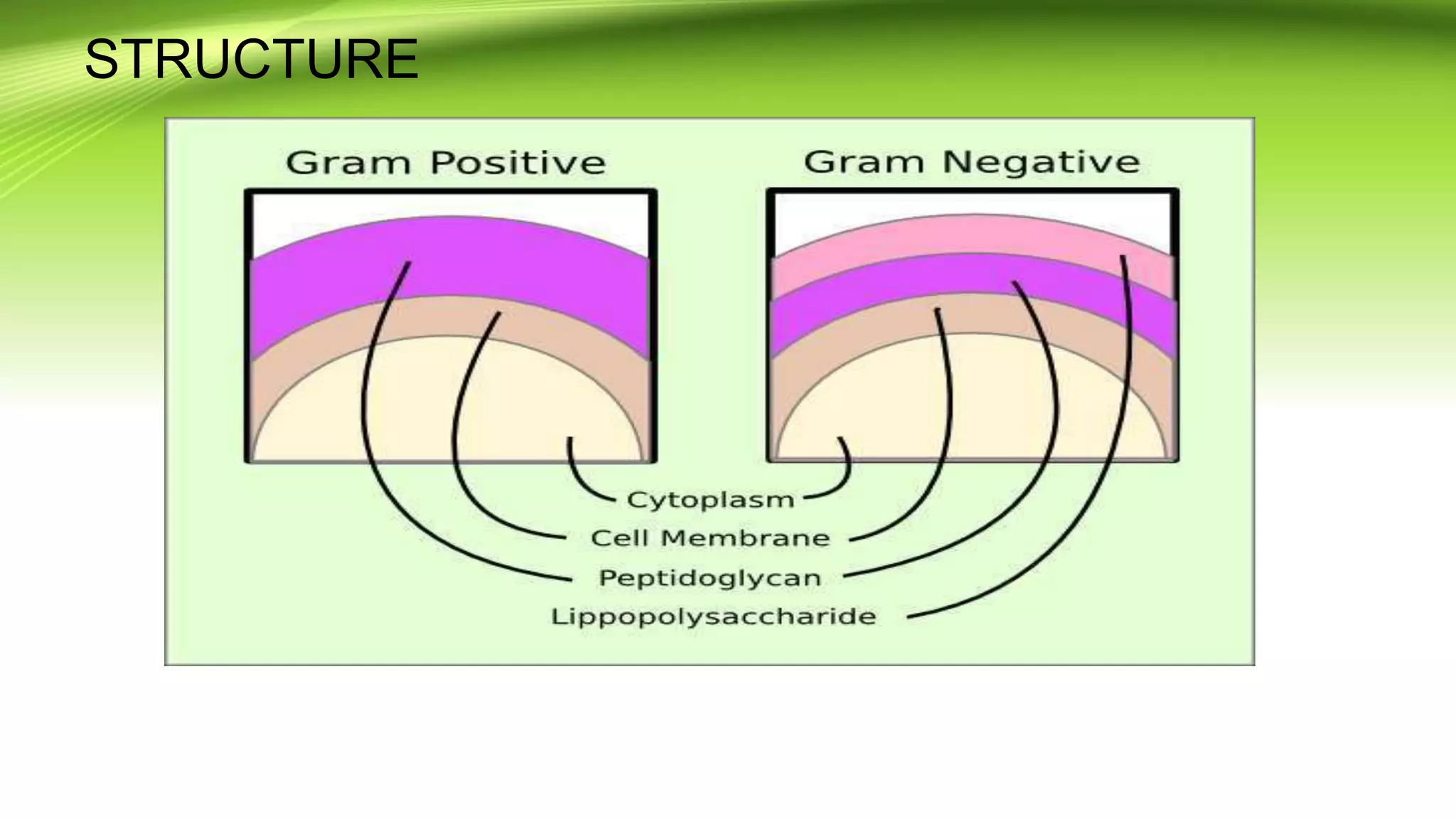
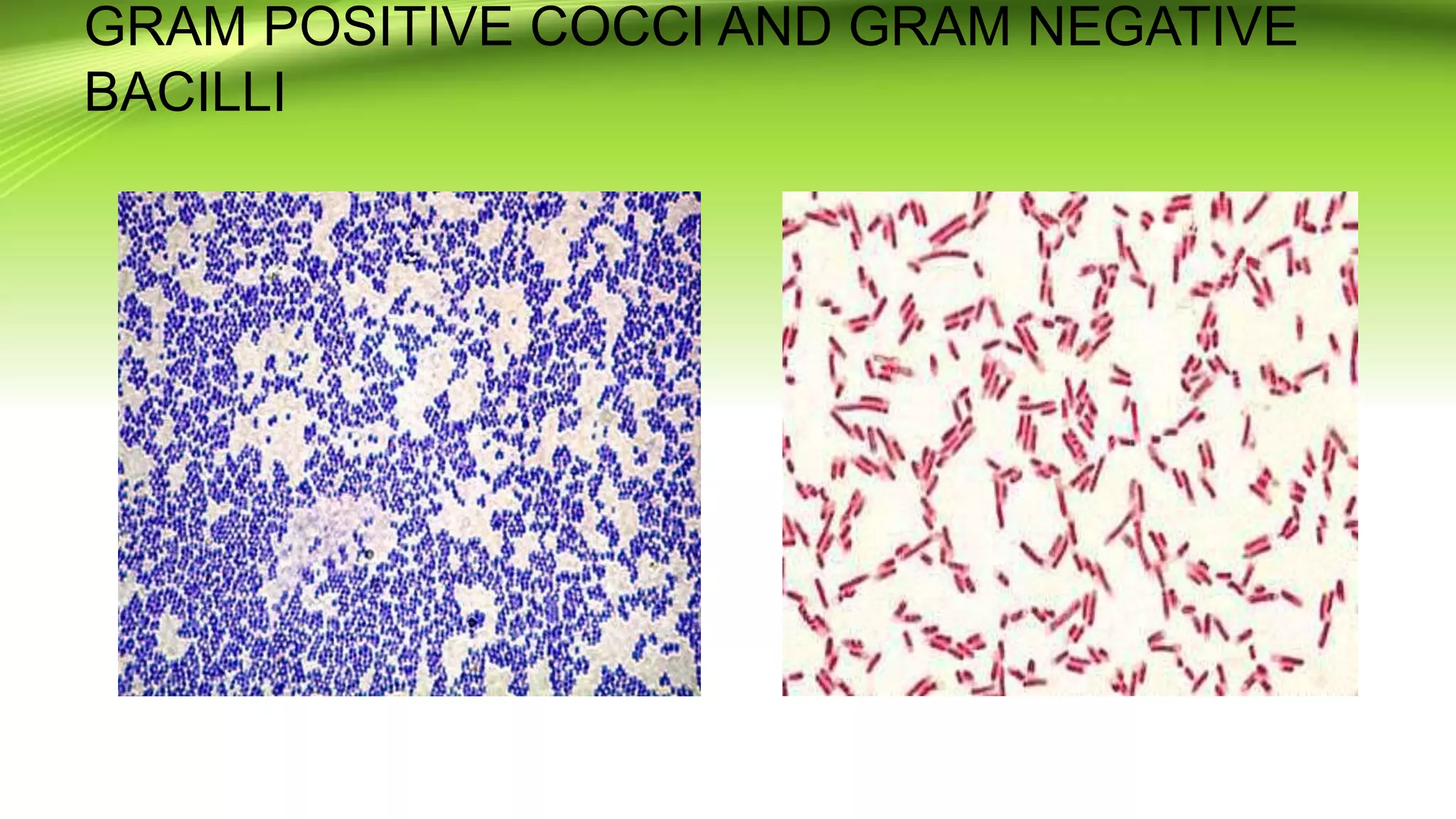
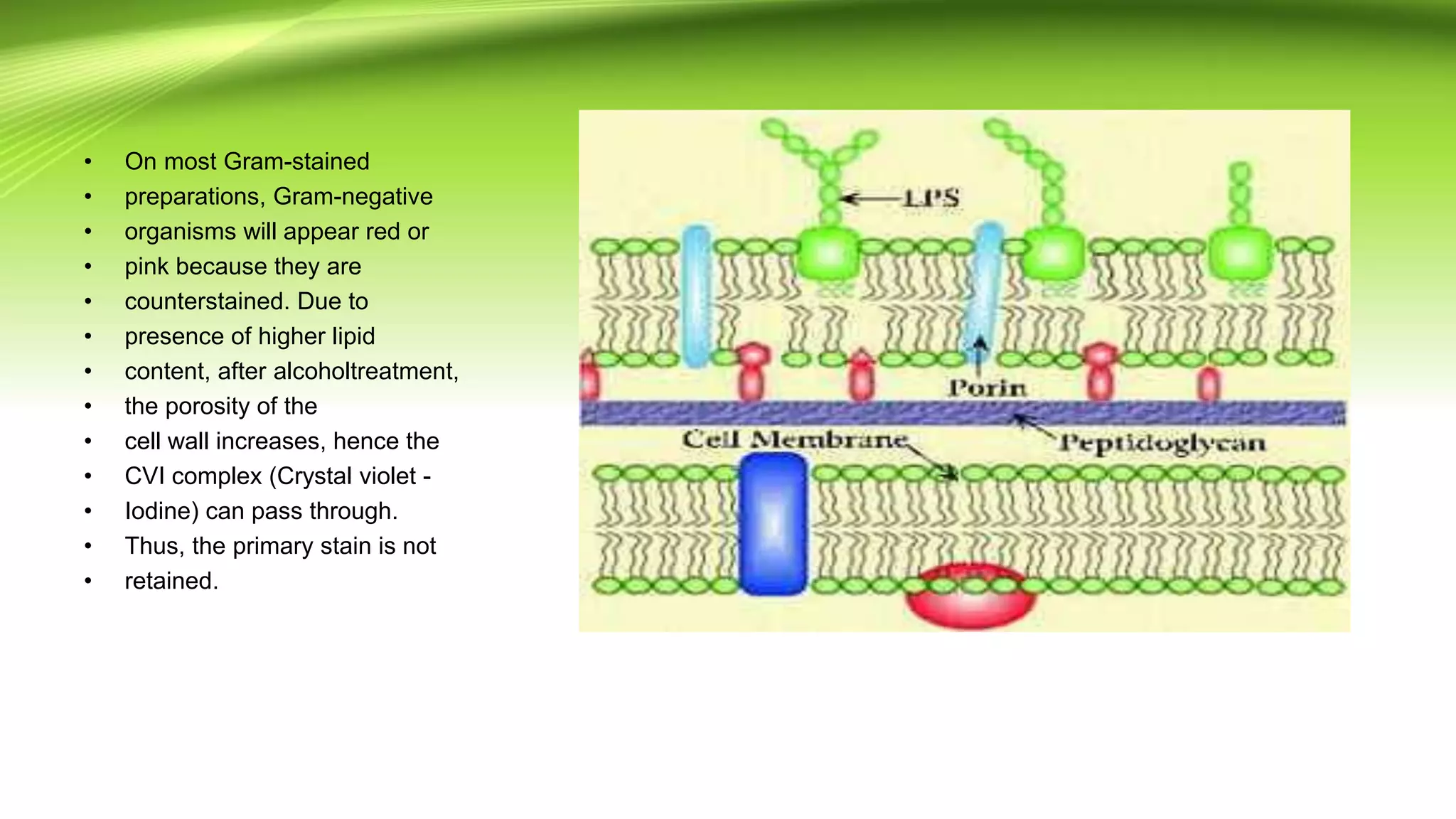
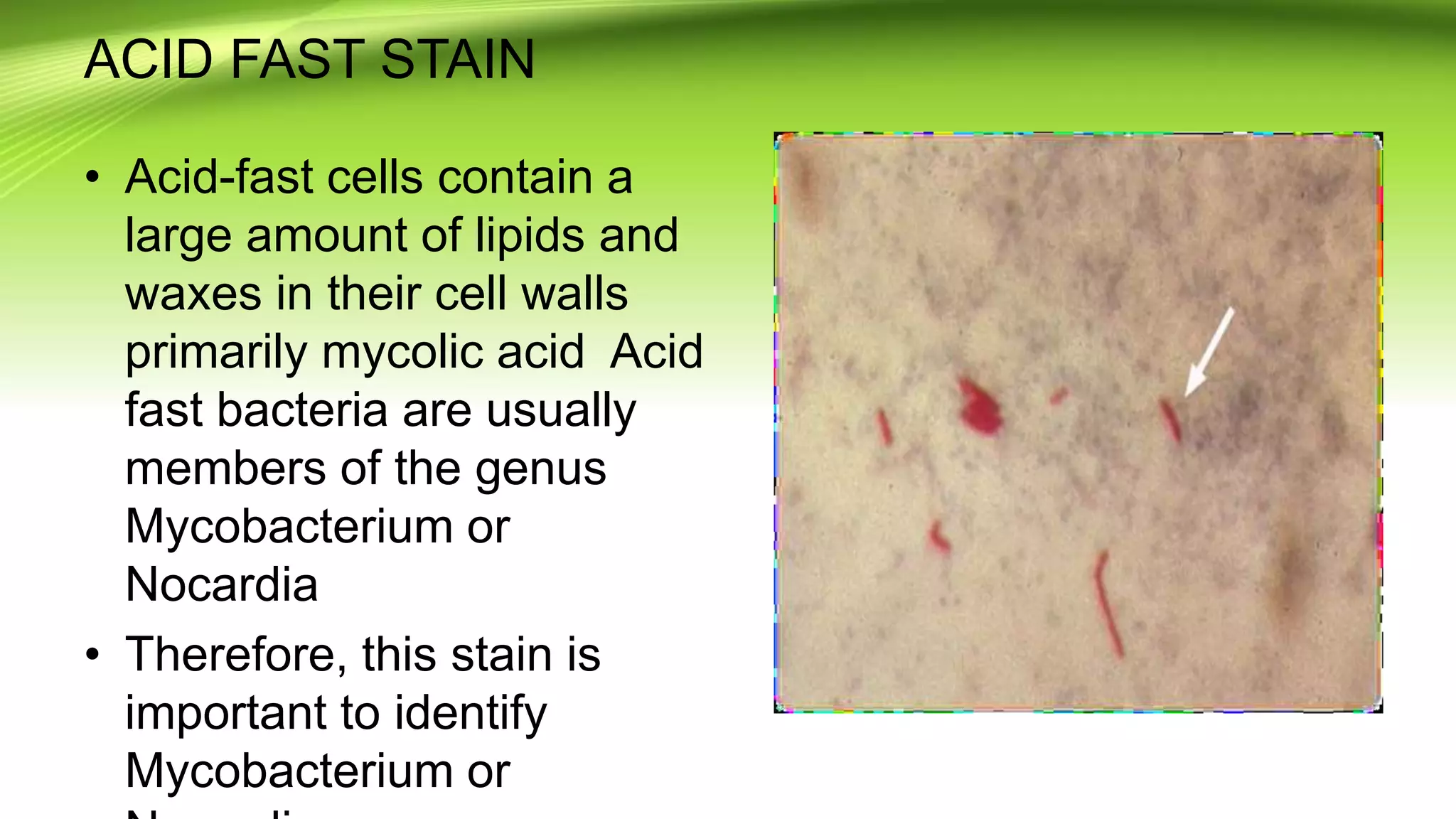
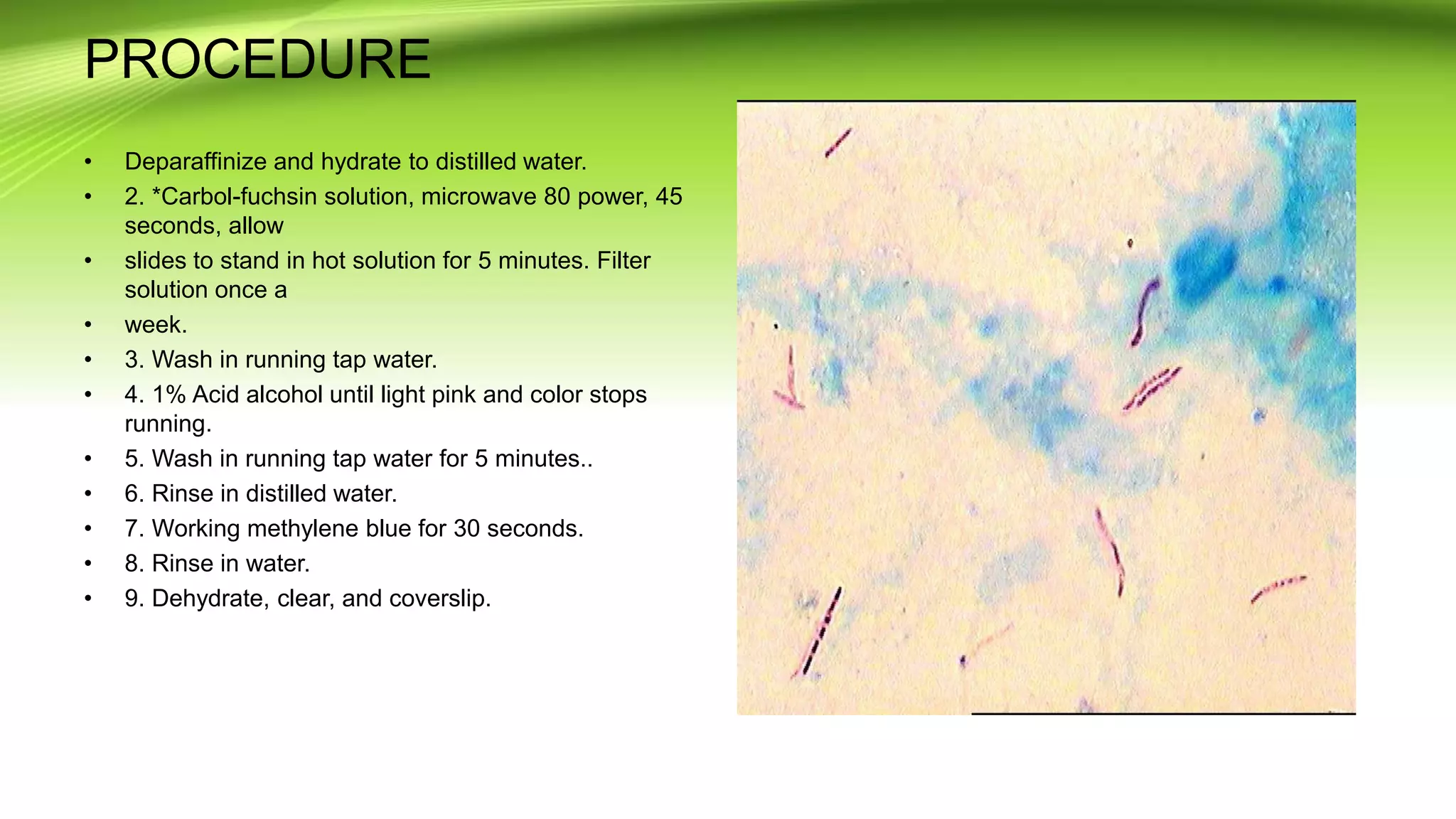
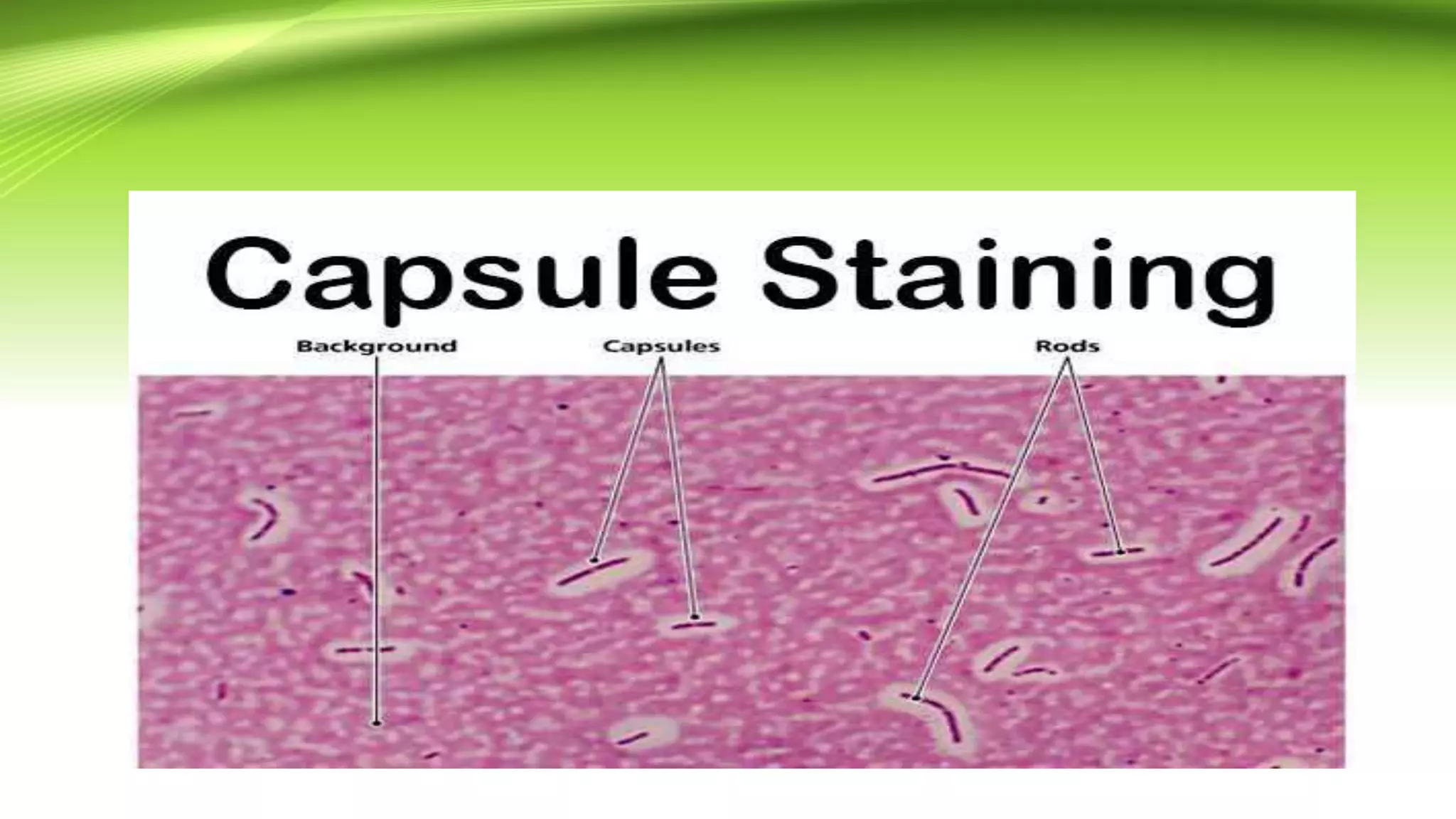
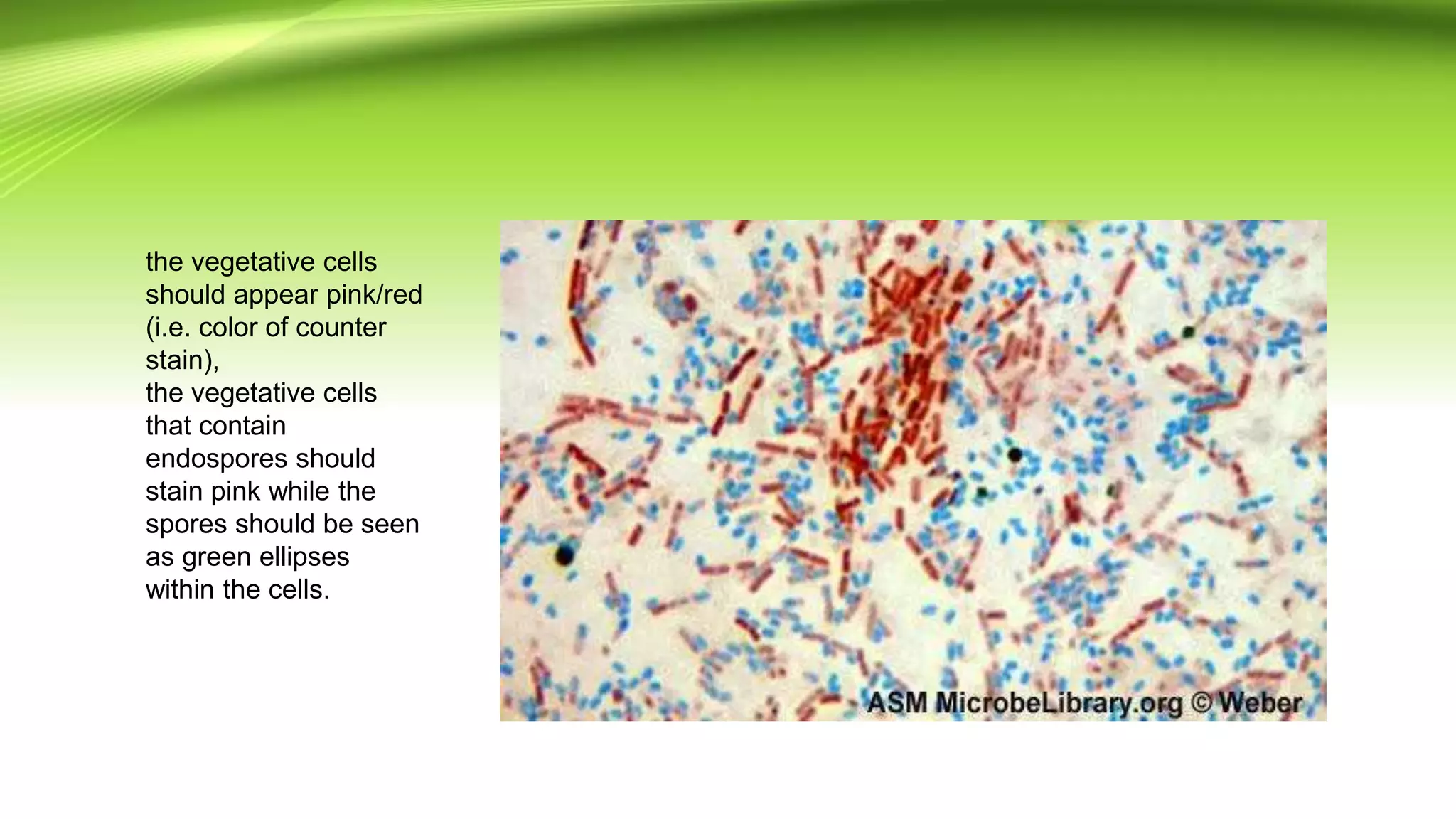
Gram staining is used to classify bacteria based on differences in cell wall composition. It involves staining with crystal violet and iodine, then decolorizing and counterstaining. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain while gram-negative bacteria take up the counterstain. Acid-fast staining is used to identify mycobacteria by using heat to bind primary stain within acid-fast cell walls. Capsule staining uses India ink's dark background to contrast unstained capsules around stained cells. Spore staining employs malachite green and heat to permanently stain endospores within decolorized vegetative cells.