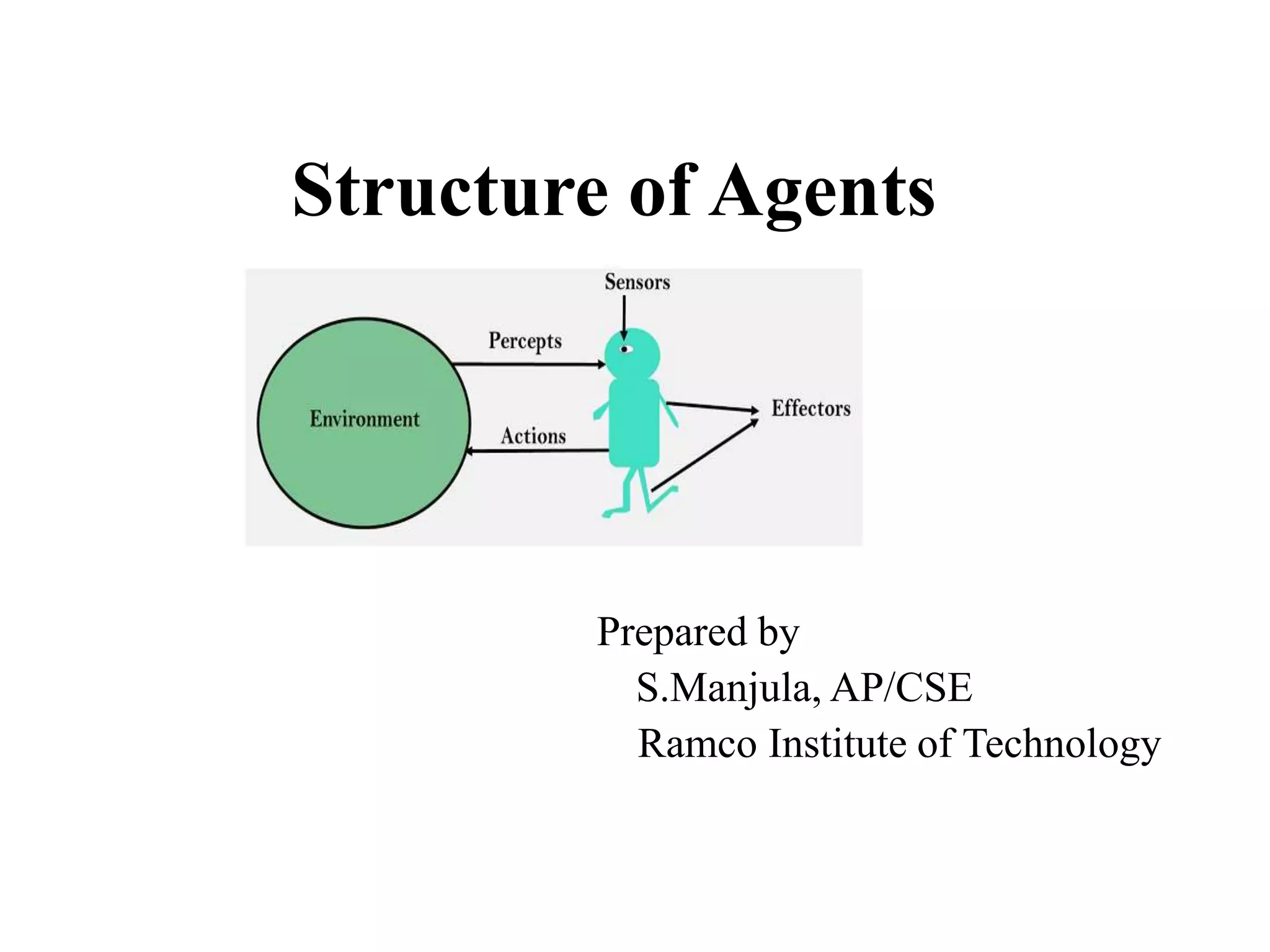
The document discusses different types of AI agents based on their structure and capabilities:
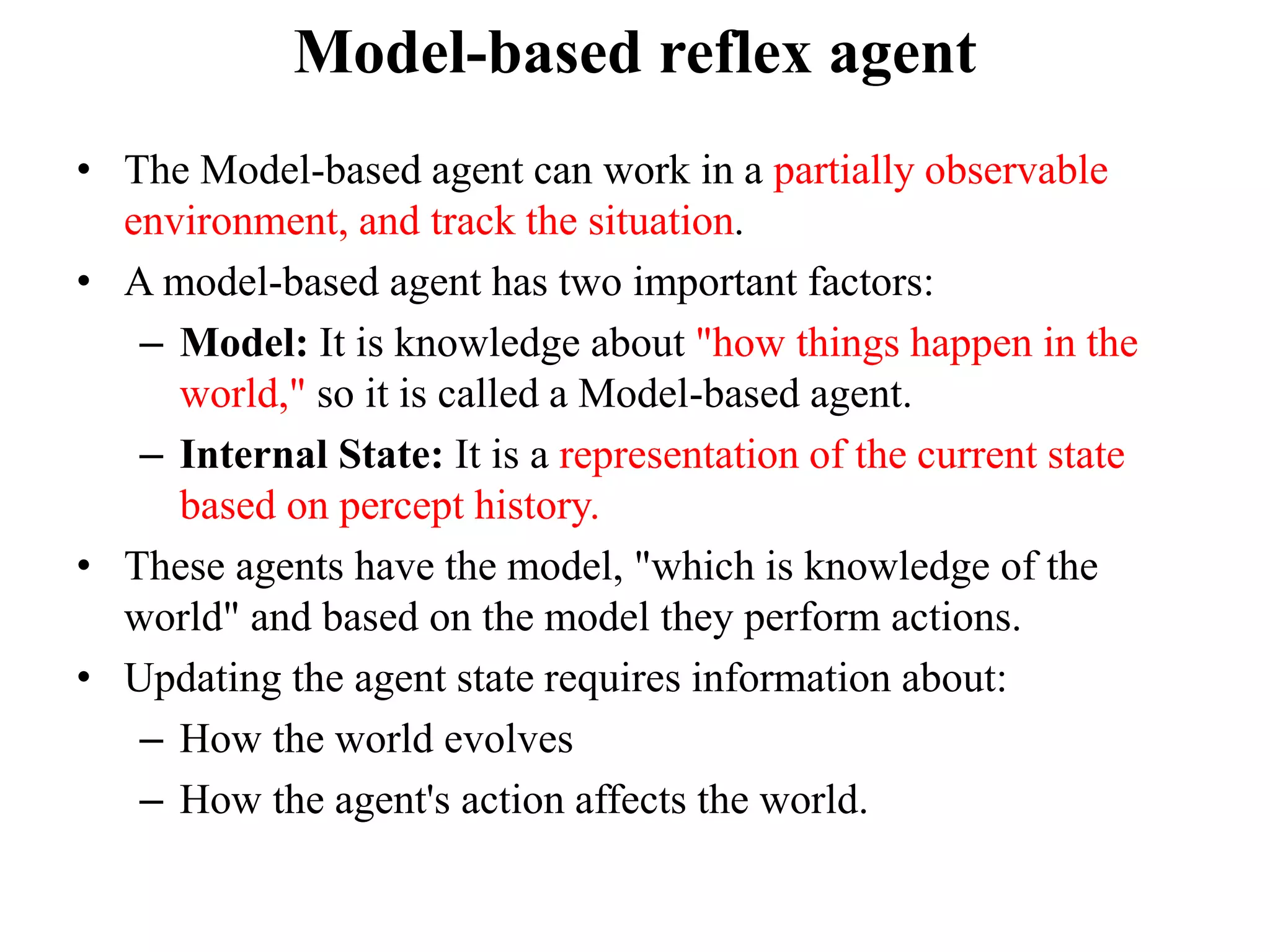
- Simple reflex agents take actions based solely on current percepts without considering history. Model-based reflex agents also track an internal state based on percept history.
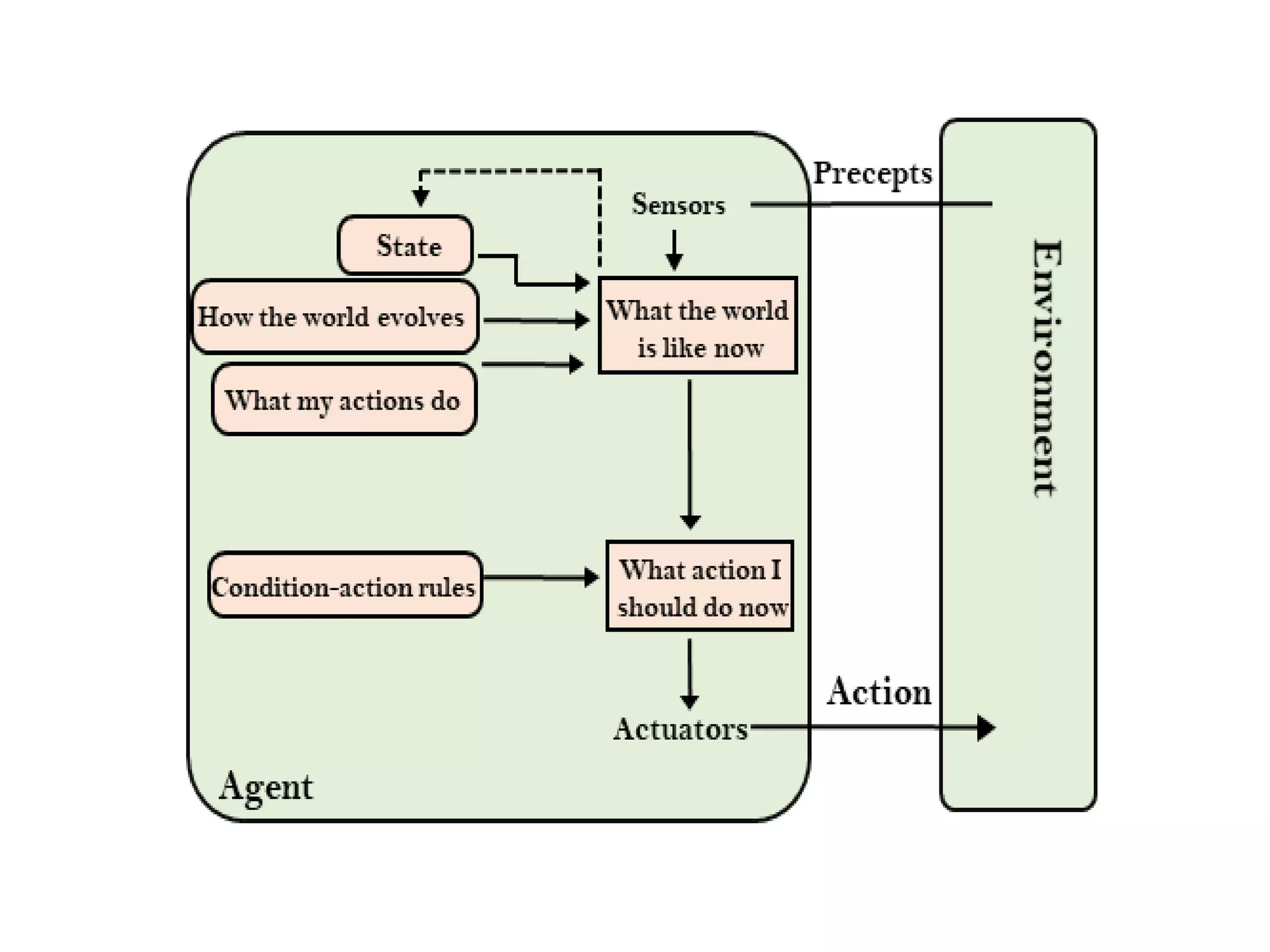
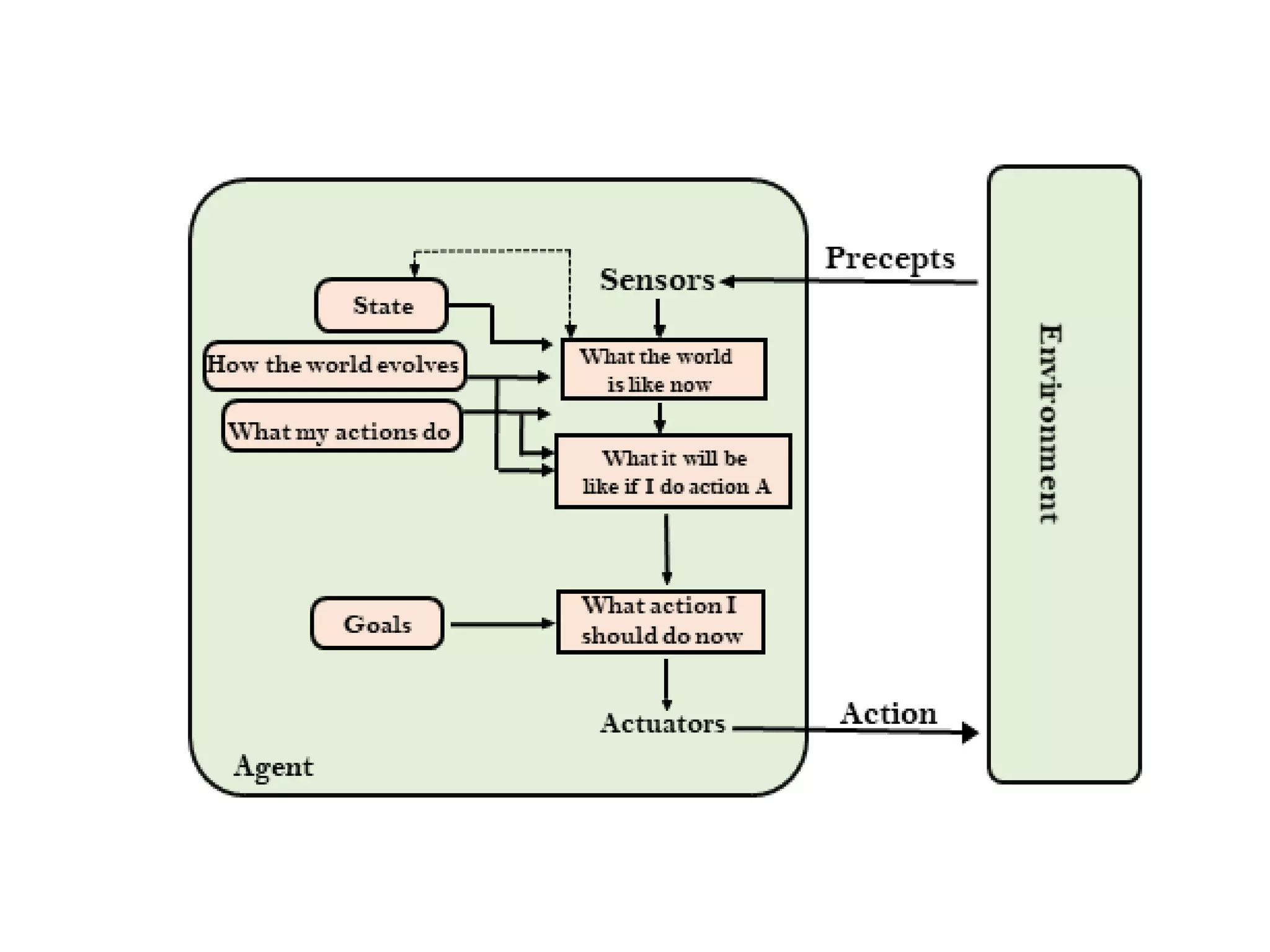
- Goal-based agents expand on model-based agents by considering goals and planning long sequences of actions to achieve goals.
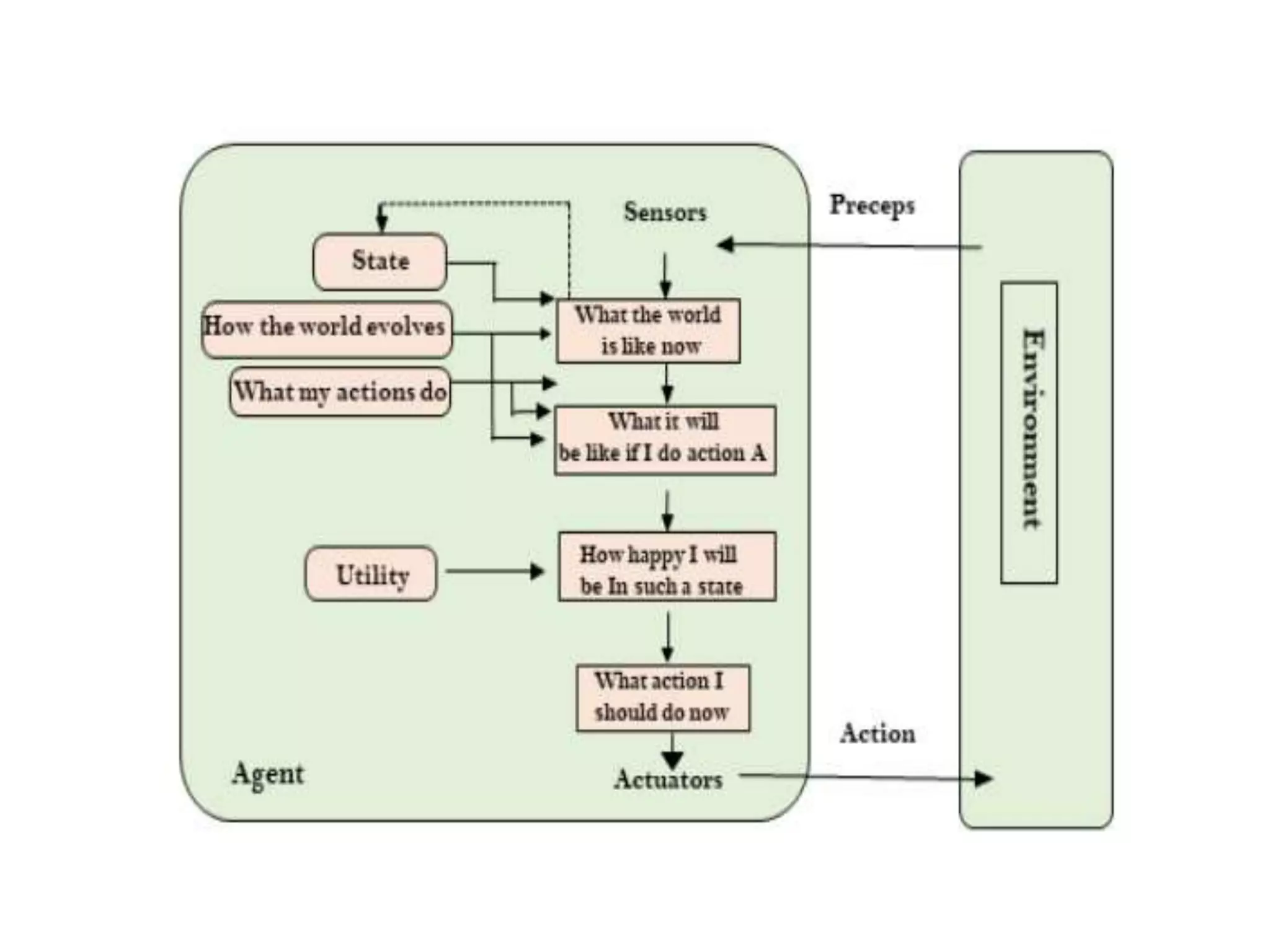
- Utility-based agents act not just on goals but the best way to achieve goals by considering the utility of different states.
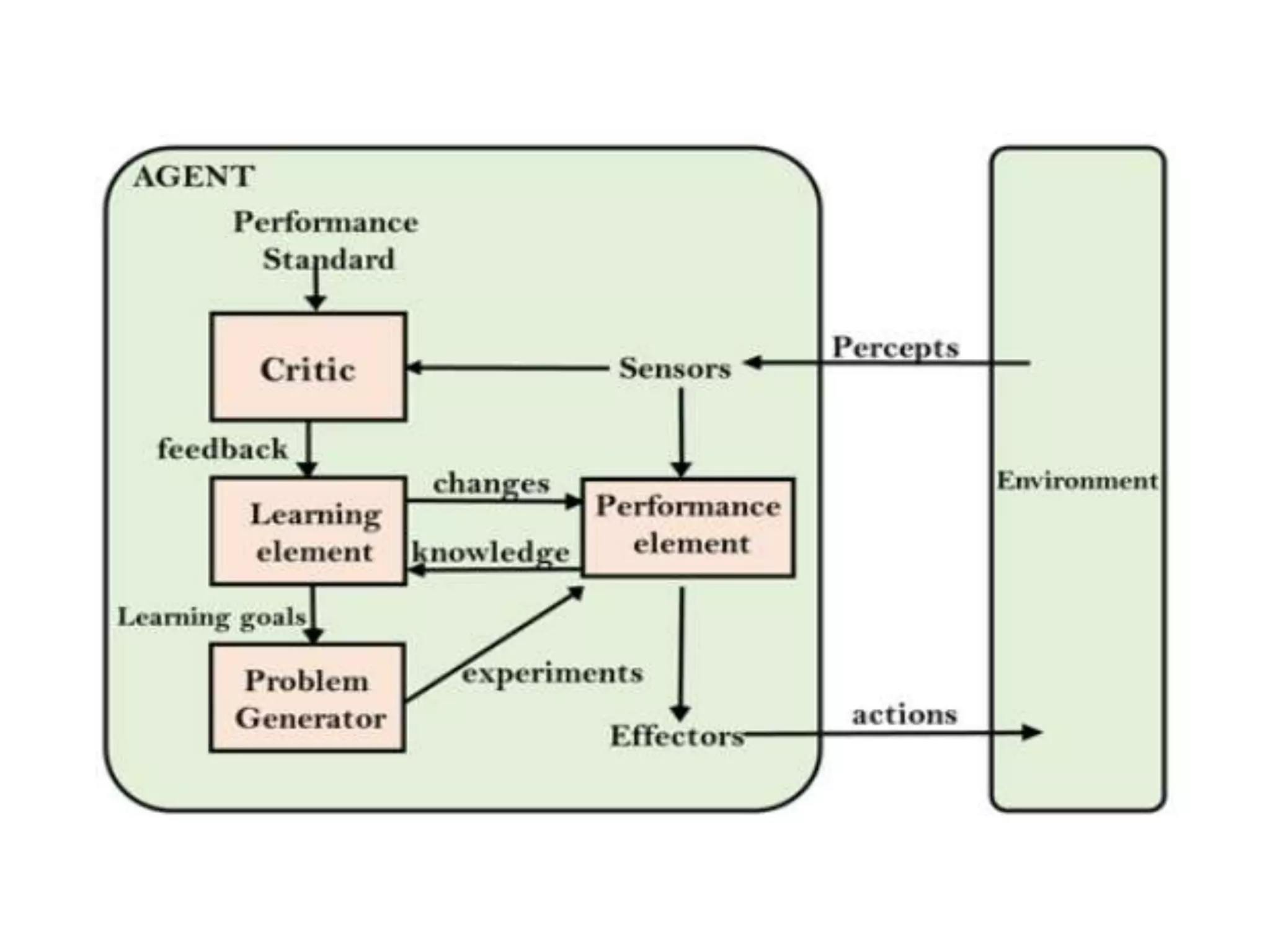
- Learning agents can improve their performance over time by learning from experiences, with components like a learning element, critic, and problem generator that help adapt automatically.
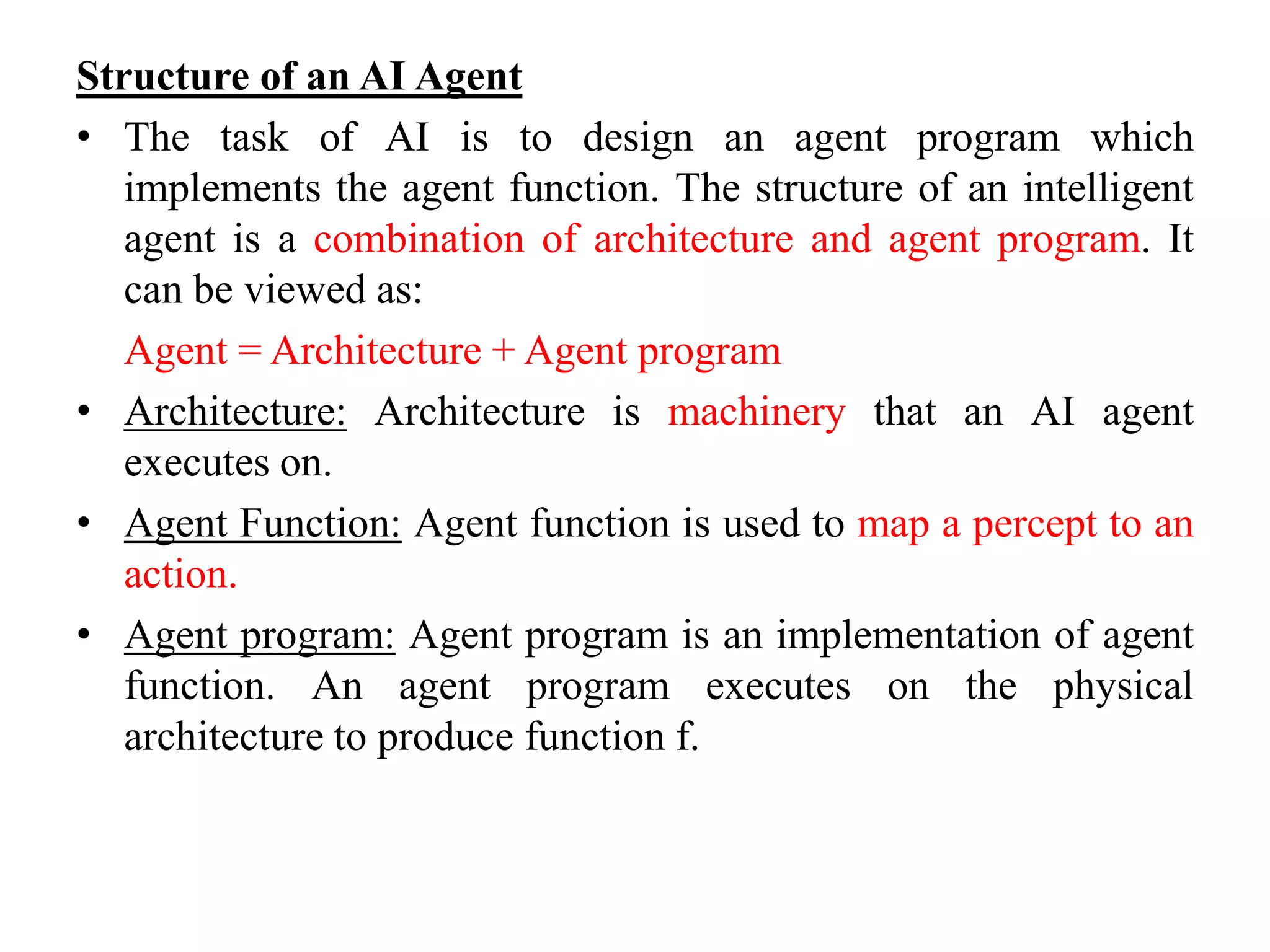


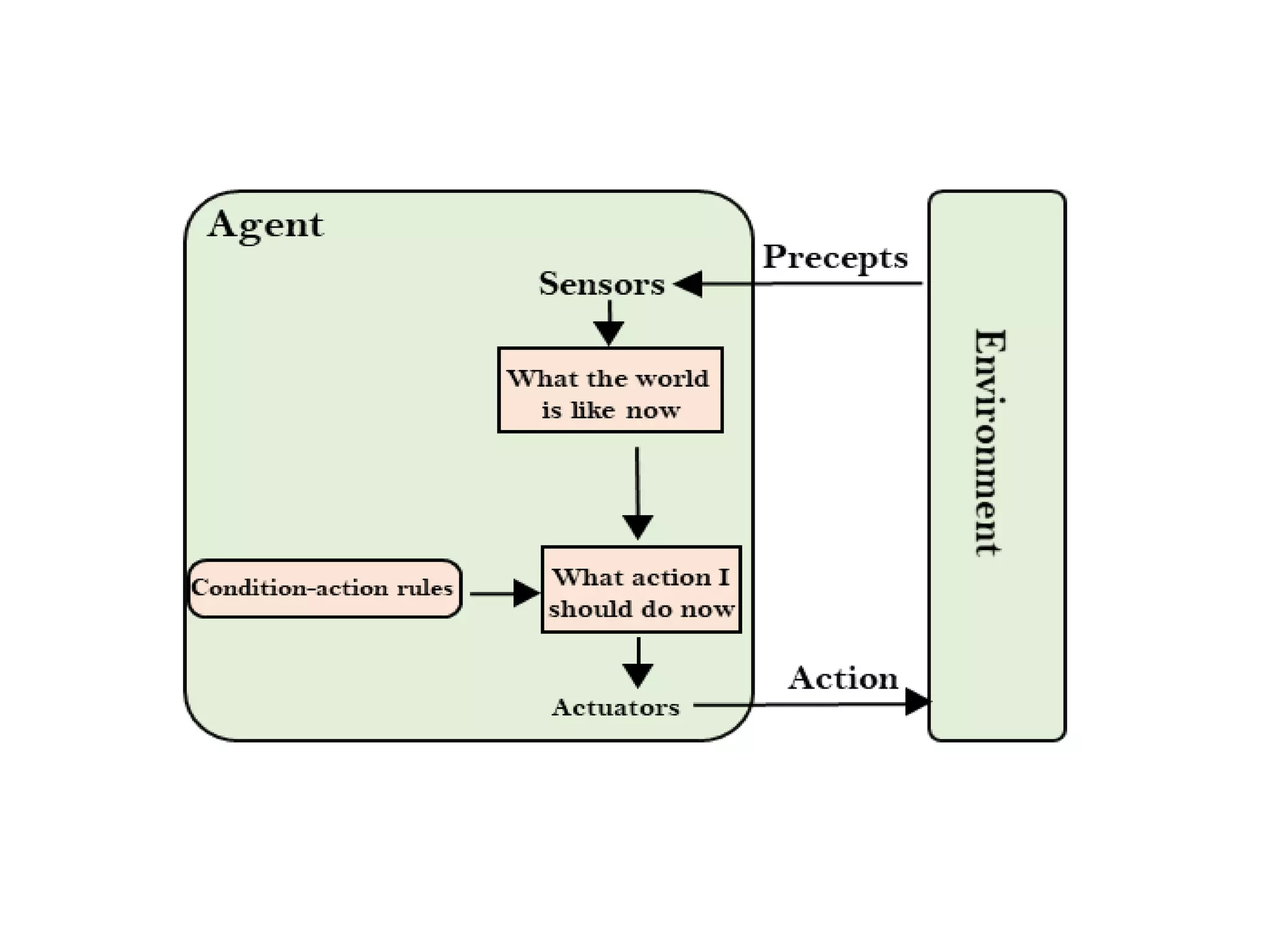
![Agent Function
function SIMPLE-REFLEX-AGENT(percept) returns
action
static: rules, a set of condition-action rules
state <— lNTERPRET-lNPUT(percept)
rule<- RULE-MATCH(state, rules)
action <- RULE-ACTION[rule]
return action](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structureofagents-200121034628/75/Structure-of-agents-6-2048.jpg)