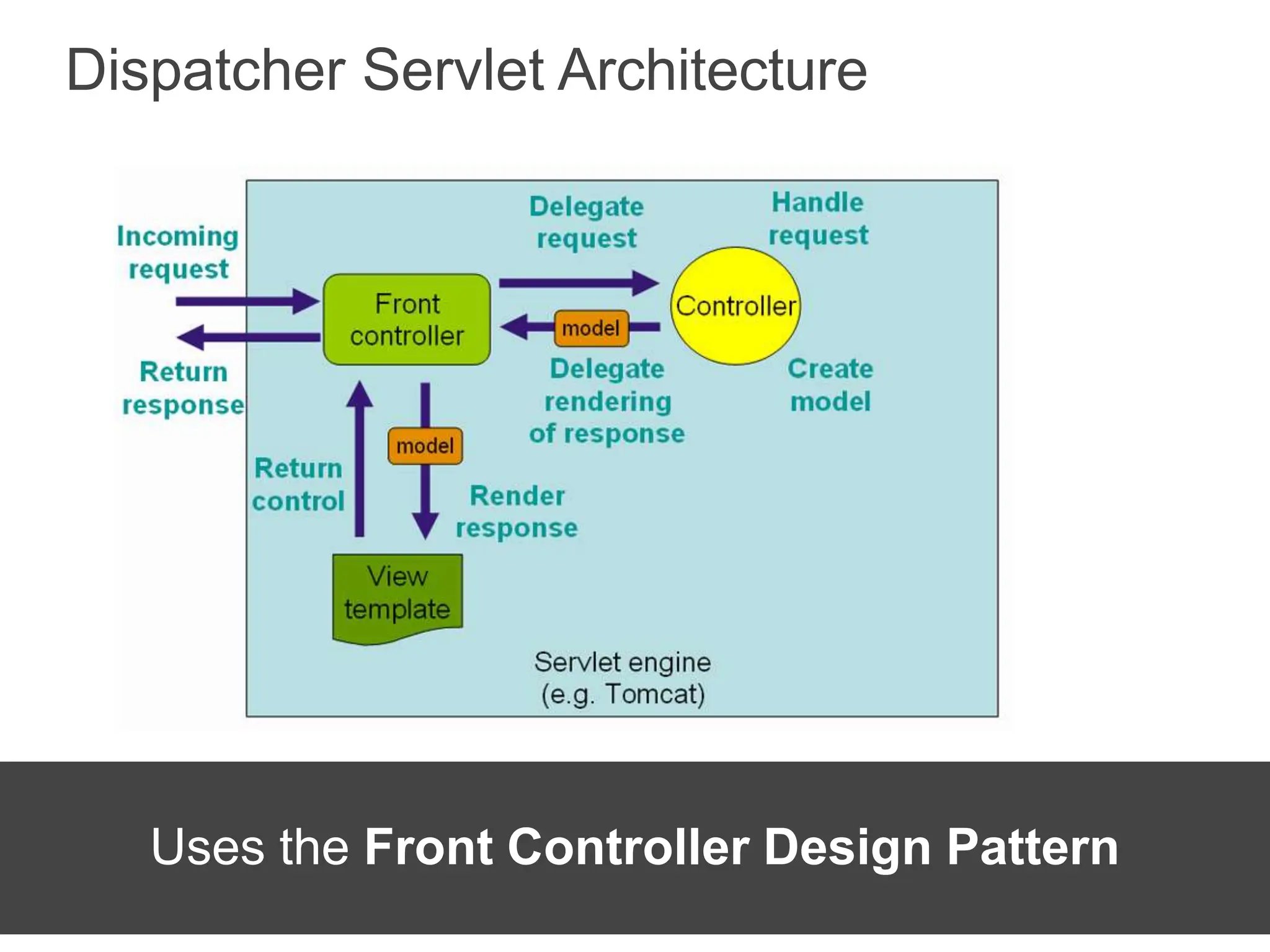
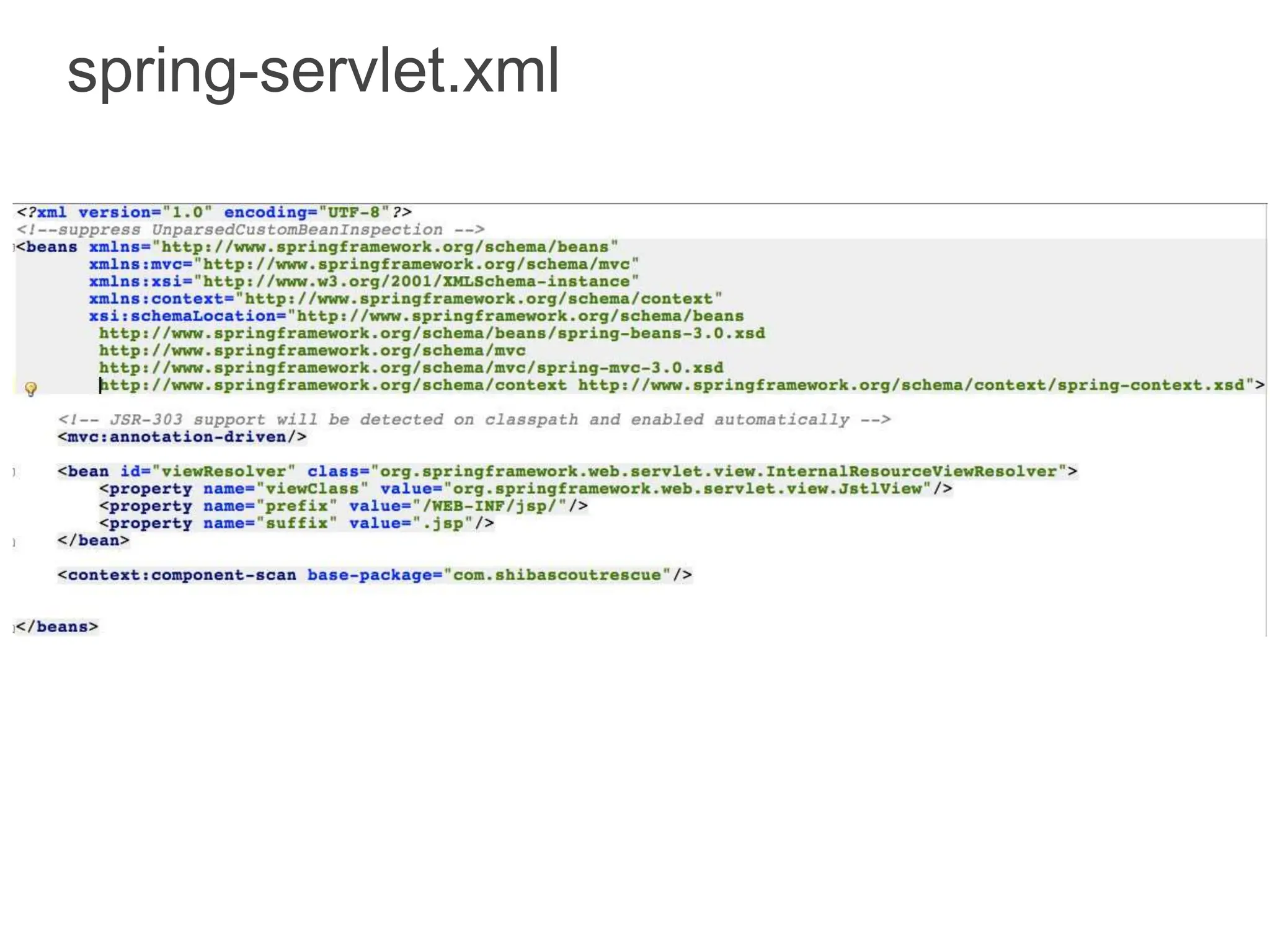
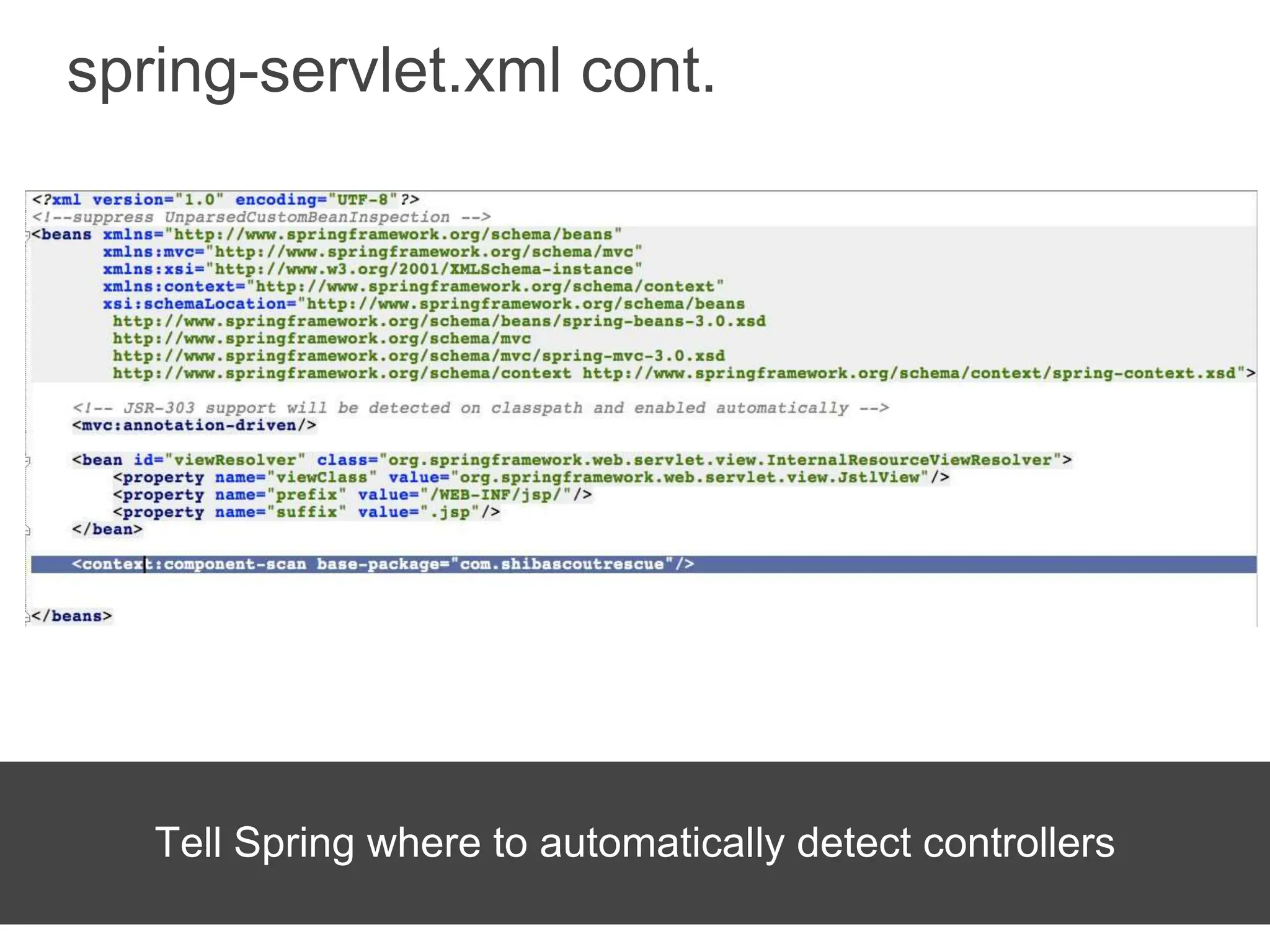
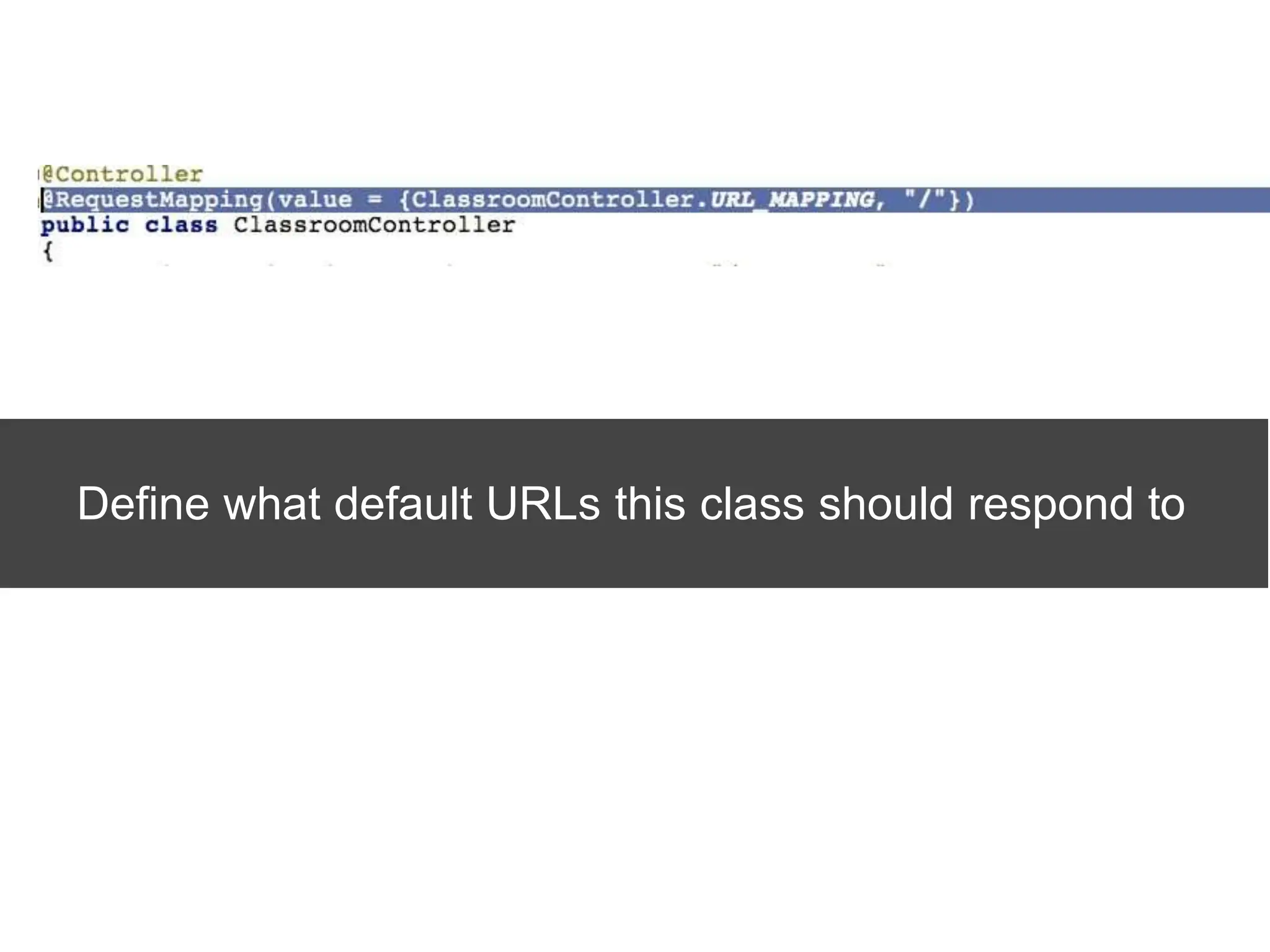
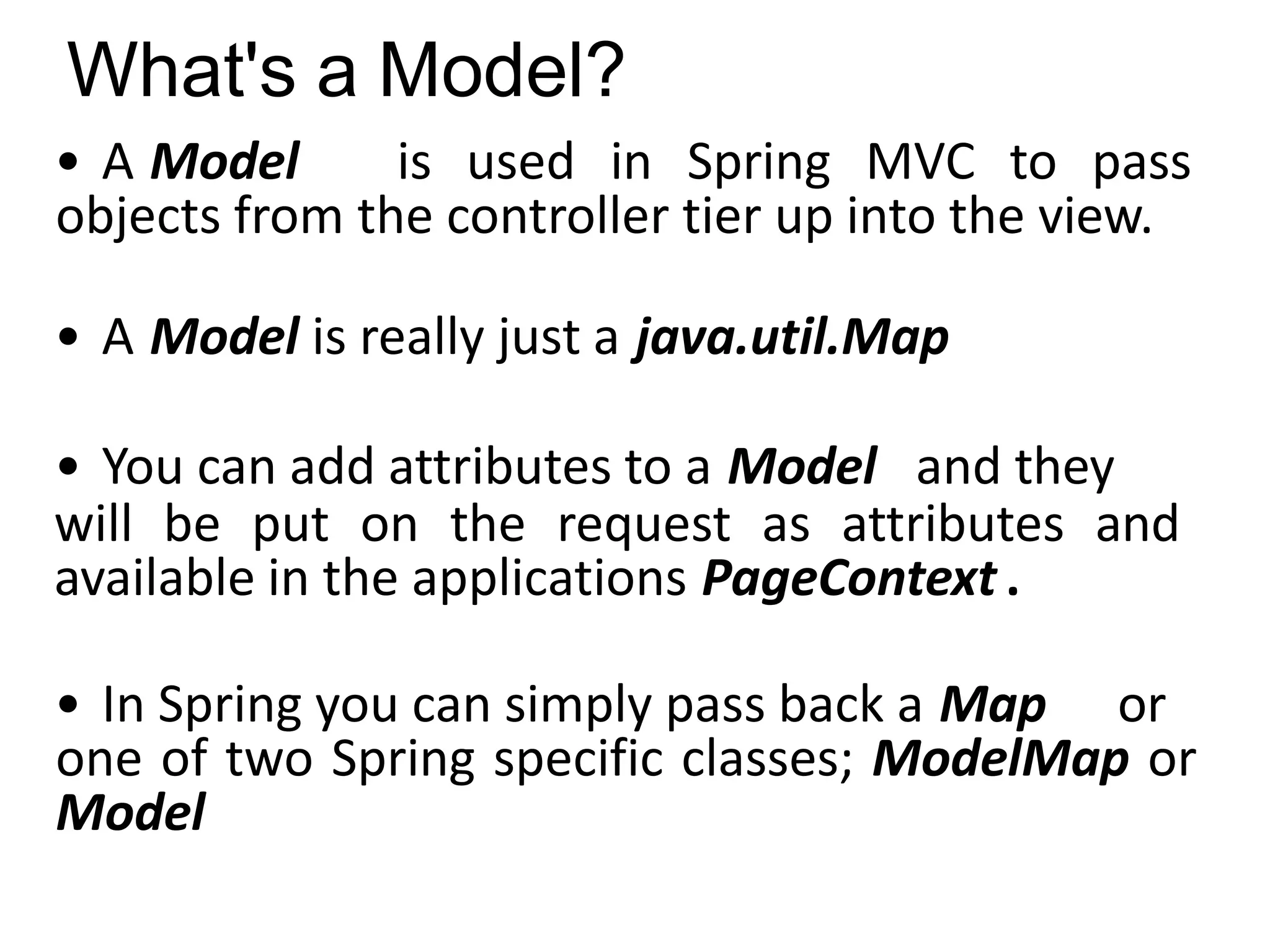
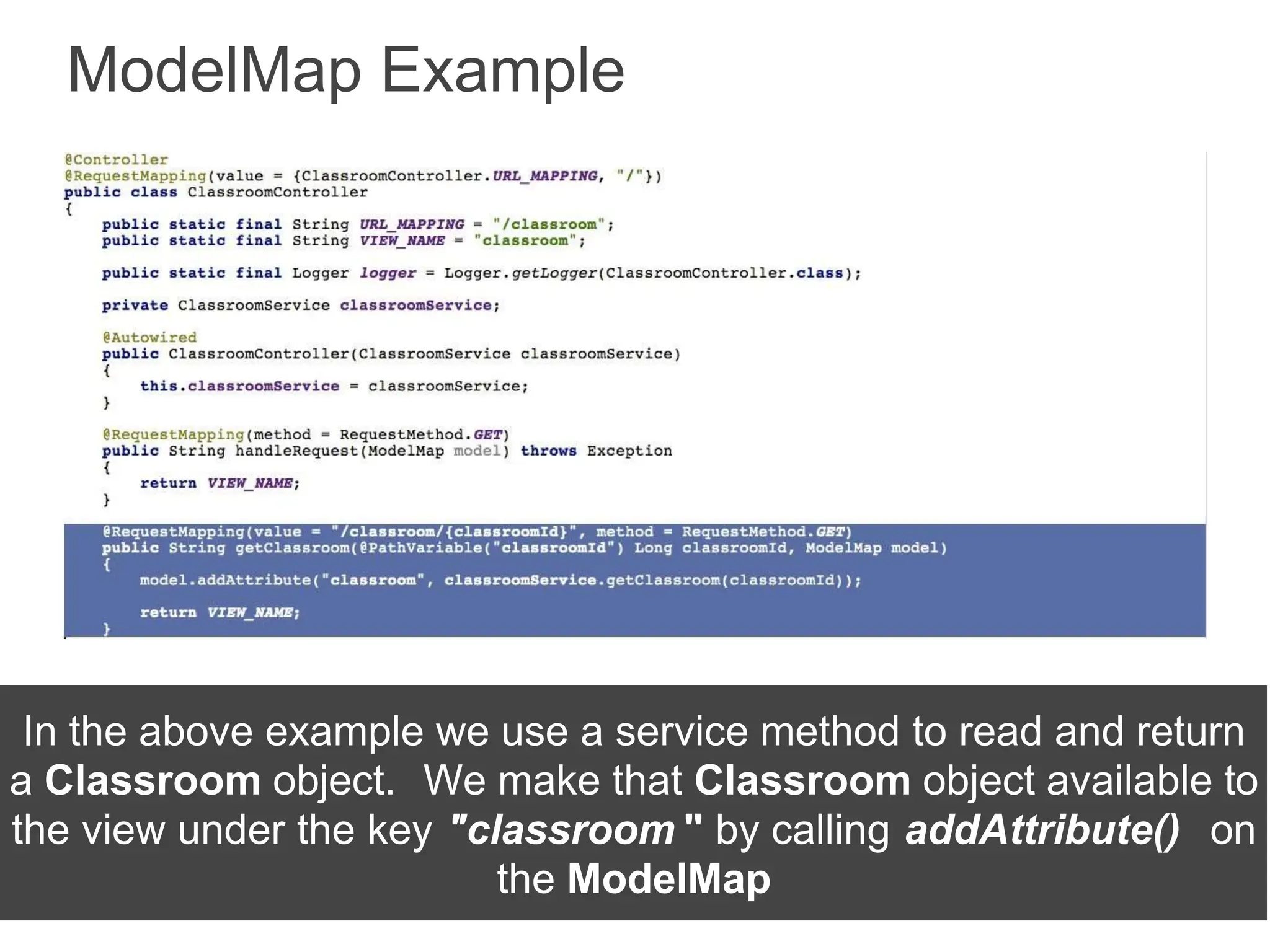
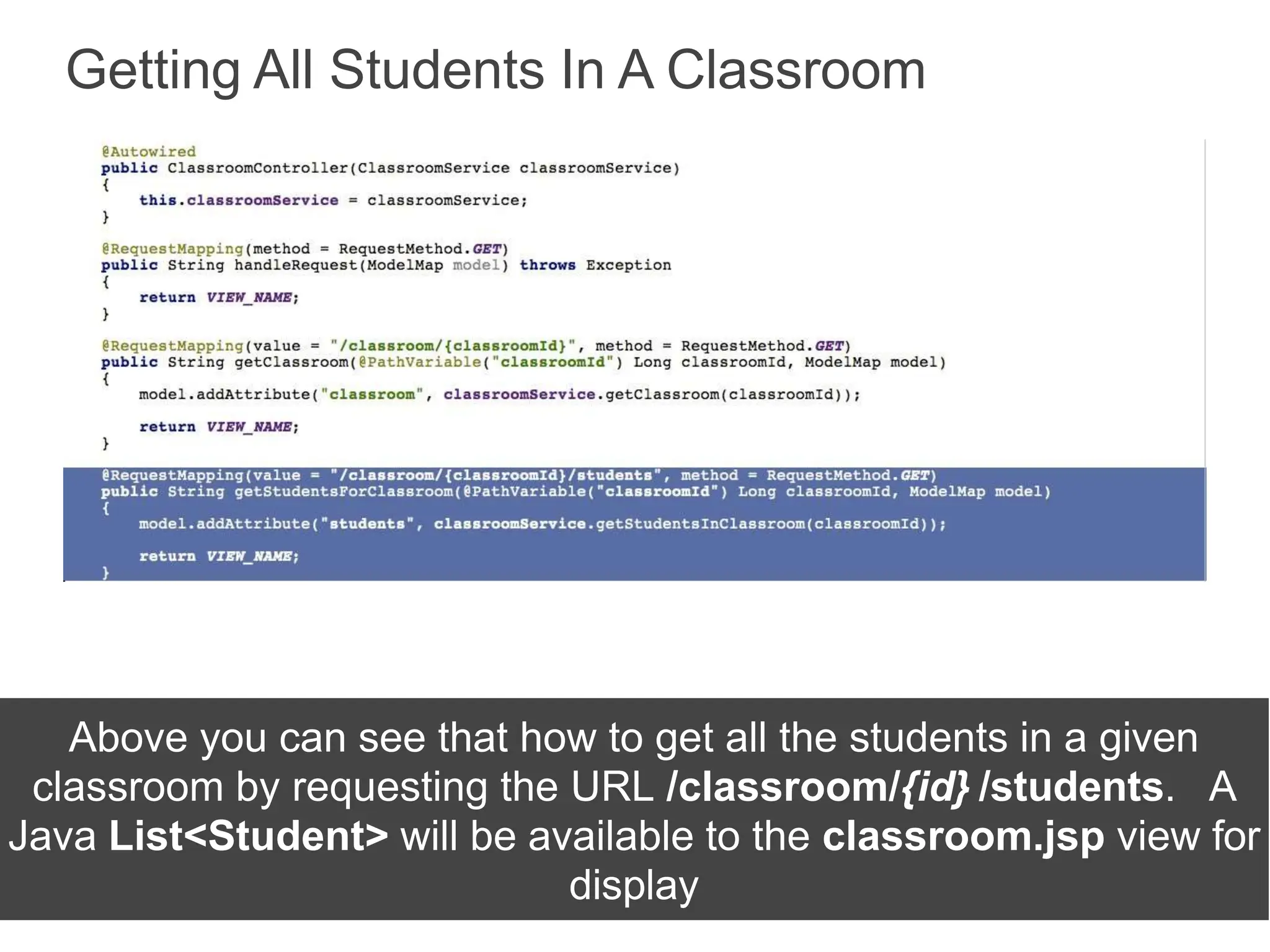
Spring Framework and Spring MVC are frameworks for building Java web applications. Spring MVC is a model-view-controller framework that simplifies writing and testing Java web apps. It integrates with the Spring dependency injection framework. The DispatcherServlet handles all incoming requests and routes them through controllers with customizable logic. Controllers use the Front Controller design pattern and are defined using annotations to map URLs to methods. Models are used to pass data from controllers to views, represented as Java Maps.