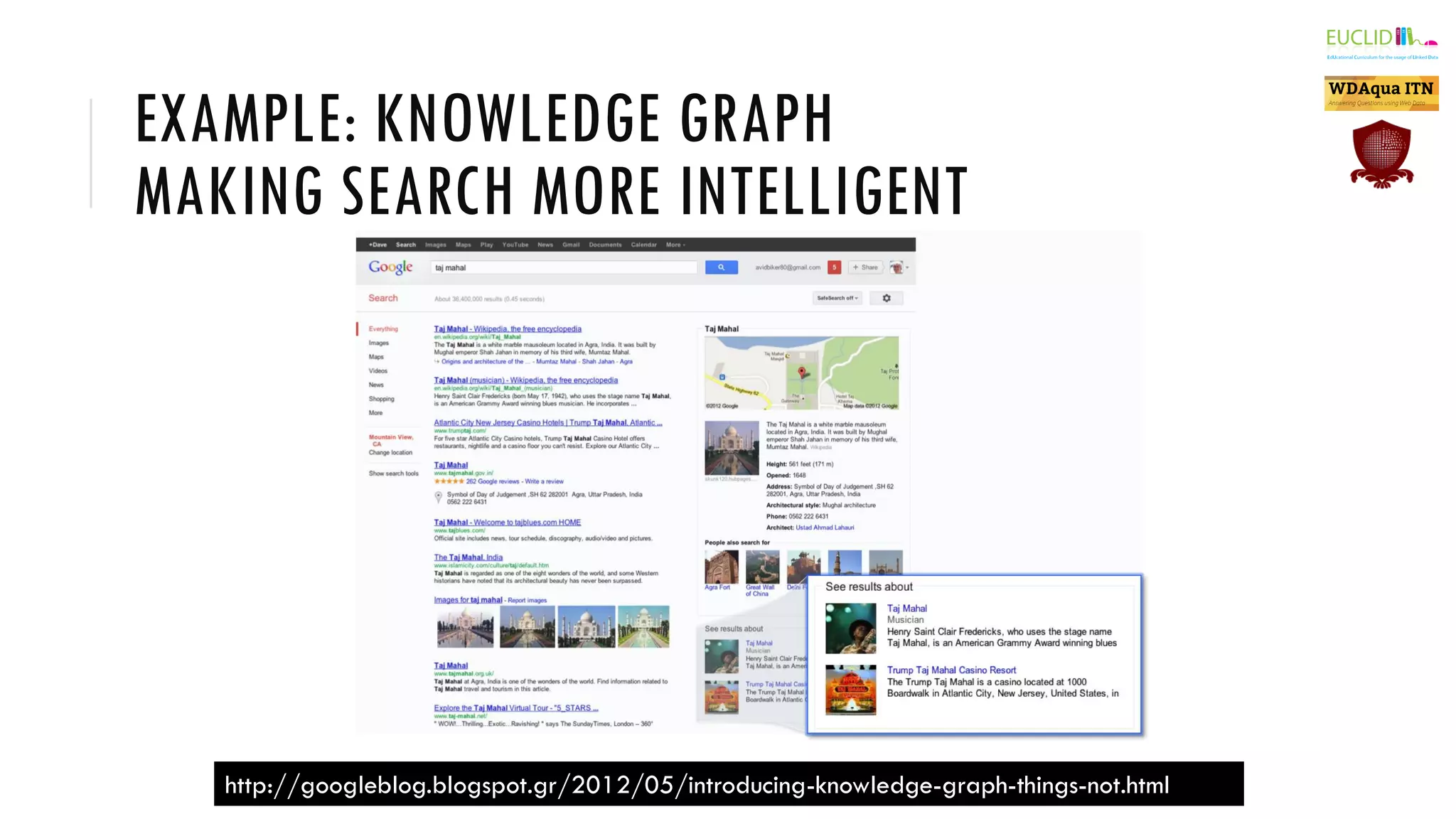
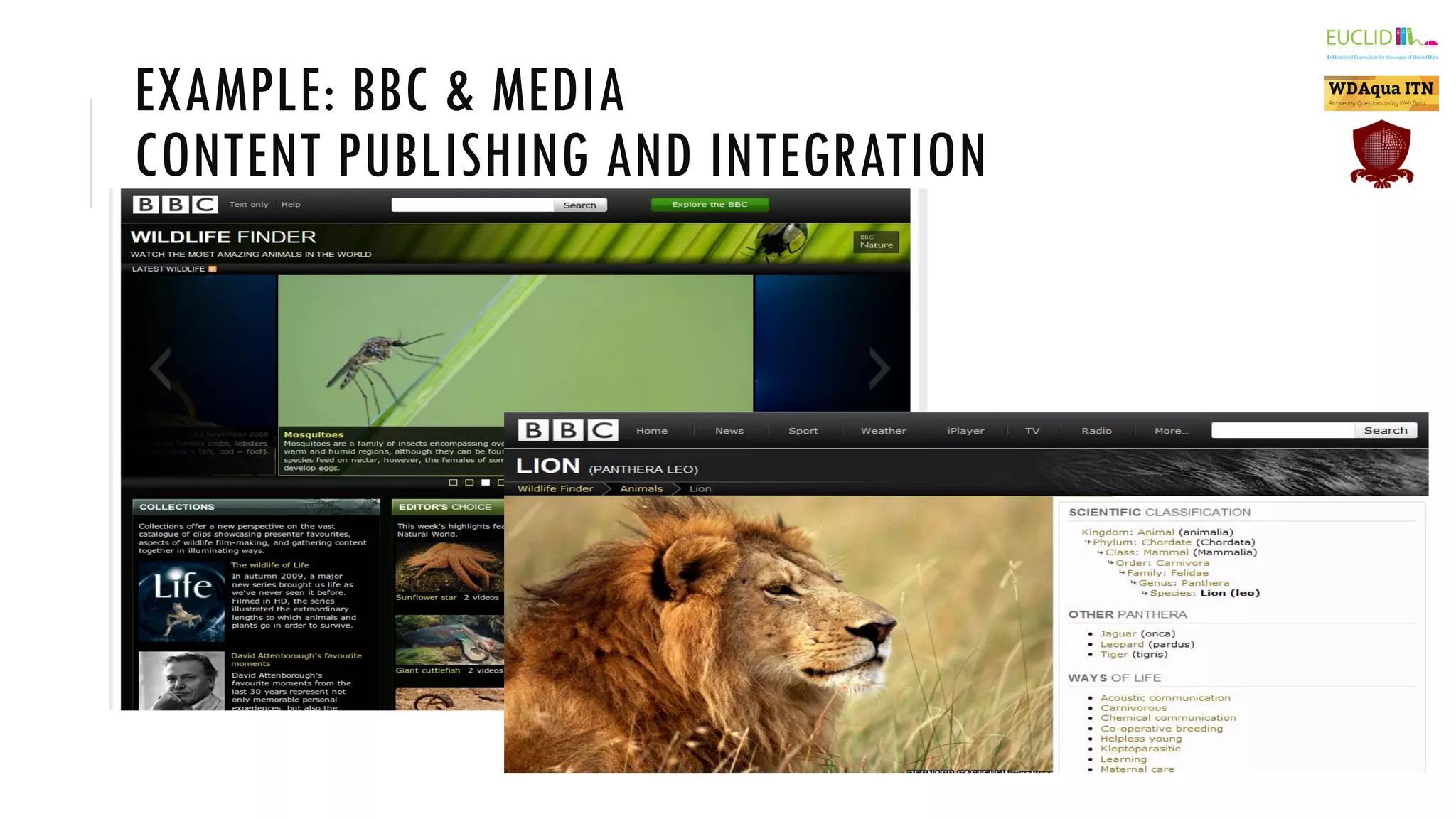
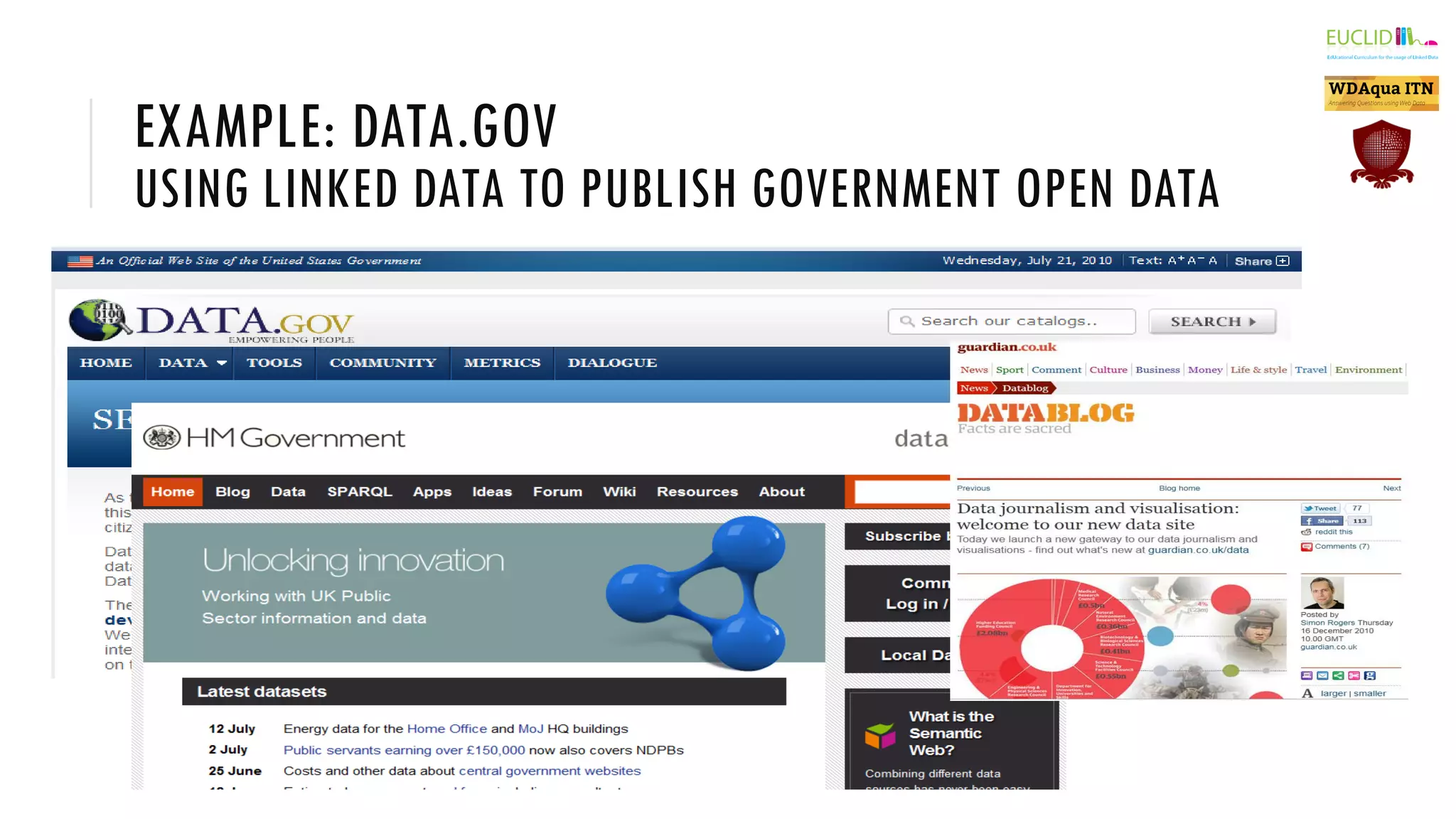
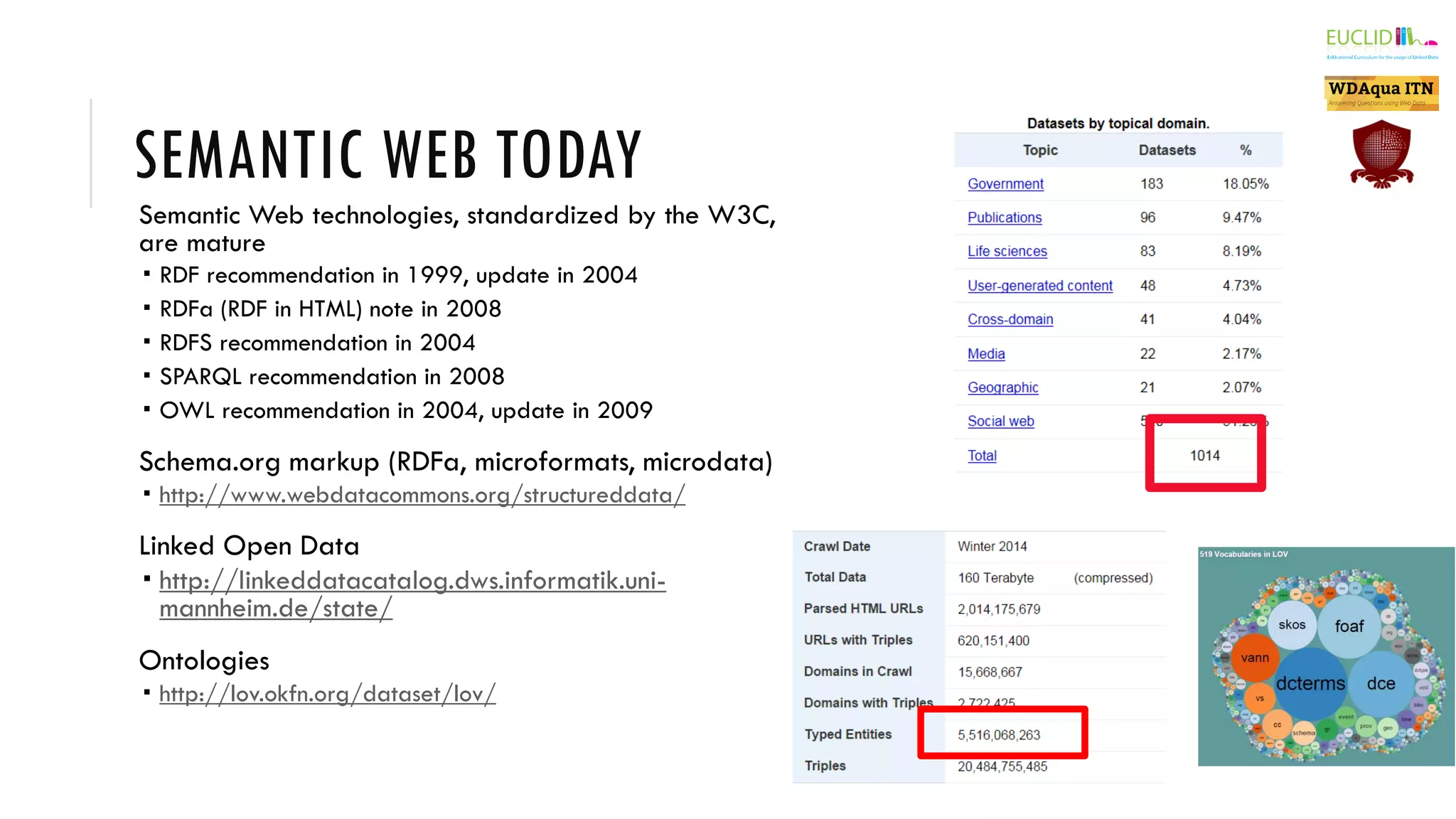
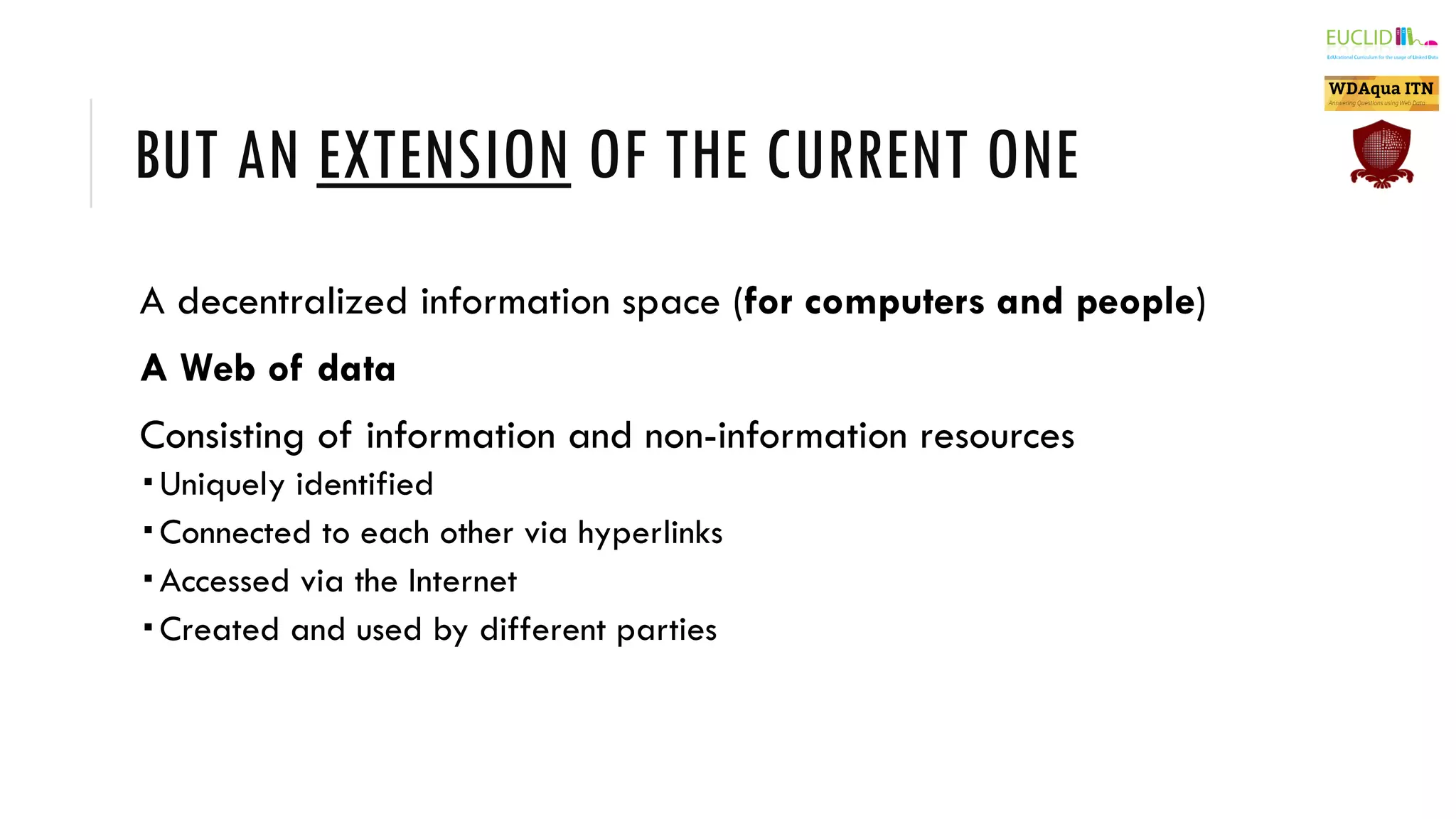
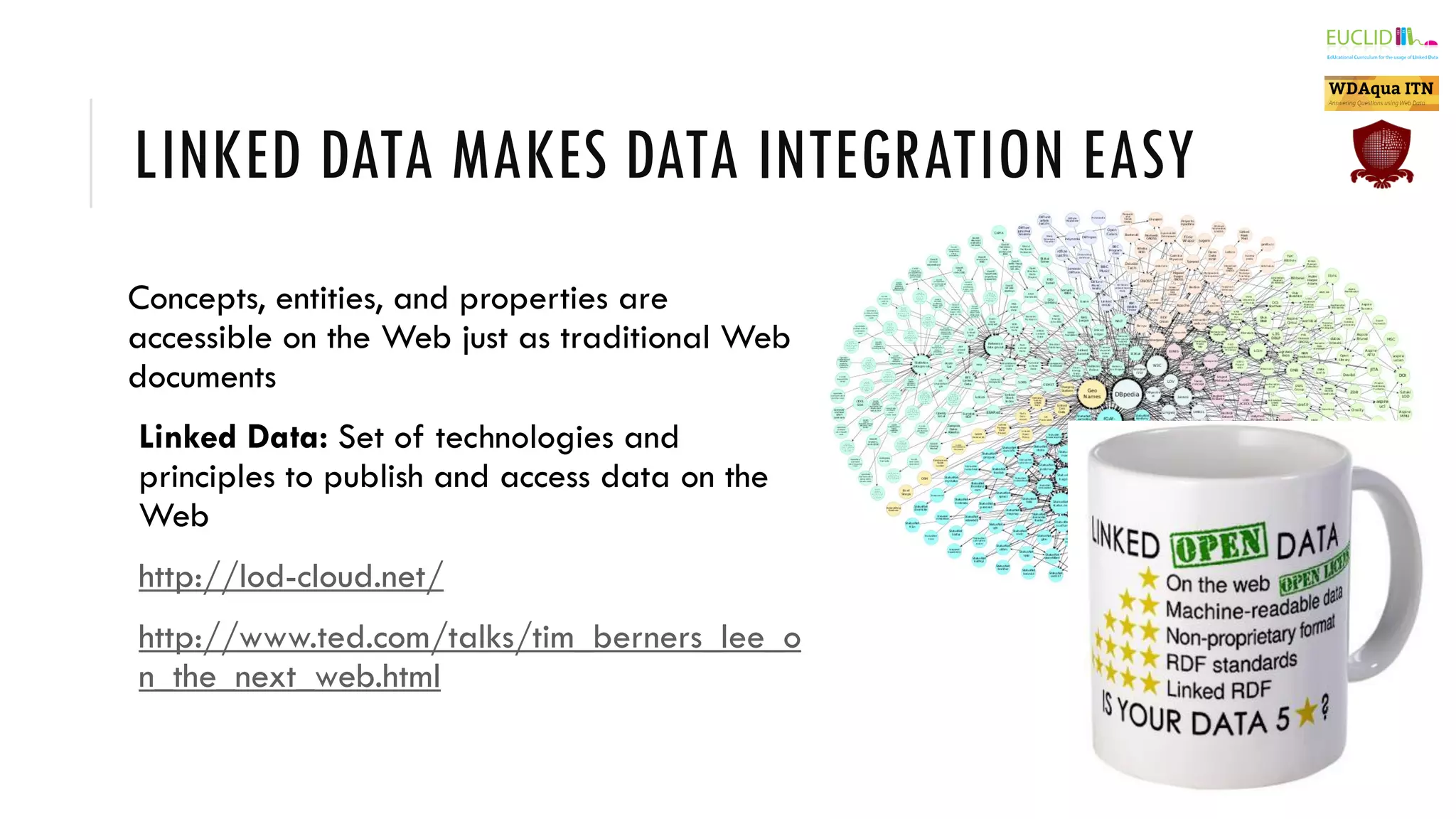
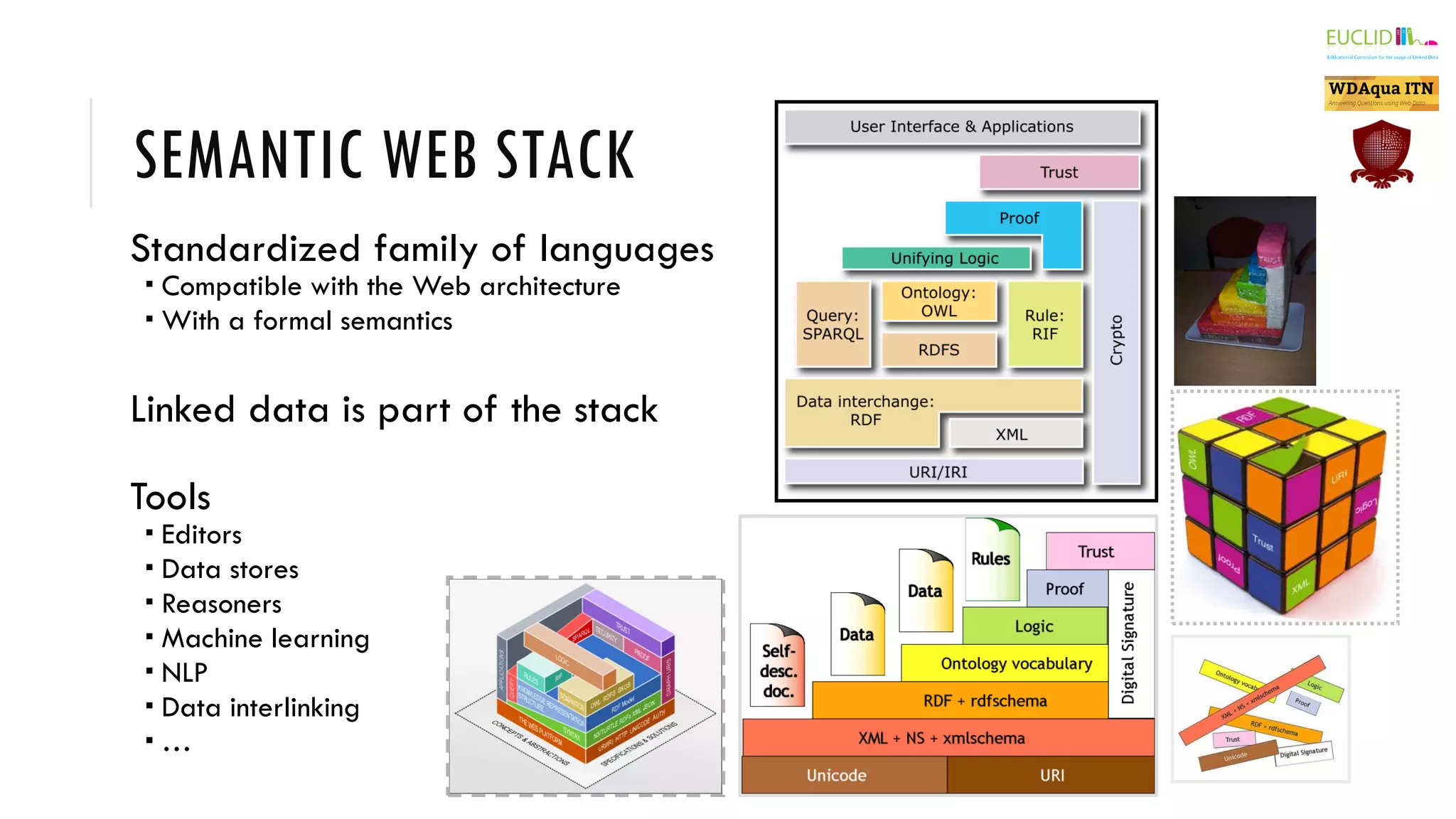
The document introduces the Semantic Web, which extends the current web by encoding additional metadata and meaning about web resources using formal knowledge representation languages. This allows machines to better understand and process web information, enabling computers and people to cooperate more effectively. Key aspects of the Semantic Web include uniquely identified resources connected by hyperlinks, metadata encoded using ontologies, and linked open data which makes data integration easier by publishing concepts, entities, and properties on the web. Examples are given of applications such as knowledge graphs, content publishing and integration, and social graphs.

![THE BEGINNINGS
“The Semantic Web is not a separate
Web but an extension of the current
one, in which information is given well-
defined meaning, better enabling
computers and people to work in
cooperation”
[Berners-Lee, Hendler & Lassila, 2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eswc2015ssintroduction-151022132824-lva1-app6891/75/The-Semantic-Web-An-Introduction-2-2048.jpg)


![COMPUTERS AND PEOPLE WORK IN
COOPERATION
Artificial intelligence: “the science and engineering of making intelligent
machines”
[John Mc Carthy, http://www-formal.stanford.edu/jmc/whatisai/whatisai.html]
Areas of AI
Knowledge representation
Inference
Logics
Search
Planning and scheduling
Pattern recognition
Learning
Natural language processing
Computer vision
Robotics
....](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eswc2015ssintroduction-151022132824-lva1-app6891/75/The-Semantic-Web-An-Introduction-6-2048.jpg)
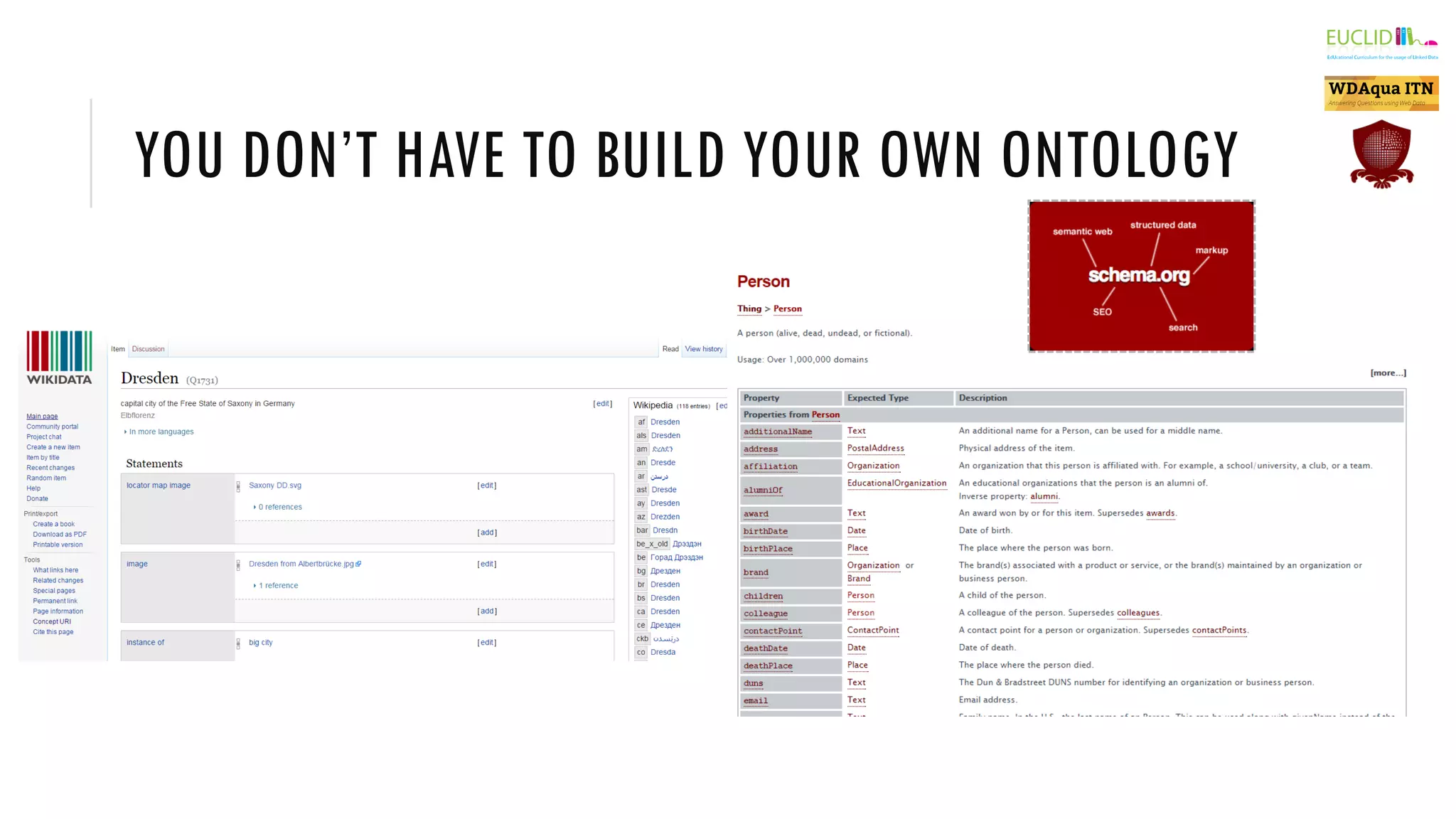
![MEANING ON THE WEB
Add metadata to Web resources
Different types of links
Encode additional information about metadata entities and links in
ontologies
No global information schemas
Incomplete and inconsistent
[Examples from Wikipedia]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eswc2015ssintroduction-151022132824-lva1-app6891/75/The-Semantic-Web-An-Introduction-7-2048.jpg)
![FROM THE SEMANTIC WEB TO SEMANTIC
TECHNOLOGIES
“The Semantic Web provides a
common framework that allows data to
be shared and reused across
application, enterprise, and community
boundaries”
[W3C]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eswc2015ssintroduction-151022132824-lva1-app6891/75/The-Semantic-Web-An-Introduction-11-2048.jpg)