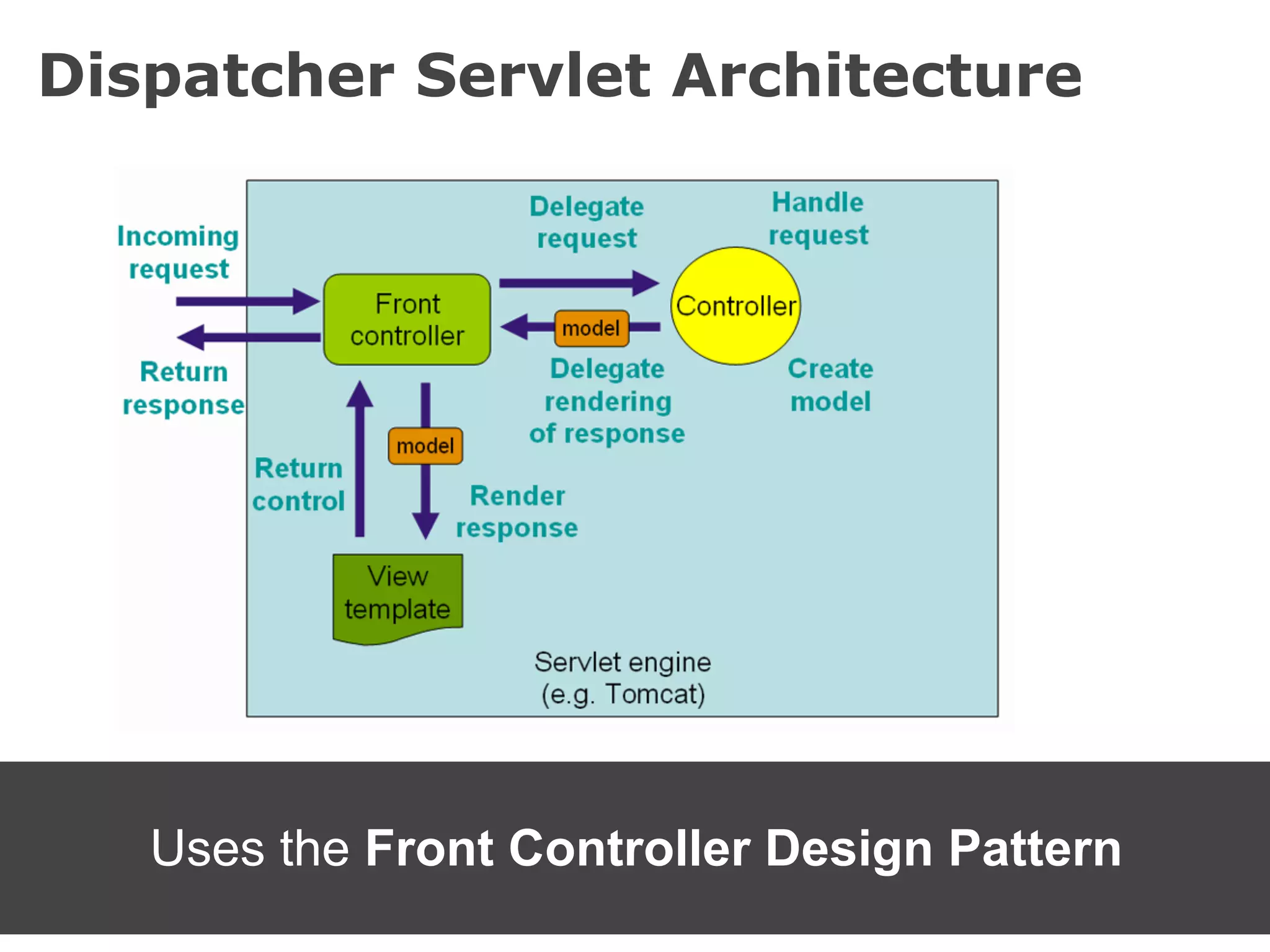
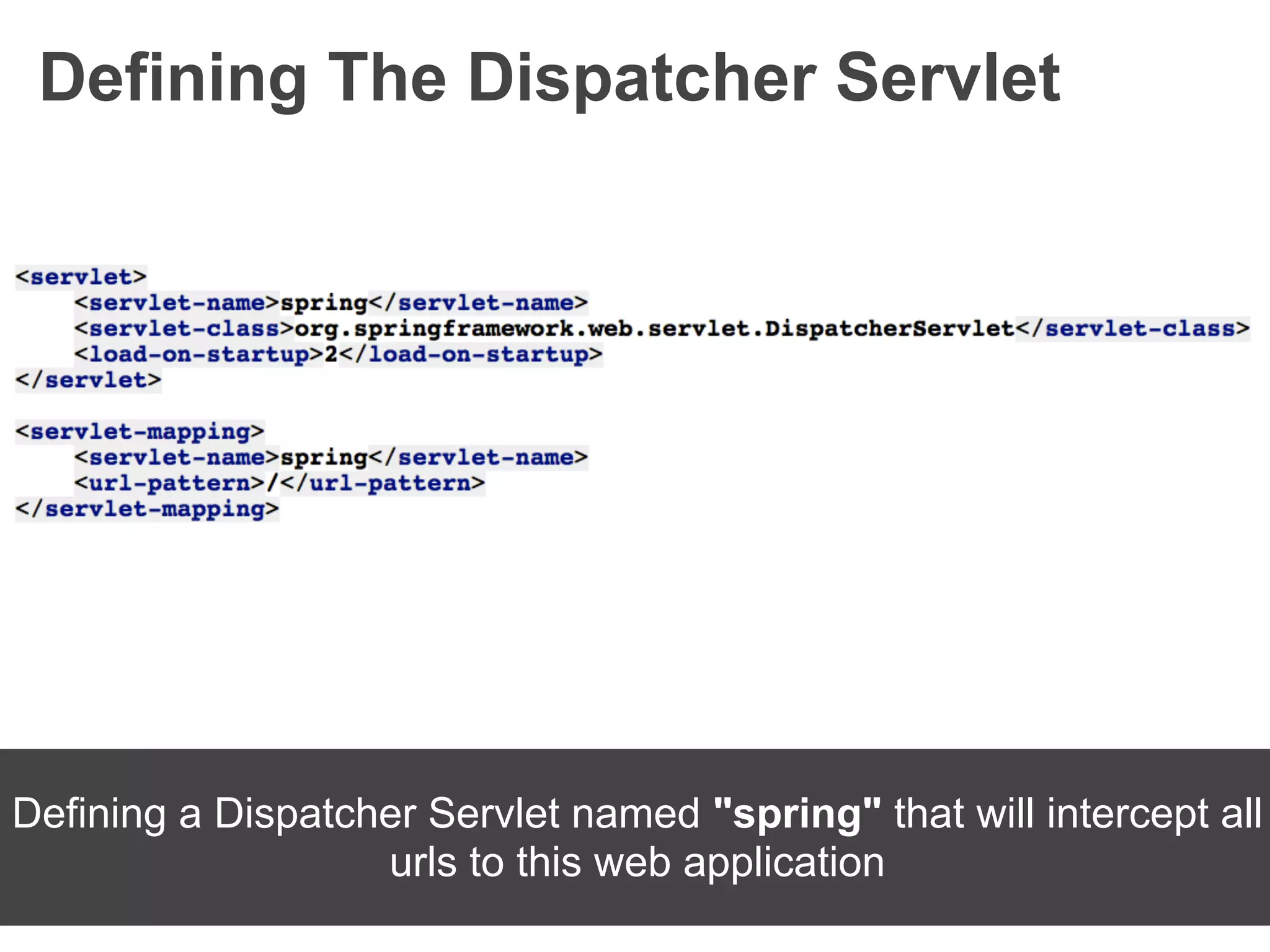
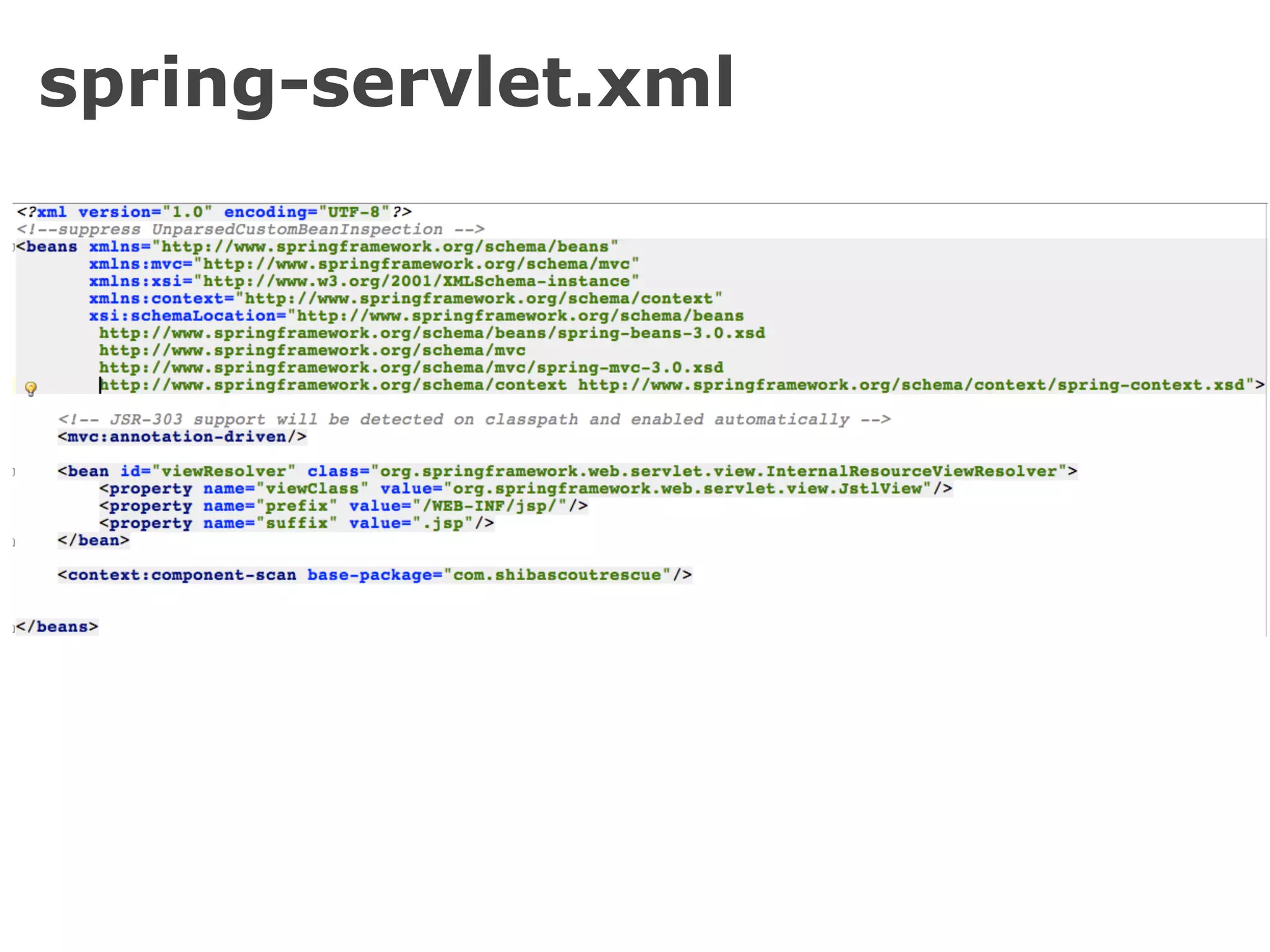
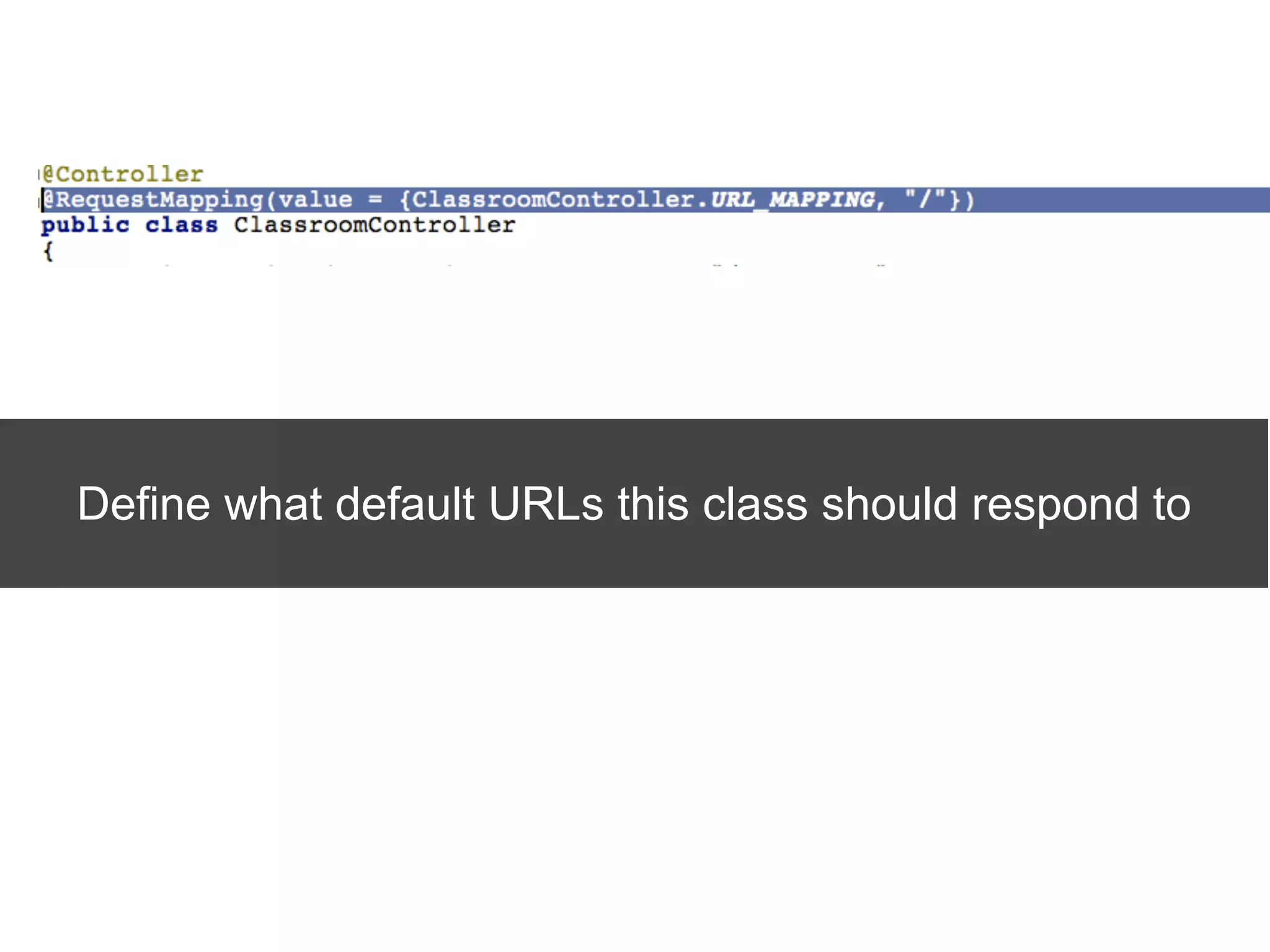
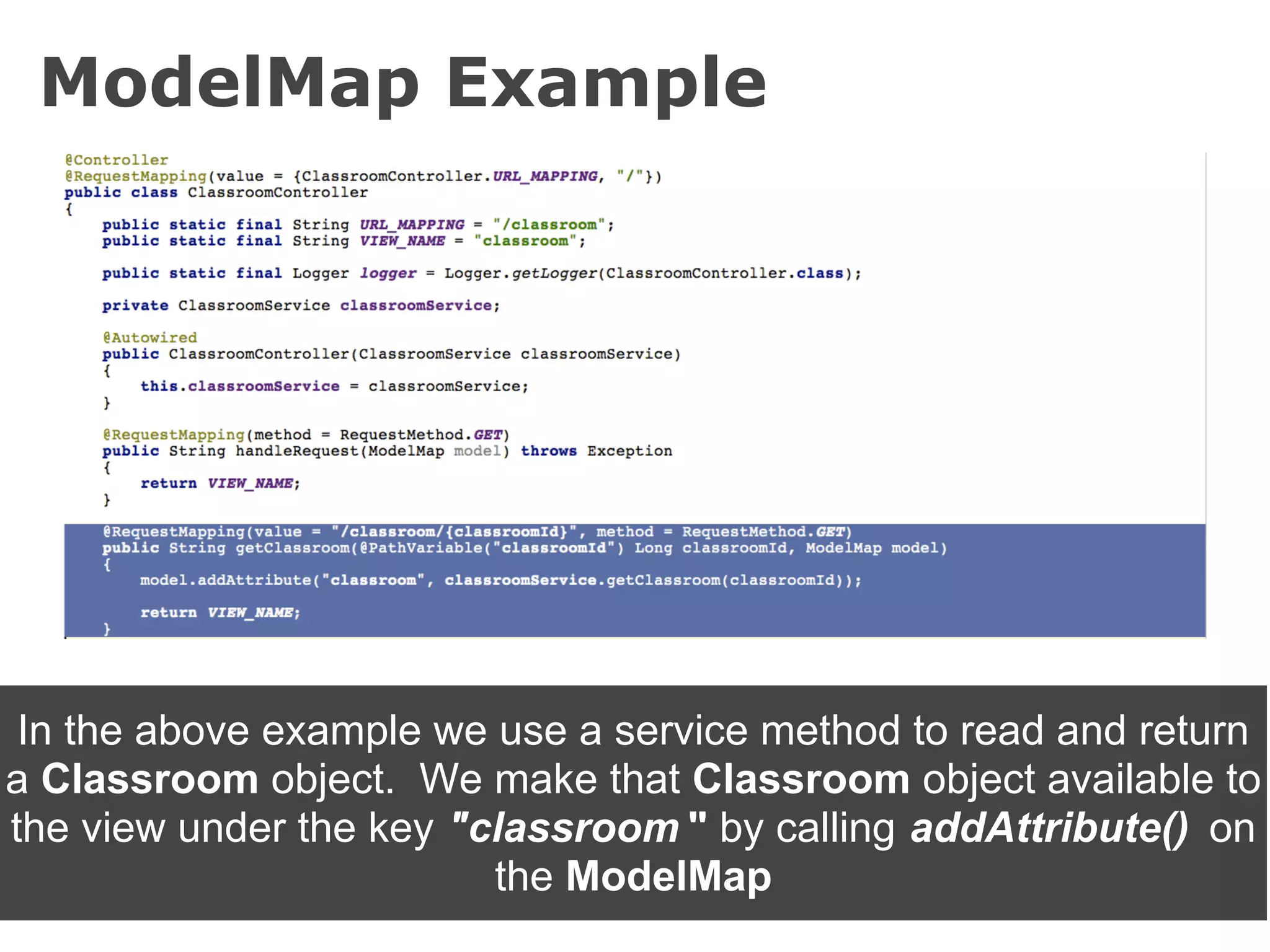
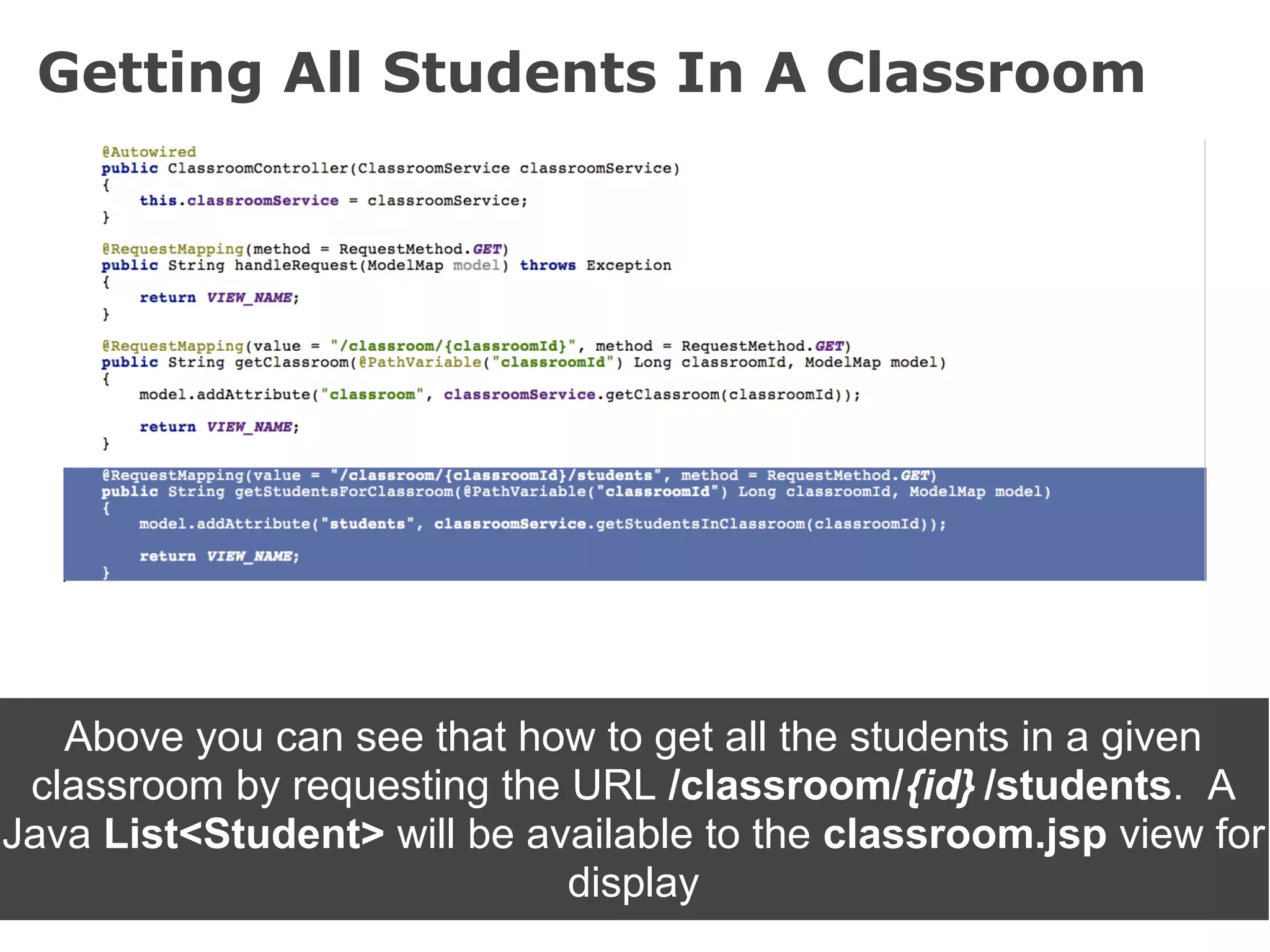
The document discusses the Spring MVC framework, a model-view-controller solution designed to simplify Java web application development. It emphasizes integration with dependency injection, supports RESTful URLs, and promotes good software engineering principles. Additionally, it explains the use of DispatcherServlet, auto-wiring, and model management for efficient handling of web requests and responses.