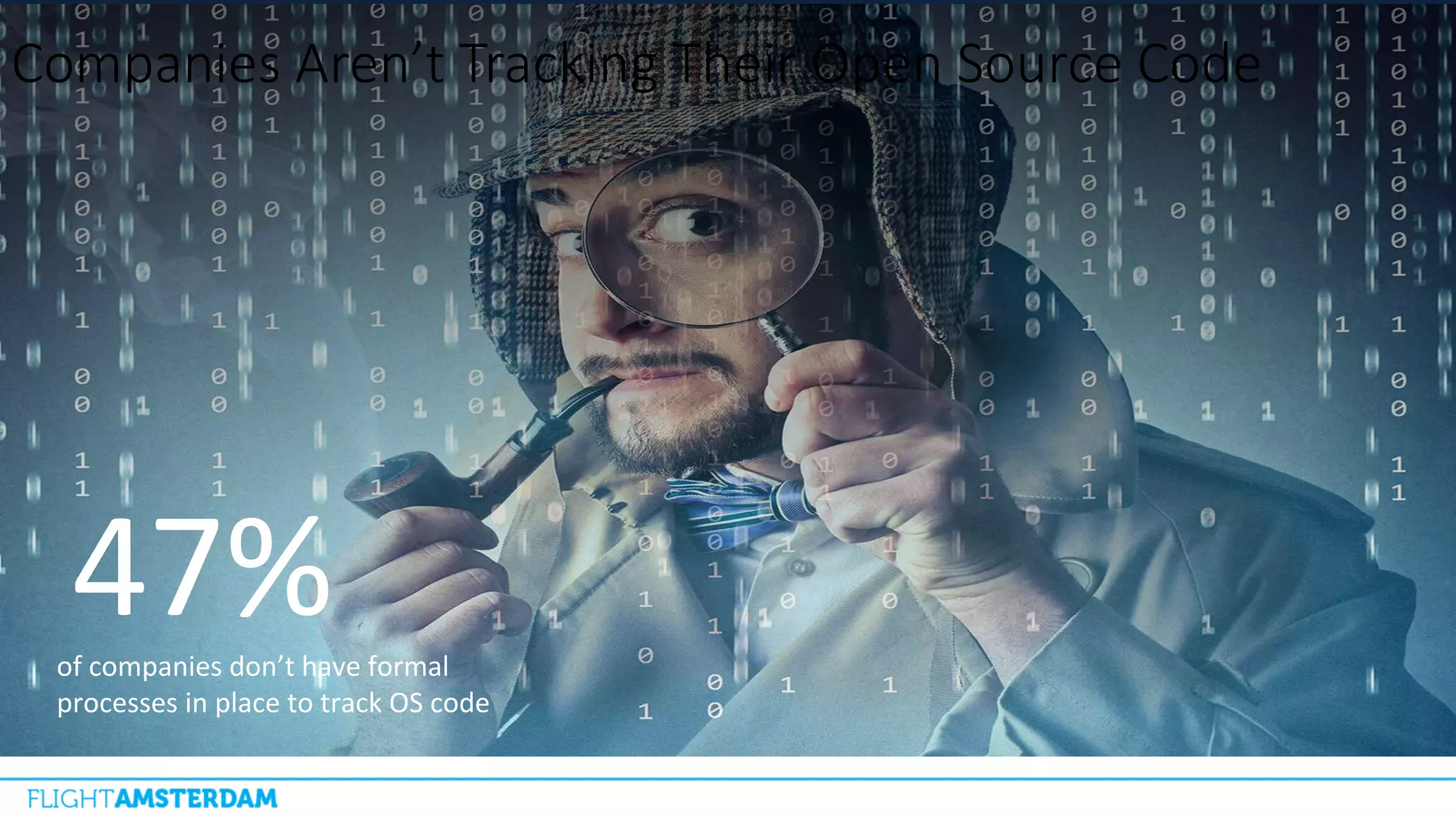
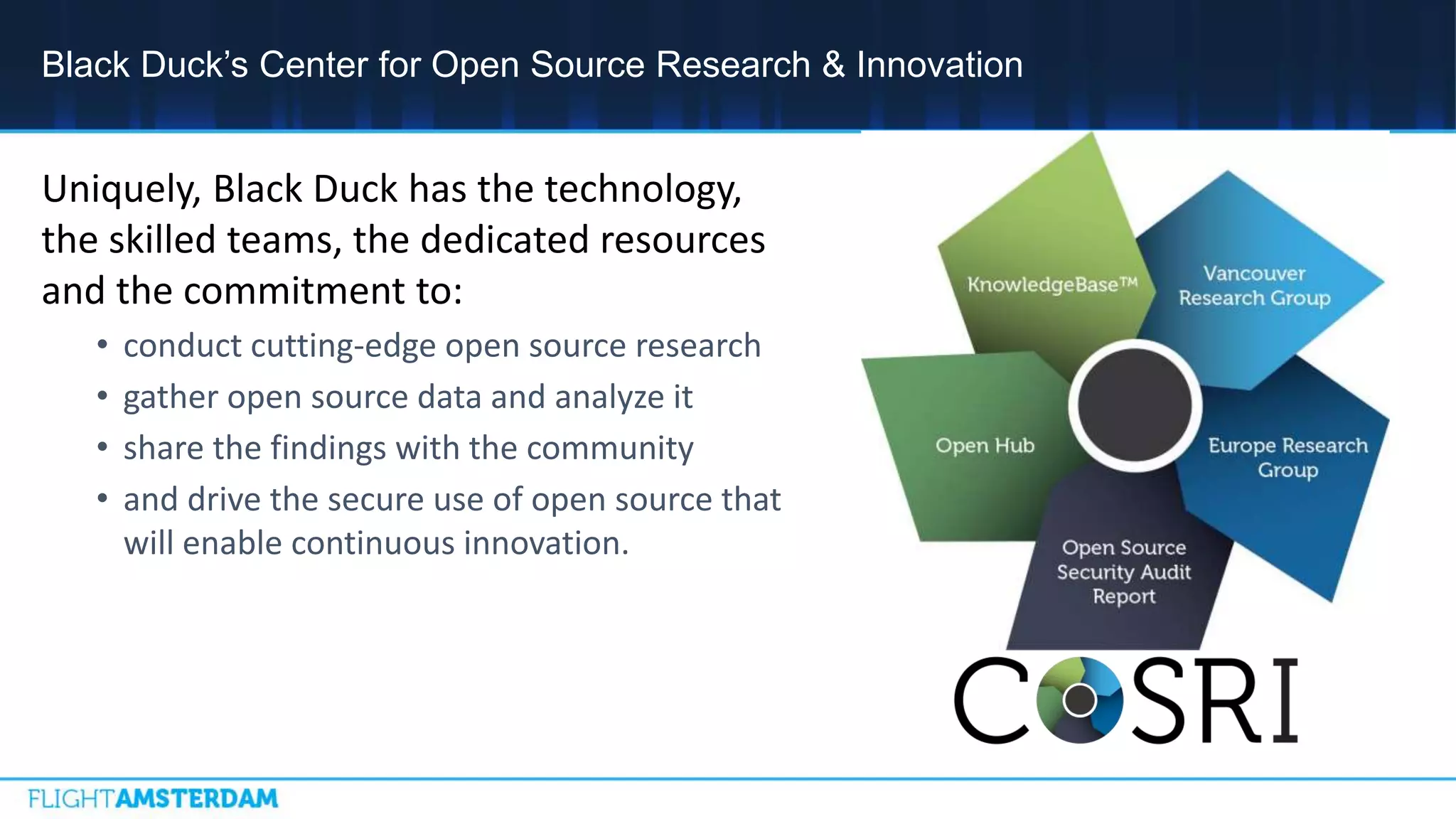
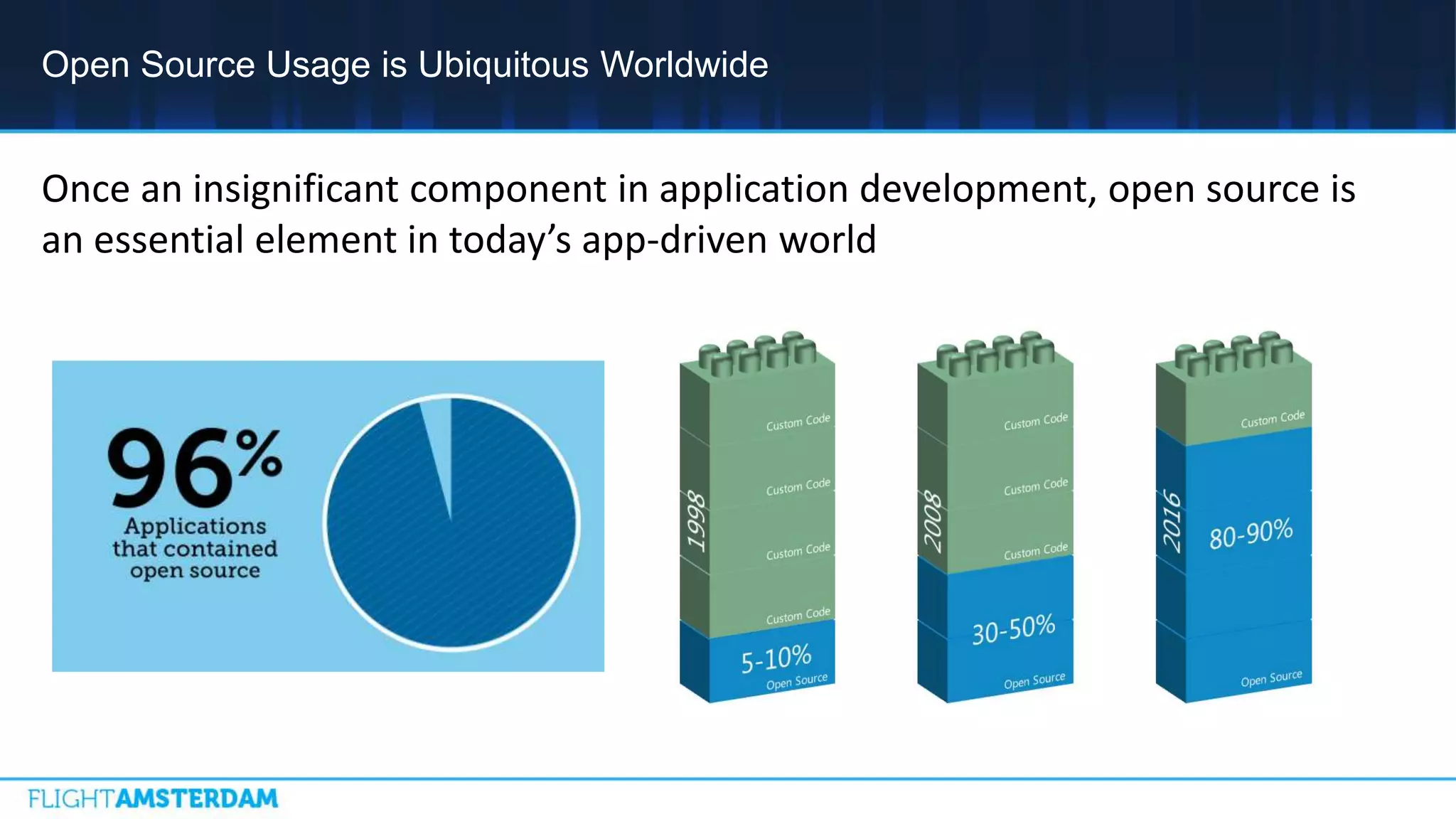
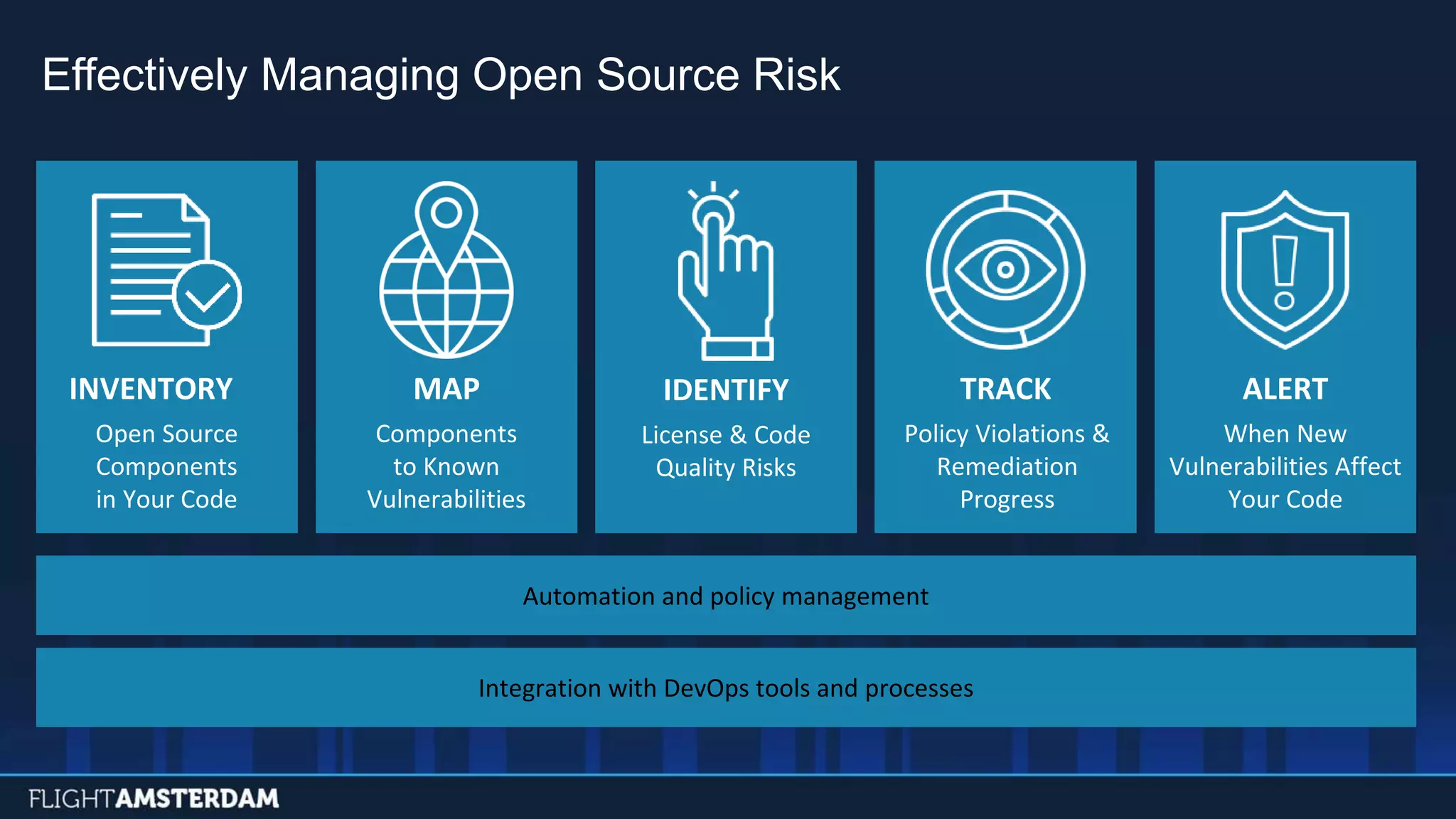
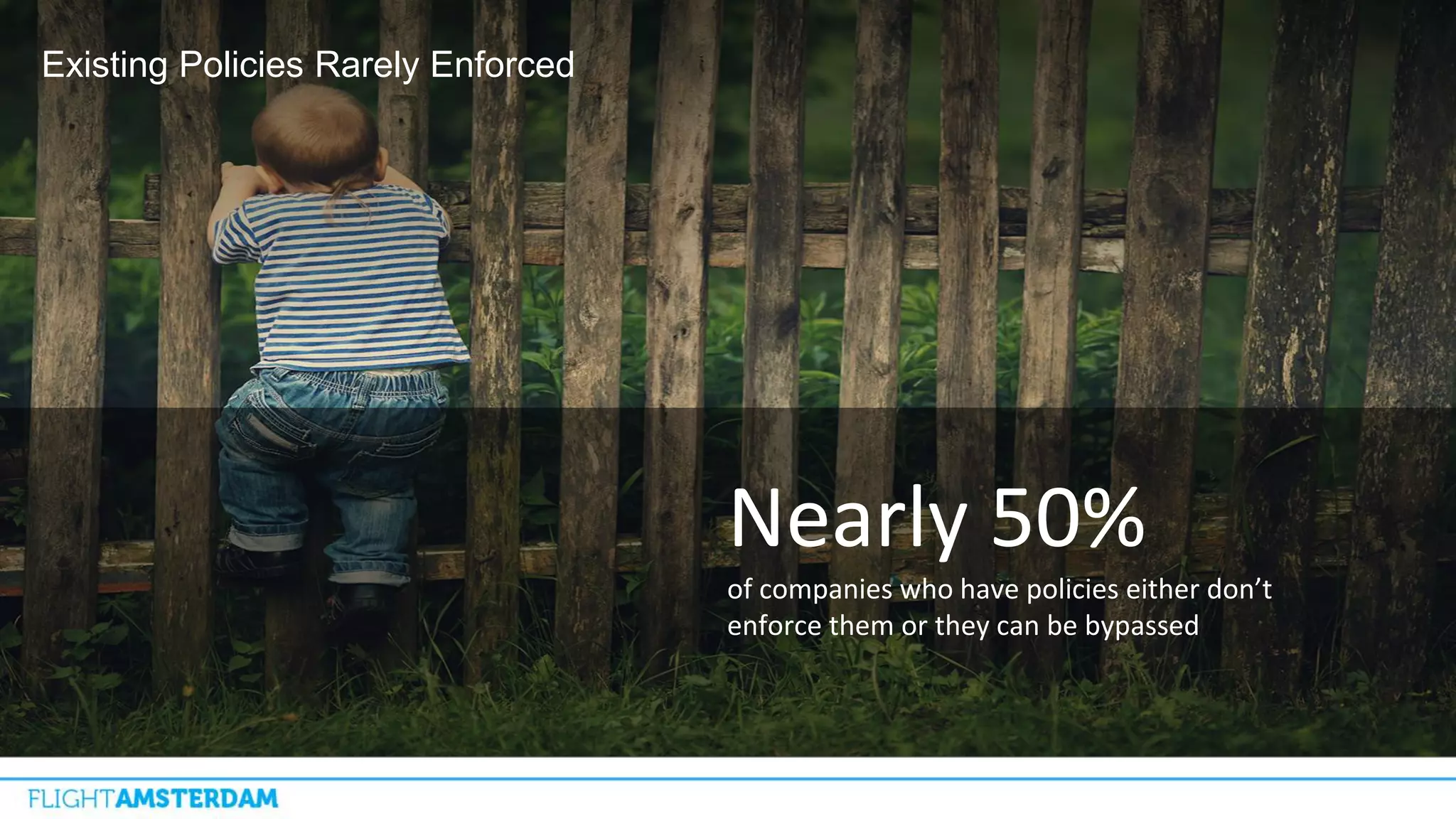
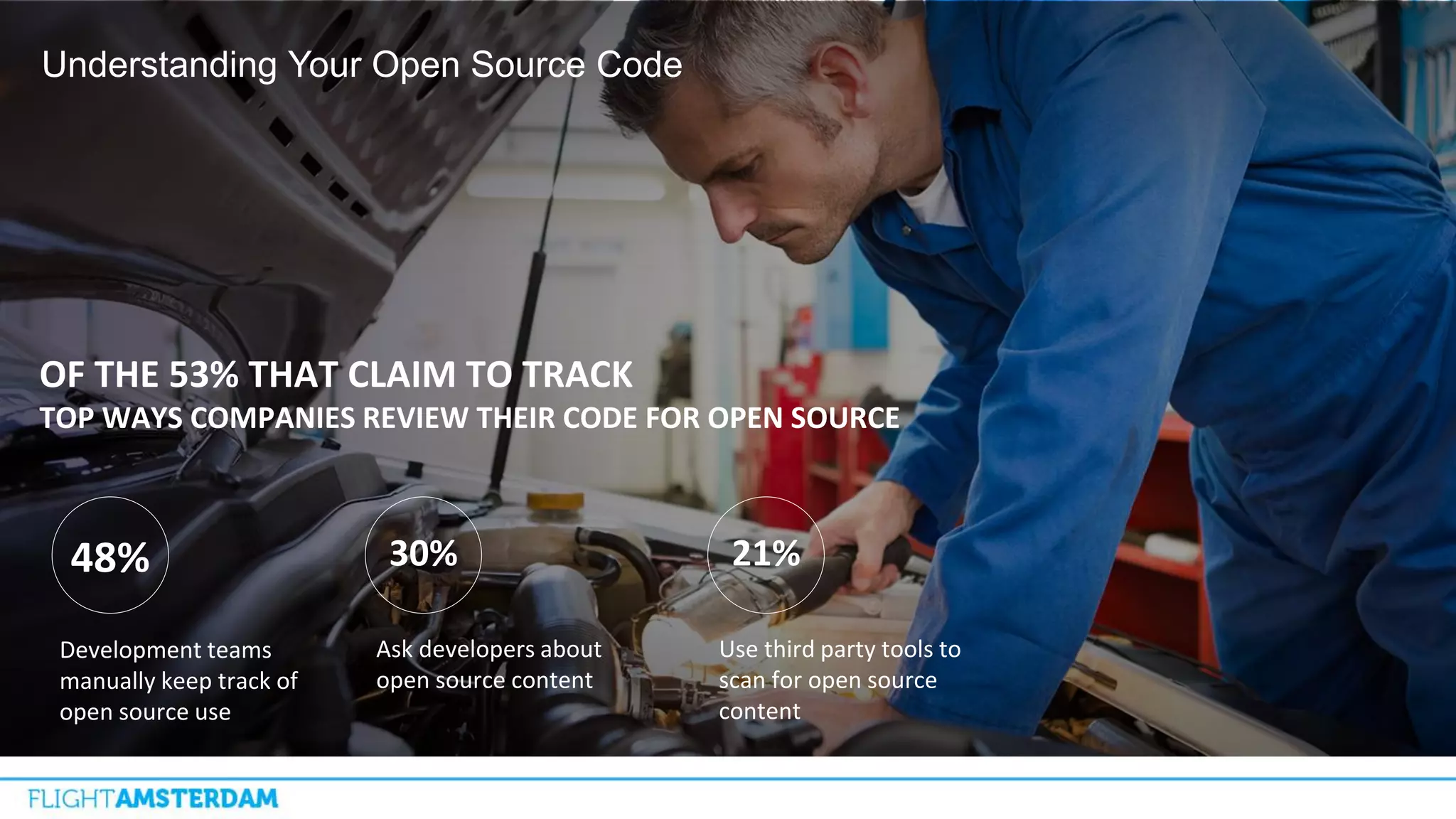
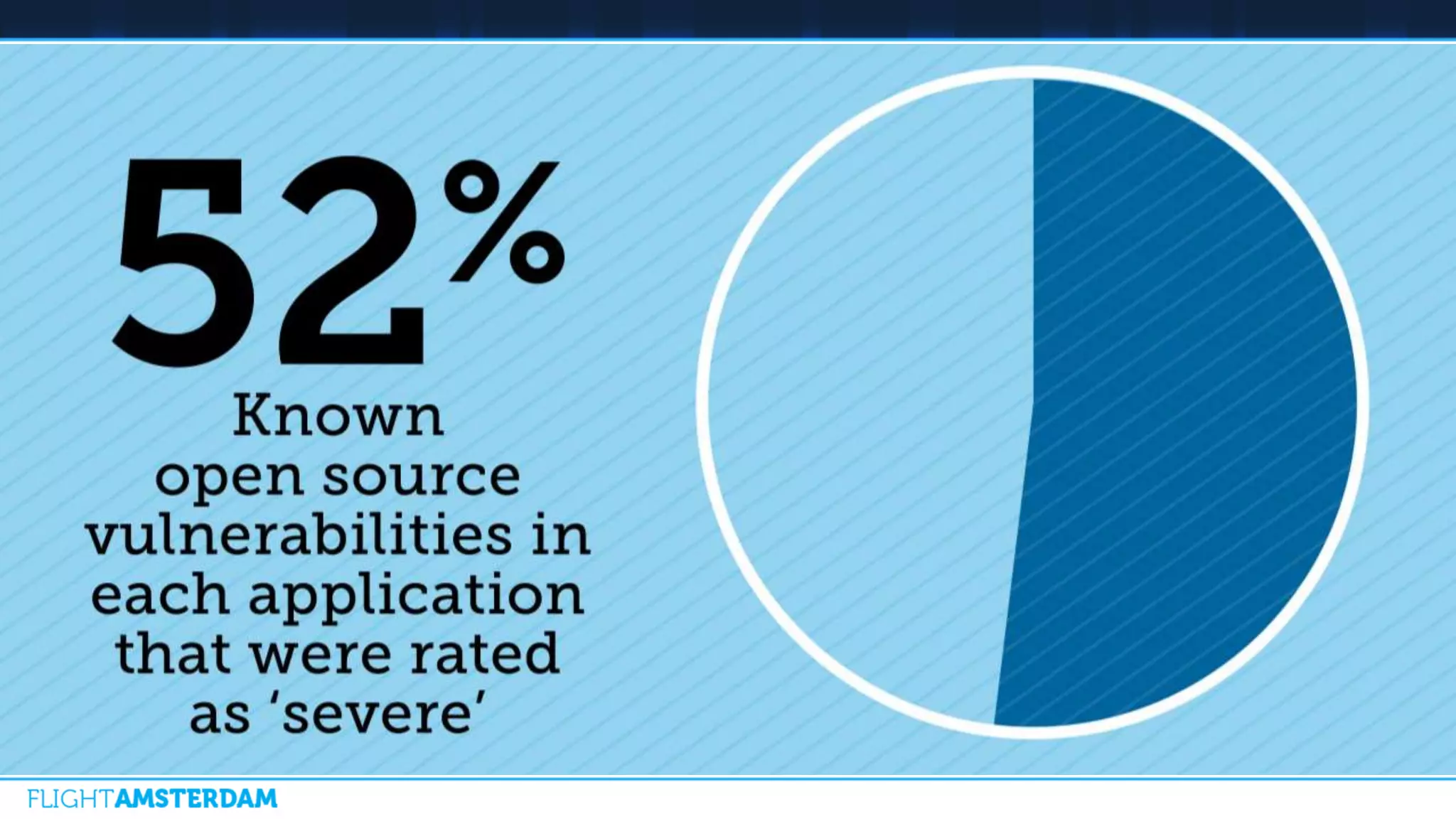
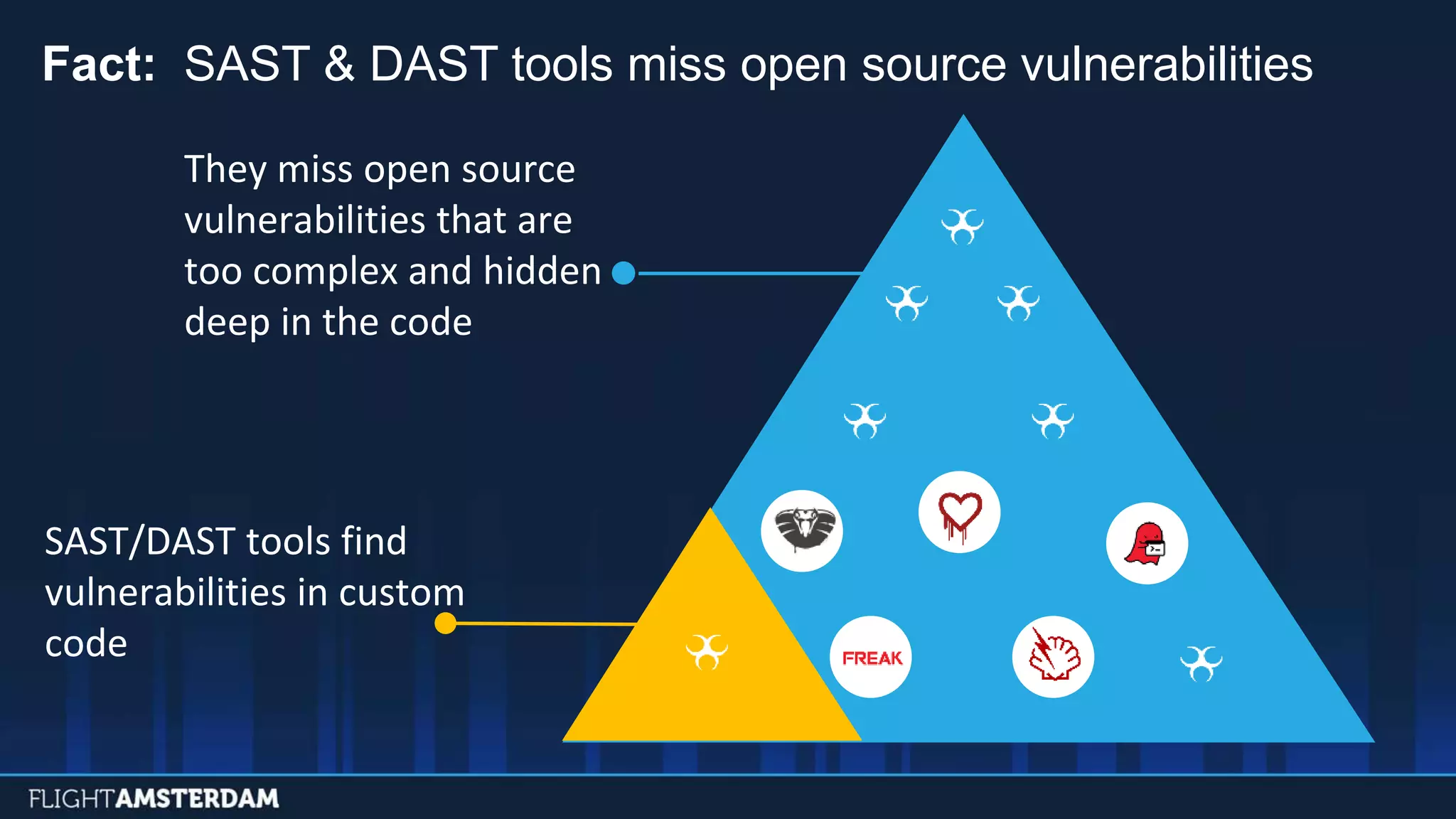
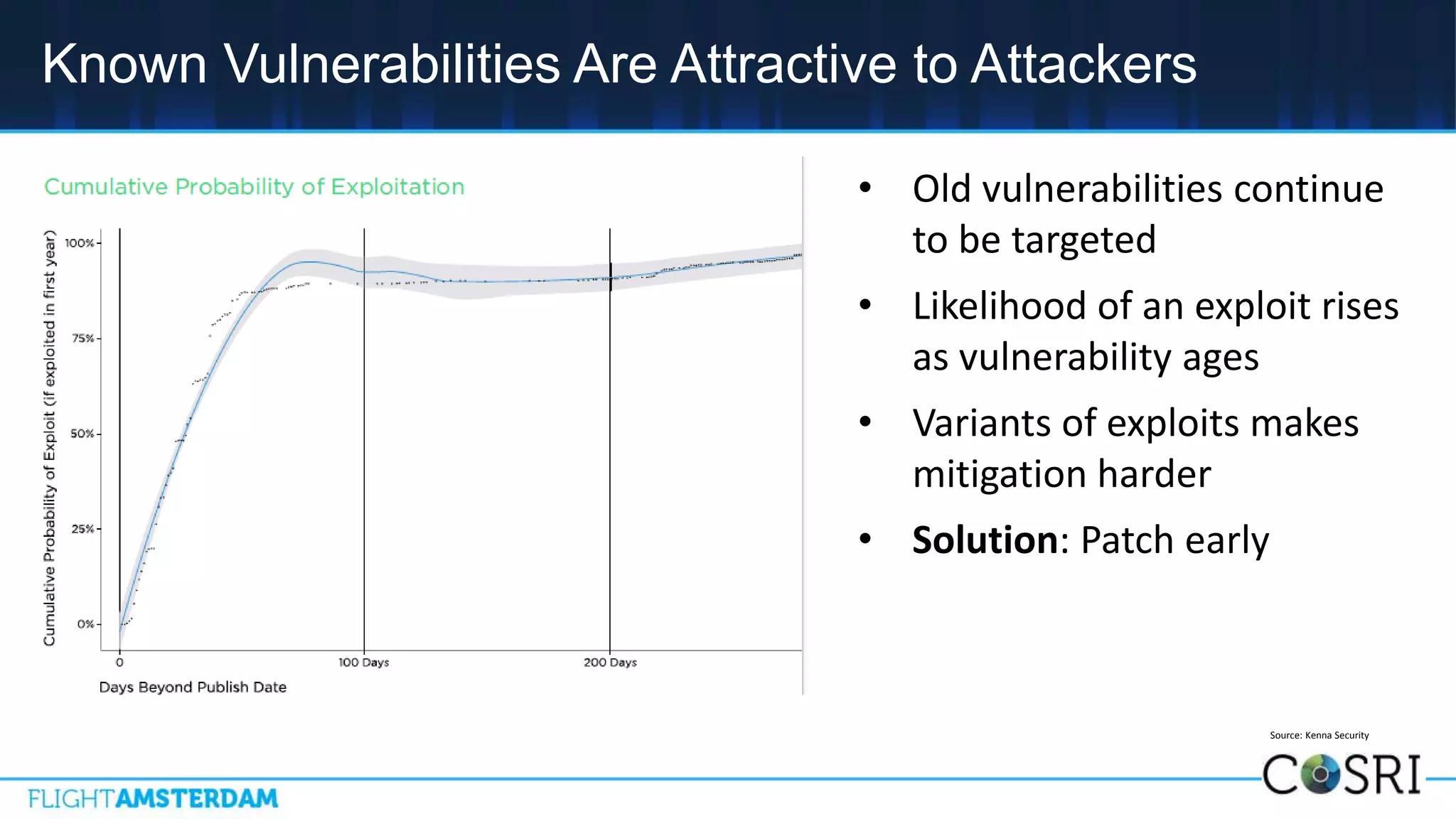
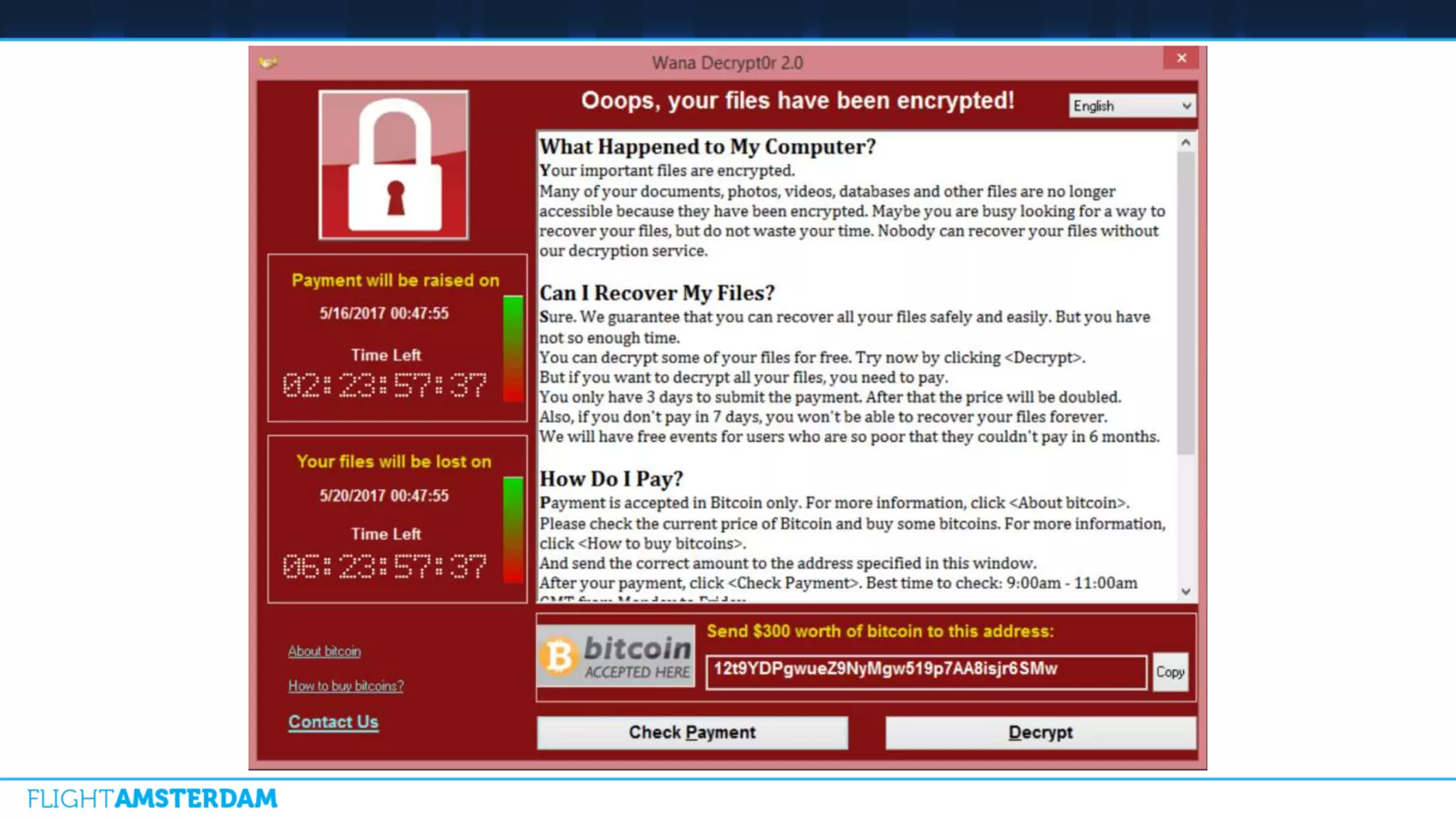
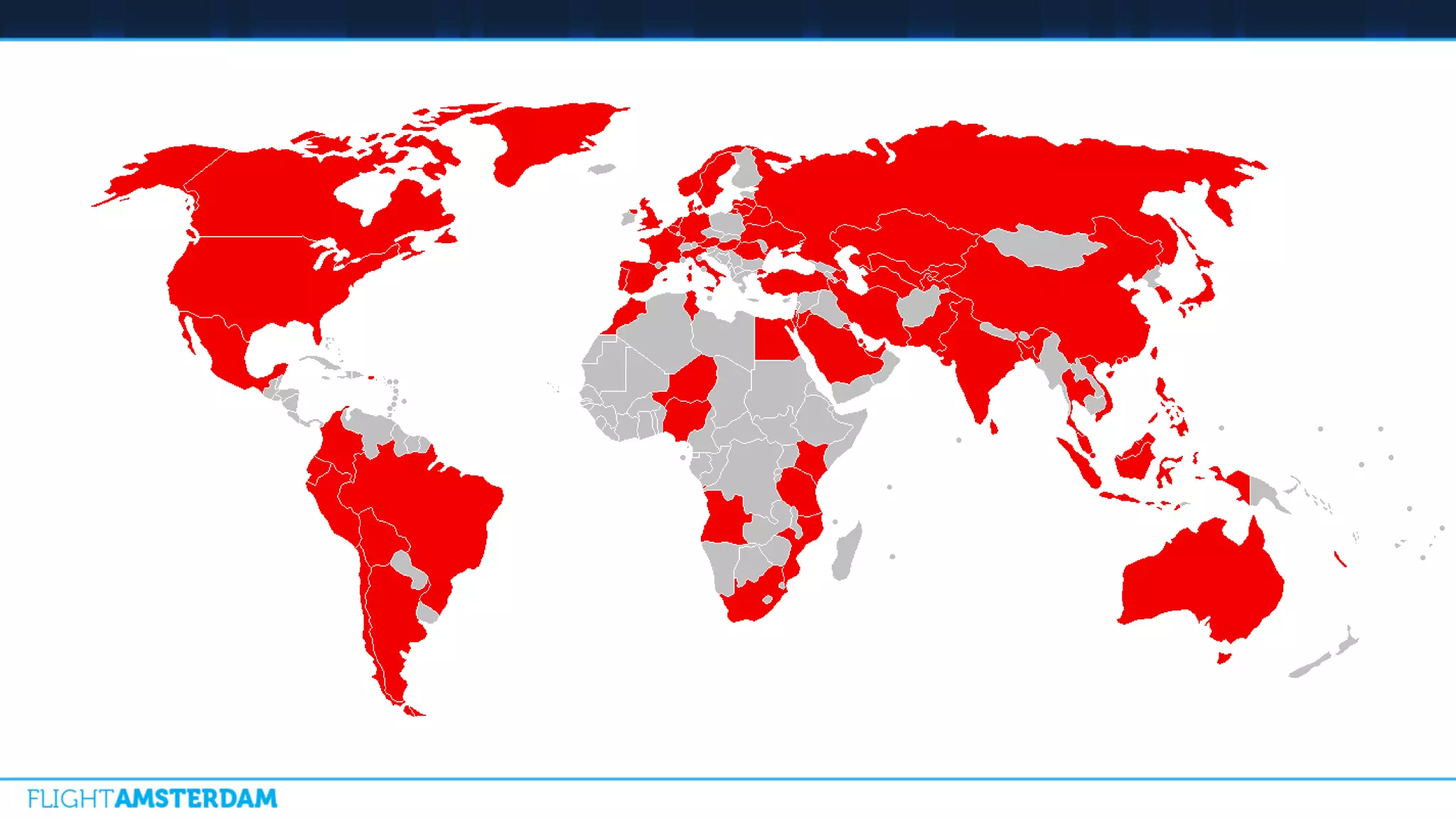
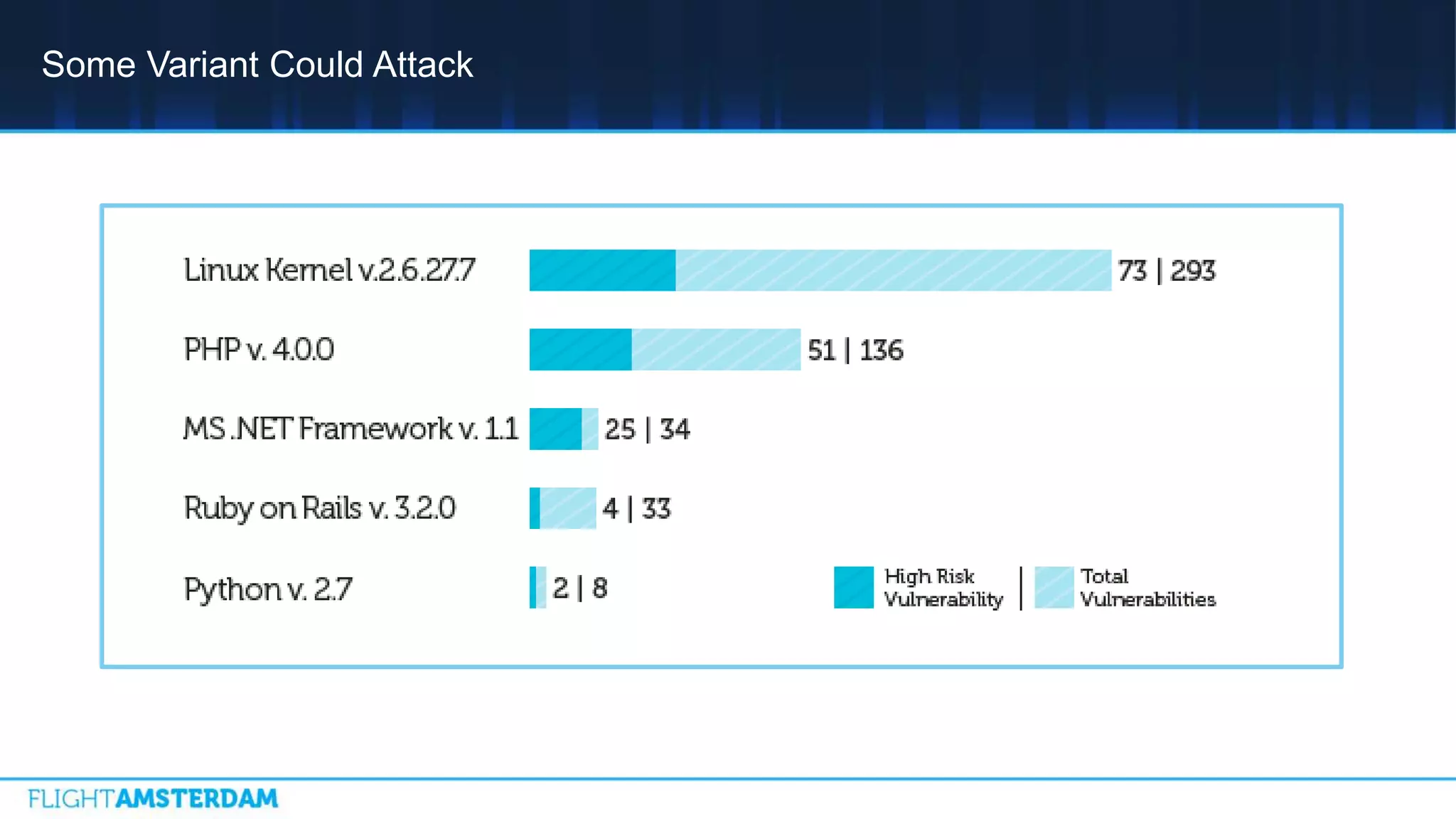
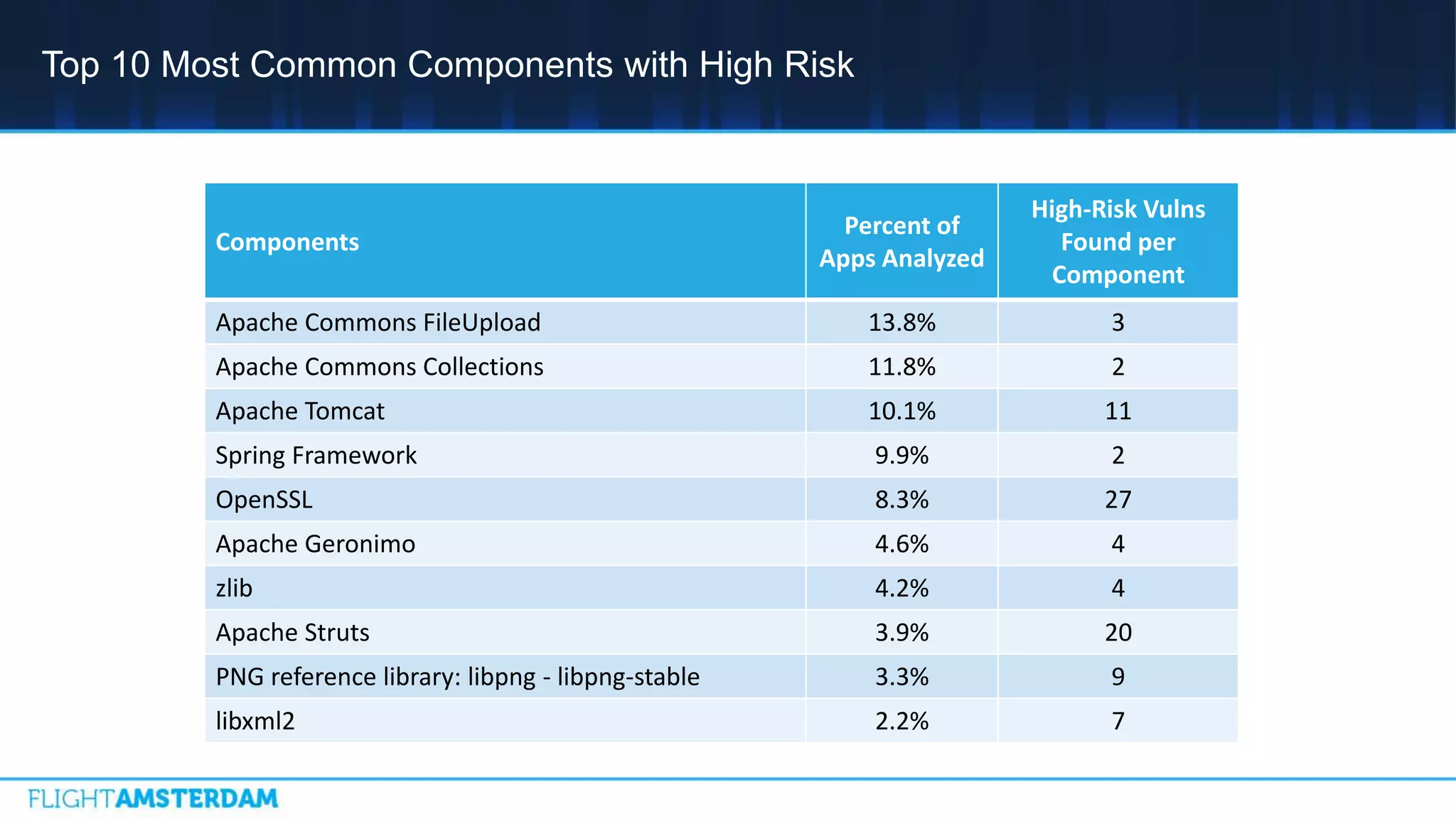
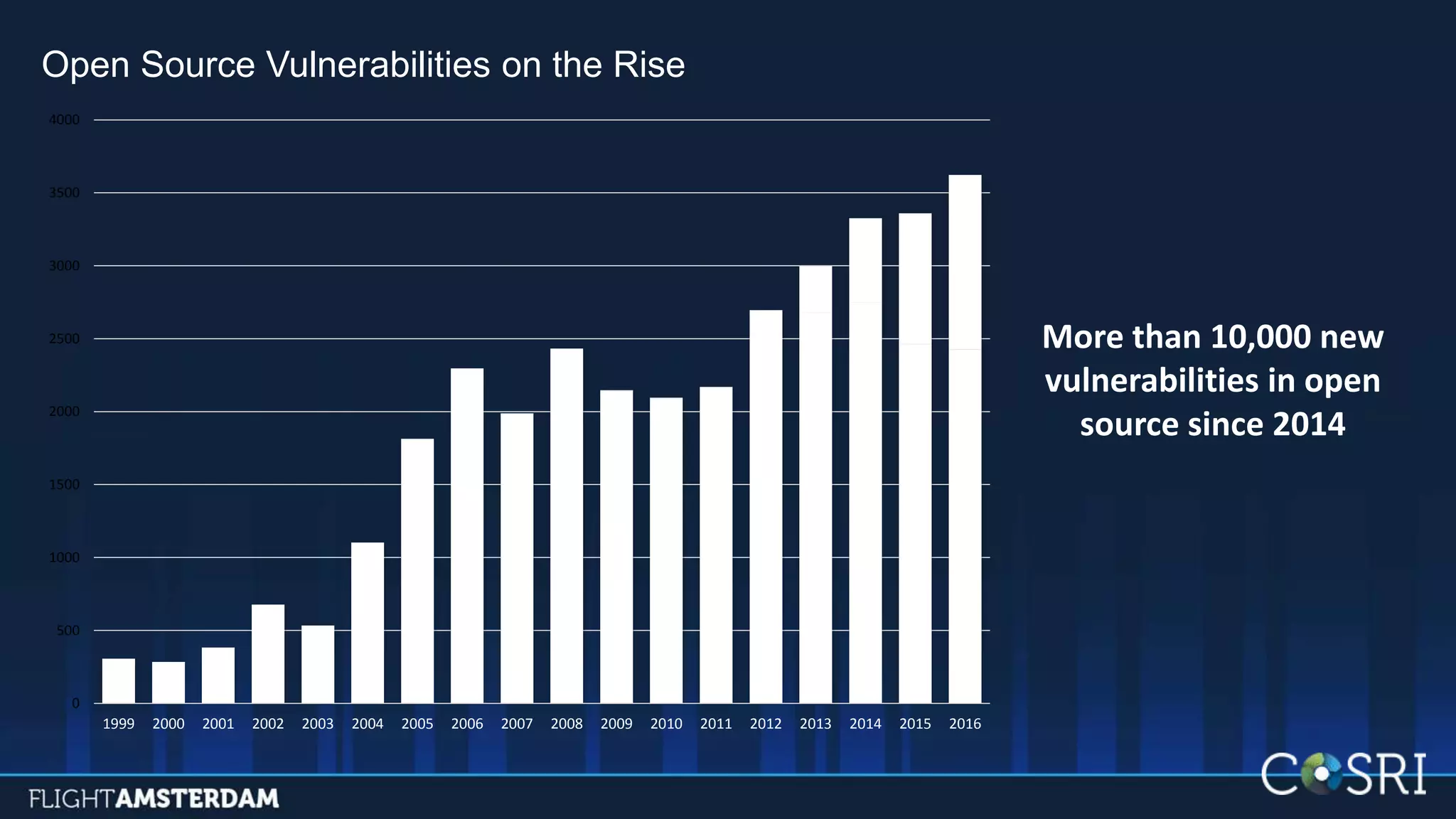
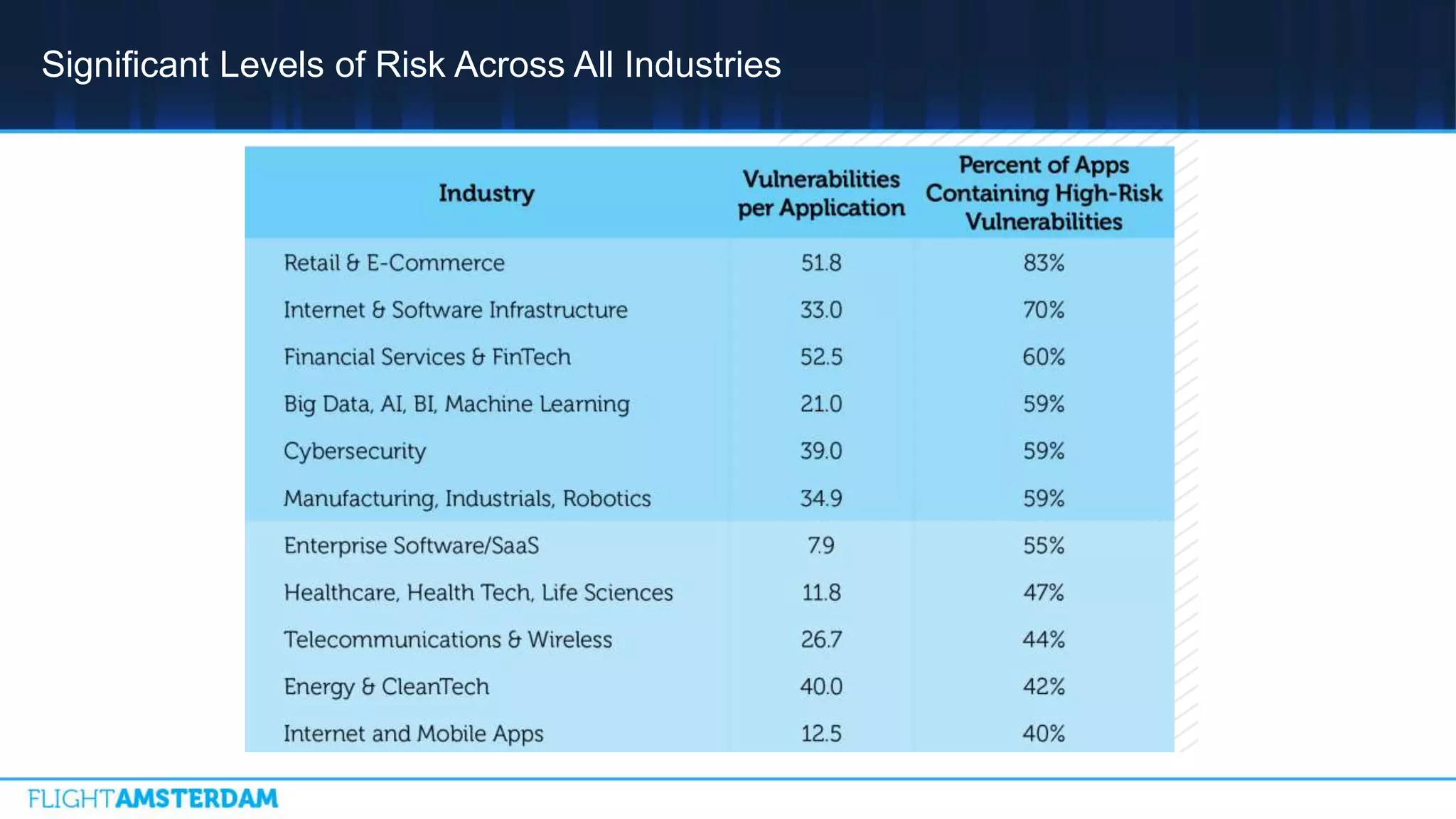
This document summarizes information from a conference on open source software. It discusses trends showing that open source adoption continues to increase rapidly and is now essential to most development strategies. However, open source security and management practices have not kept pace. Many organizations do not have formal policies or processes to track, inventory, or remediate known open source vulnerabilities. Common vulnerabilities in widely used open source components continue to be exploited years later. The document outlines challenges but also the value that open source brings through reduced costs, accelerated innovation, and time to market. It concludes by emphasizing the need for sustained efforts to promote more secure use of open source.