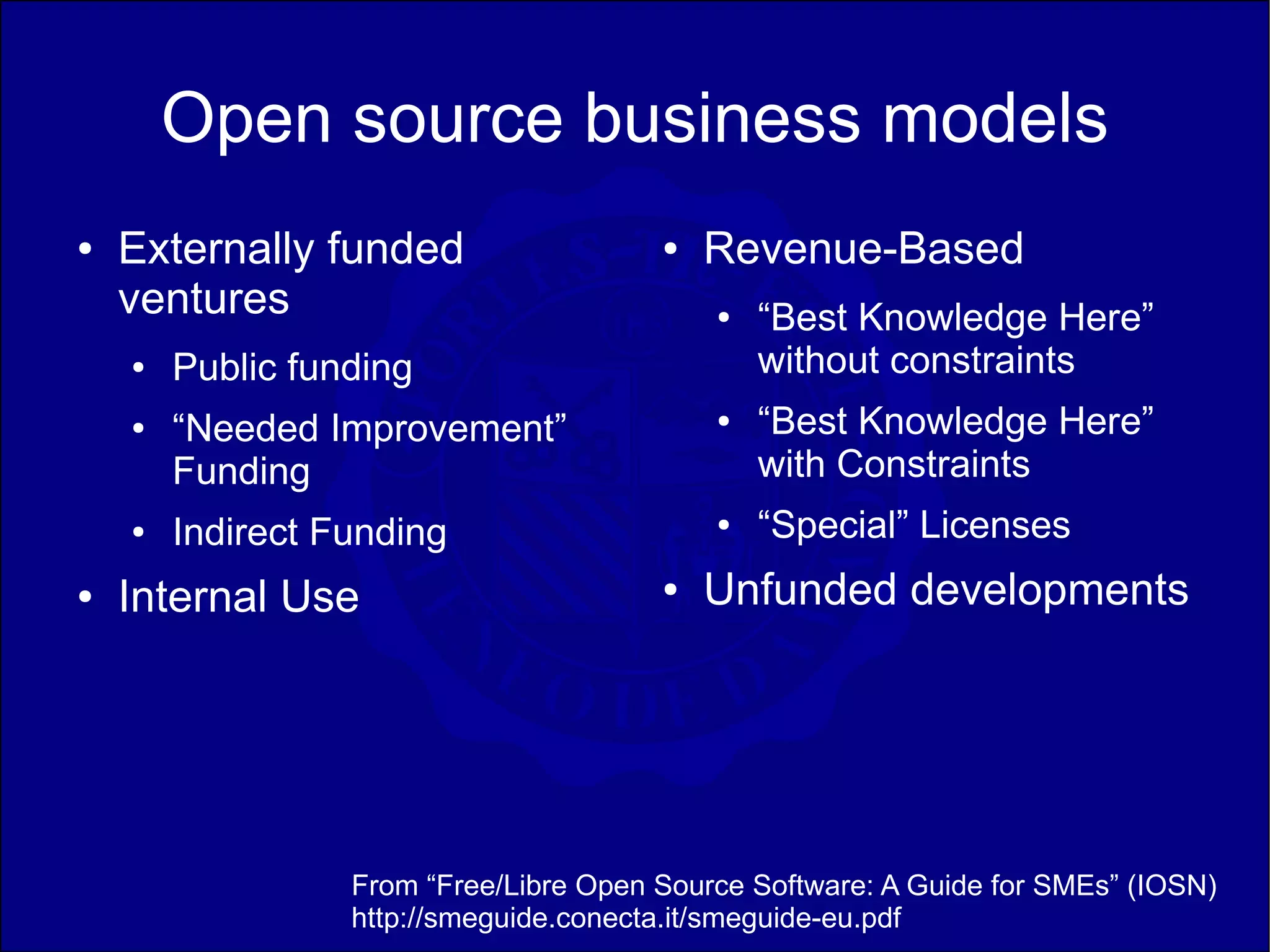
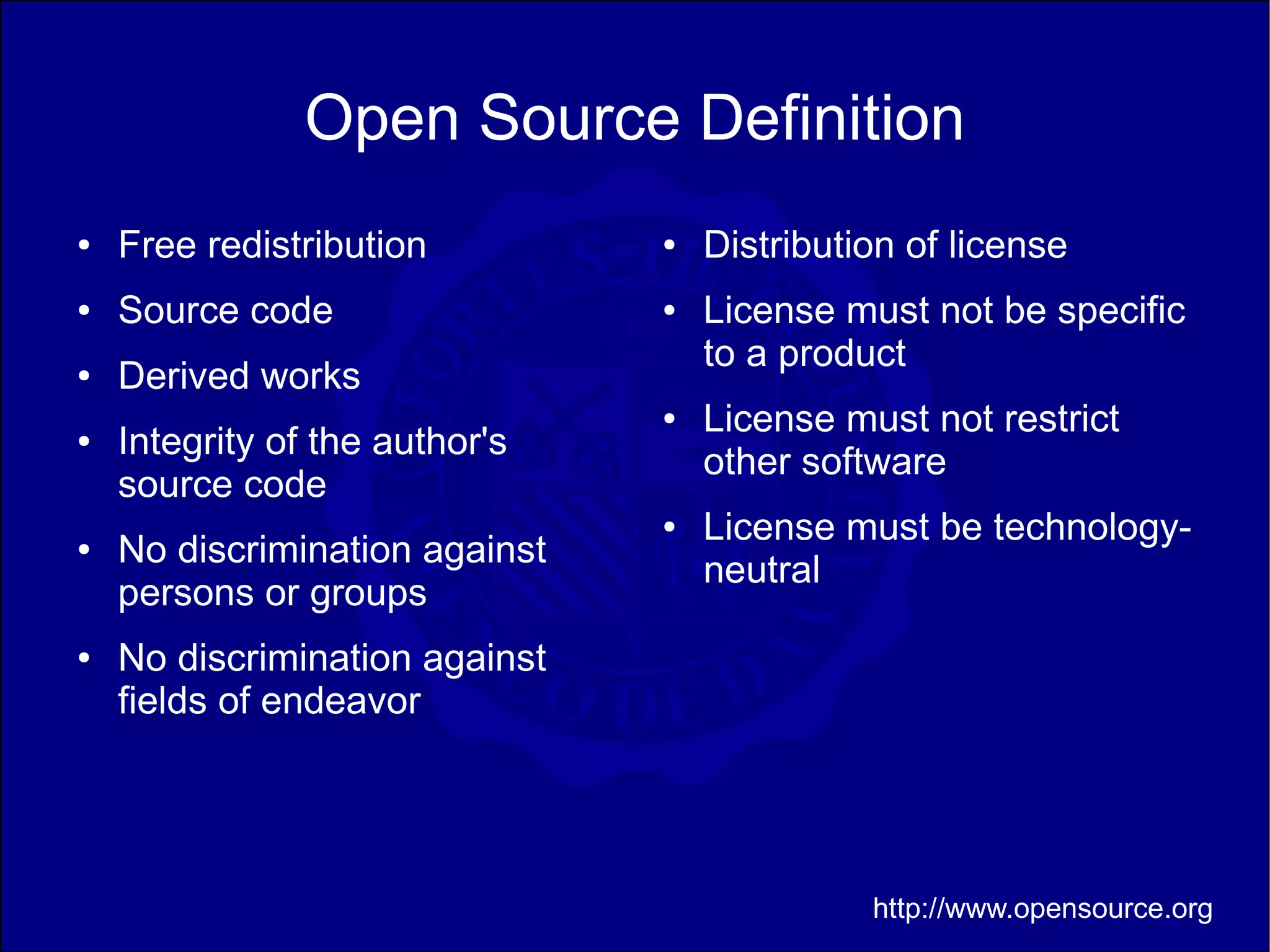
This document discusses teaching open source software in universities. It describes courses on operating systems and information security that incorporated open source tools and distributions like Ubuntu, Linux, Apache, and MySQL. Student surveys found initial resistance to unfamiliar open source environments but growing interest as they learned about licensing, business models, and development methodologies. The author reflects on lessons learned and ways to improve open source education, such as introducing version control earlier and allowing more flexibility for creative projects.