0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views3 pagesCS1 Note 1 - Introduction
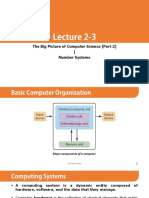
A computer is an electronic device that processes data to provide meaningful information. It has characteristics like speed, accuracy, memory, and versatility. Computers have gone through generations from using vacuum tubes to integrated circuits to modern technology. The basic components of a computer are the input, output, storage, arithmetic logic, and control units. There are different types of computers like notebooks, PCs, workstations, mainframes, supercomputers, and handheld devices.
Uploaded by
Ifat NixCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views3 pagesCS1 Note 1 - Introduction
A computer is an electronic device that processes data to provide meaningful information. It has characteristics like speed, accuracy, memory, and versatility. Computers have gone through generations from using vacuum tubes to integrated circuits to modern technology. The basic components of a computer are the input, output, storage, arithmetic logic, and control units. There are different types of computers like notebooks, PCs, workstations, mainframes, supercomputers, and handheld devices.
Uploaded by
Ifat NixCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3