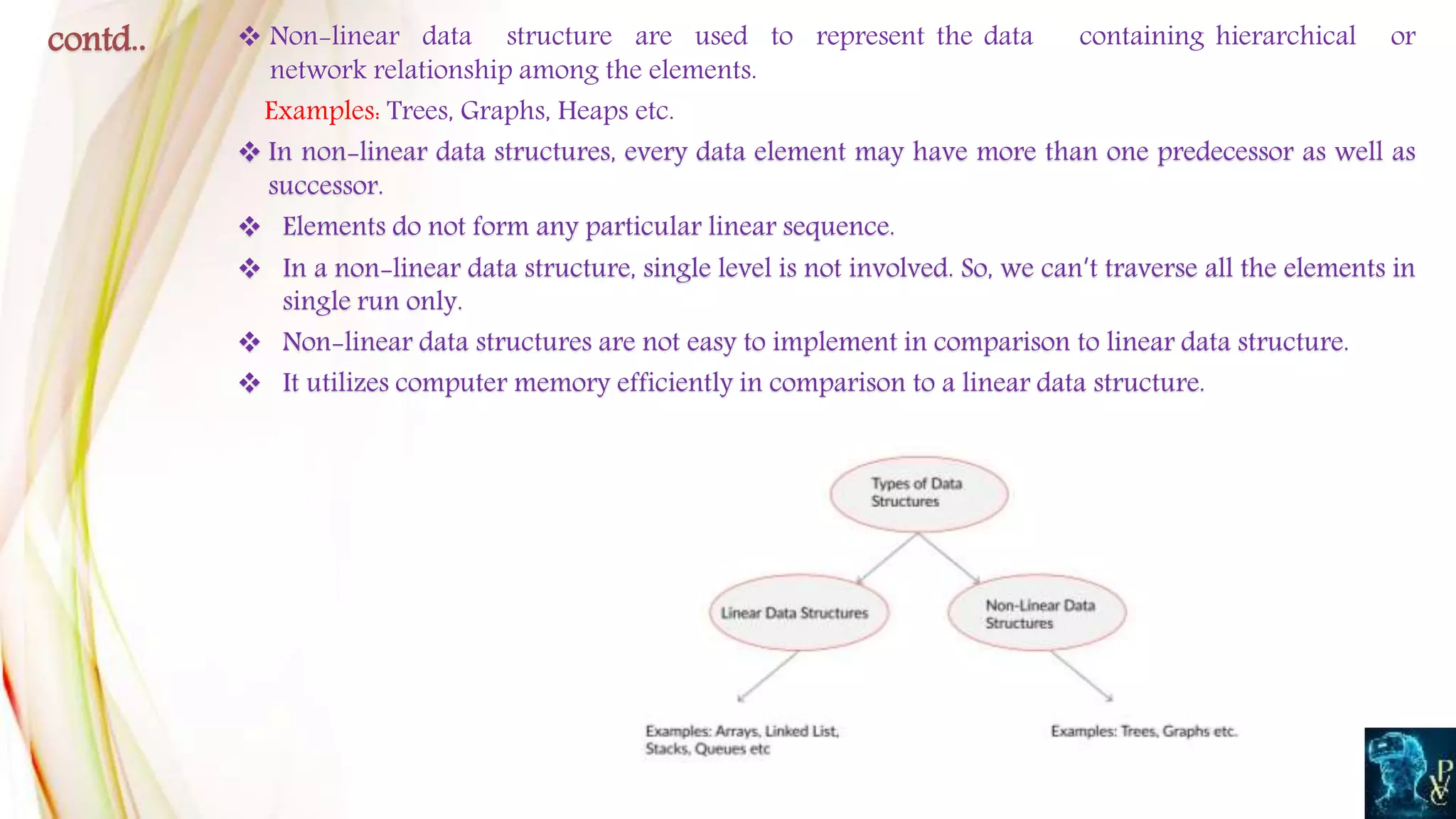
This document provides a comprehensive overview of data structures, defining data structures as a way to organize and store data for efficient access and usage. It categorizes data structures into various types, including primitive vs. non-primitive, linear vs. non-linear, and static vs. dynamic, highlighting their characteristics and differences. Additionally, it discusses persistent and ephemeral data structures, along with their operational distinctions in programming paradigms.