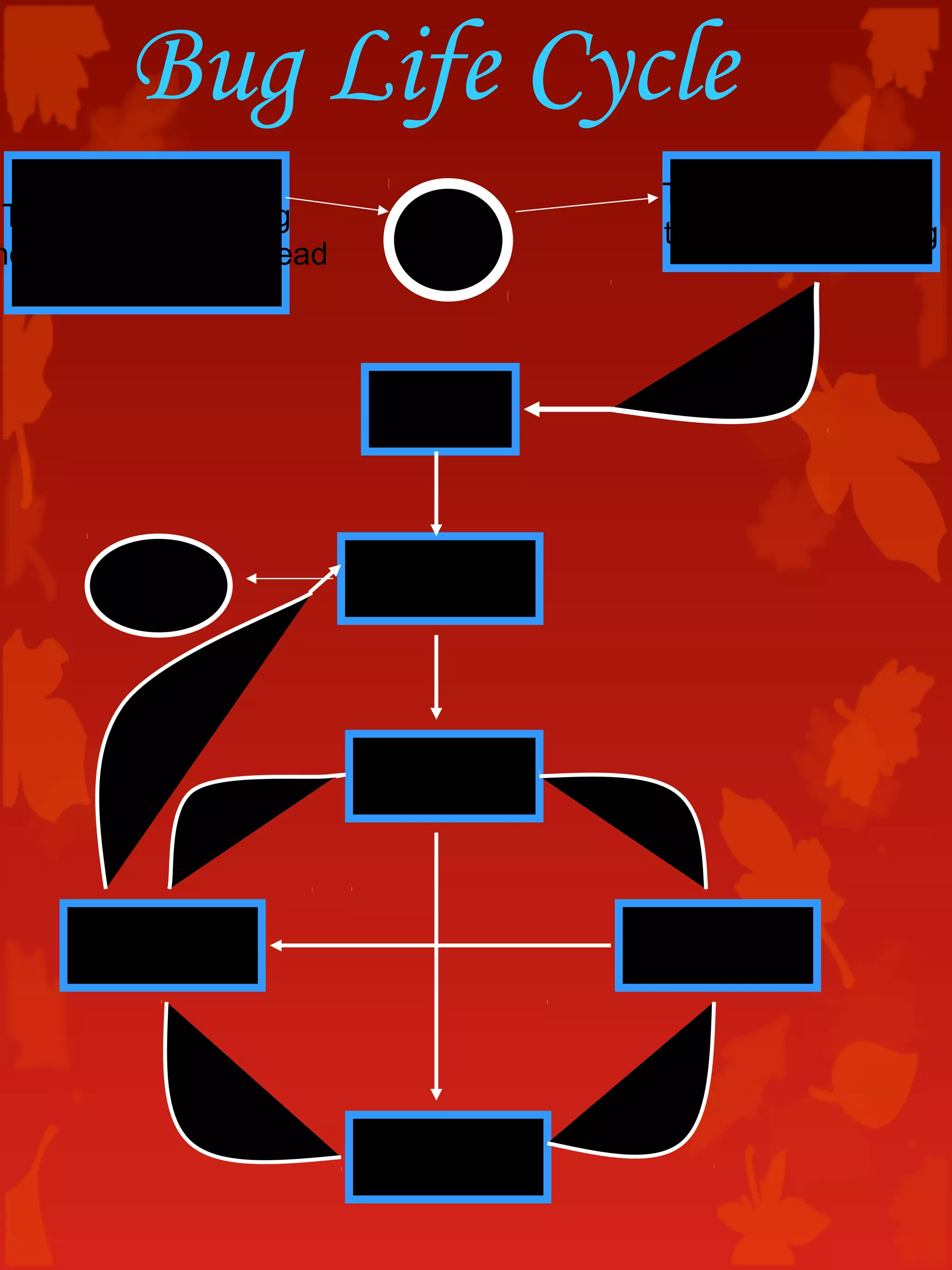
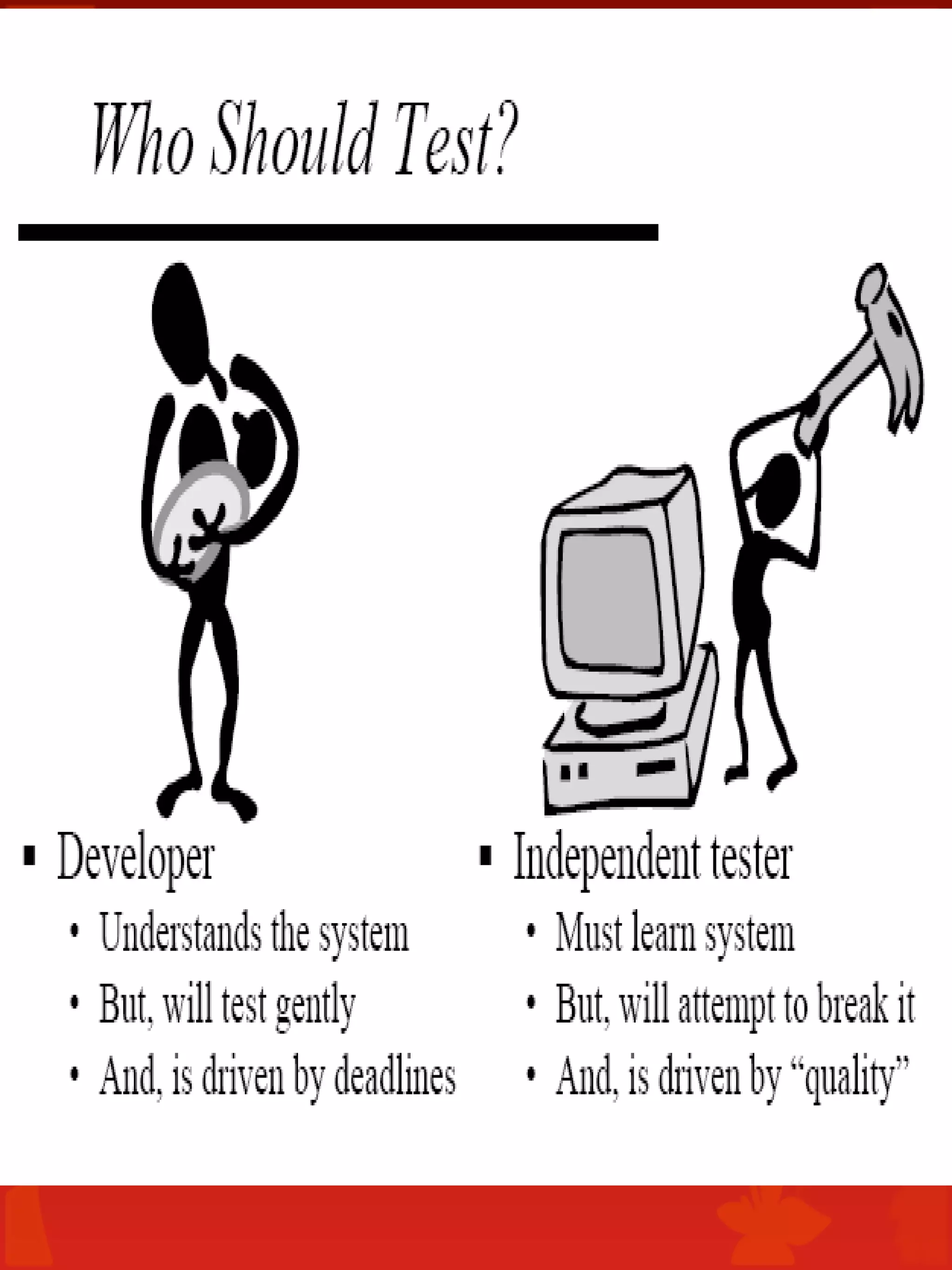
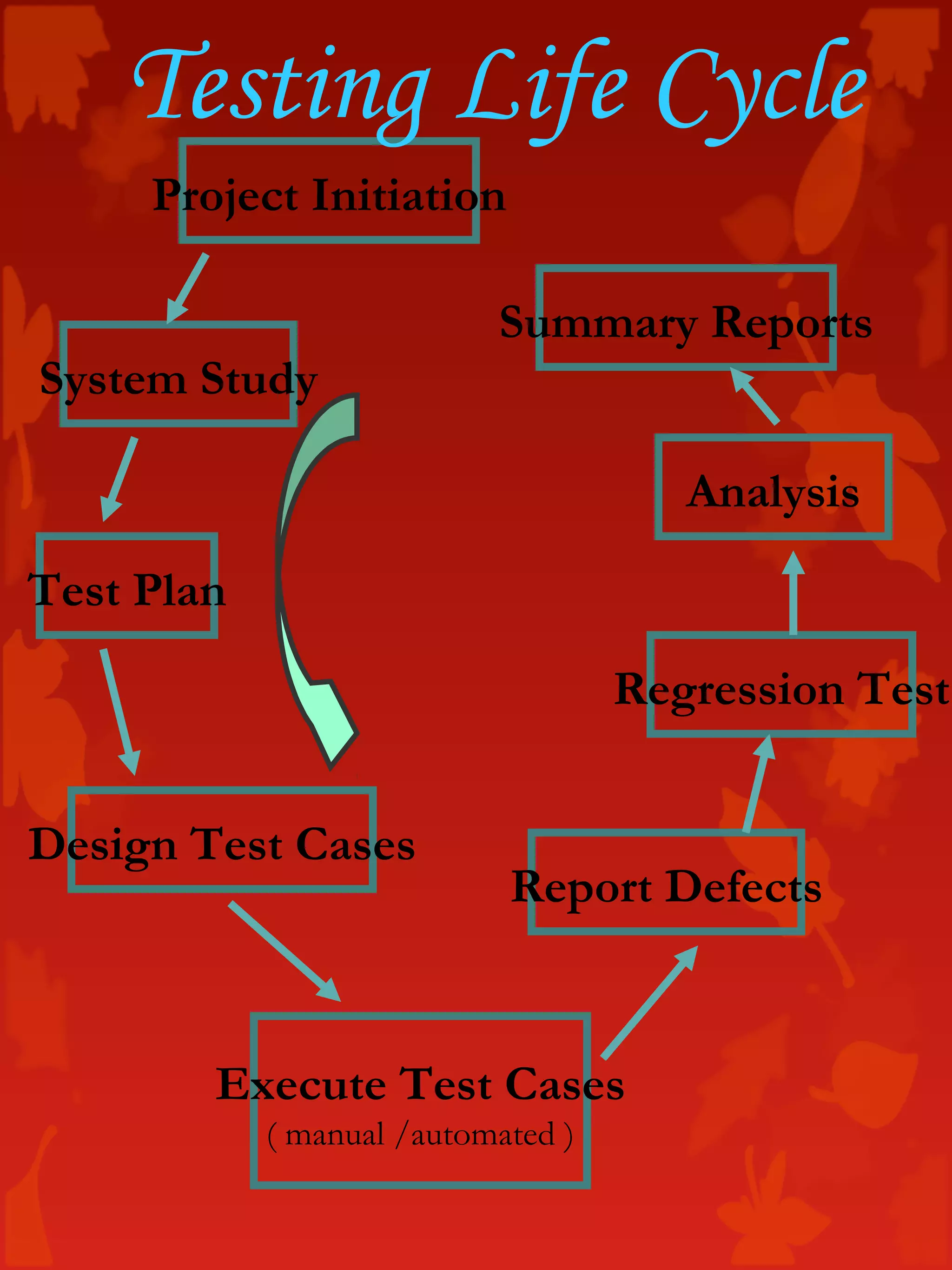
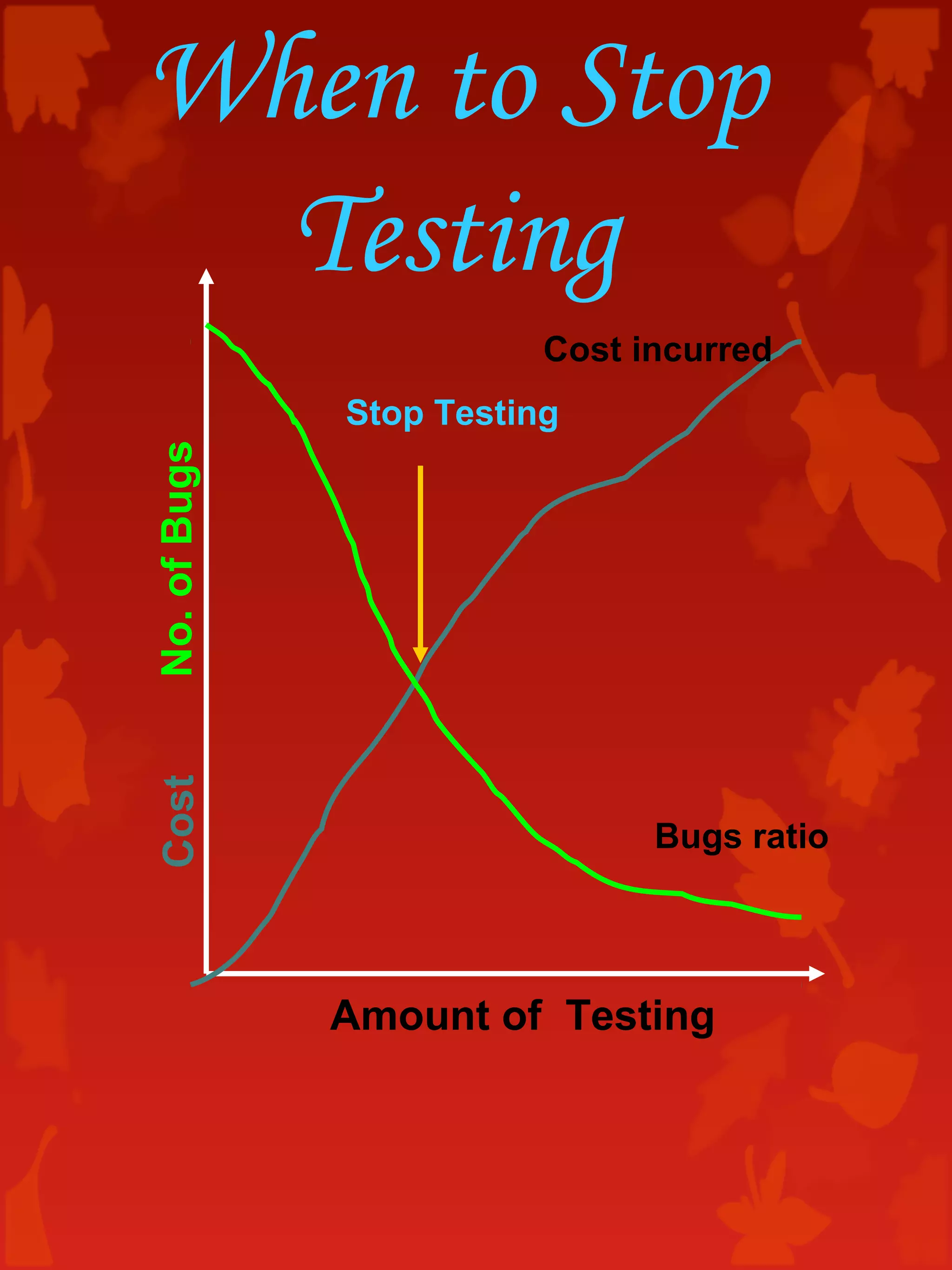
The document discusses software testing concepts including the importance of testing, the testing life cycle, types of testing, quality assurance and control, and bug reporting. It provides definitions and descriptions of key testing terms like errors, bugs, faults, failures, test plans, test cases, unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and regression testing. Testing roles like testers, QA leads, and test analysts are also outlined.