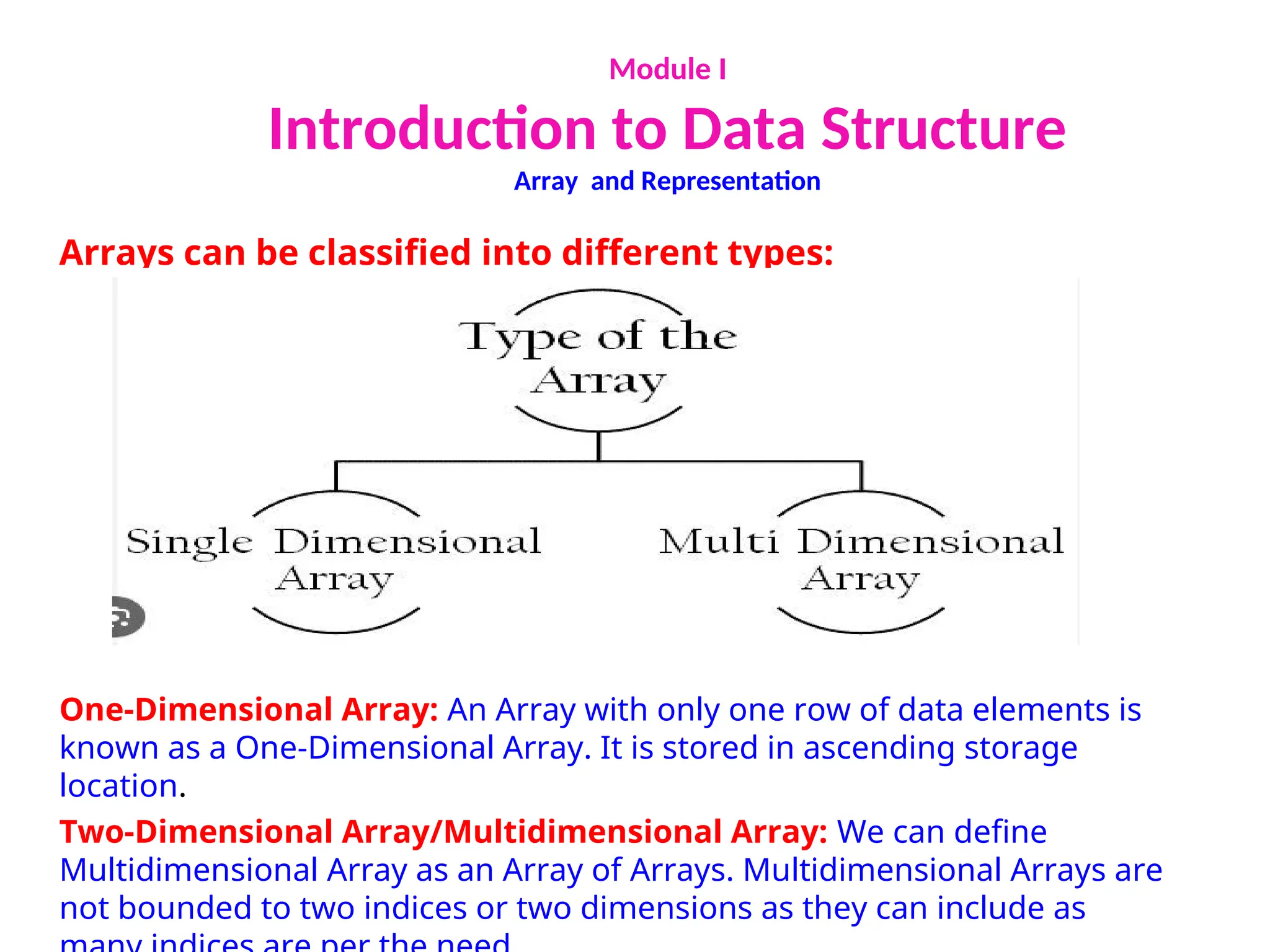
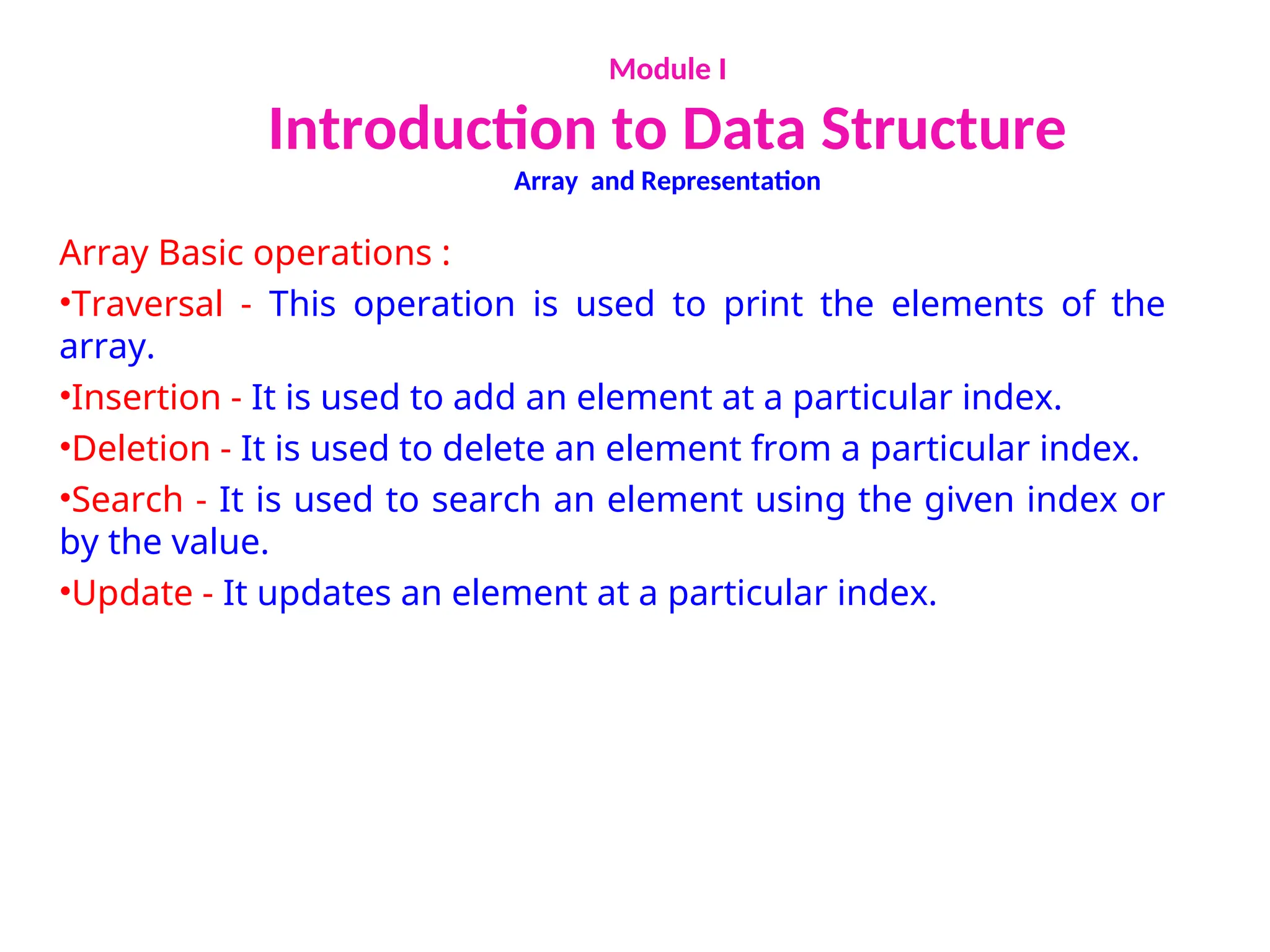
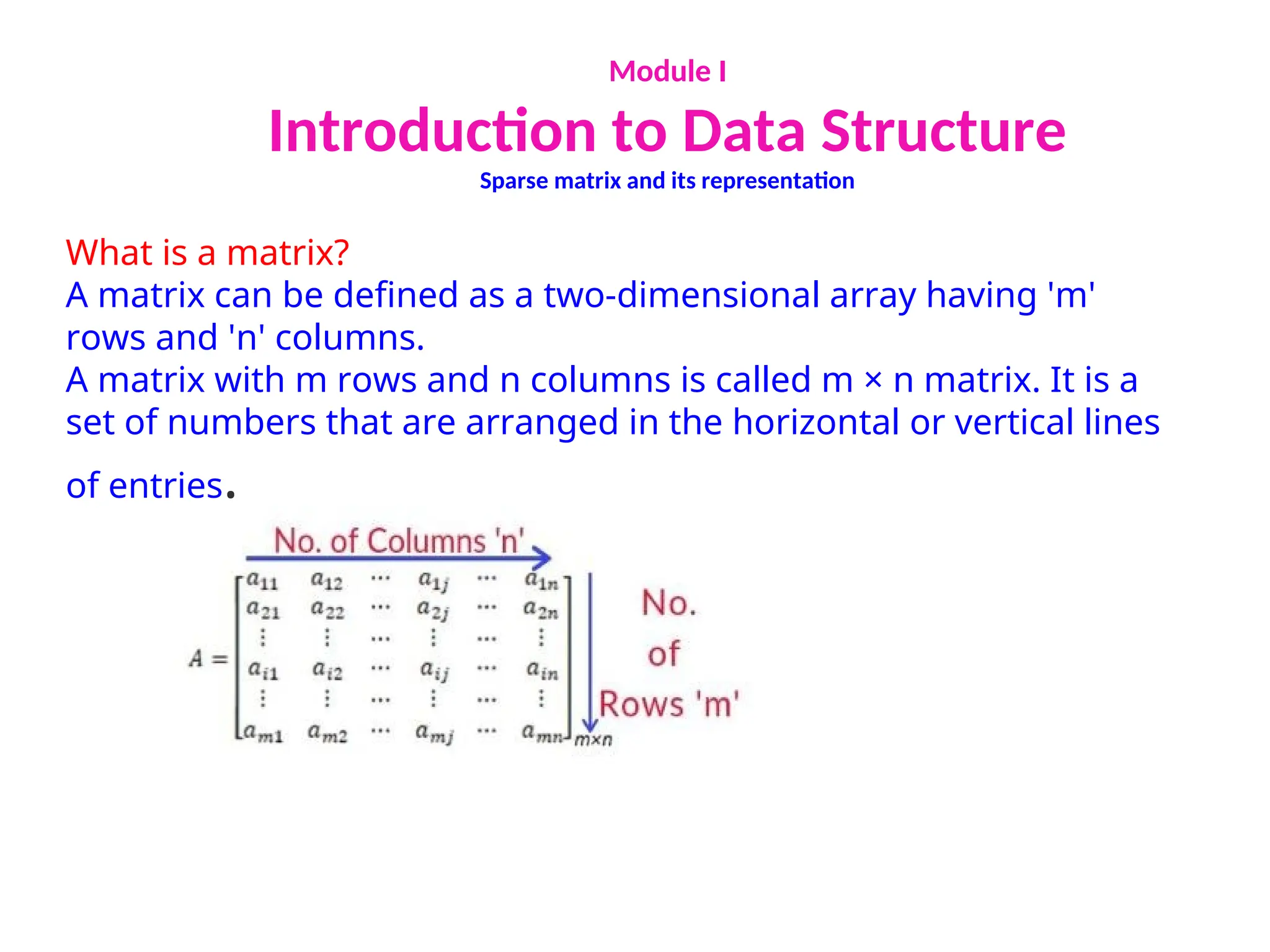
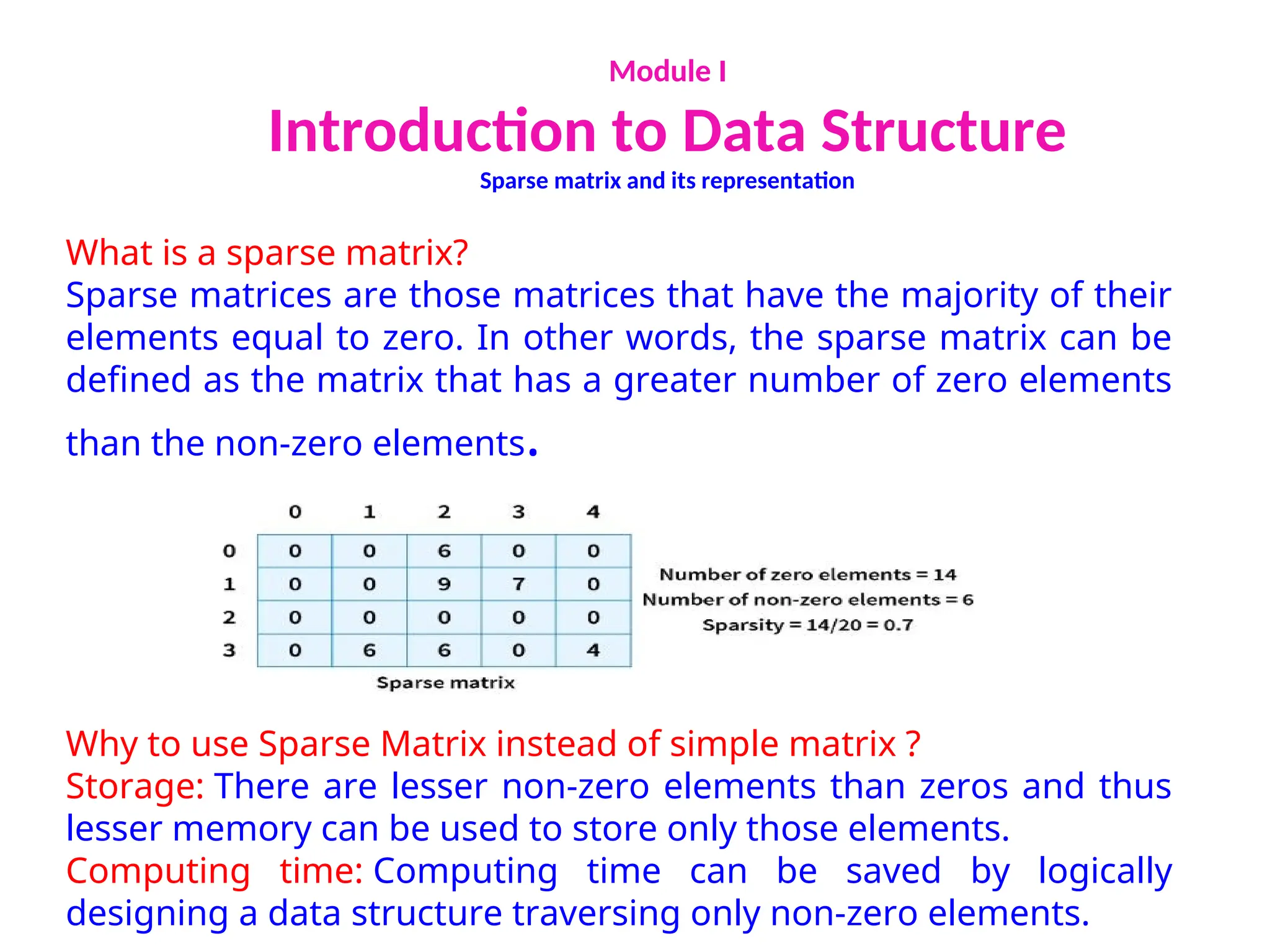
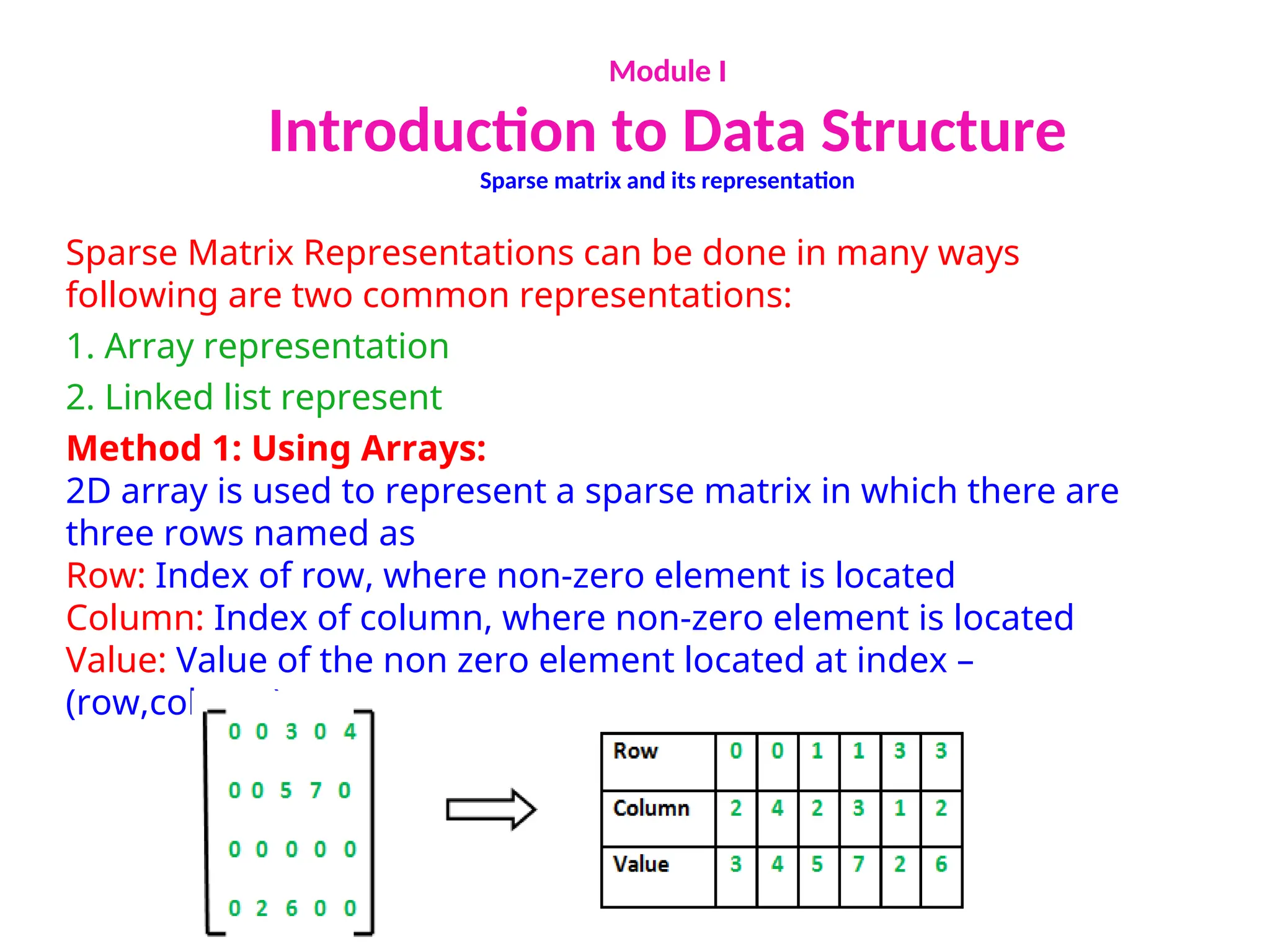
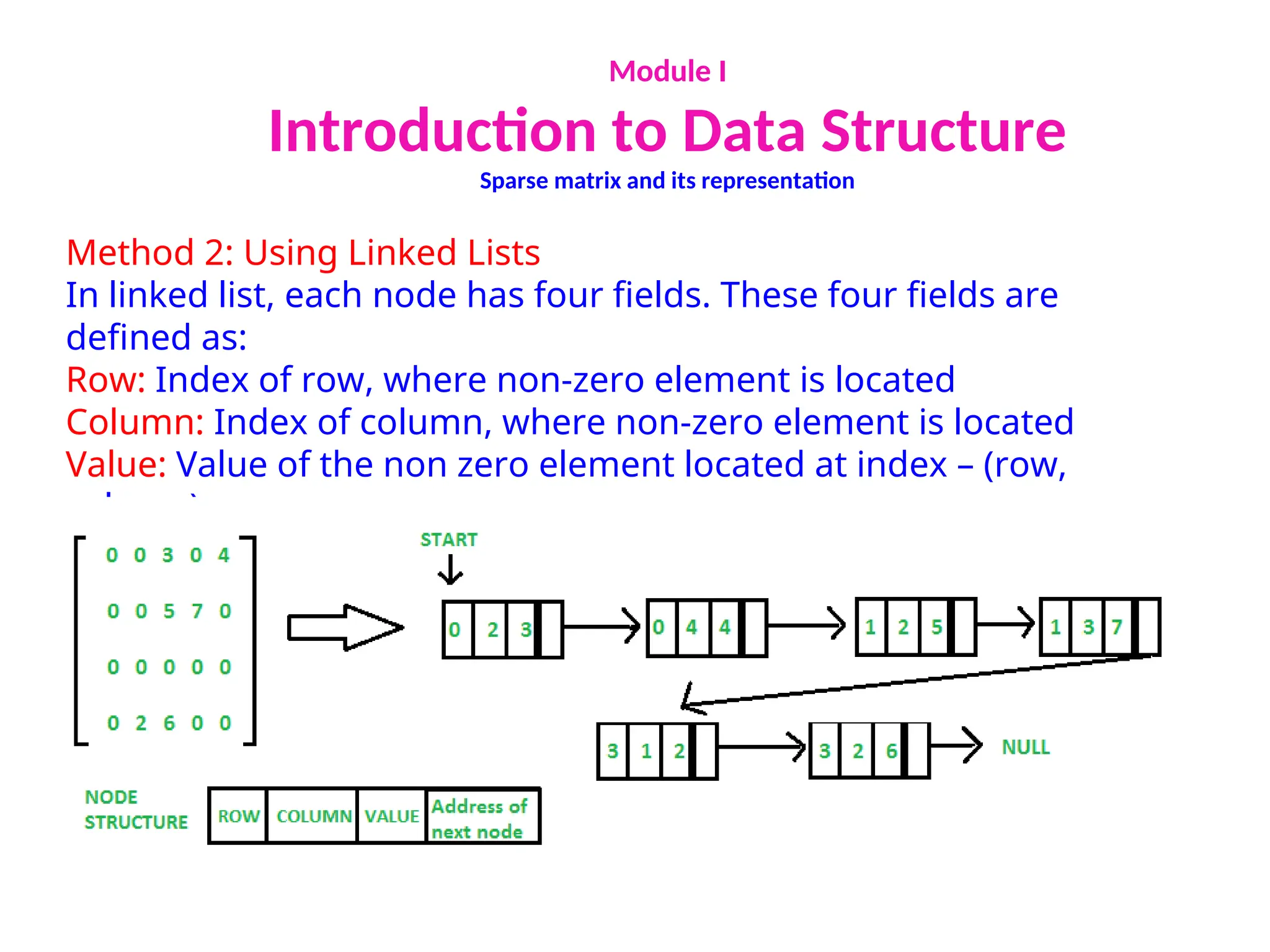
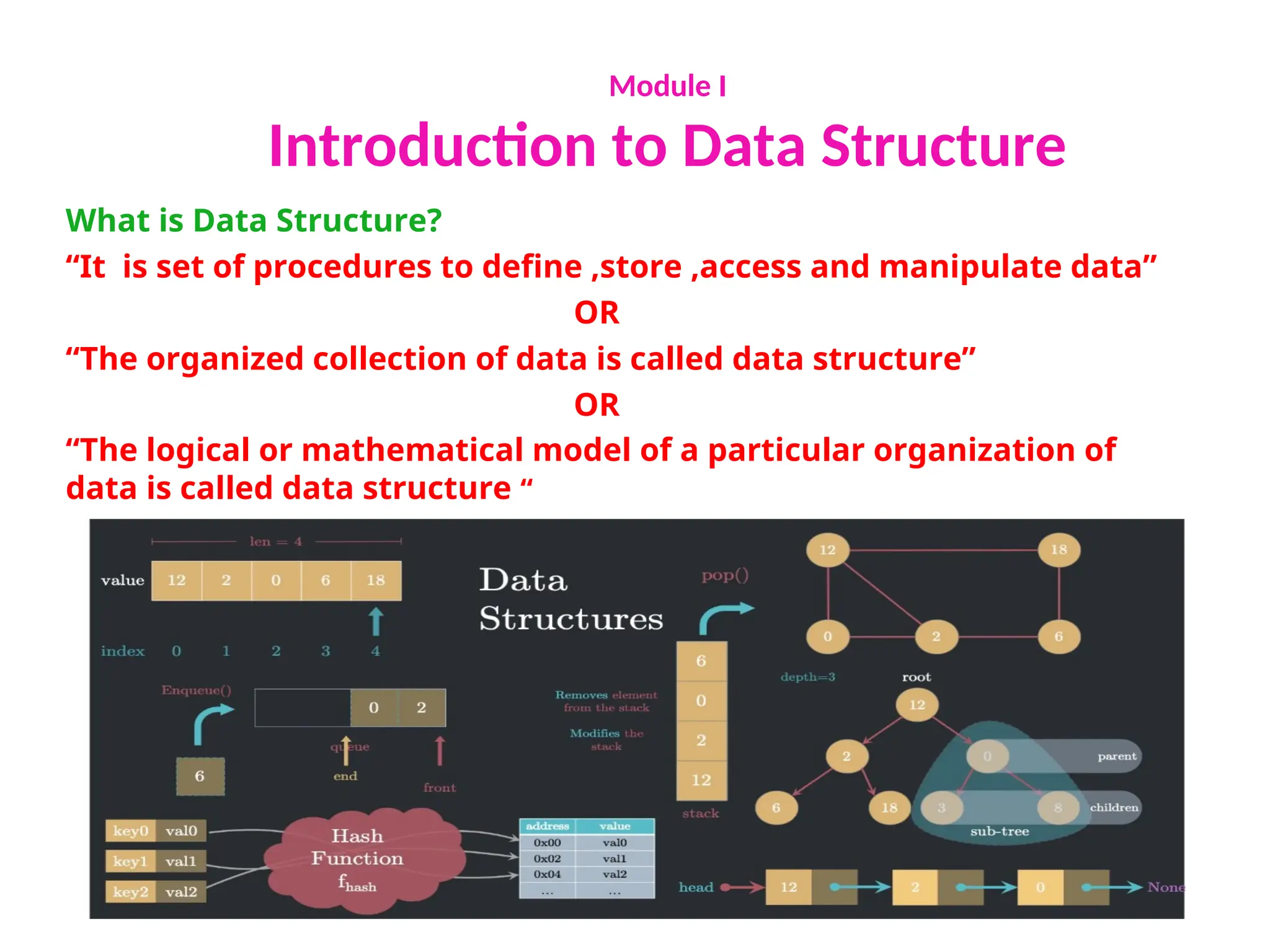
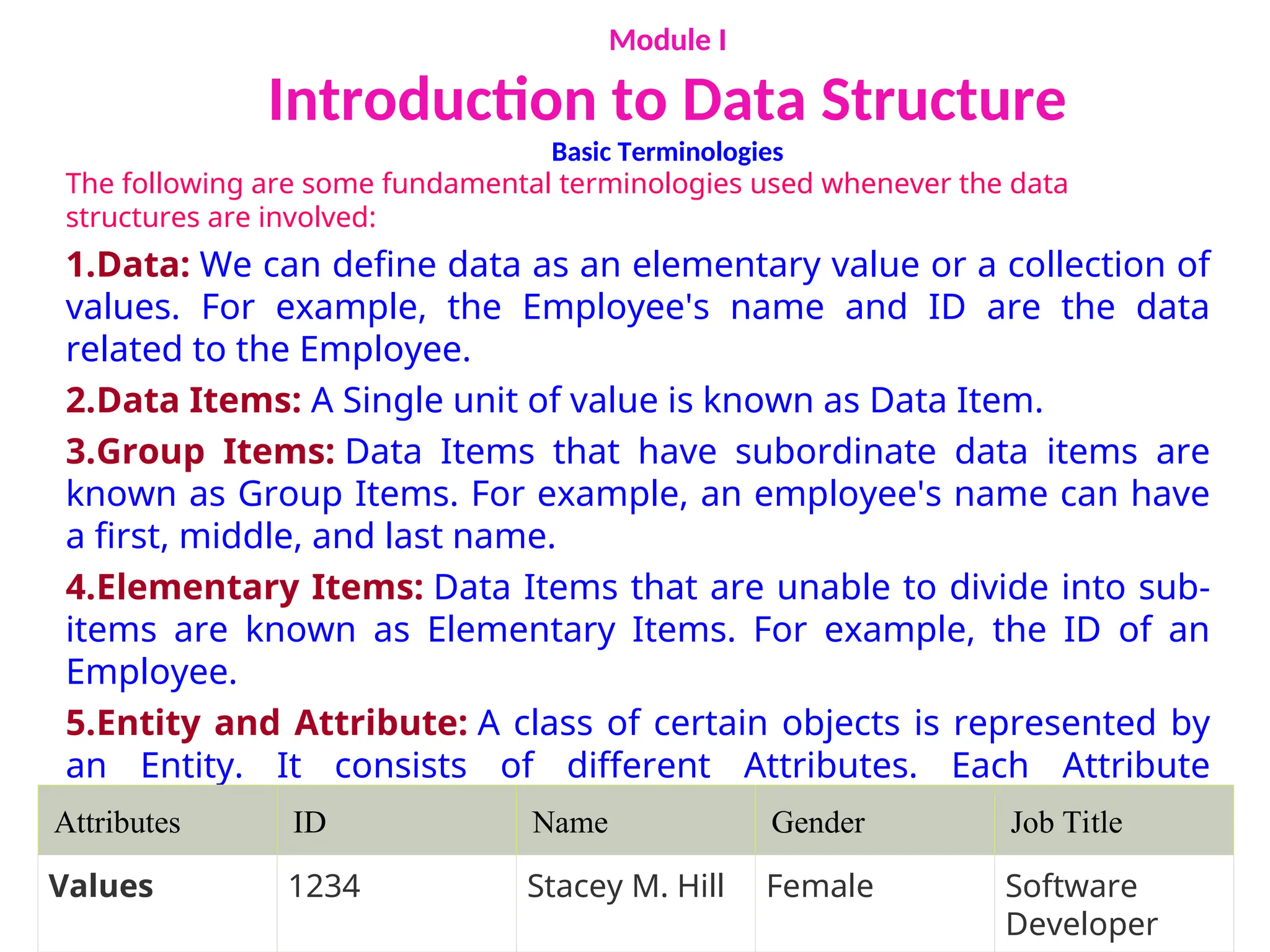
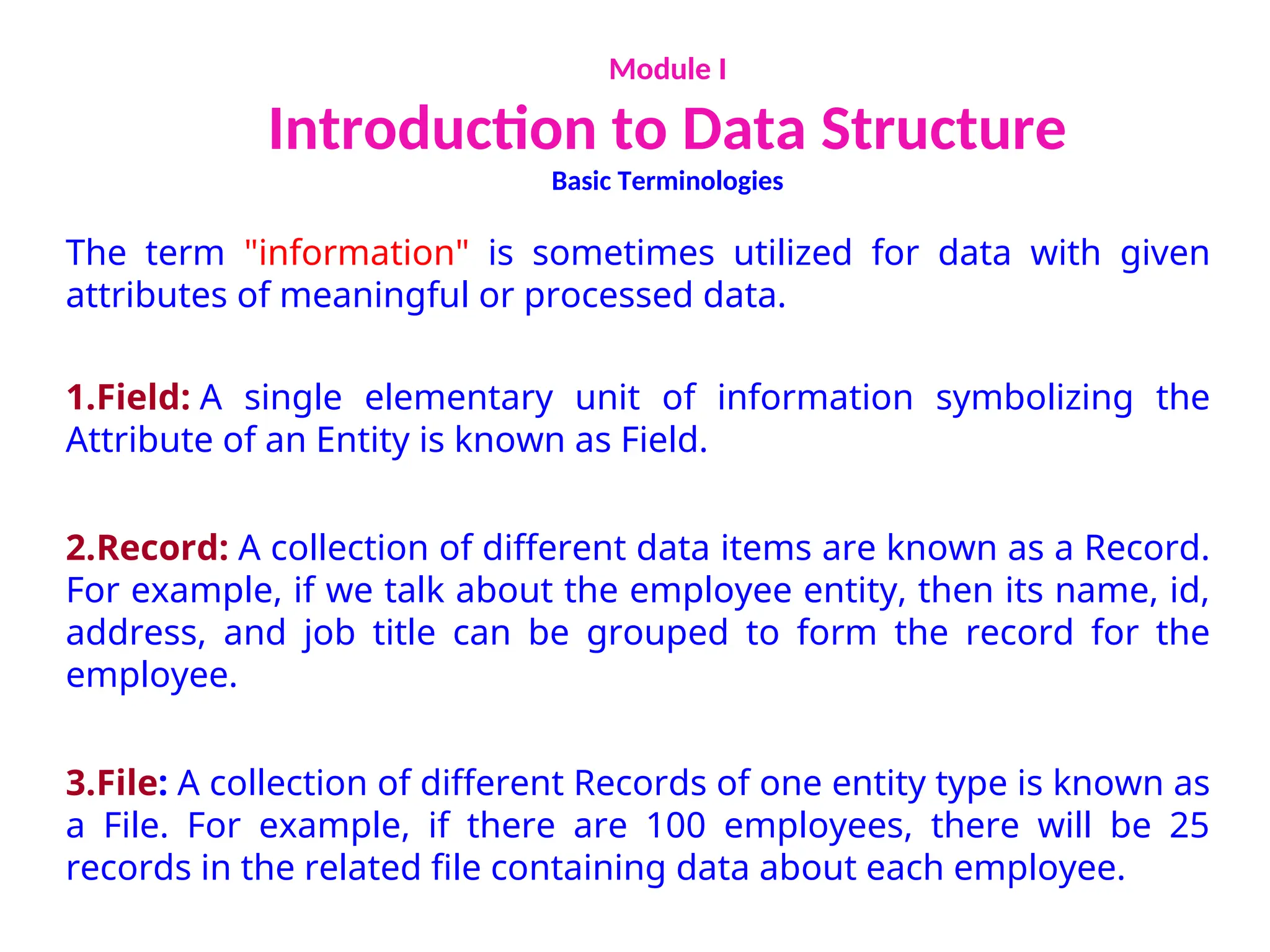
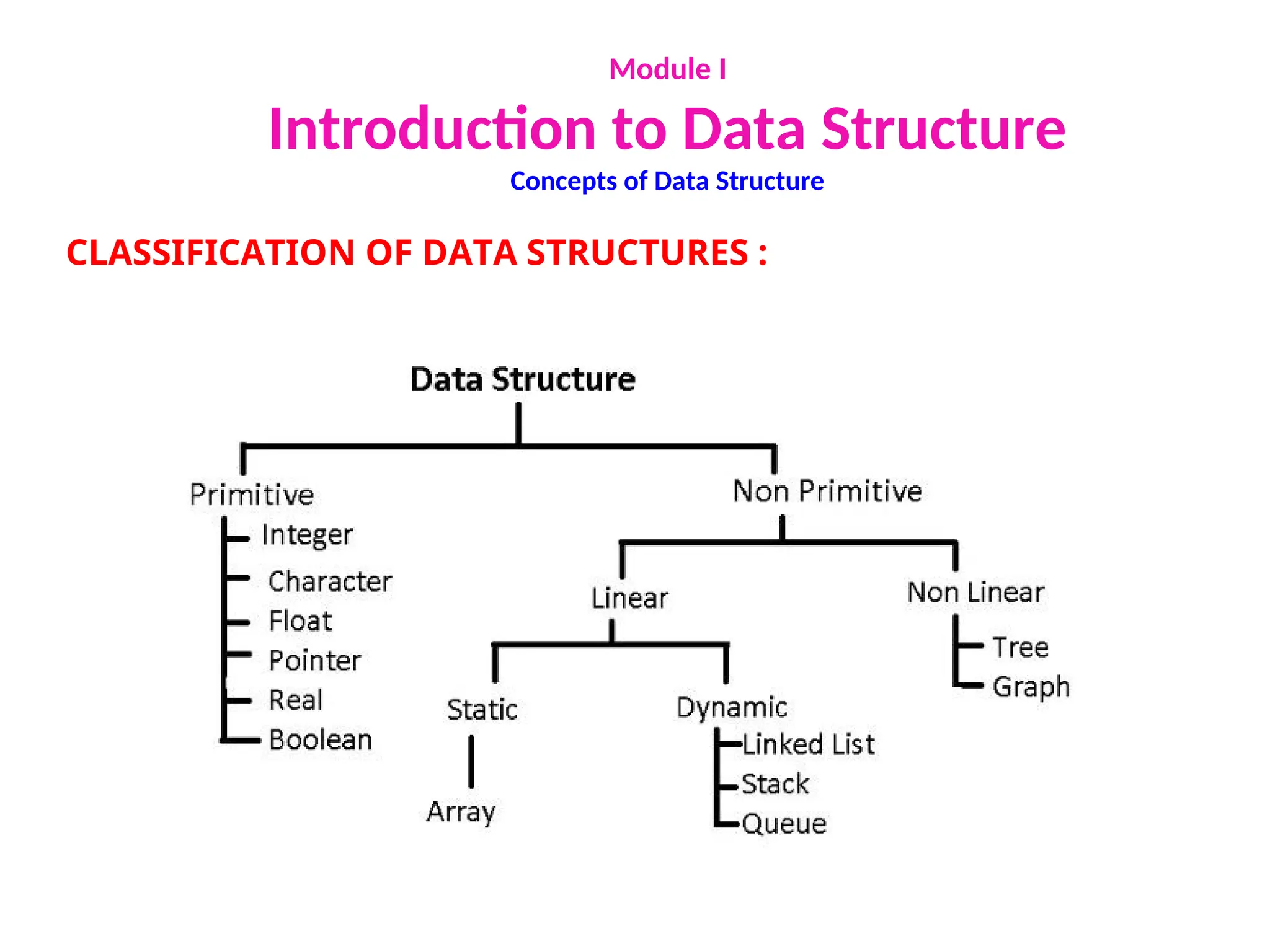
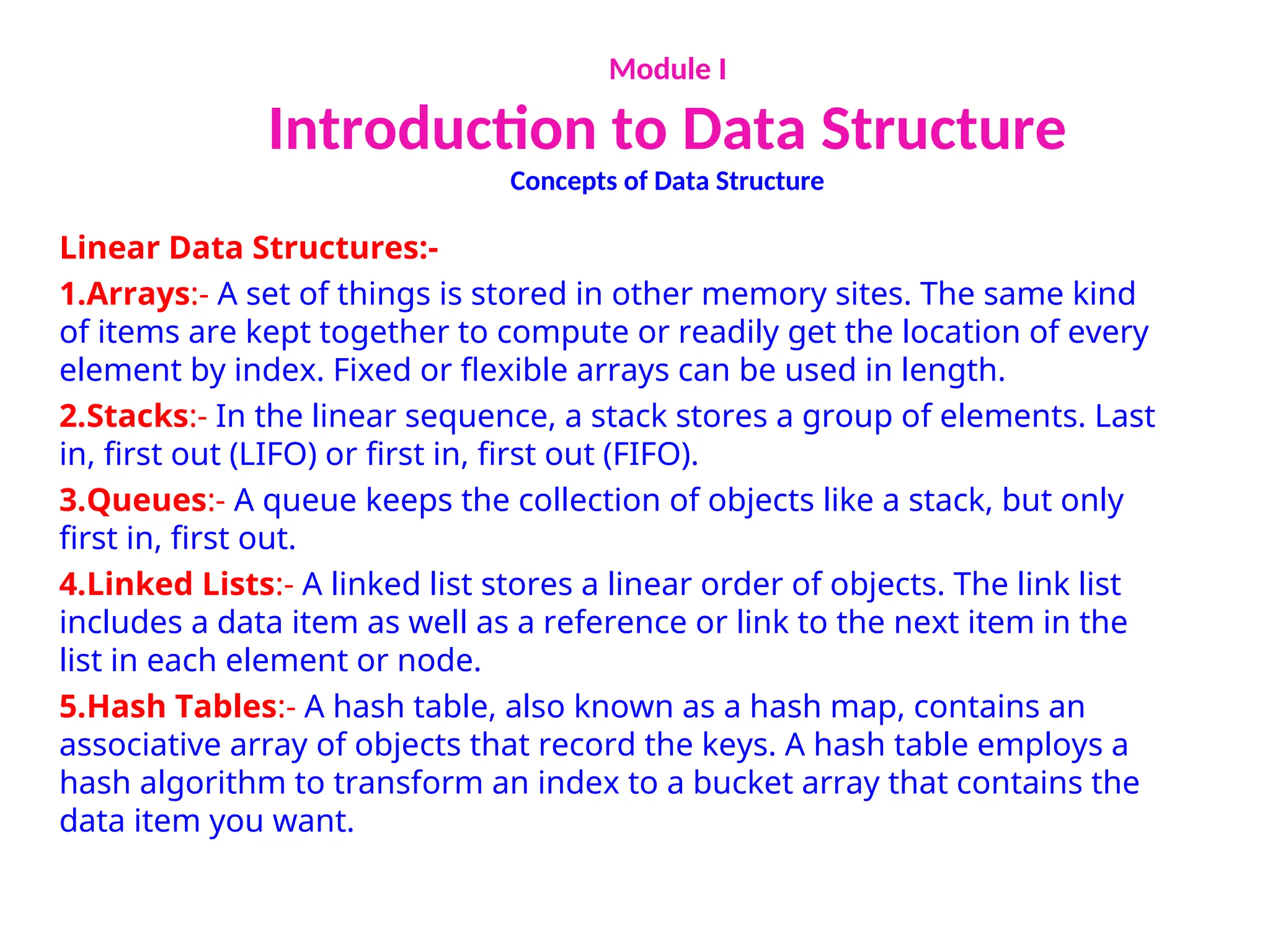
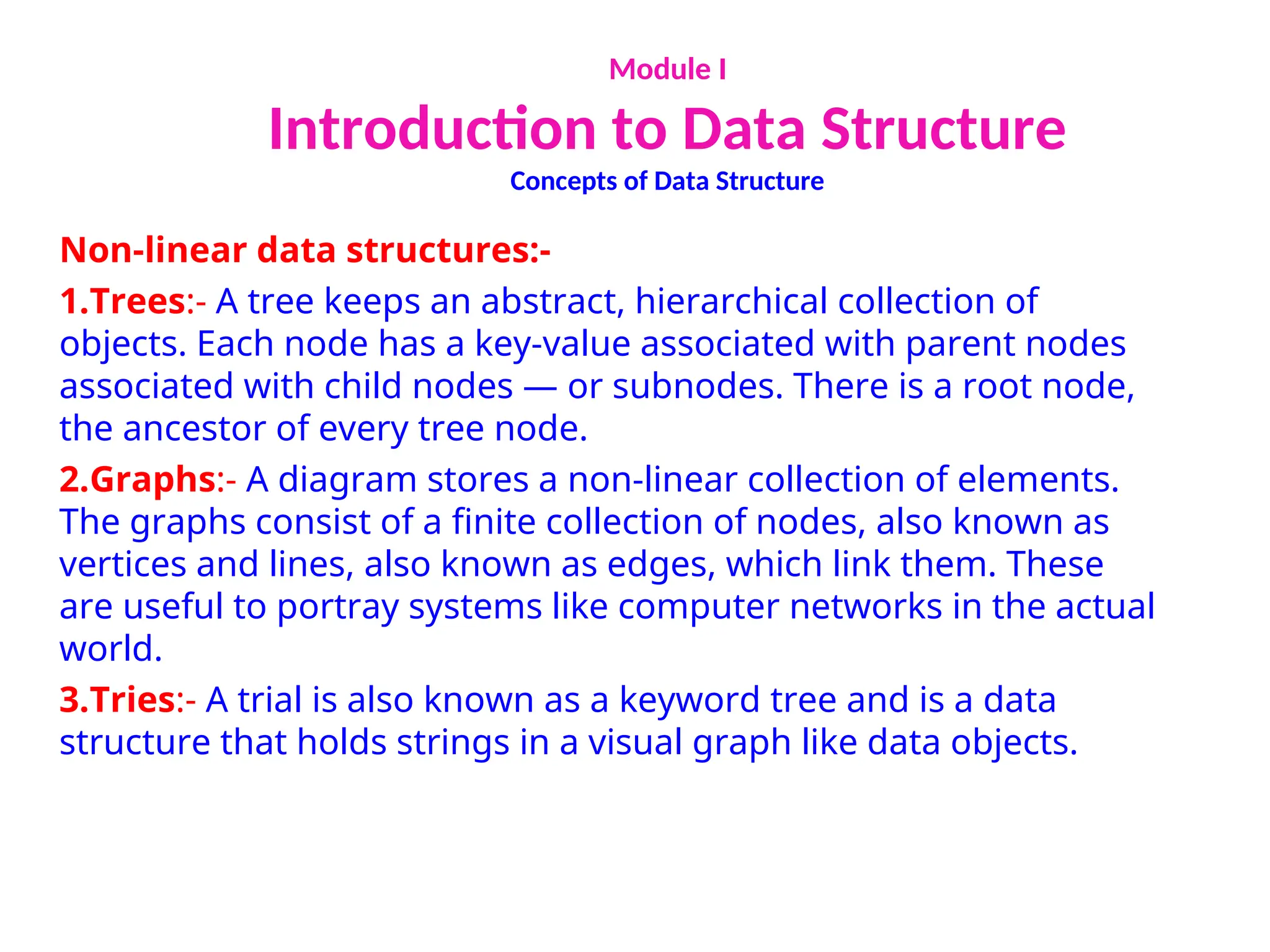
The document provides an introduction to data structures, explaining their definitions, basic terminologies, and various types including primitive and non-primitive structures. It discusses the importance of data structures for managing and processing data efficiently, as well as their roles in computer science and software development. Additionally, it covers concepts such as arrays, sparse matrices, and their representations, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of different data structures.
![Module I
Introduction to Data Structure
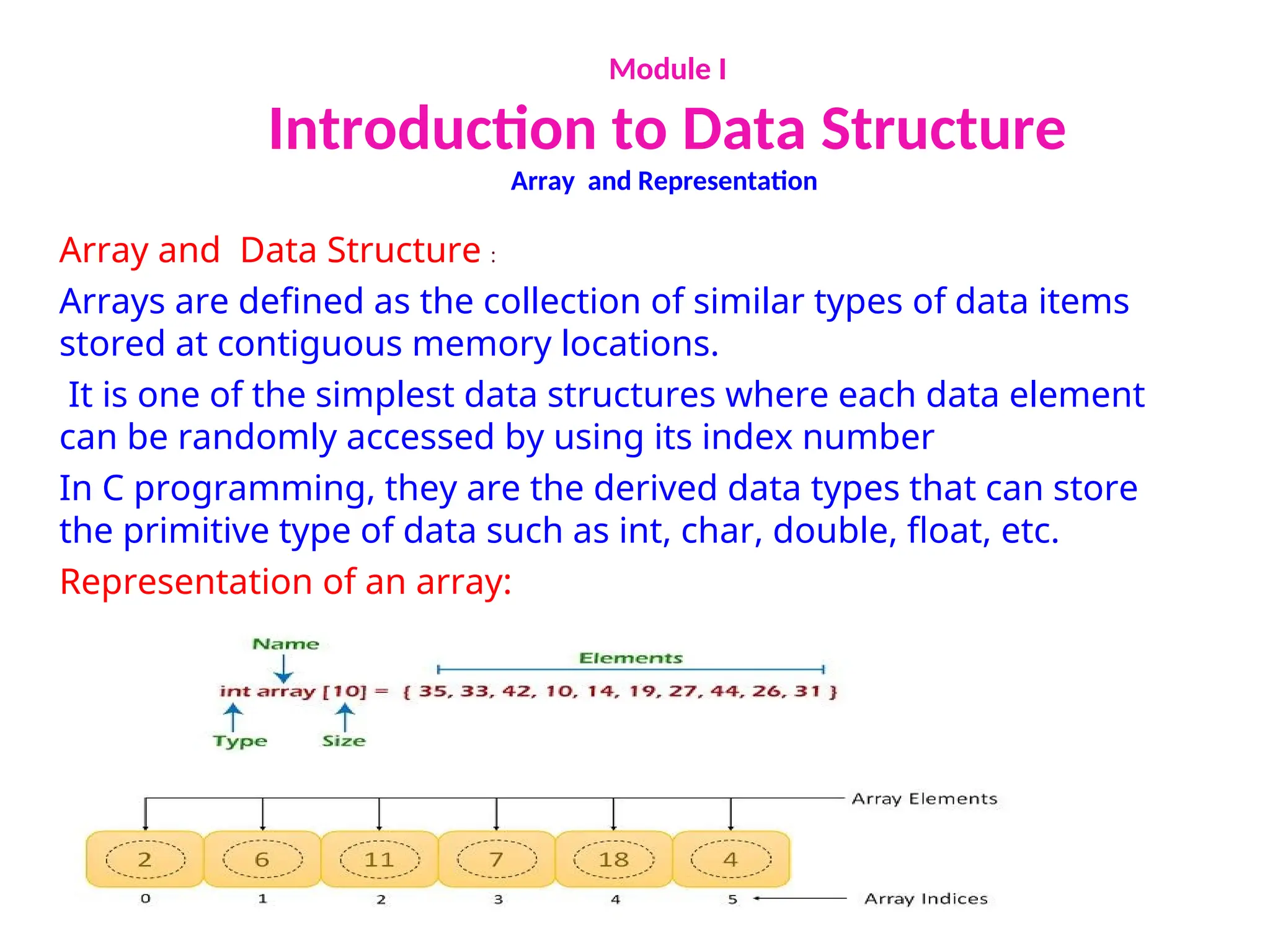
Array and Representation
Memory allocation of an array :
1. 0 (zero-based indexing): The first element of the array will be
arr[0].
2. 1 (one-based indexing): The first element of the array will be
arr[1].
3. n (n - based indexing): The first element of the array can reside
at any random index number](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diplomadspptmodule12023bwu-250130180011-3983597f/75/The-Stack-in-Data-structure-and-algorithm-13-2048.jpg)