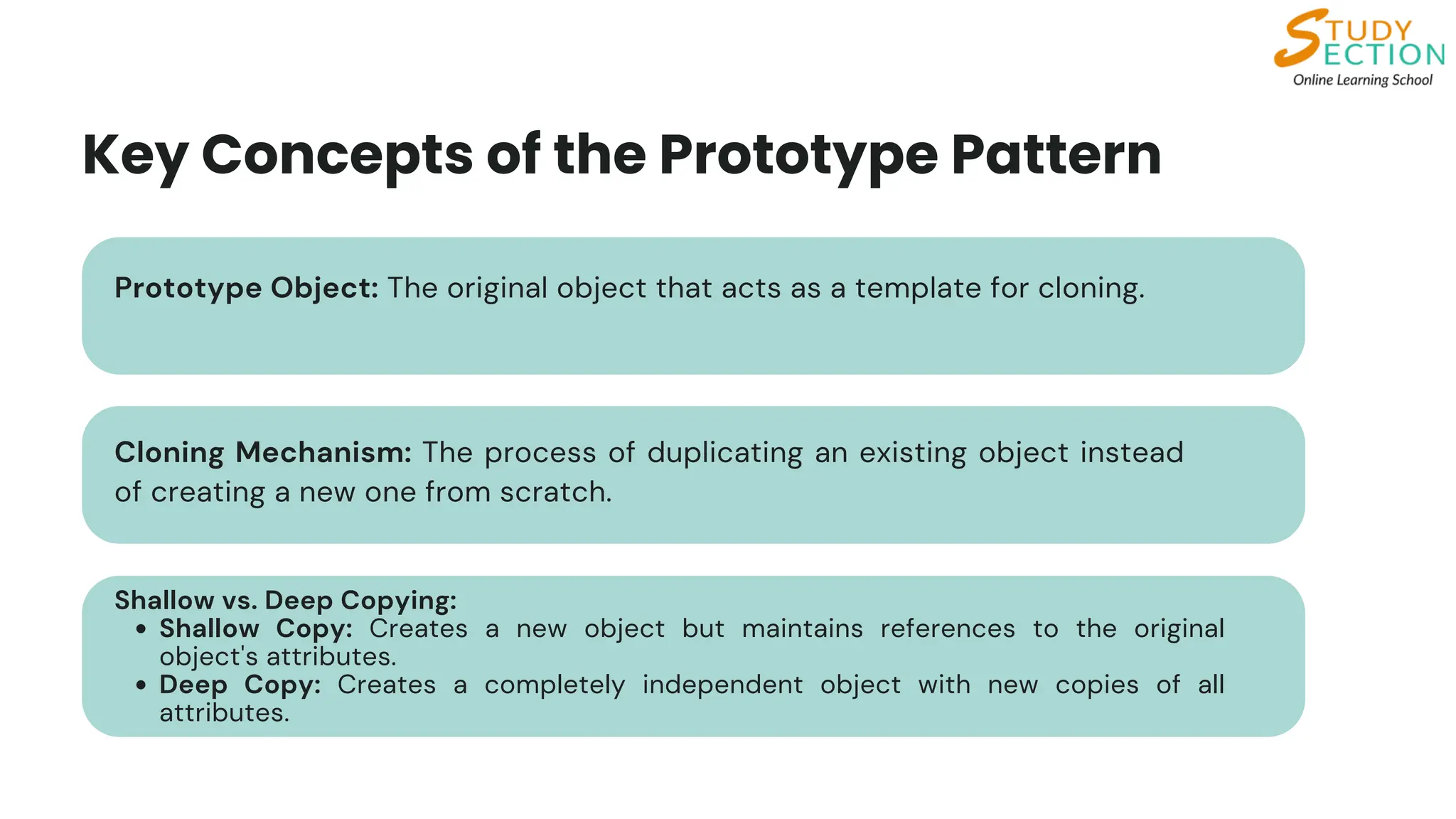
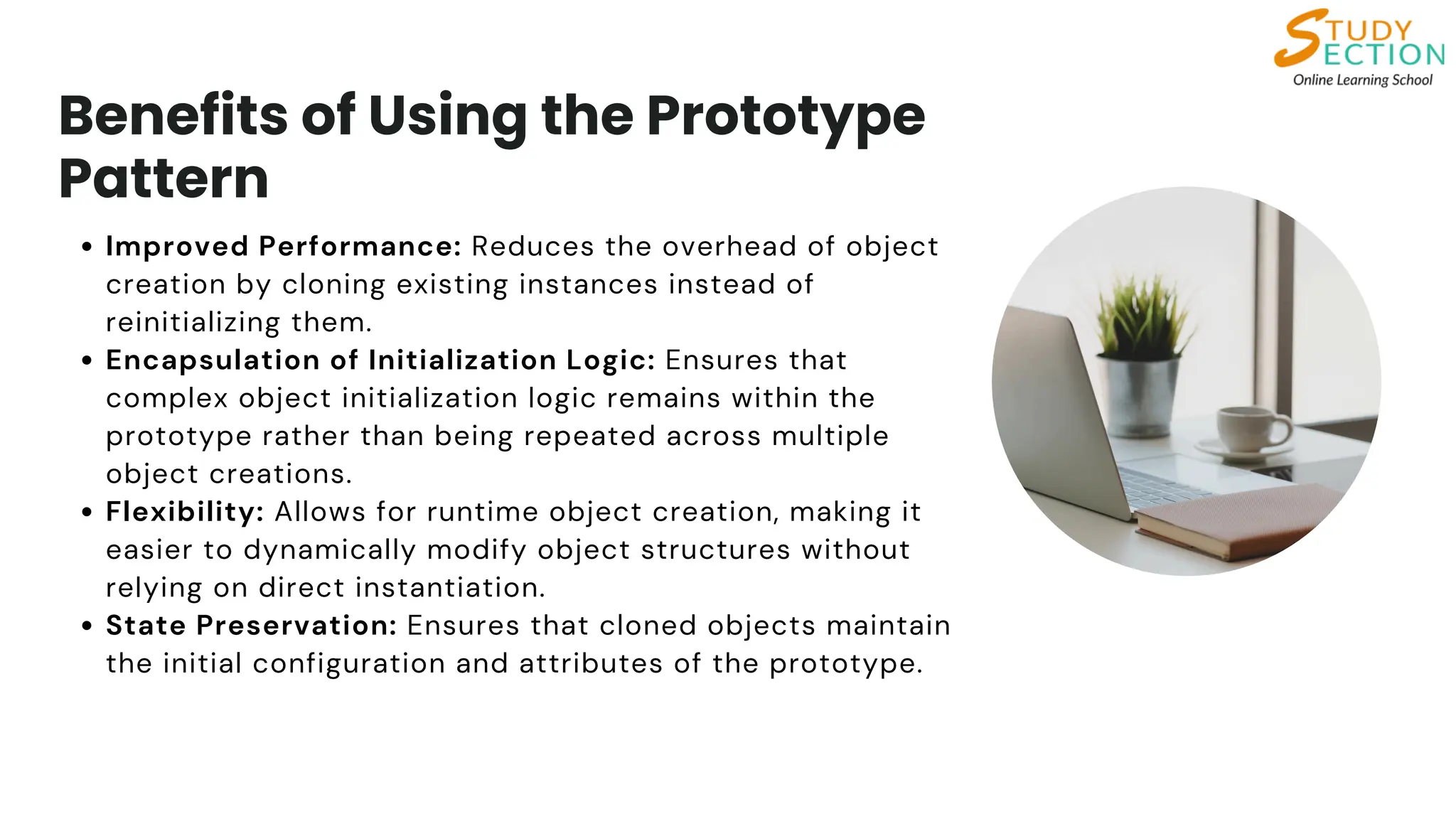
Understand the Prototype pattern, a creational design pattern that enables object creation by duplicating an existing prototype instead of building from scratch. This approach is especially useful when object creation is complex or resource-intensive. In Python, you can implement it using the copy module or a custom clone method.
Want to see it in action? Check out our latest post where we explain this pattern with an example!