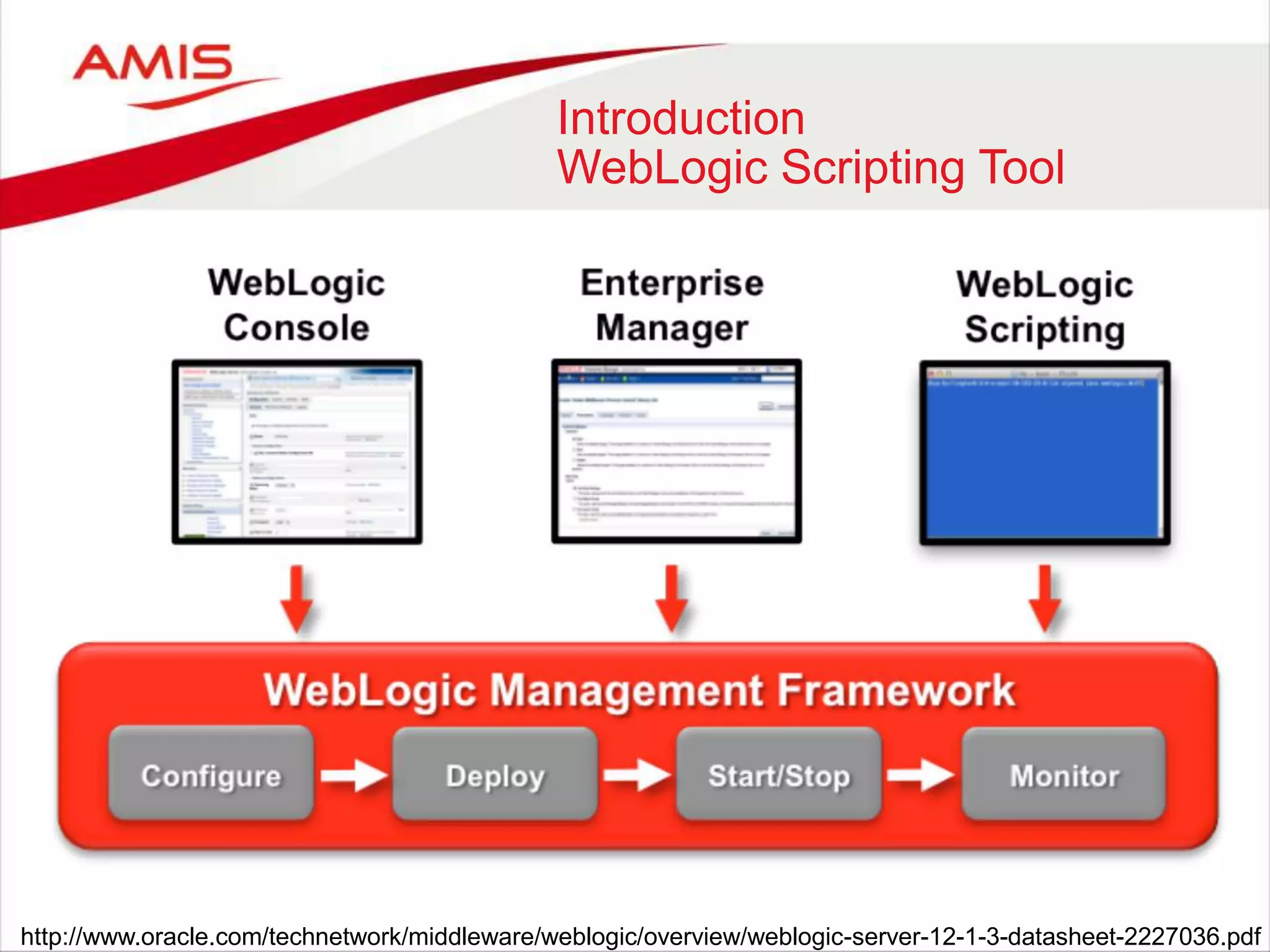
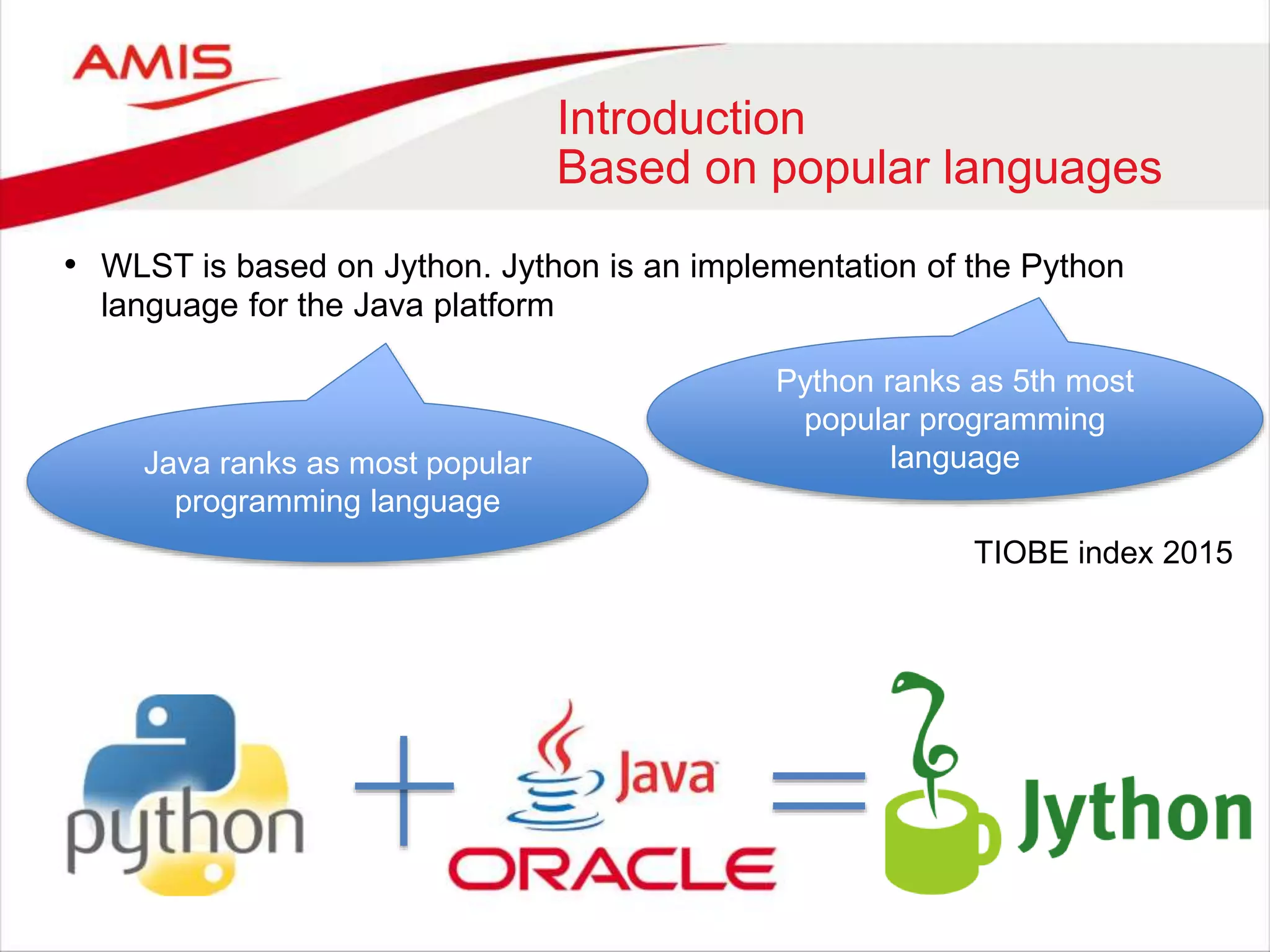
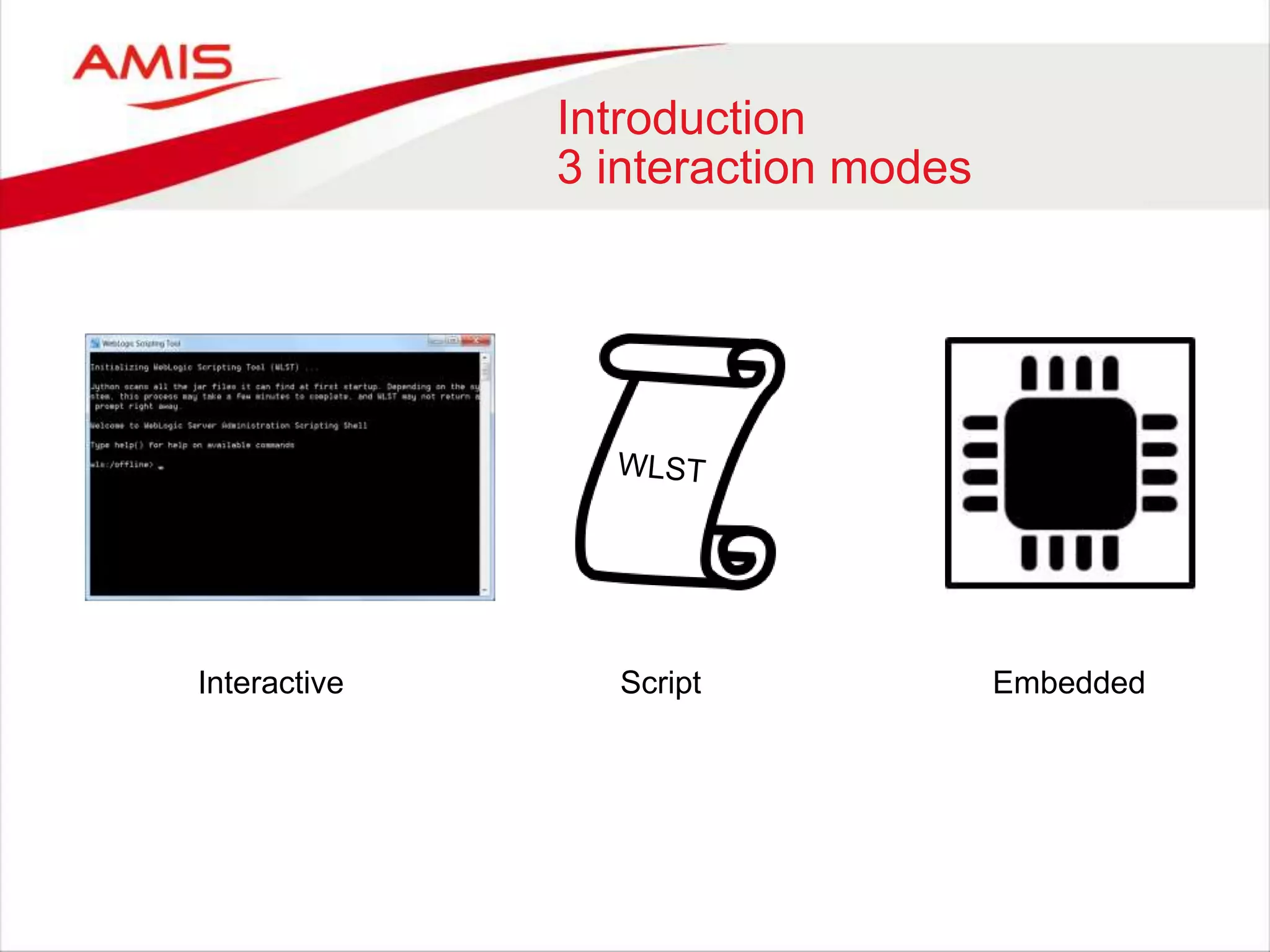
The document discusses the WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST), which is based on Jython, a Java implementation of Python, highlighting its usage, features, and future developments. It covers how to extend WLST with Java APIs, manage configurations, deployments, and monitoring within WebLogic environments. Additionally, it notes upcoming changes in WebLogic Server 12c and the potential shift to RESTful management services.








![Using Java with WLST
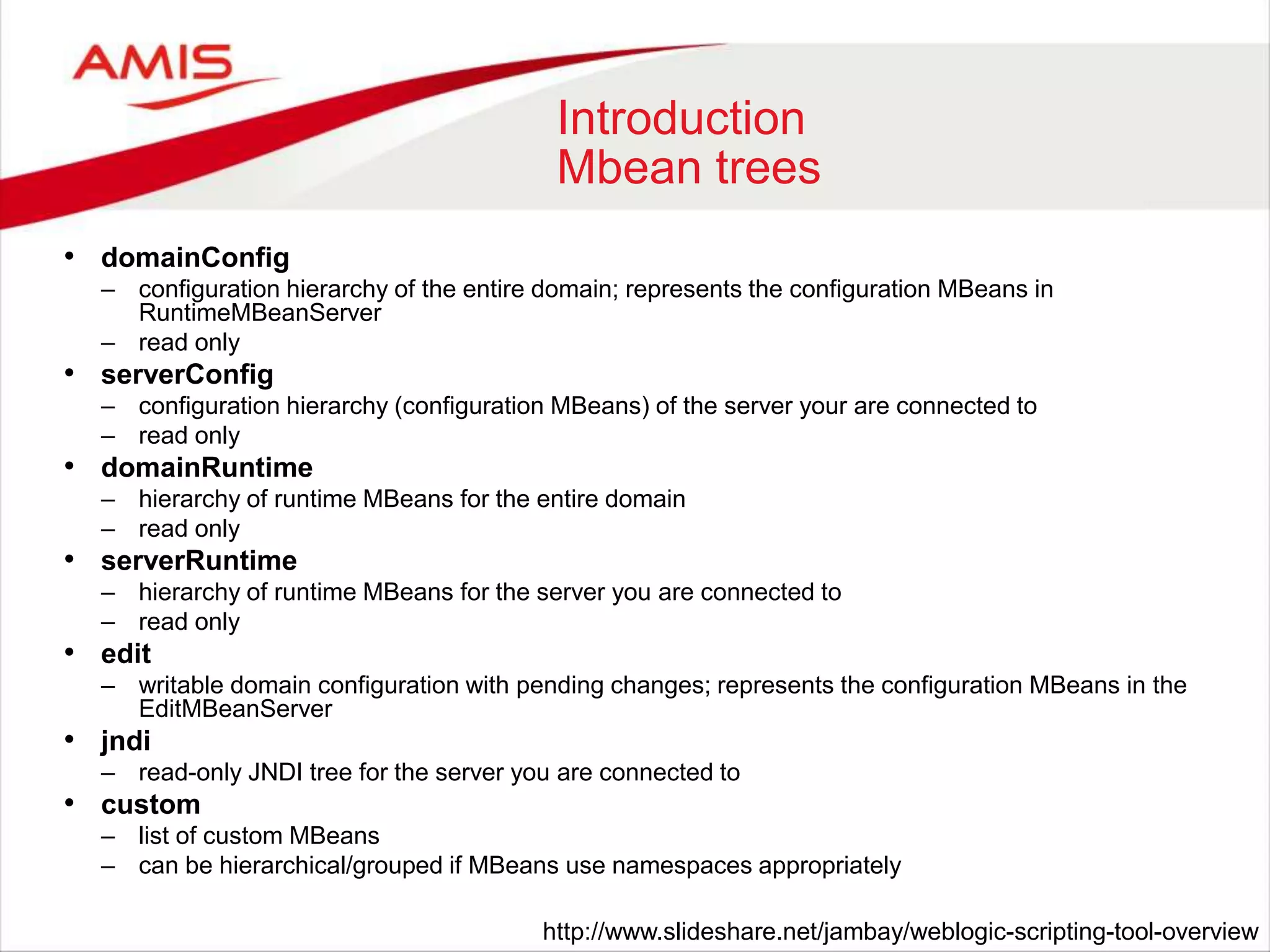
Methods
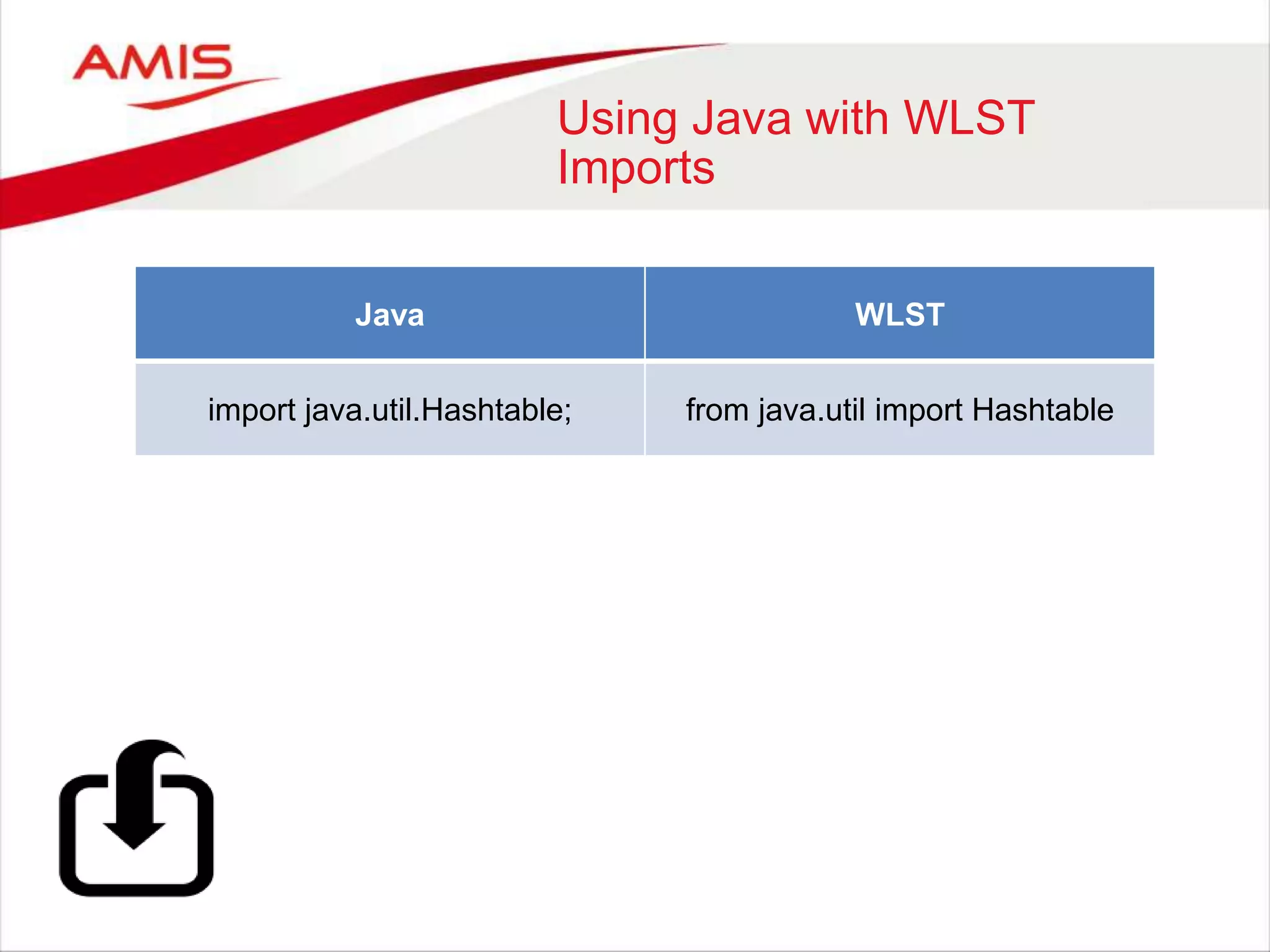
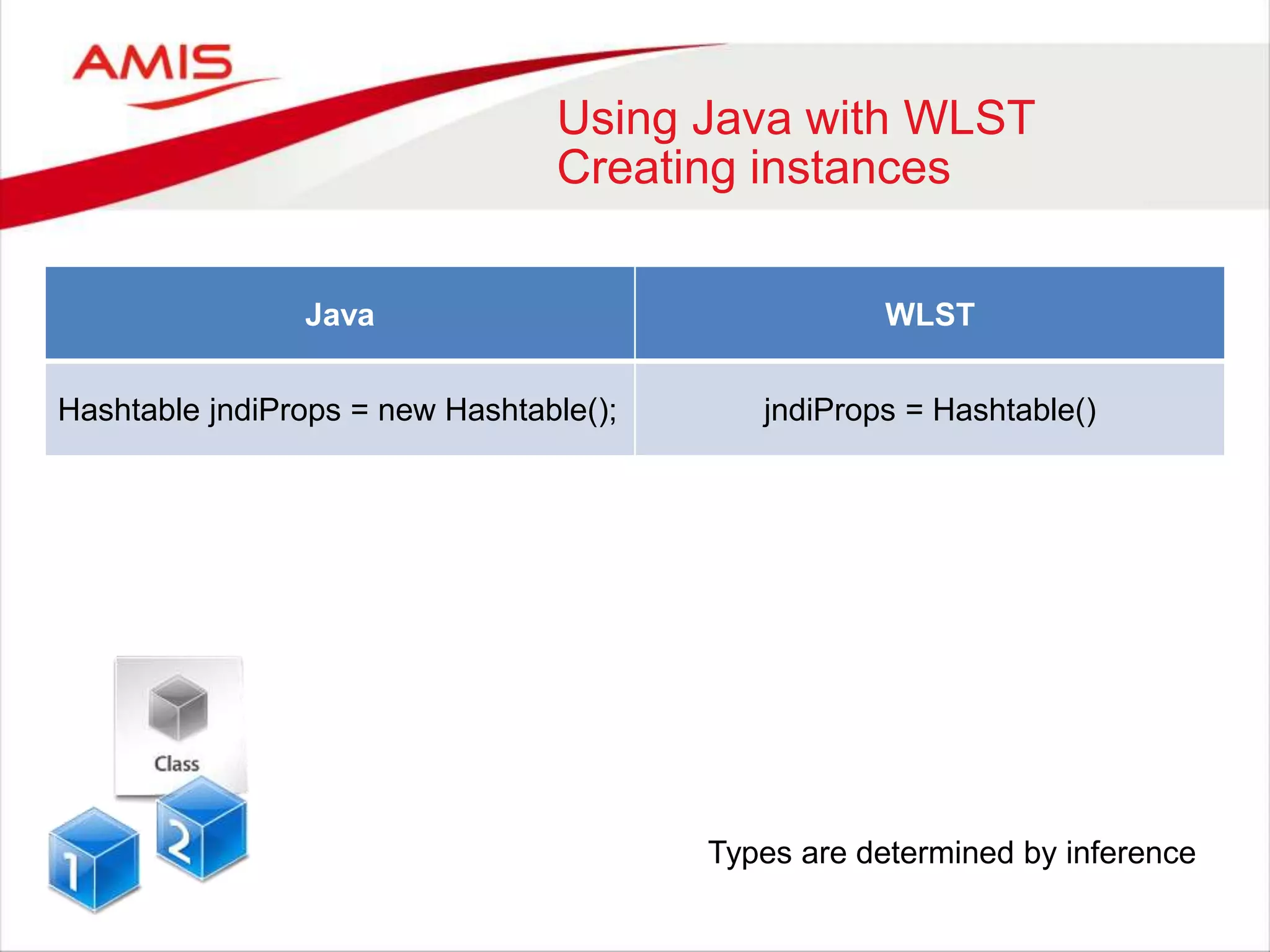
Java WLST
private String
getDNToUndeploy(CompositeData[]
compositeData) throws Exception
def getDNToUndeploy(compositeData):
Python has no true private methods
Exceptions are determined by inference](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weblogicscriptingtoolmadecool-160605093343/75/WebLogic-Scripting-Tool-made-Cool-19-2048.jpg)
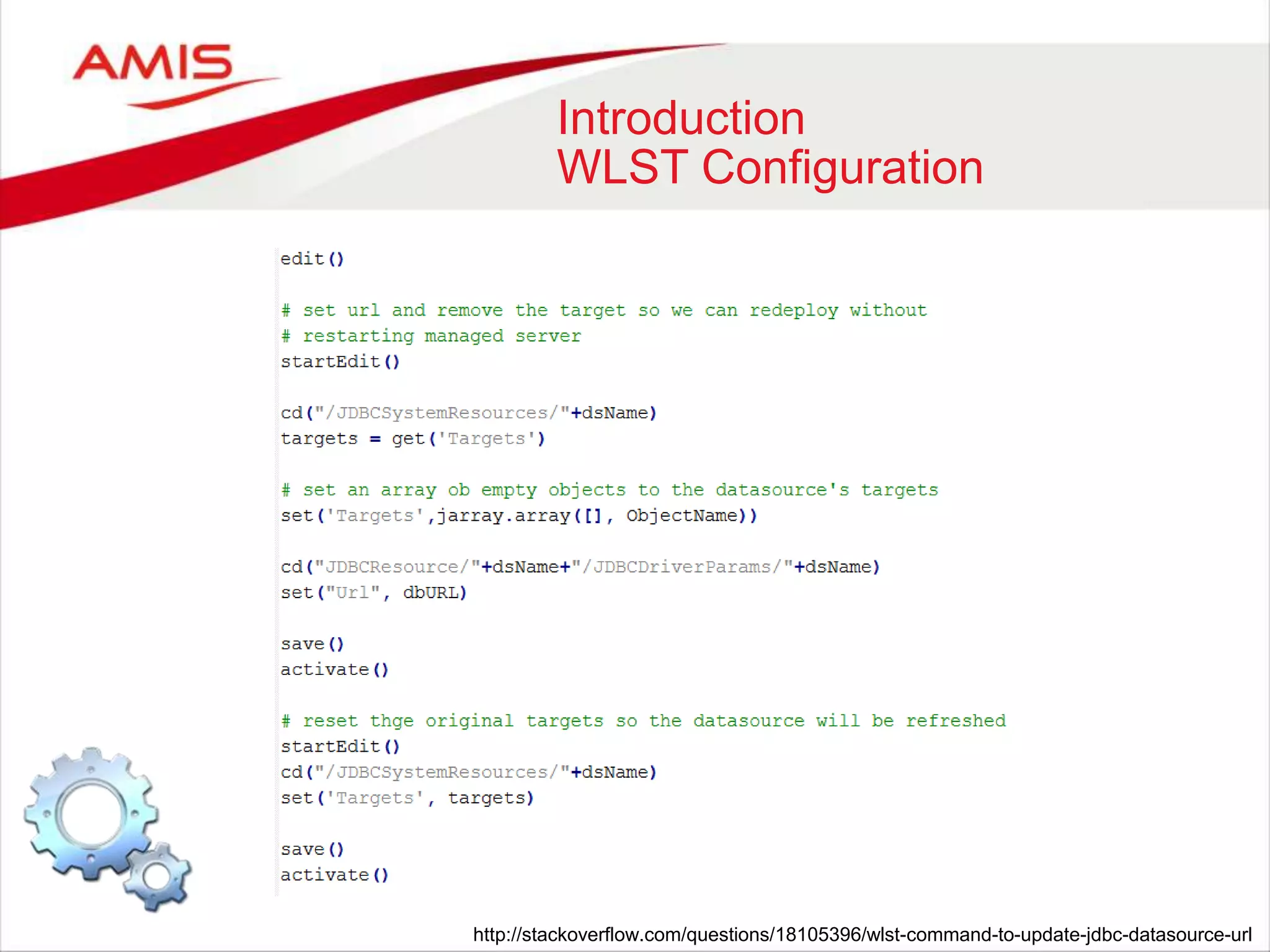
![Using Java with WLST
Arrays
Java WLST
int[] intArray = { 1, 2, 3};
from jarray import array
intArray = array ([1, 2, 3],’i’)
Java primitives arrays can be created
in Jython with the jarray module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weblogicscriptingtoolmadecool-160605093343/75/WebLogic-Scripting-Tool-made-Cool-20-2048.jpg)




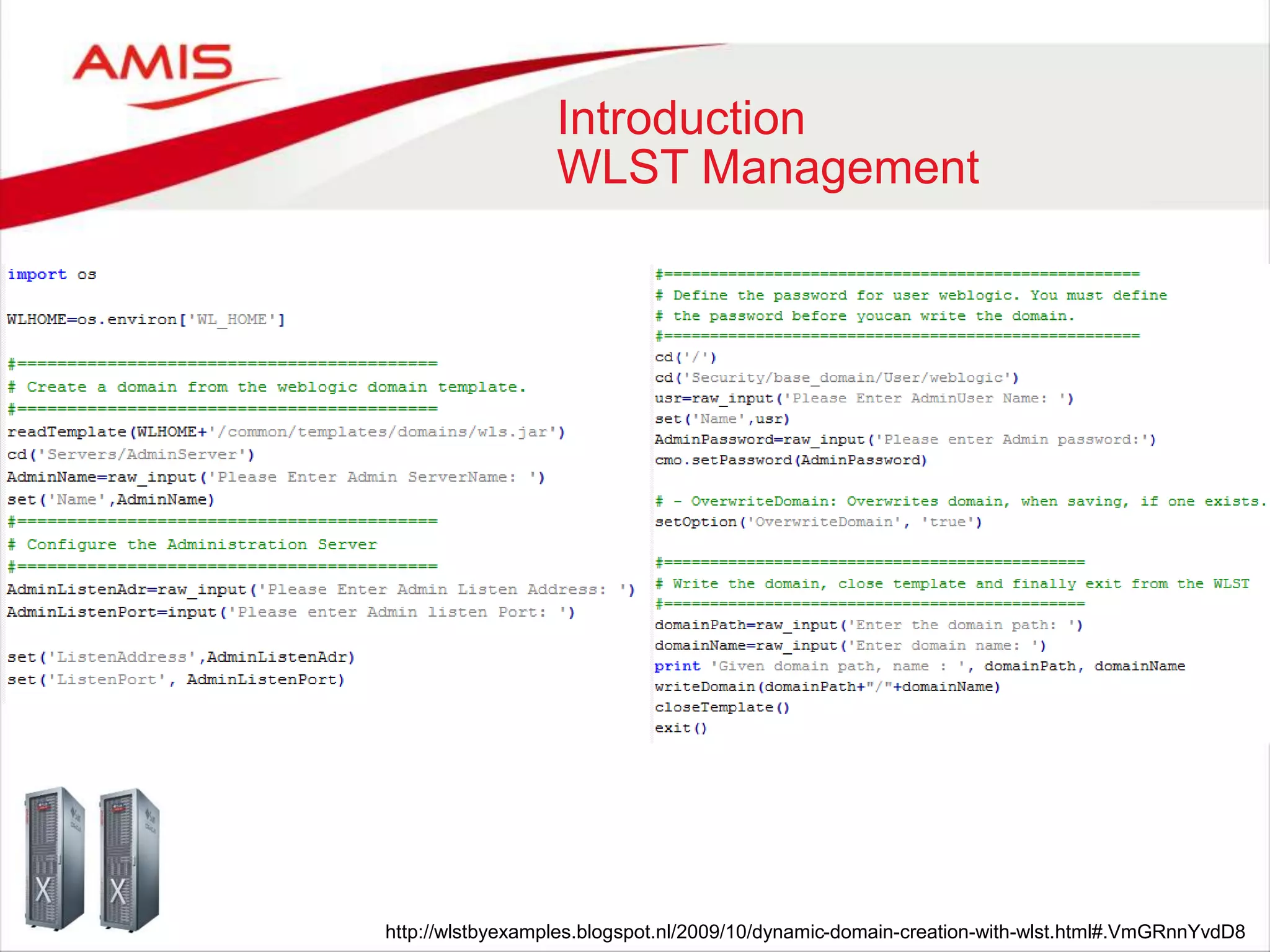
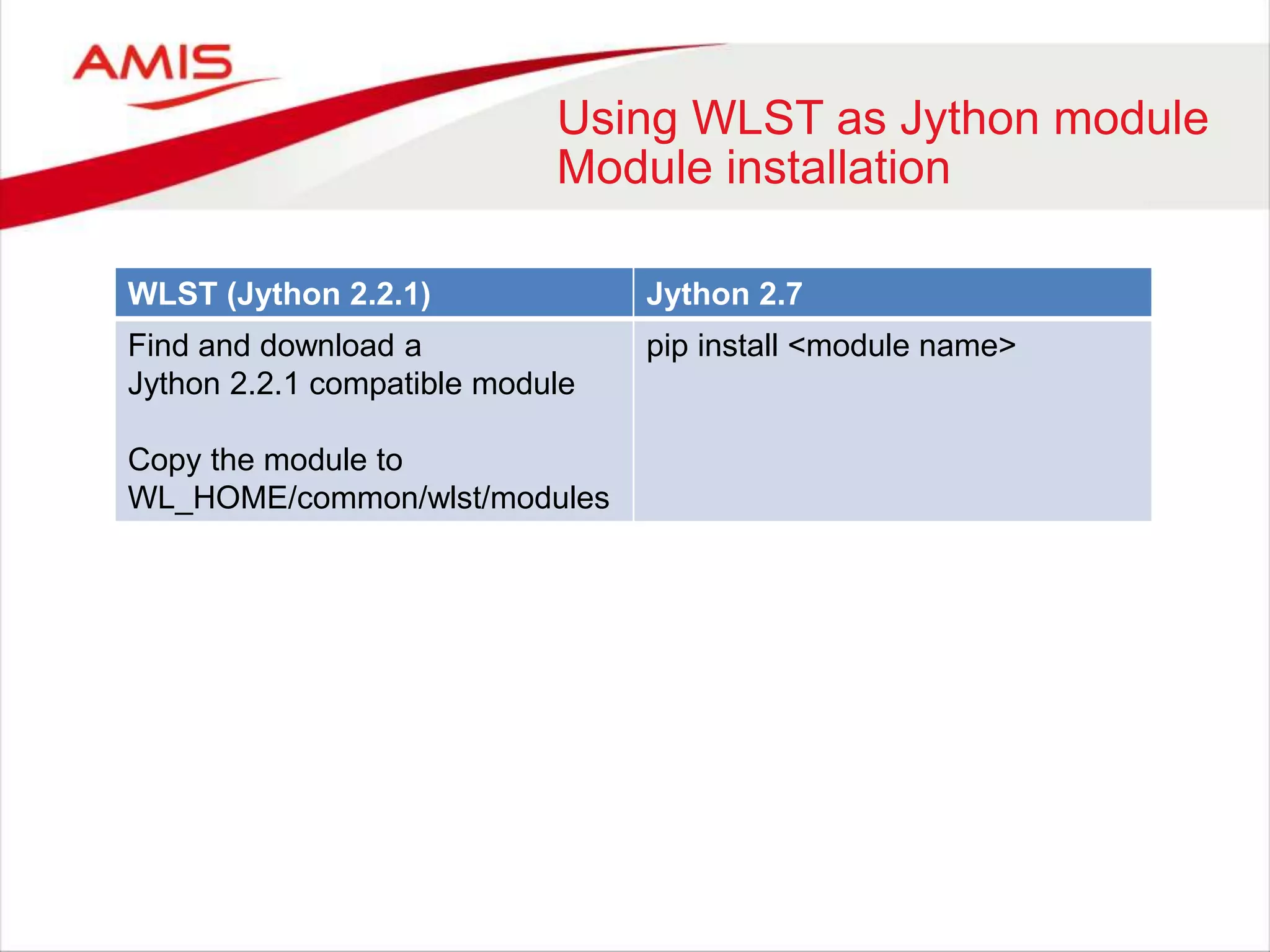
![Using WLST as Jython module
Argument parsing in WLST
import getopt
url = None
user = None
password = None
opts, args =
getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], "e:u:p:")
for opt, arg in opts:
print opt, arg
if opt in "-e":
env = arg
if opt in "-p":
password = arg
if opt in "-u":
user = arg
print "URL: "+url
print "Username: "+username
print "Password: "+password
import sys;
print "URL: "+sys.argv[1]
print "Username: "+sys.argv[2]
print "Password: "+sys.argv[3]
Manual argument checking
and processing!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weblogicscriptingtoolmadecool-160605093343/75/WebLogic-Scripting-Tool-made-Cool-25-2048.jpg)


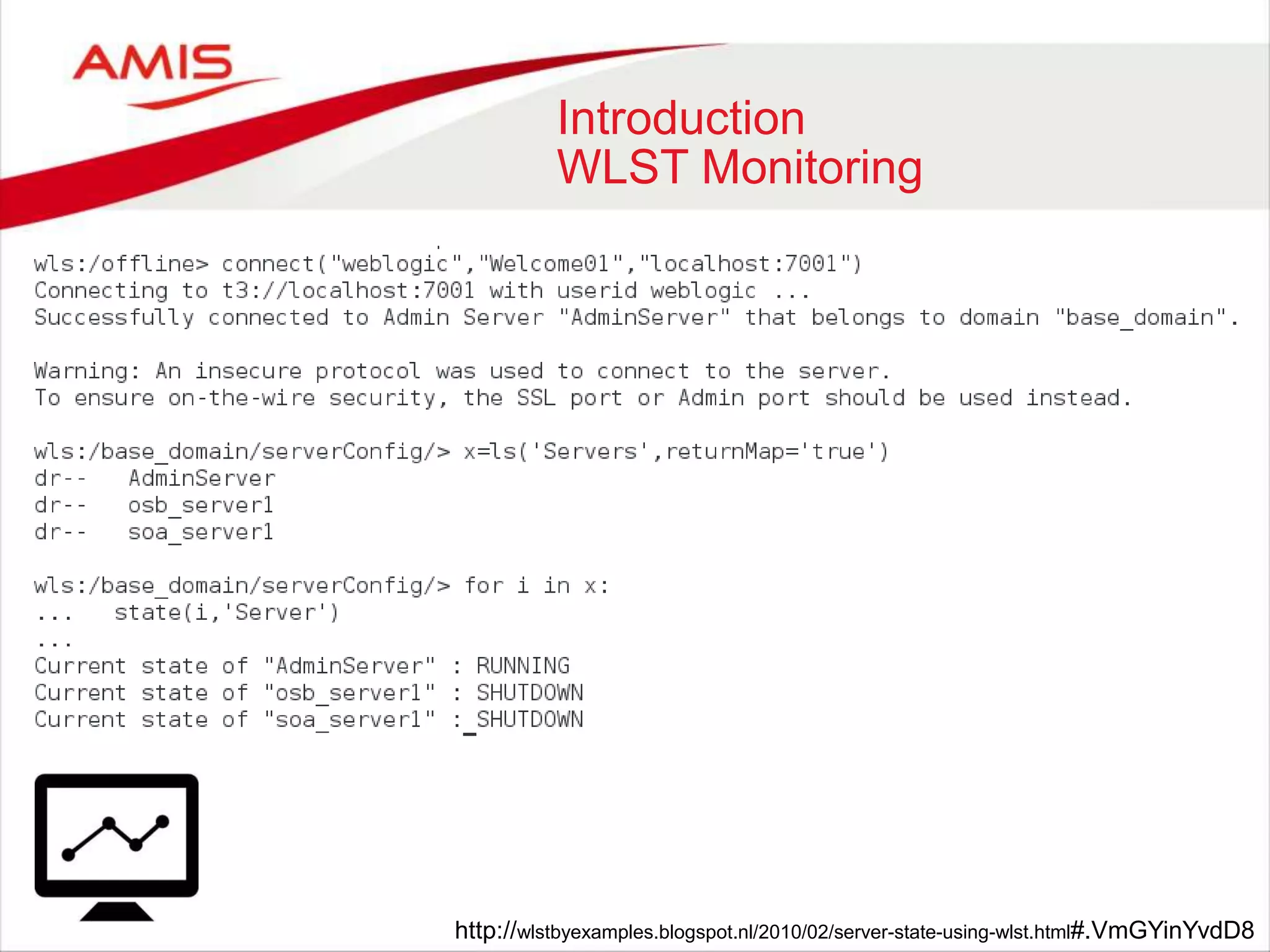
![Using WLST as Jython module
Classpath
• Start wlst.sh / wlst.cmd
– import os
– print os.environ[‘CLASSPATH’]
• Add the wlfullclient.jar and <WLS_HOME>/oracle_common/modules/*
• Done ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/weblogicscriptingtoolmadecool-160605093343/75/WebLogic-Scripting-Tool-made-Cool-30-2048.jpg)