0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views10 pagesBlock Diagram Guide
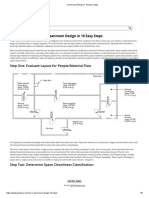
The block diagram shows the key unit operations in a simplified manufacturing process through geometric shapes connected by arrows. It includes the main inputs and outputs at each stage as well as some process parameters. The block diagram is established early in the feasibility study to depict the process at a conceptual level and estimate costs. It serves as a reference throughout the project design phases.
Uploaded by
SwazelleDianeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
173 views10 pagesBlock Diagram Guide
The block diagram shows the key unit operations in a simplified manufacturing process through geometric shapes connected by arrows. It includes the main inputs and outputs at each stage as well as some process parameters. The block diagram is established early in the feasibility study to depict the process at a conceptual level and estimate costs. It serves as a reference throughout the project design phases.
Uploaded by
SwazelleDianeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10