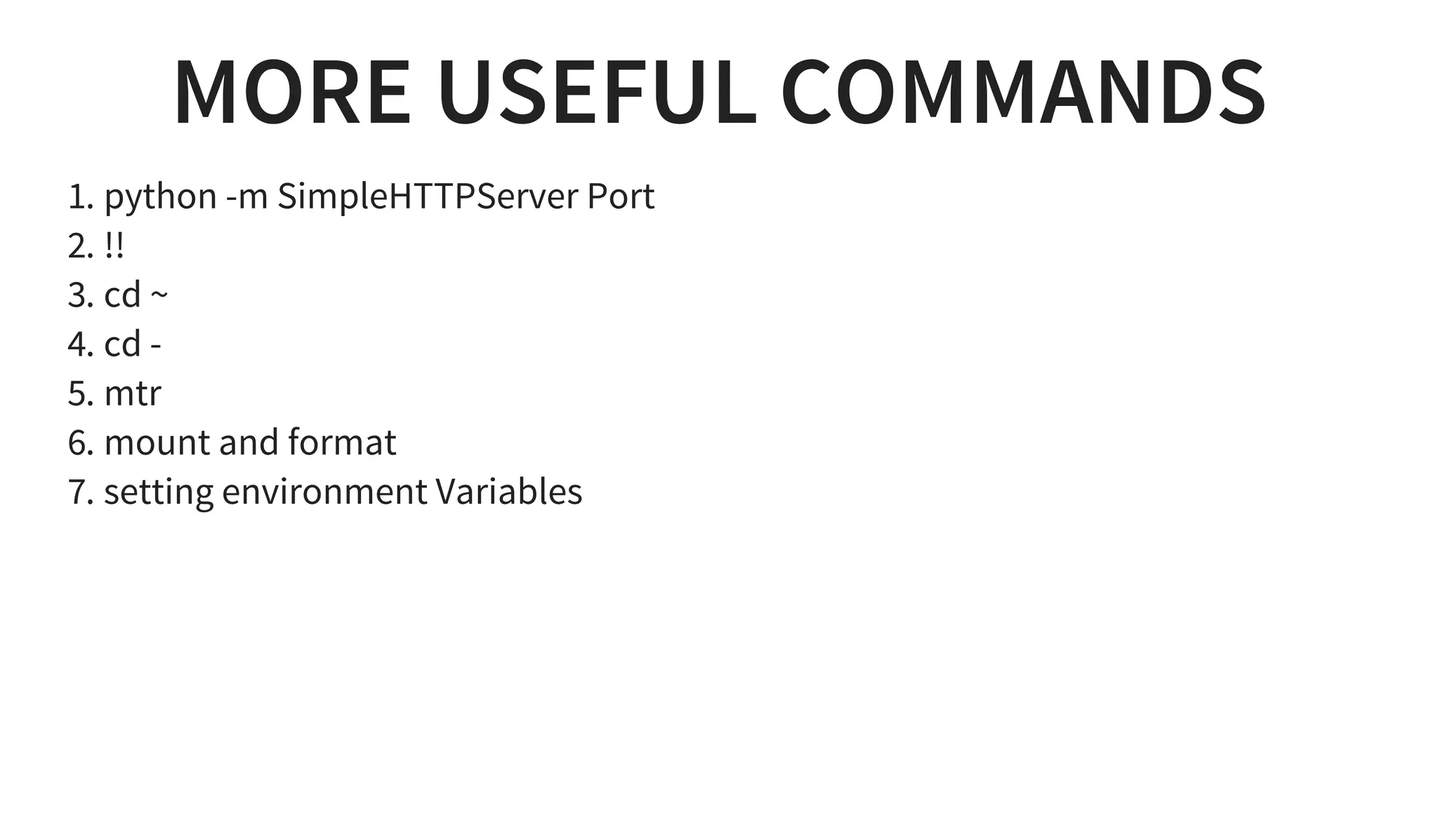
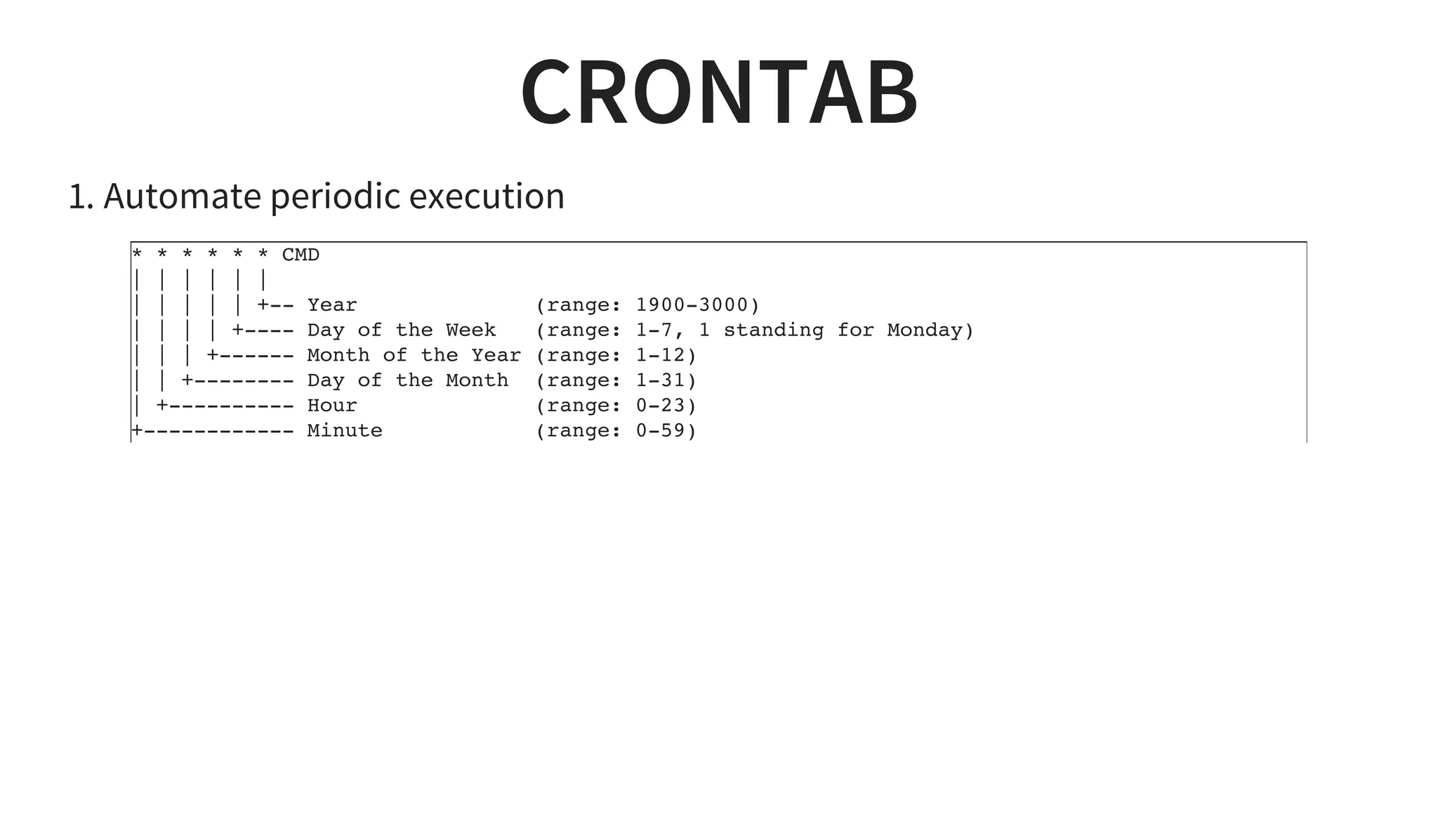
2. It covers important commands like ls, grep, sed and editors like vim. It also summarizes installing software, automation with cronjobs and configuring services like SSH.
3. Finally, it touches on shell scripting basics like variables, conditions and loops to automate tasks. It provides examples of overloading commands and writing custom scripts.