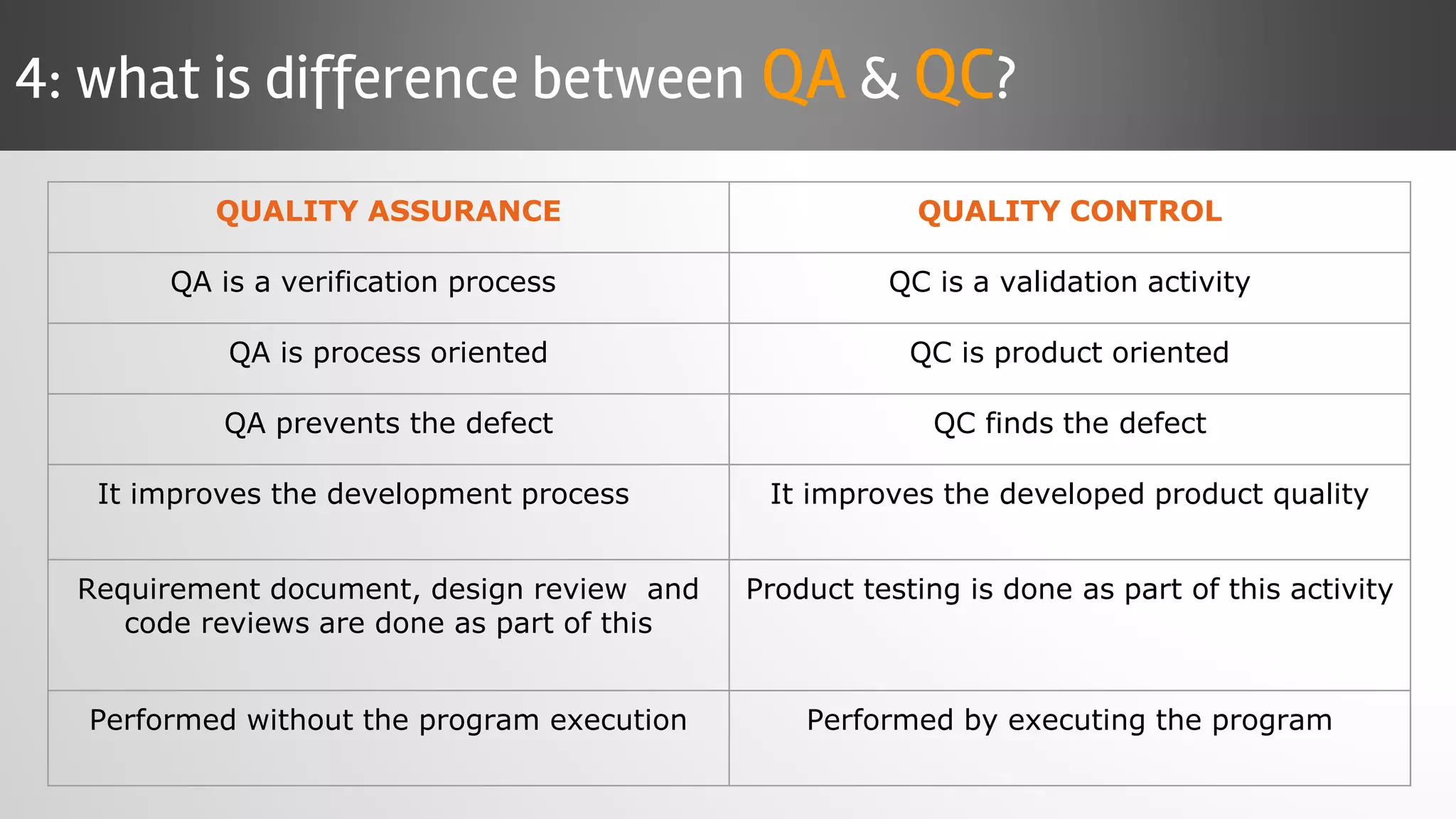
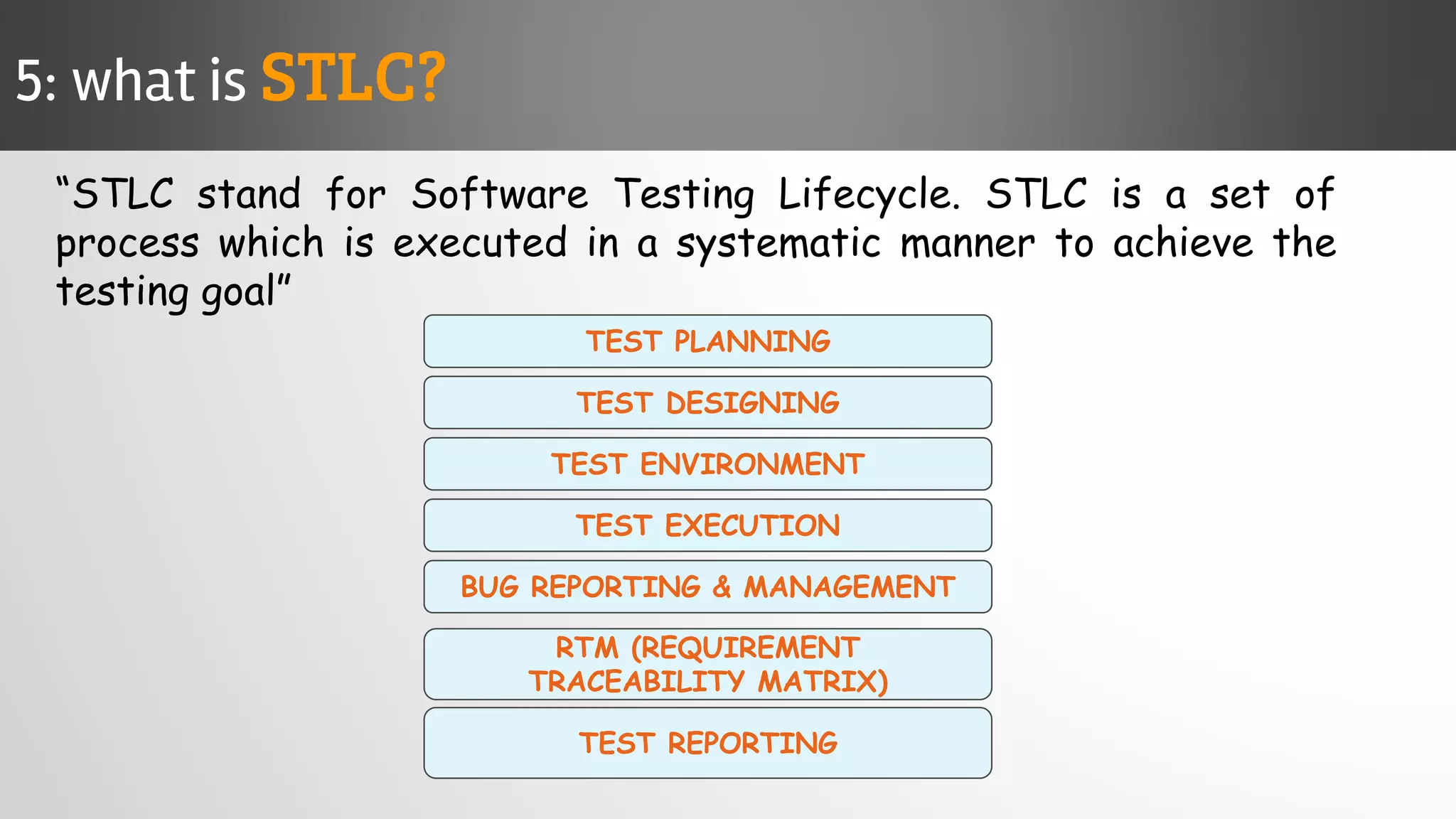
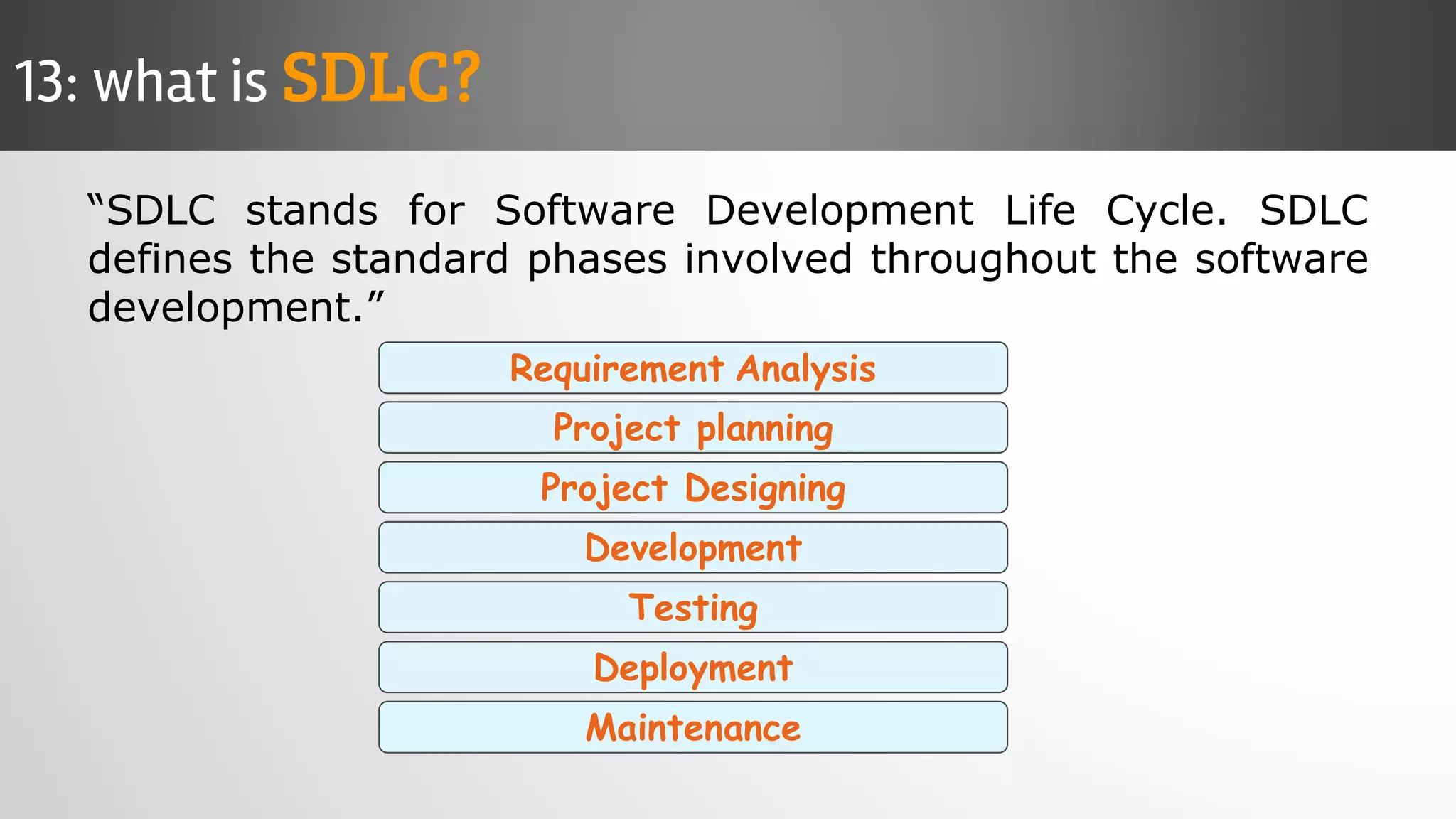
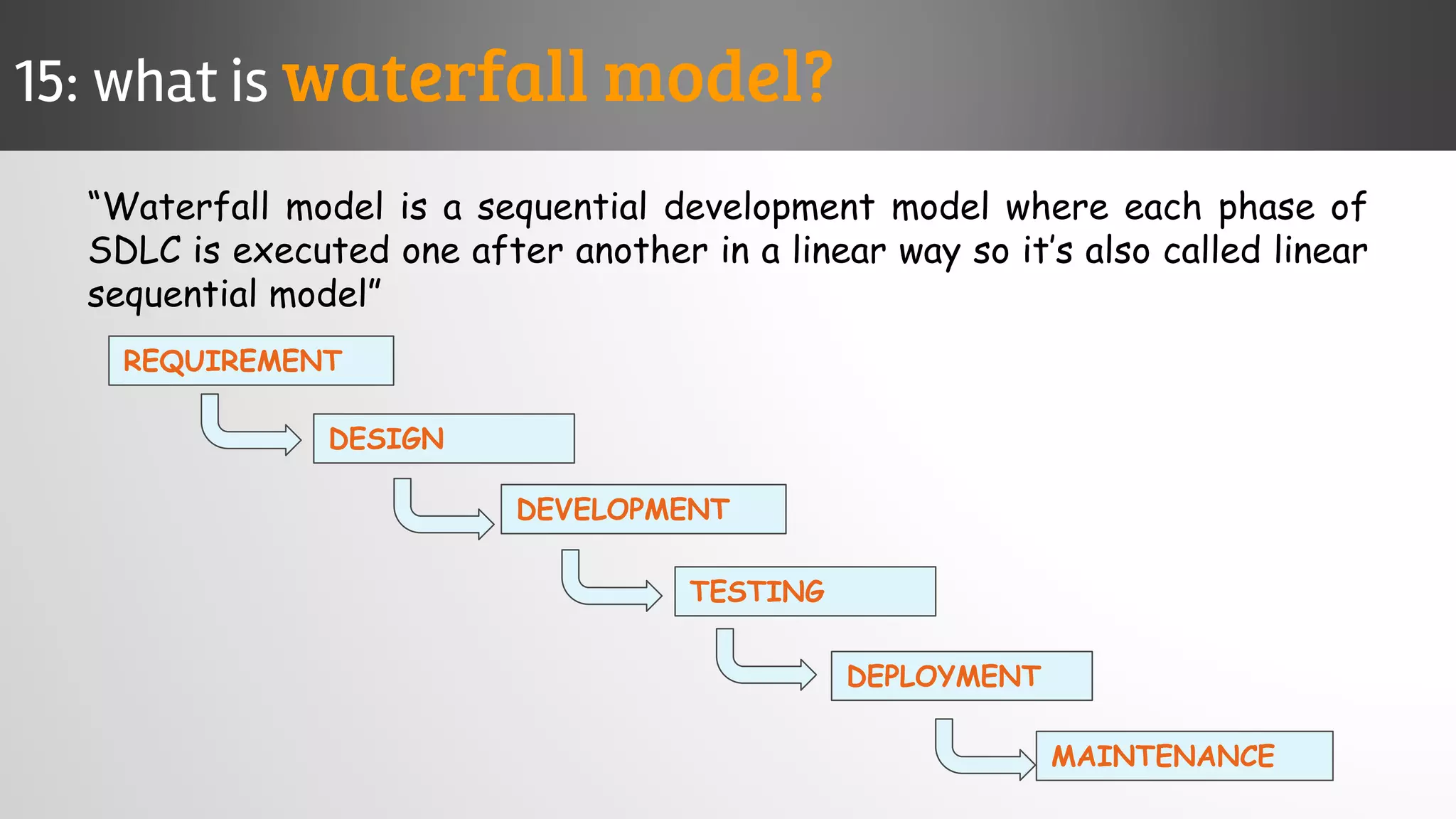
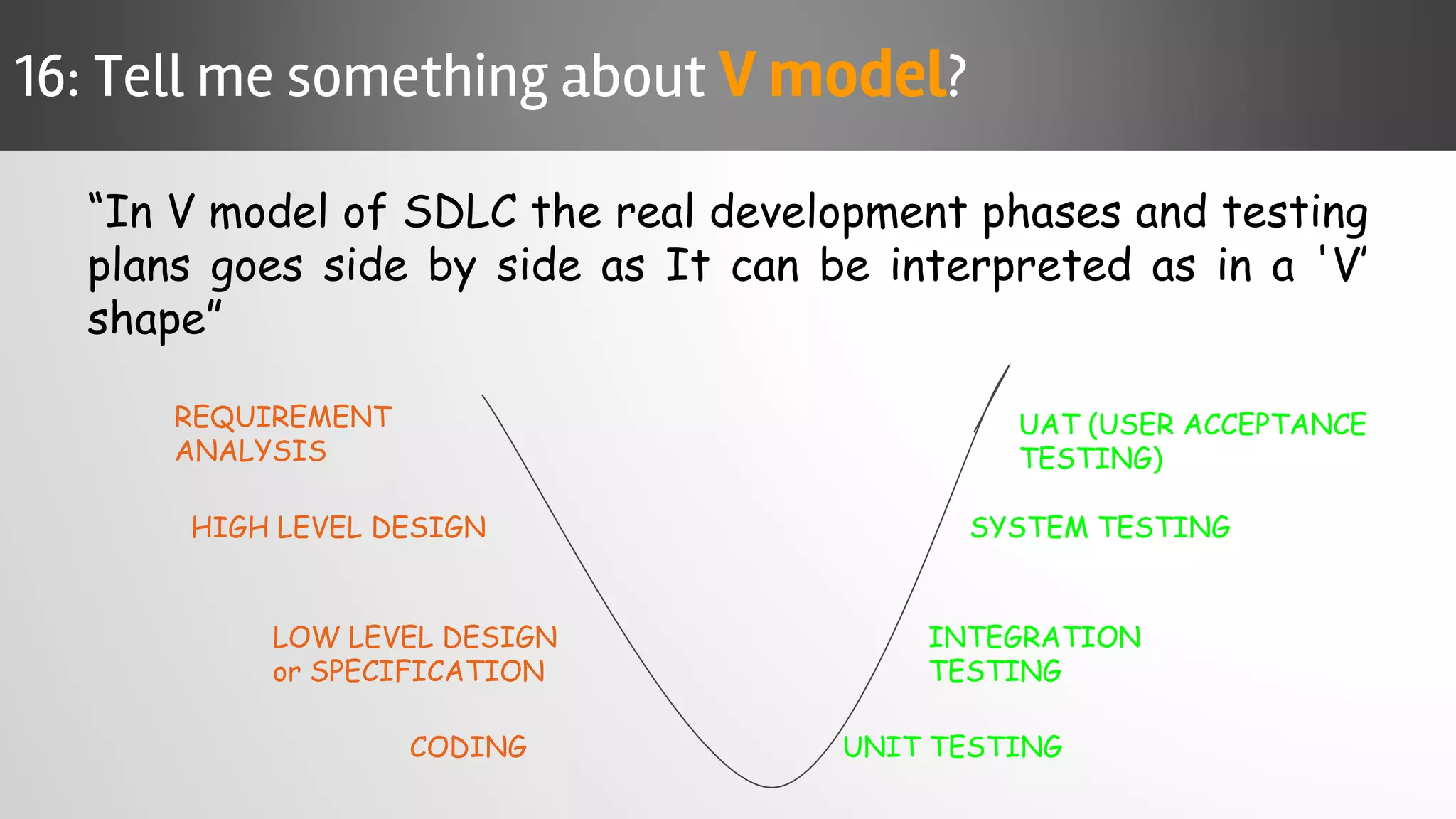
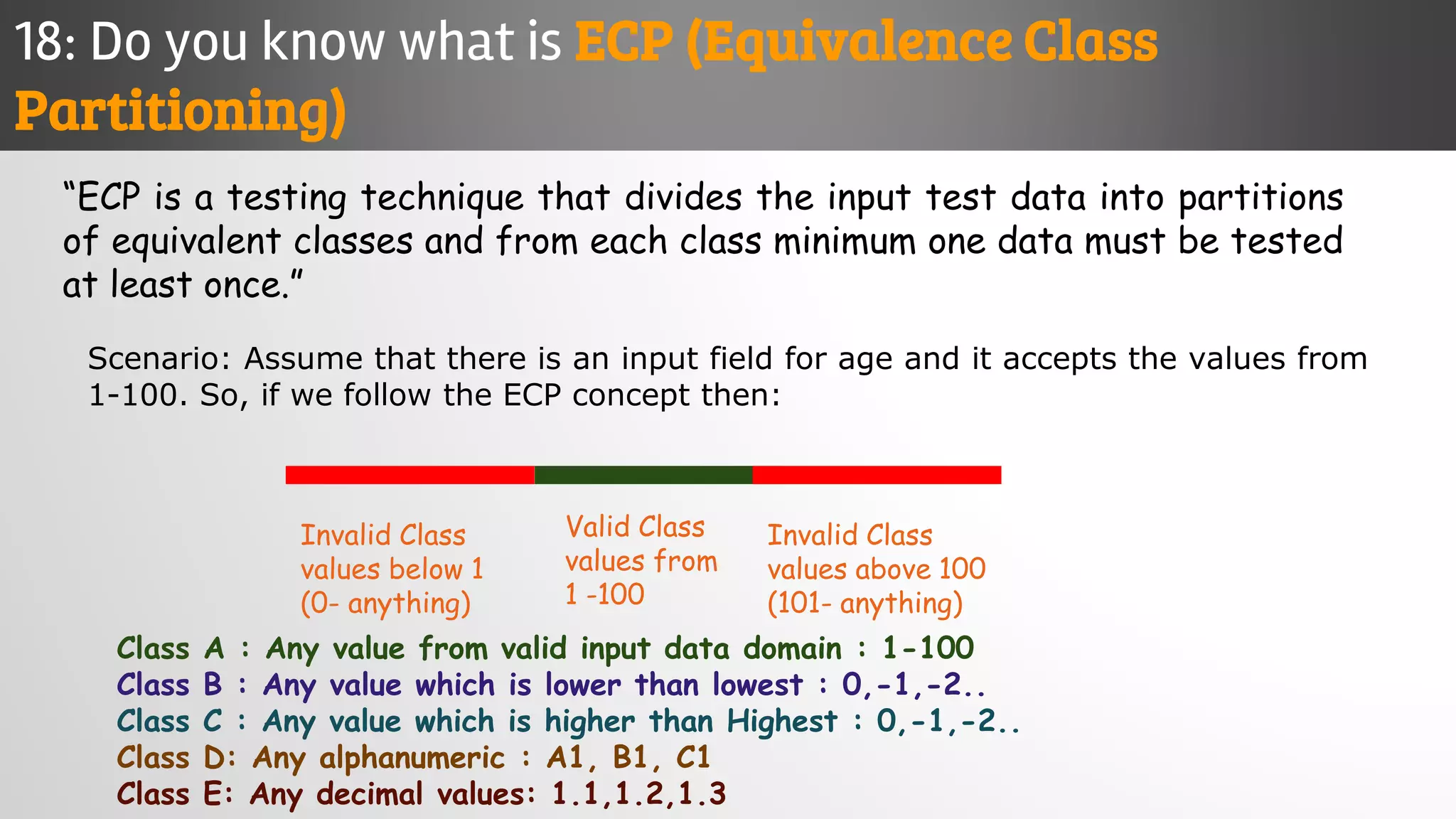
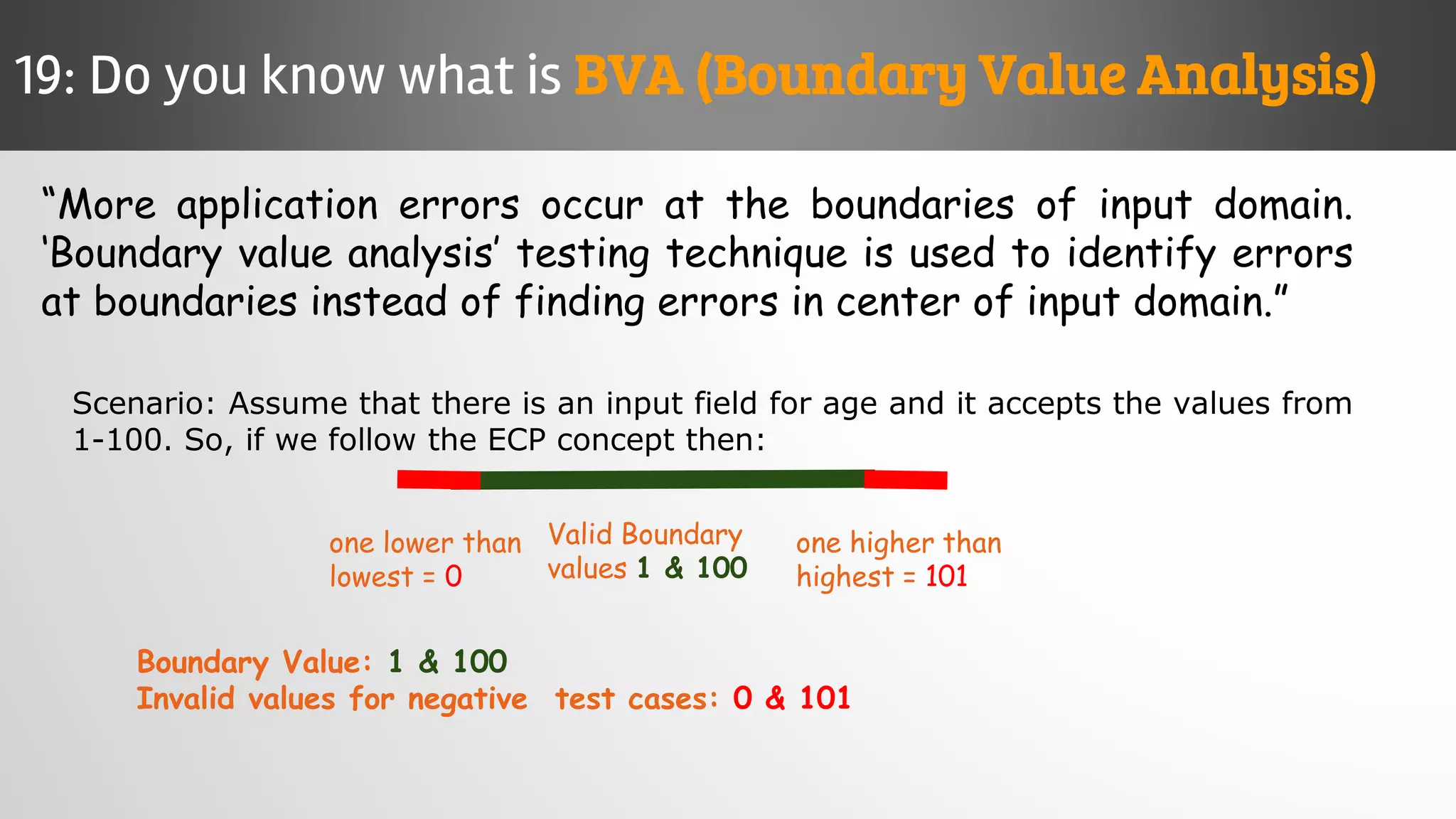
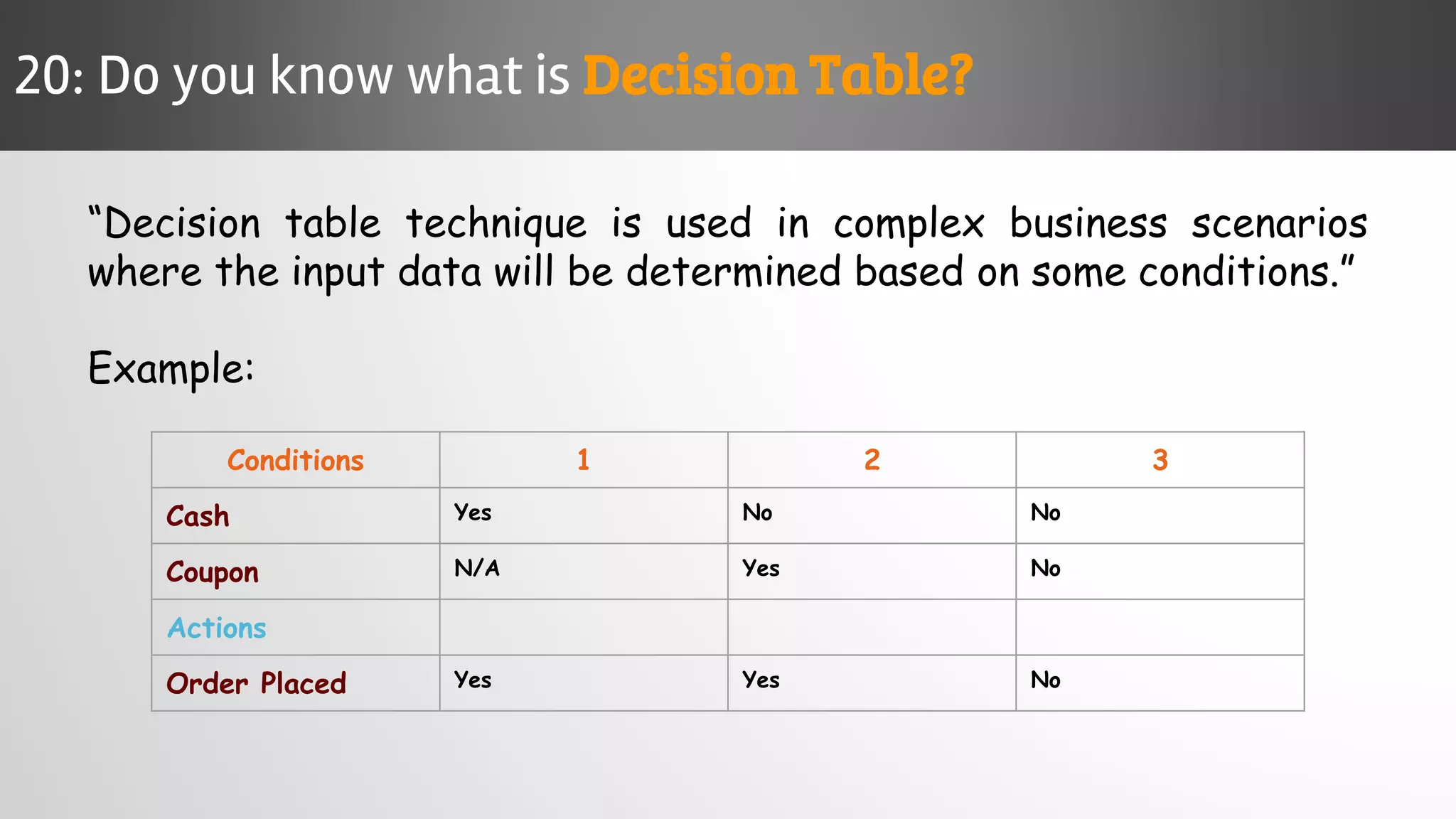
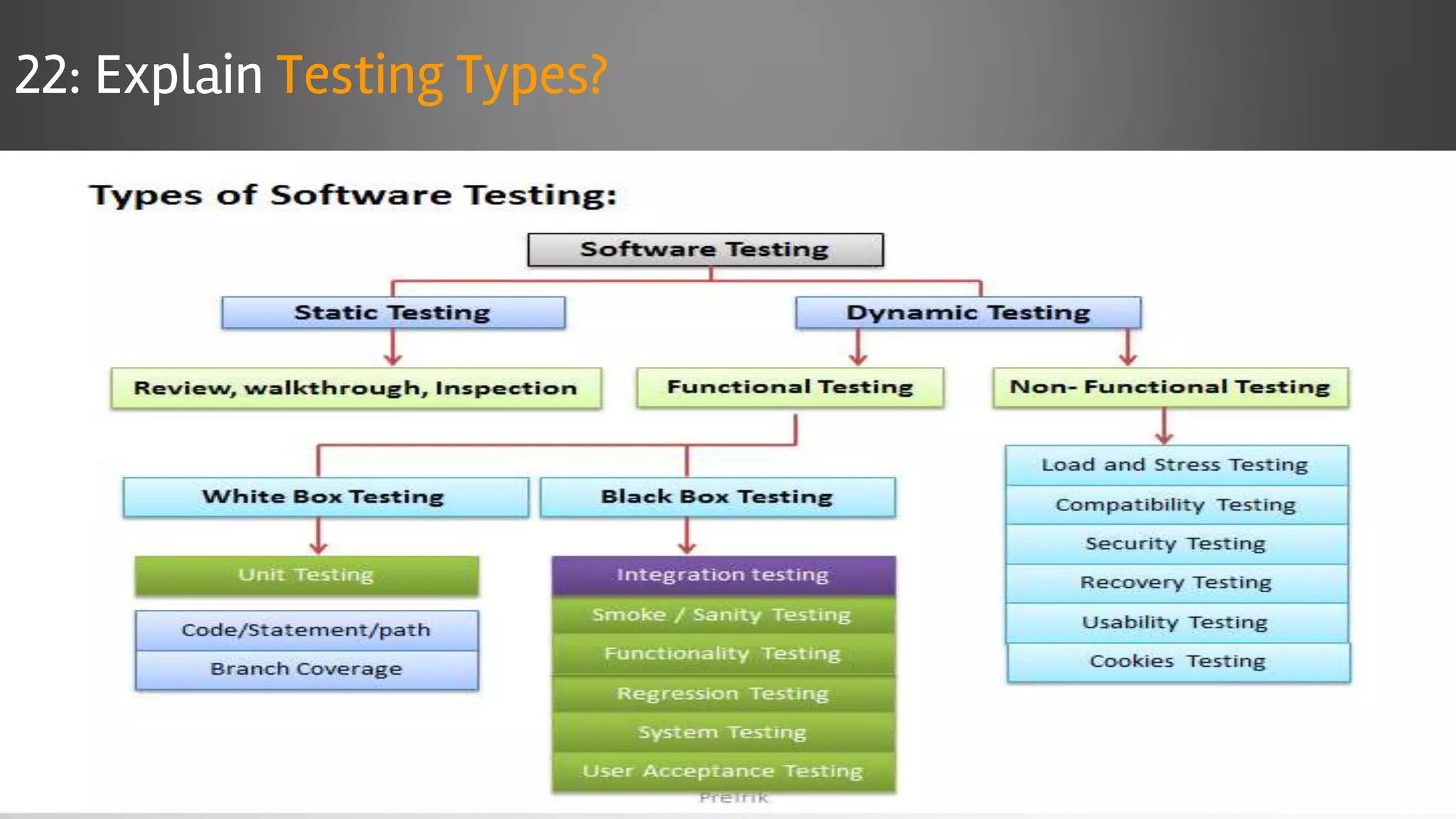
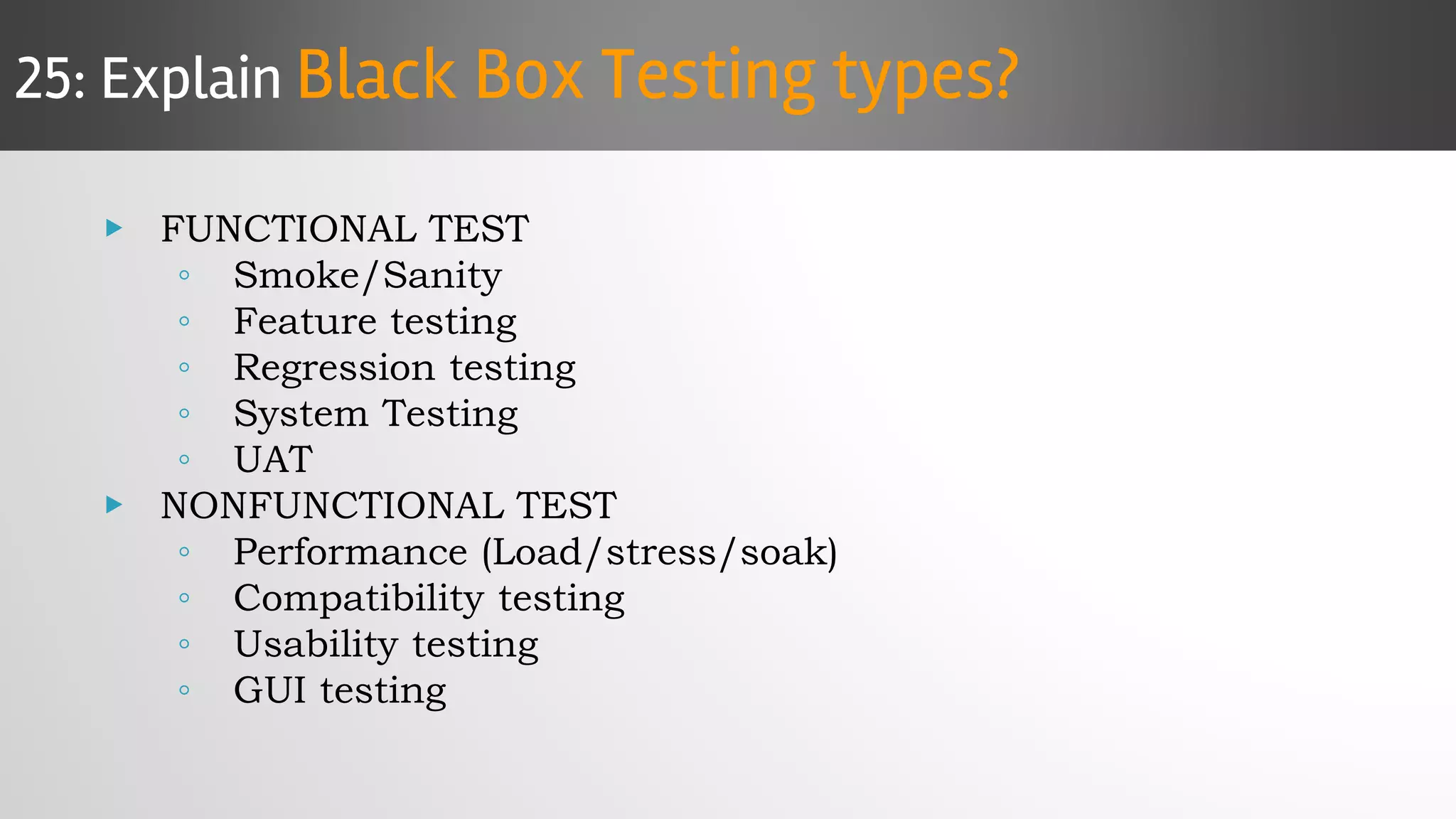
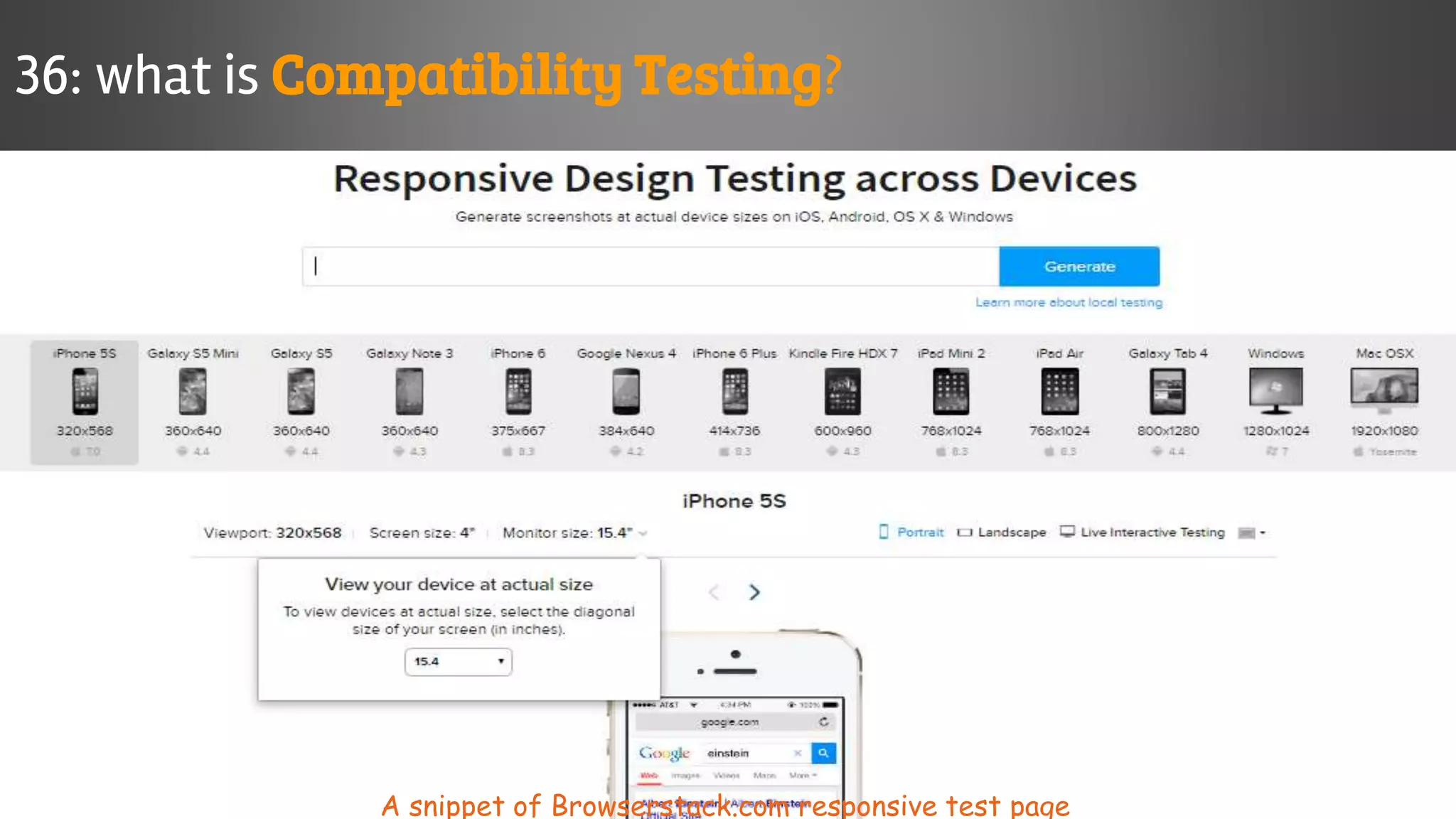
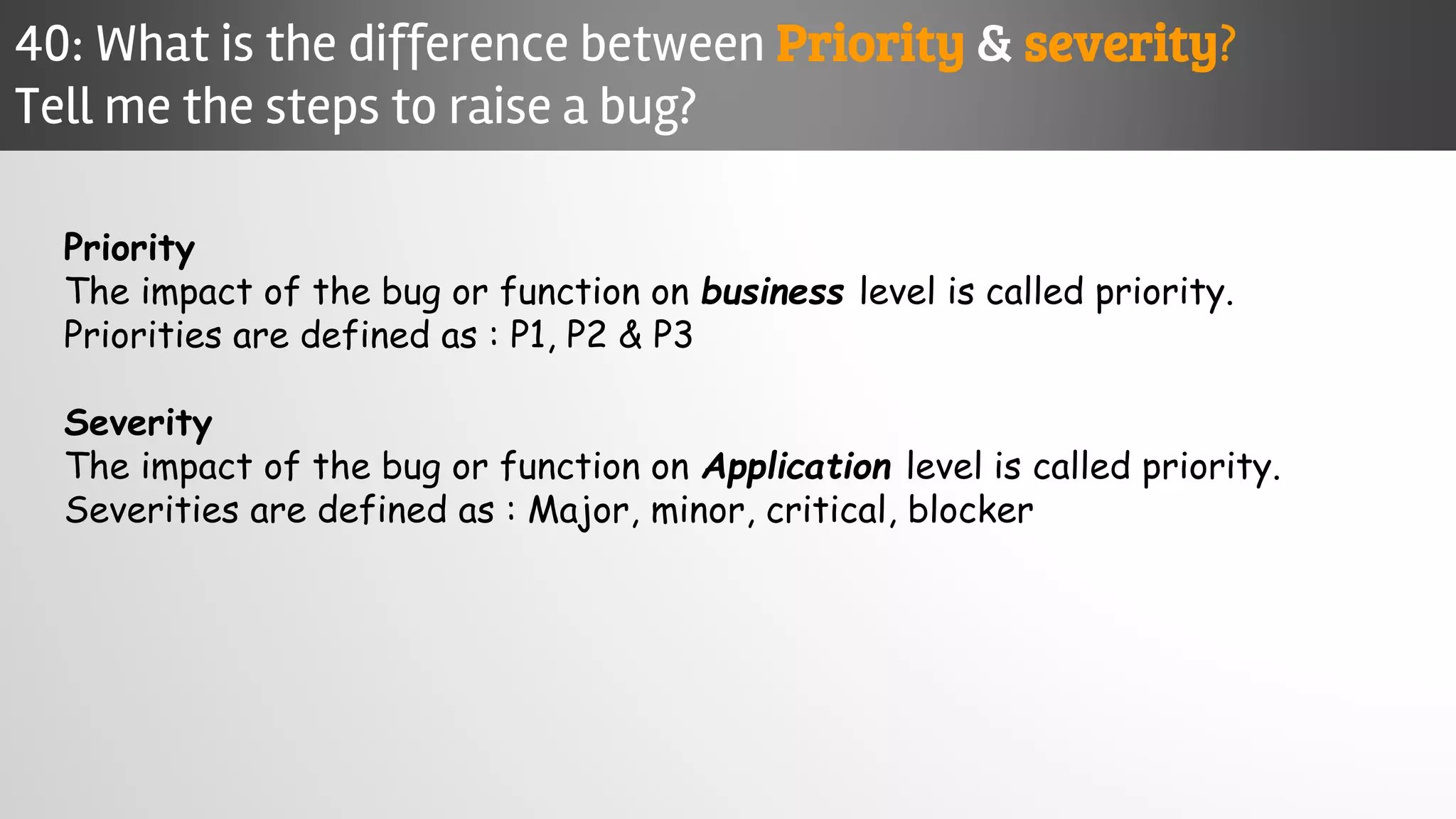
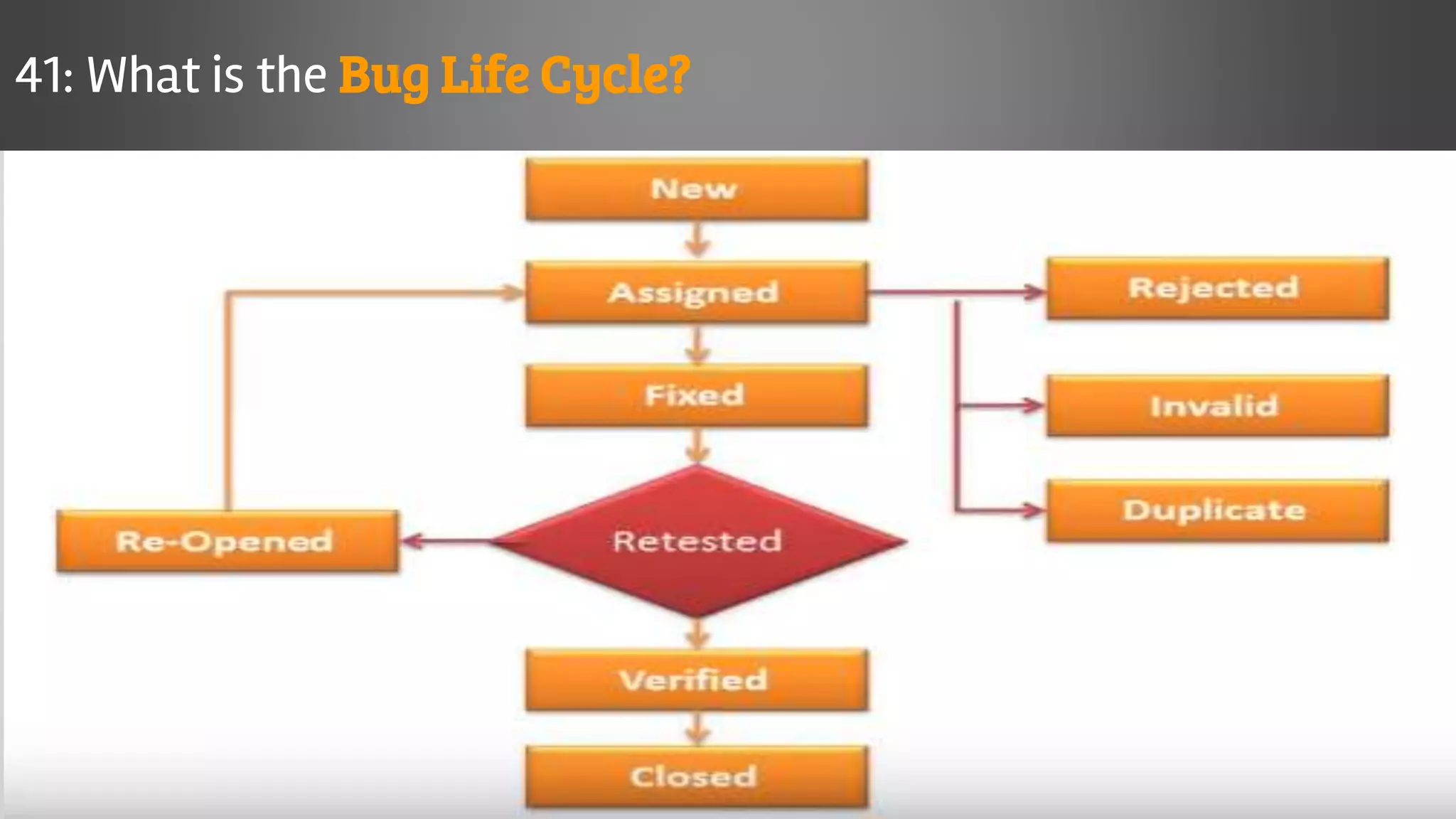
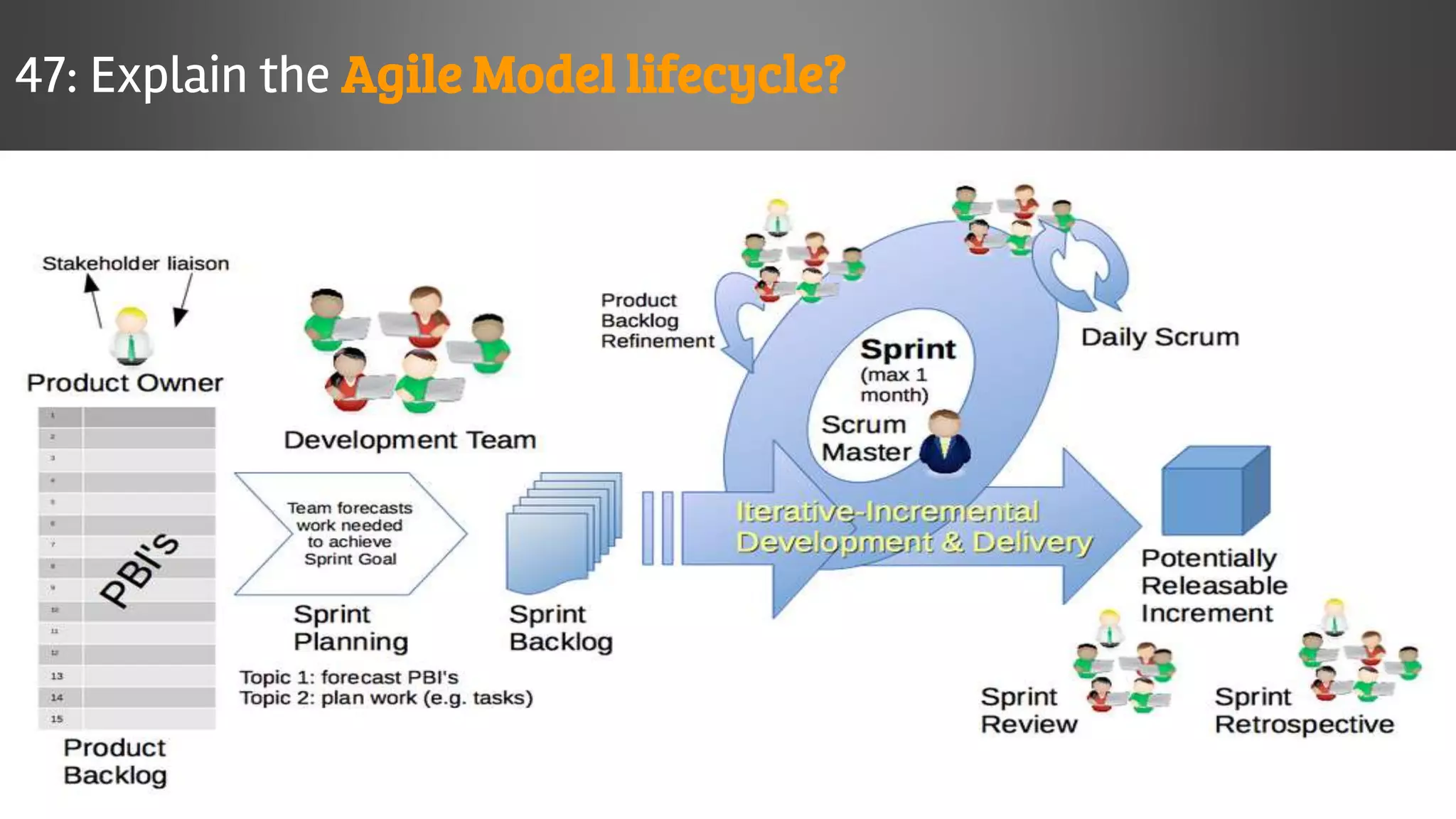
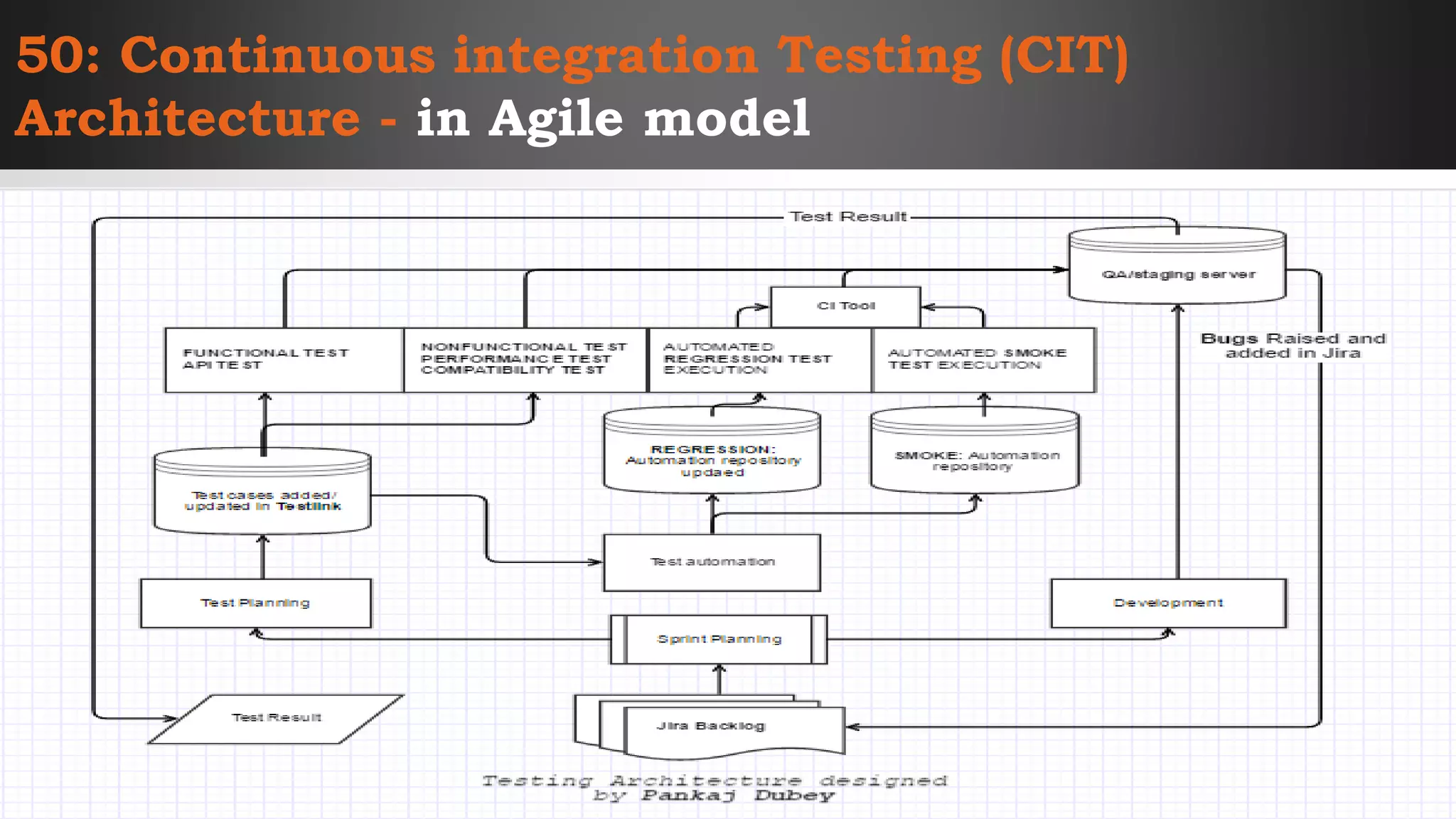
The document outlines key concepts and interview questions related to manual software testing, including the importance of testing, quality assurance (QA), and quality control (QC). It details various testing processes such as software testing lifecycle (STLC), test planning, test designing, and different types of testing (black box, white box, integration, system, and user acceptance testing). The document also discusses bug management, performance testing, tools for test management, and the agile model in software development.