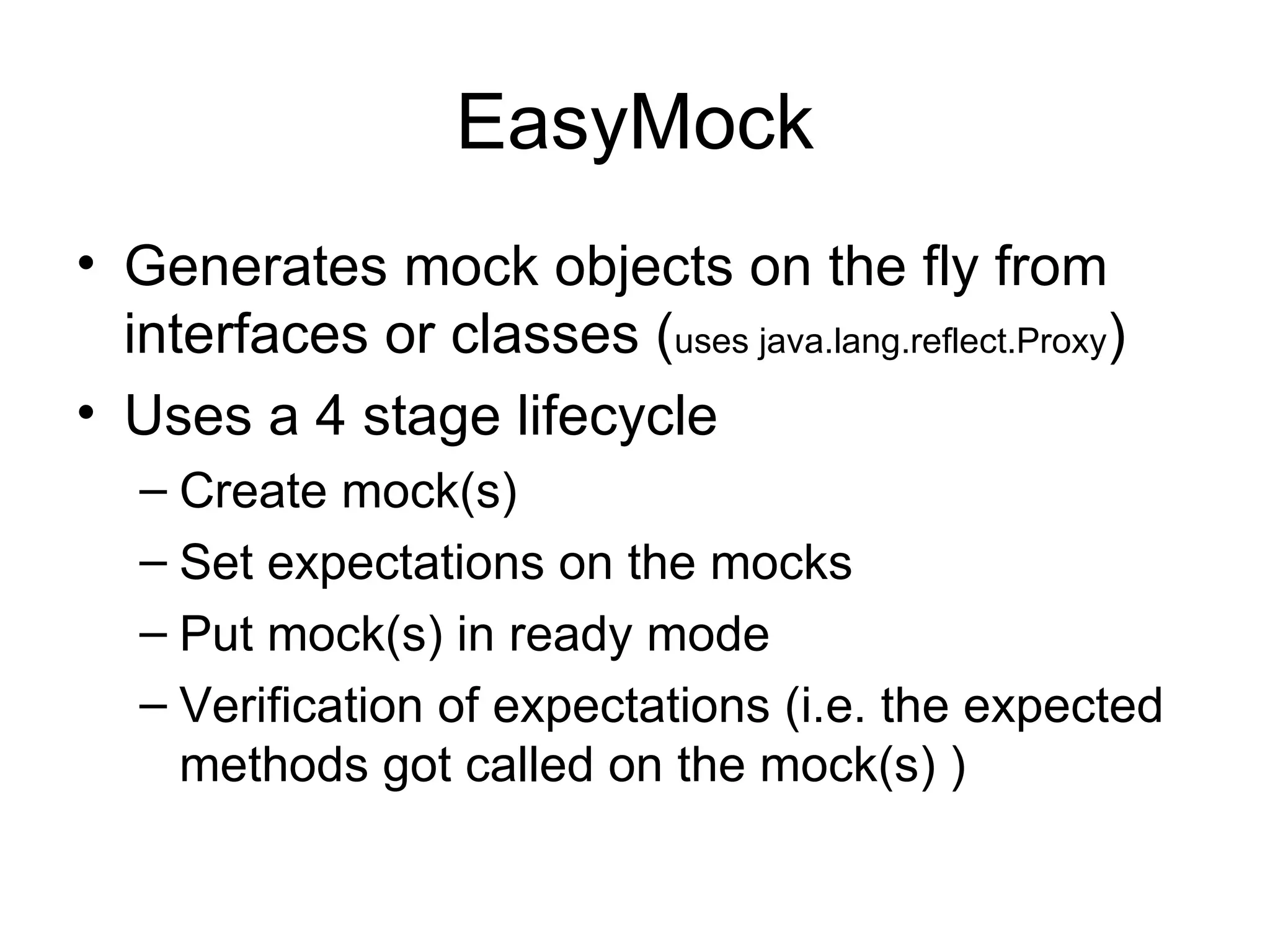
This document discusses using mock objects to test classes without relying on dependencies like databases. It introduces mock frameworks like Mockito, JMock and EasyMock that generate mock implementations to return canned responses. The advantages are removing grunt work, easily simulating collaborators, and allowing true unit tests without integration. A demo shows improving test coverage from 64% to 100% by using EasyMock to mock dependencies instead of manual mocks.