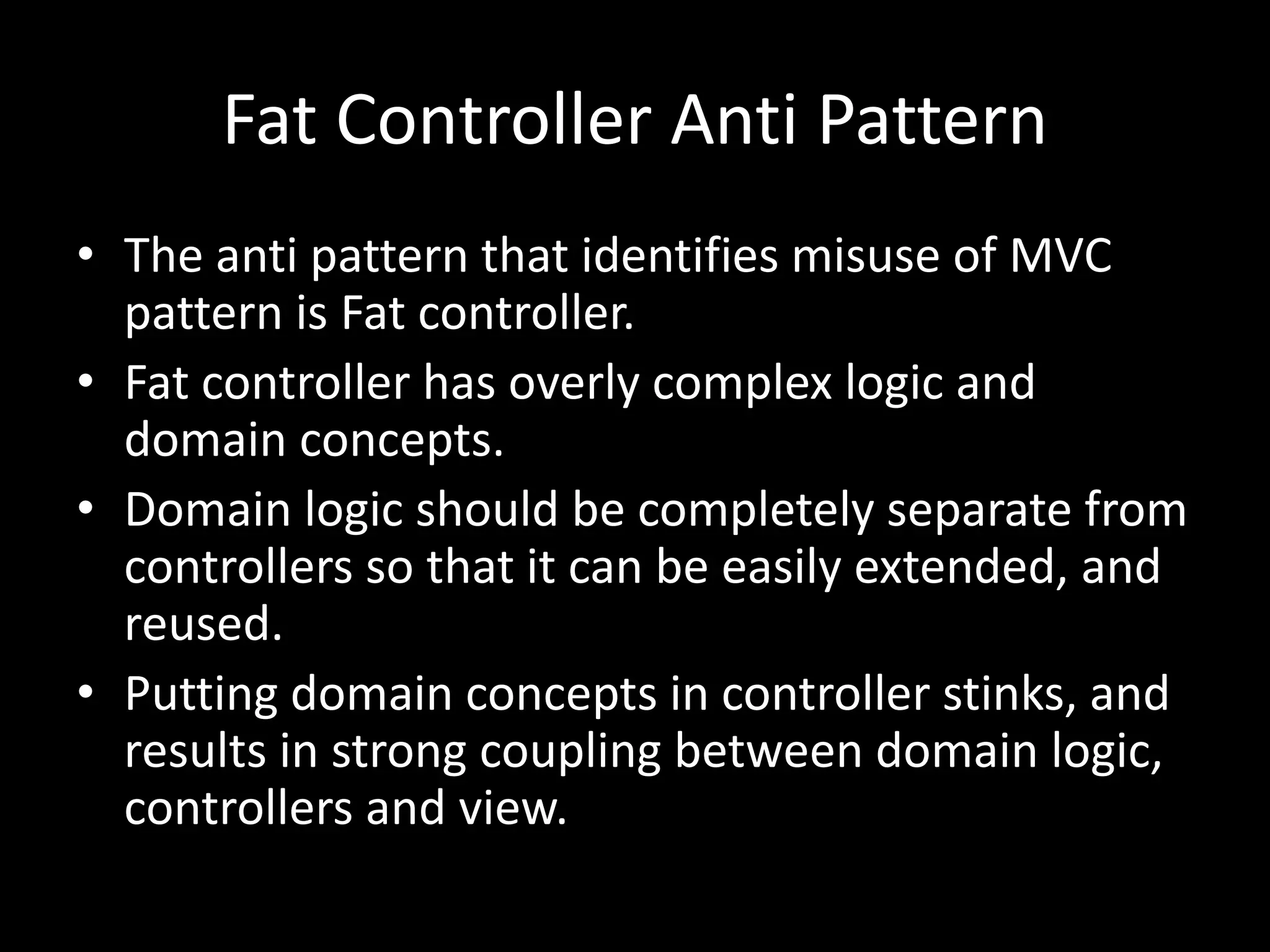
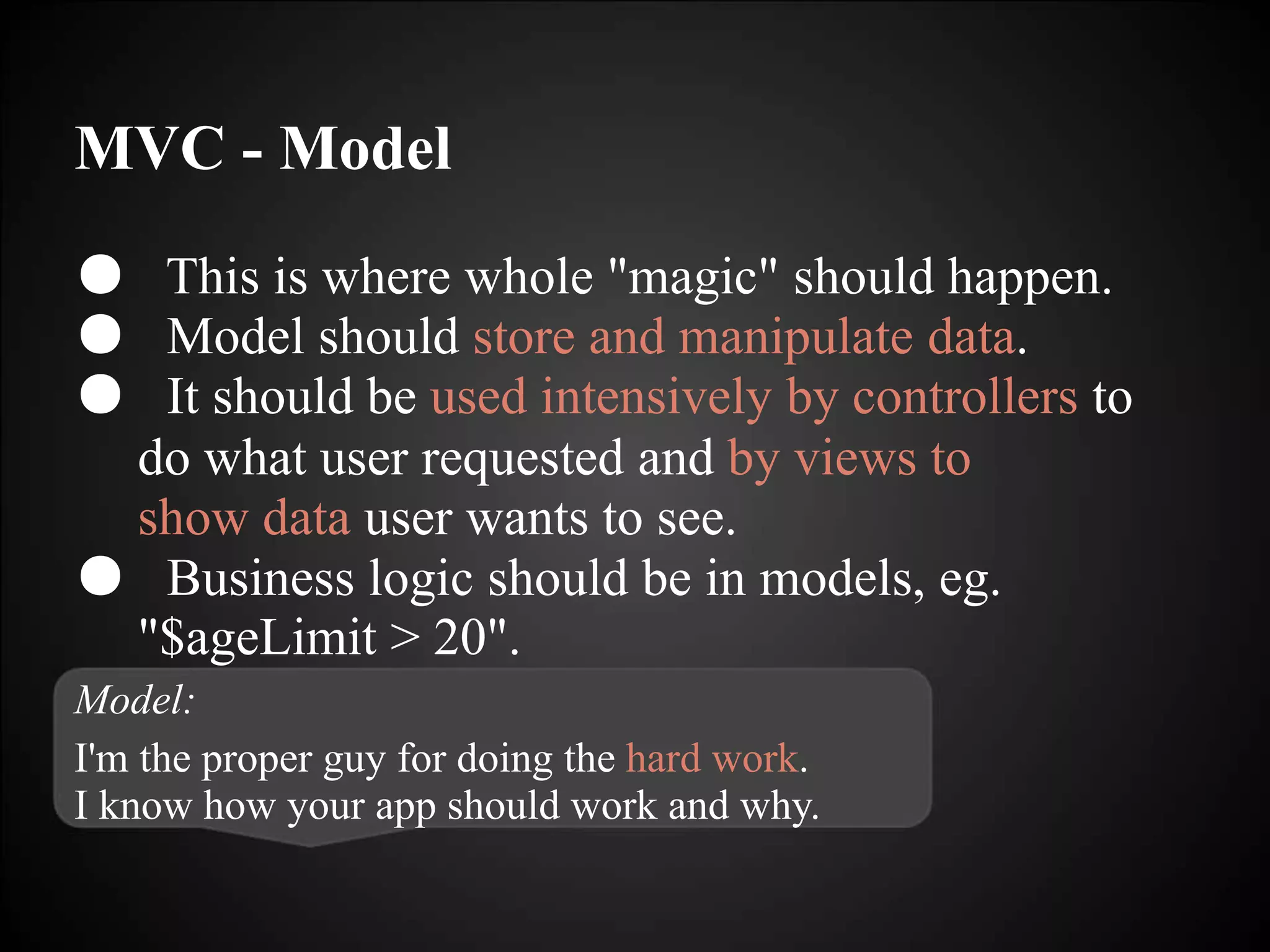
This document discusses the proper implementation of the MVC design pattern compared to common anti-patterns. It emphasizes that the model should contain all business logic, while the controller acts as a thin translator between the user, model and view. The view simply displays data from the model. When implemented correctly with thin controllers and fat models, MVC promotes separation of concerns, reusability, and testability. Common mistakes include putting too much logic in controllers or allowing direct access between views and models. The document provides examples of proper and improper implementations of each MVC component in various languages and frameworks.