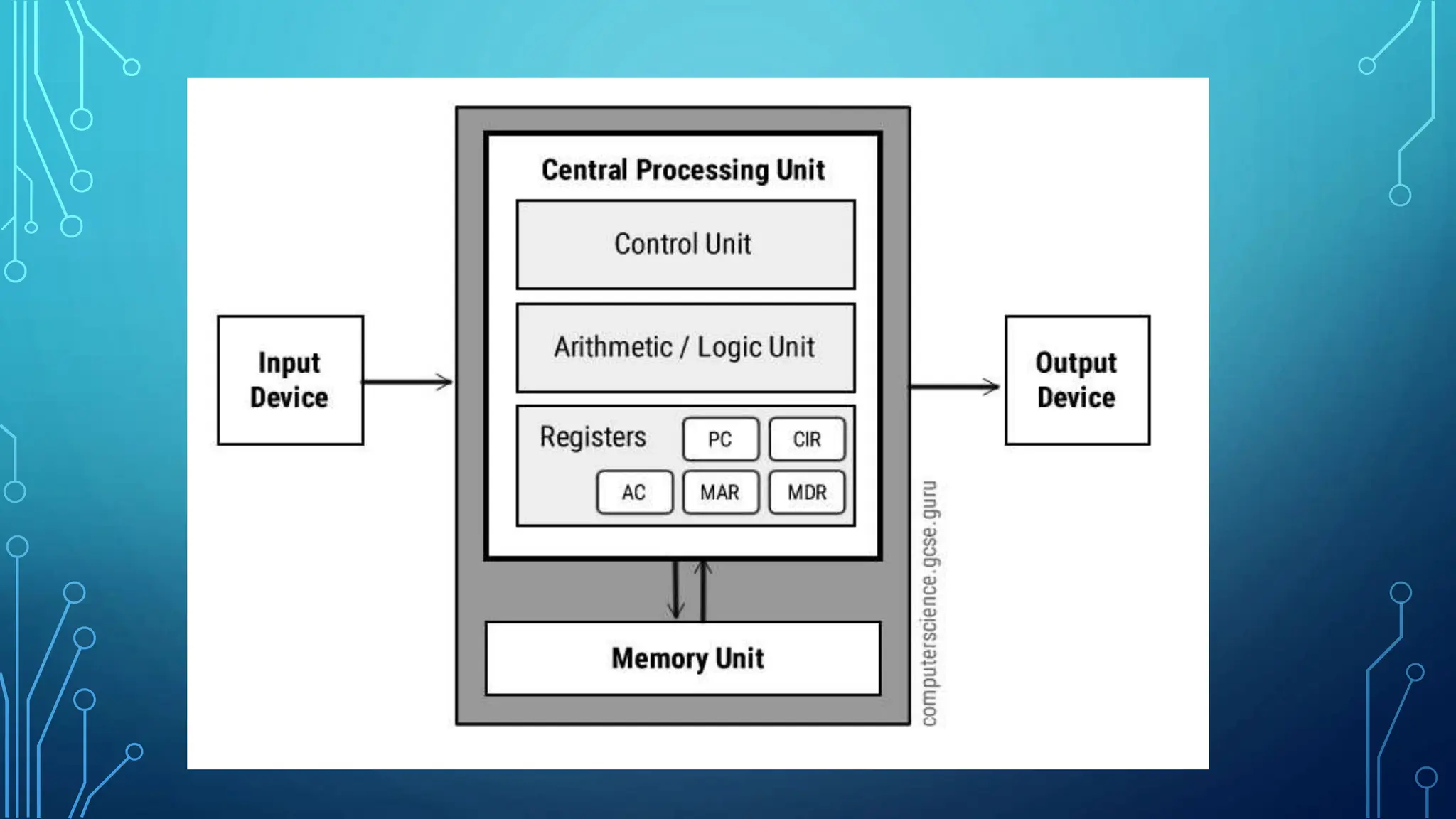
The von Neumann architecture, introduced by John von Neumann in 1945, describes a computer design that includes a control unit, arithmetic and logic unit, memory unit, registers, and input/output components, following the stored-program concept. In this architecture, data and instructions are stored in the same memory, and key components include registers for fast data storage and various buses for communication between the CPU, memory, and peripherals. This foundational design remains prevalent in modern computing systems.