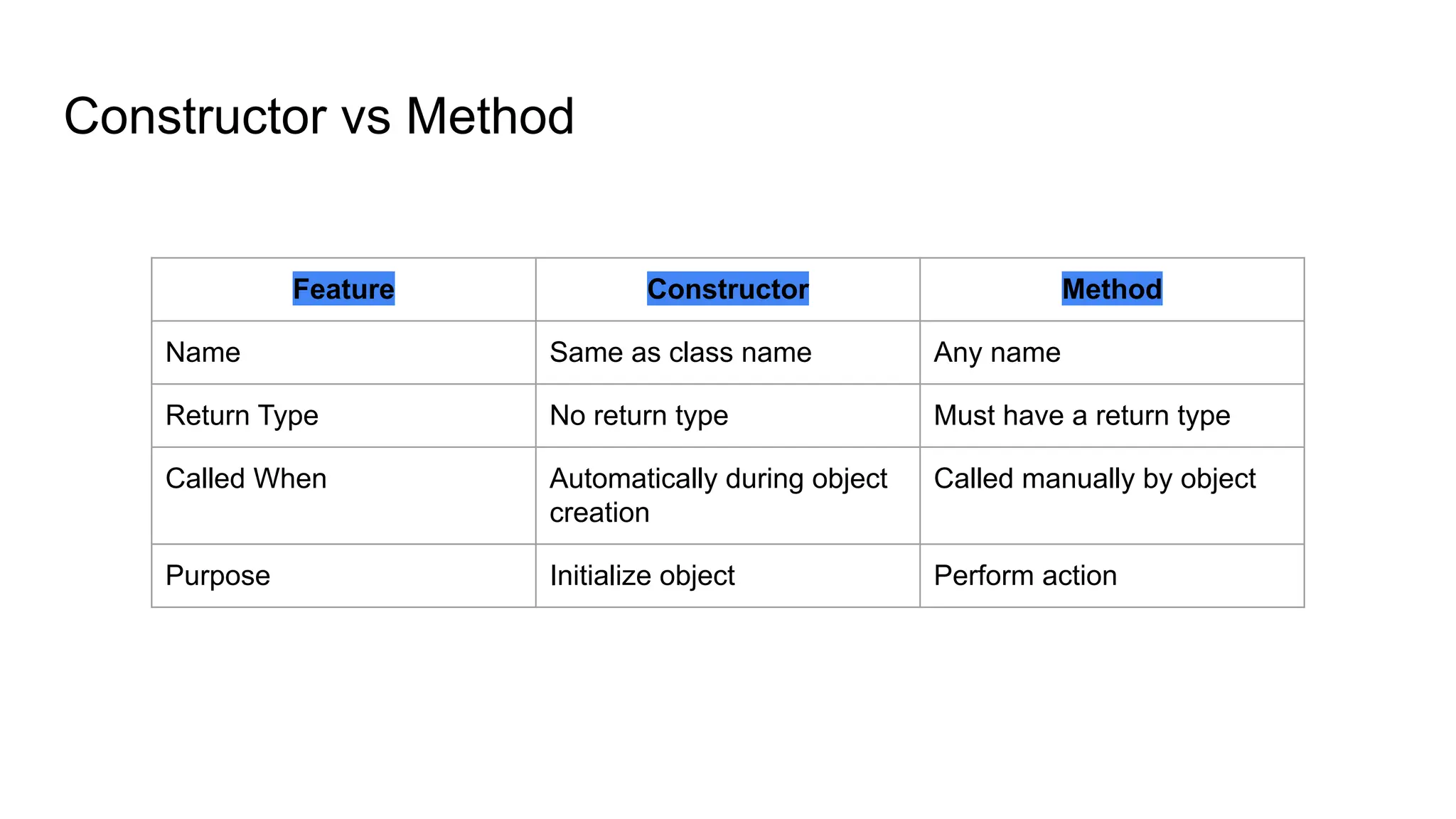
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java is built around the idea of classes and objects. A class is a blueprint that defines the properties and behaviors of objects, while methods, constructors, and access specifiers help in organizing and controlling how objects work. Java also provides important keywords like this, final, static, abstract, and finalize to enhance class functionality.
Inheritance allows one class to acquire the properties and methods of another class, promoting code reusability. Java supports single and multilevel inheritance, and concepts like method overriding, dynamic method dispatch, abstract classes, and the super keyword make inheritance powerful and flexible.
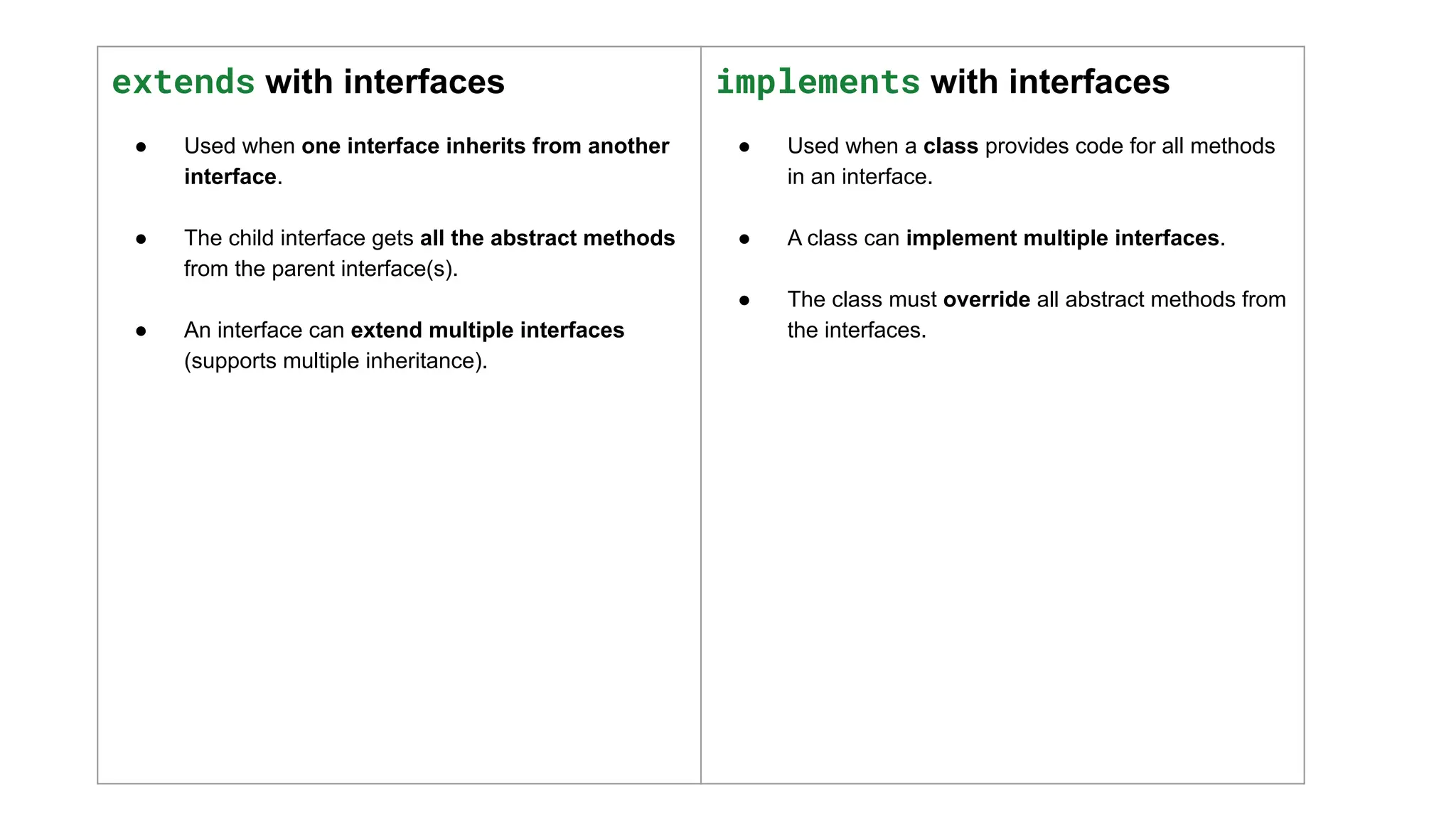
Interfaces in Java define a contract of methods that a class must implement. They support multiple inheritance in Java and encourage polymorphism. Interfaces can also be extended to create more specialized behaviors.
Packages act as containers for classes and interfaces. They help in grouping related classes, avoiding name conflicts, and maintaining modular and reusable code. Java supports both built-in and user-defined packages, making large applications easier to manage.
Overall, this unit builds a strong foundation in Java’s OOP principles, focusing on reusability, modularity, and abstraction, which are essential for developing structured and scalable applications.















![class Book {
String title;
int pages;
// Constructor
Book(String t, int p) {
title = t;
pages = p;
}
// Overloaded method
void display() {
System.out.println(title + " has " + pages + "
pages.");
}
void display(String author) {
System.out.println(title + " by " + author);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book b1 = new Book("Java Basics",
250);
b1.display();
b1.display("John");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-21-2048.jpg)


![Command Line Arguments in Java
Command line arguments are values passed to a Java program when it is run from
the command line.
● They are passed during program execution.
● They are stored in the String[] args array in the main() method.
● Useful when you want to provide input without using Scanner or GUI.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-24-2048.jpg)
![Example Program
public class CommandLineExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Number of arguments: " + args.length);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Argument " + i + ": " + args[i]);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-25-2048.jpg)


![public class Calculator {
// Method with one int parameter
void add(int a) {
System.out.println("Sum: " + (a + 10));
}
// Method with two int parameters
void add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("Sum: " + (a + b));
}
// Method with two double parameters
void add(double a, double b) {
System.out.println("Sum: " + (a + b));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calc = new Calculator();
calc.add(5); // calls method with
one int
calc.add(5, 10); // calls method with
two ints
calc.add(2.5, 3.5); // calls method
with two doubles
}
}
Output:
Sum: 15
Sum: 15
Sum: 6.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-28-2048.jpg)






![b. Static Method
● Can be called without creating object.
● Can access only static data.
class MyClass {
static void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello from static method!"); }}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass.sayHello(); // No need to create an object
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-35-2048.jpg)


![class Counter {
static int count = 0;
Counter() {
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter c1 = new Counter(); // count becomes 1
Counter c2 = new Counter(); // count becomes 2
Counter c3 = new Counter(); // count becomes 3
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-38-2048.jpg)


![abstract class Animal {
abstract void sound(); // abstract method (no body)
void sleep() { // normal method
System.out.println("Sleeping...");
}}
class Dog extends Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Bark!");
}}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Animal a = new Animal(); // Cannot create object of abstract class
Animal myDog = new Dog();
myDog.sound(); // Output: Bark!
myDog.sleep(); // Output: Sleeping...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-41-2048.jpg)

![class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Eating...");
}}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("Barking...");
}}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d = new Dog();
d.eat(); // From Animal
d.bark(); // From Dog
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-43-2048.jpg)
![b) Multilevel Inheritance
A chain of inheritance — one class inherits from another, which inherits from another.
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("Barking...");
}
}
class Puppy extends Dog {
void weep() {
System.out.println("Weeping...");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Puppy p = new Puppy();
p.eat(); // From Animal
p.bark(); // From Dog
p.weep(); // From Puppy
}
}
OUTPUT
Eating...
Barking...
Weeping...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-44-2048.jpg)

![class Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Animal makes a
sound");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Cat meows");
}
}
public class TestDispatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a; // Reference of superclass
a = new Dog(); // Dog object
a.sound(); // Output: Dog barks
(decided at runtime)
a = new Cat(); // Cat object
a.sound(); // Output: Cat meows
(decided at runtime)
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-46-2048.jpg)

![abstract class Animal {
abstract void sound(); // abstract method
- no body
void sleep() { // normal method
System.out.println("Animal is
sleeping");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
public class TestAbstract {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Animal a = new Animal(); // ❌ Not
allowed
Dog d = new Dog();
d.sound(); // Dog barks
d.sleep(); // Animal is sleeping
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-48-2048.jpg)

![Implementing an Interface
● A class uses the keyword implements to agree to the interface’s “contract”.
● The class must provide code for all methods in the interface.
class Dog implements Animal {
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog
barks");
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Dog eats
bones");
}}
public class TestInterface {
public static void main(String[]
args) {
Dog d = new Dog();
d.sound();
d.eat();
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-50-2048.jpg)
![3. Extending Interfaces
● One interface can inherit from another using the extends keyword.
● The child interface gets all methods from the parent interface.
interface Animal {
void sound();
}
interface Pet extends Animal {
void play();
}
class Dog implements Pet {
public void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
public void play() {
System.out.println("Dog plays fetch");
}
}
public class TestExtendInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d = new Dog();
d.sound();
d.play();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-51-2048.jpg)





![Example file: TestPackage.java
import mypack.Hello; // bring Hello into this file
public class TestPackage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hello obj = new Hello();
obj.greet();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2classes-250918081804-28a1be6a/75/Unit-2-BCA-Classes-Inheritance-interface-pdf-58-2048.jpg)

