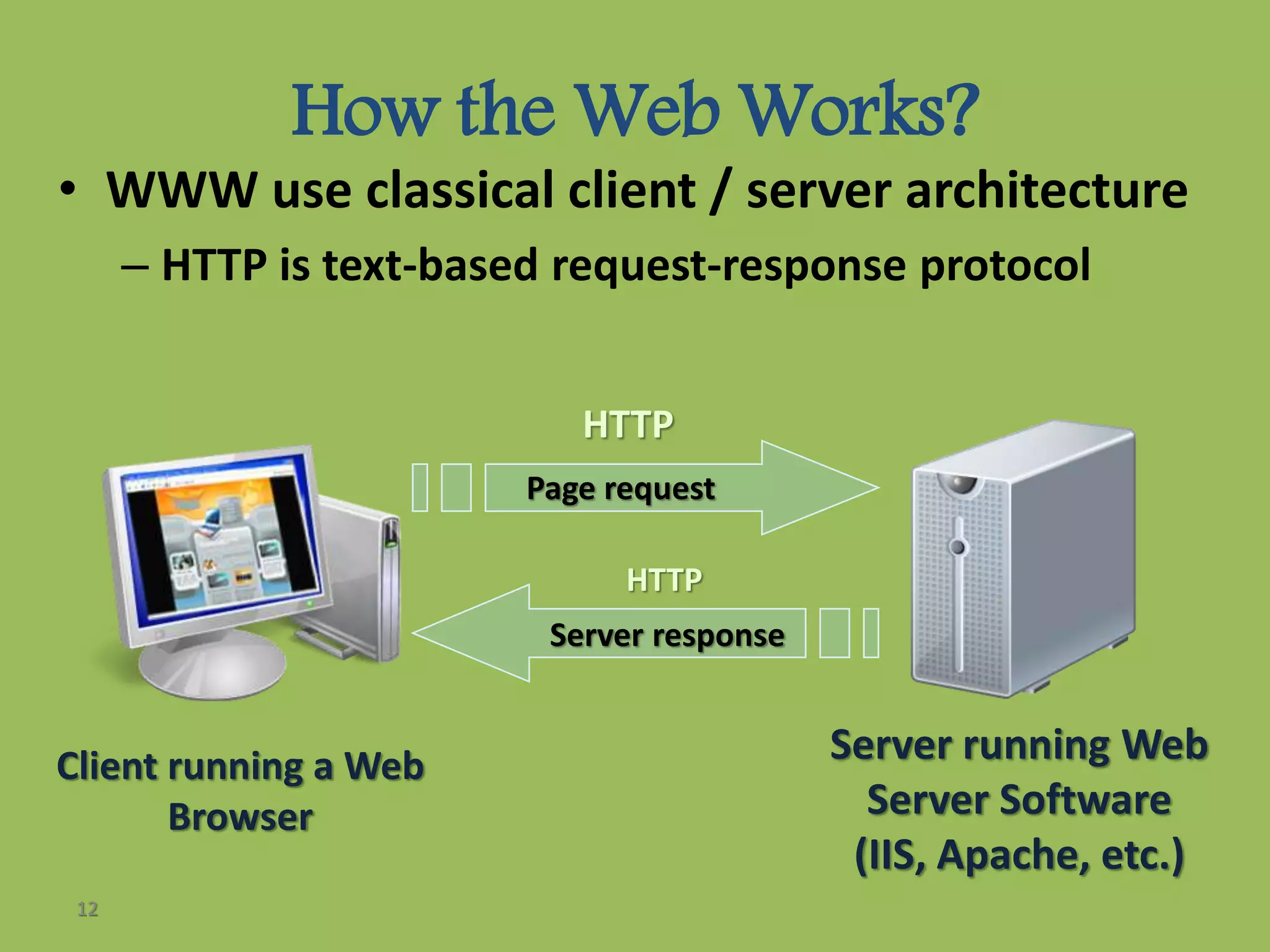
The document explains the basics of web design, detailing the differences between static and dynamic webpages. Static webpages have fixed content and display the same information to all visitors, while dynamic webpages generate different content based on user interactions and scripts. Additionally, it discusses HTML as the standard markup language for creating webpages and introduces Dynamic HTML (DHTML) for creating dynamically changing websites.