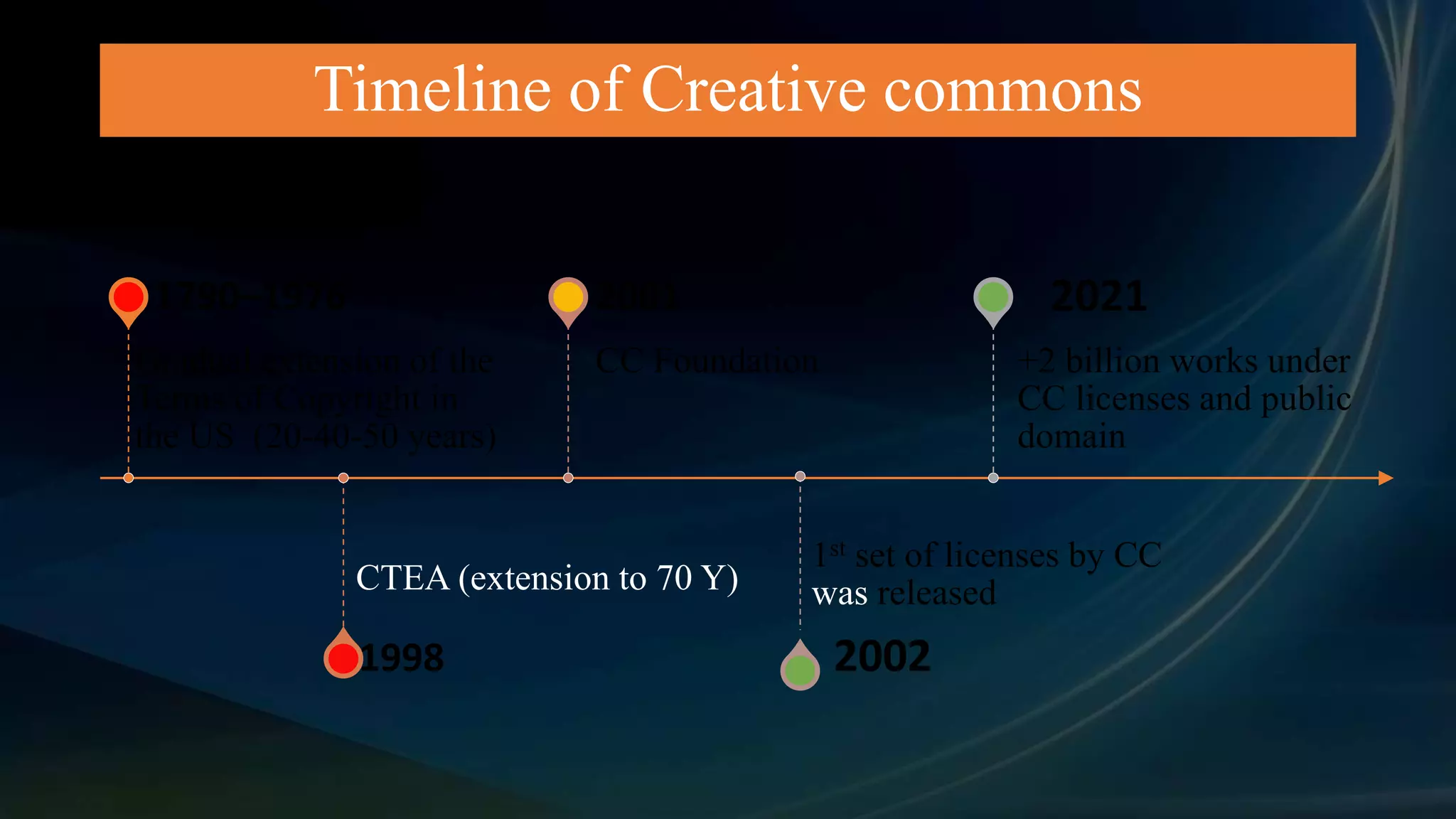
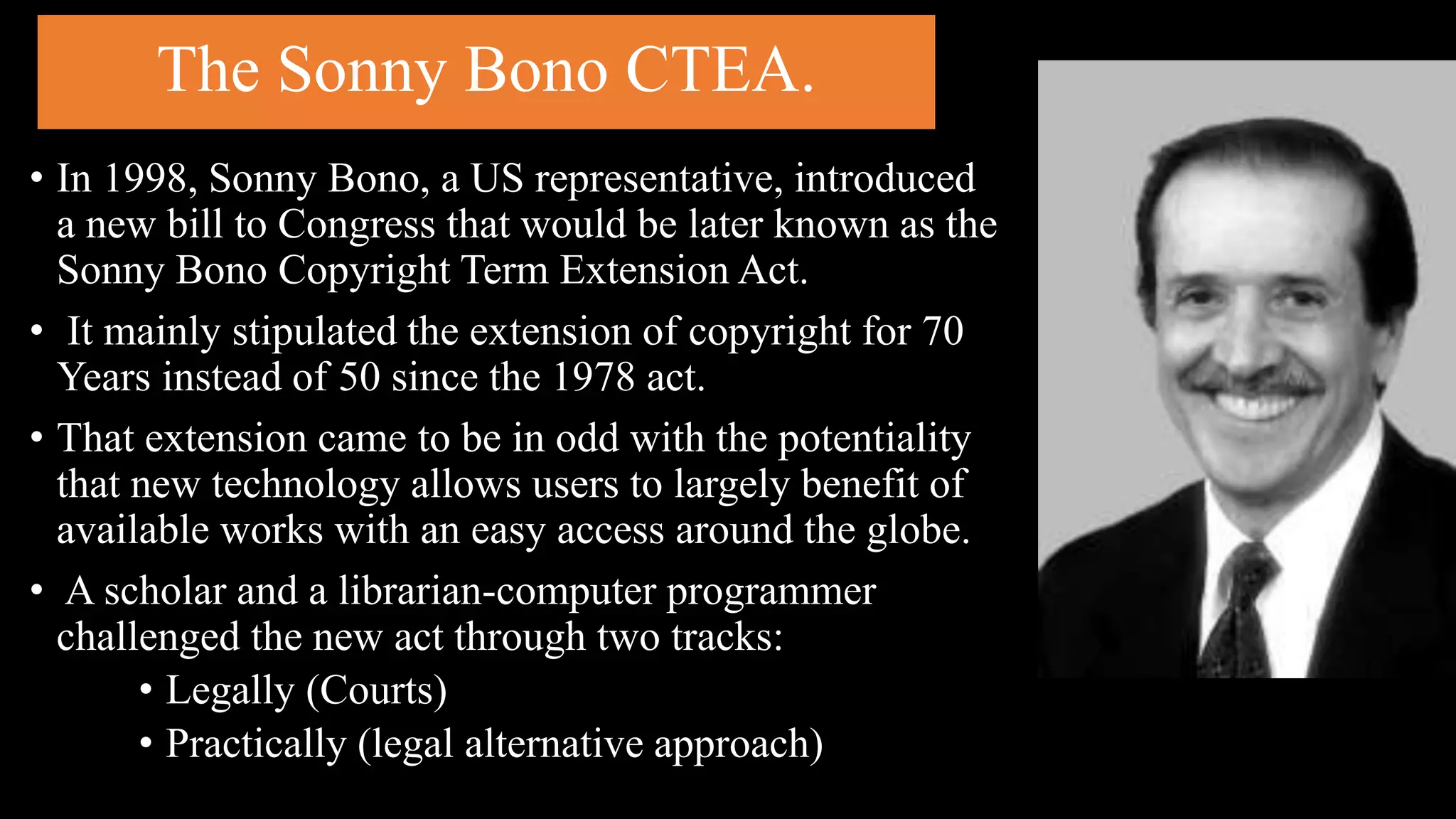
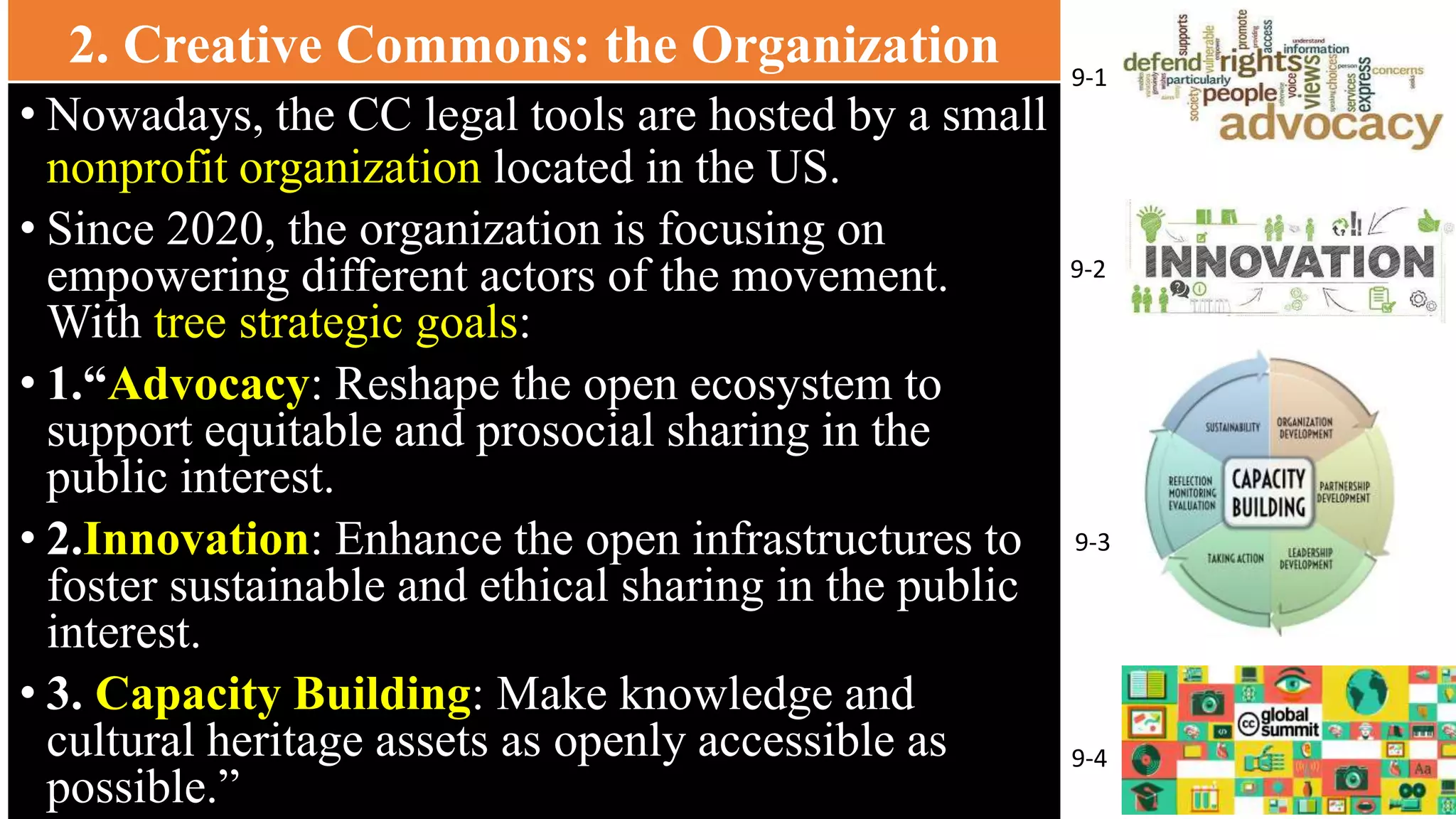
The document provides an overview of Creative Commons (CC), detailing its inception in 2001 as a response to restrictive copyright laws that complicated access to creative works. It discusses the timeline and significant legal challenges, such as Eldred v. Ashcroft, which highlighted the need for alternative licensing models. CC aims to promote sharing and collaboration by offering legal tools for creators, fostering an open ecosystem for equitable access to cultural and knowledge resources.