42 500 (0128)
42 500
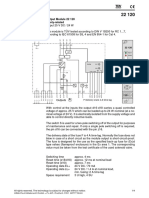
4-fold Selection Element 42 500
safety-related
2 out of 3 selection
The module is TÜV tested according to DIN V 19250 for RC 1...7,
according to IEC 61508 for SIL 4 and EN 954-1 for Cat 4.
42 500
RDY
ERR
Y1
DF1
Y2
DF2
Y3
DF3
Y4
DF4
Outputs k
If at least 2 of 3 inputs z2, d2, z4 (z6, d6, z8 etc.) are set to 1-signal, then
the output z22 (d22 etc.) is also on 1-signal. The outputs are decoupled by
diodes; they can be connected in parallel for OR functions (wired OR).
The switch DZ on the PCB of the module enables the setting of the tole-
rance time for discrepancies of the signals in 15 steps. If the set time is
exceeded, then the output z18 (d18 etc.) is on 1-signal and the LED DF1
(DF2 etc.) is on. The outputs DF are not safety-related; they can be con-
nected via a signal bus to a common annunciation.
All functions on the module are monitored by a micro-controller.
A malfunction is indicated by ERR, the output d28 is on 1-signal and the
relay contact z26-d26 opens.
The output z28-b28 is provided for the connection to the communication
module, e. g. for data transfer to a process control system.
RDY (Ready) indicates the available power supply voltage (≥ 20 V).
Switching time (Y1...Y4) approx. 2 ms
Reset time (Y1...Y4) approx. 5 ms
Switching time (DF1...DF4) 3 ms (at DZ = 0)...15 s, in 15 steps
Reset time (DF1...DF4) approx. 3 ms
Operating data 24 V DC / 90 mA
Space requirement 3 U high, 4 SU
All rights reserved. The technology is subject to changes without notice: 1/4
HIMA Paul Hildebrandt GmbH, P.O. Box 1261, 68777 Brühl
�42 500 (0128)
Communication via MODBUS
Reading of variables
Type BOOL: Function code 1
Type WORD: Function code 3
Events: Function codes 65, 66, 67
Rel. address Data type Value Meaning Rel. event no.
0 WORD 45 H Module type 42 500
1 BOOL 0 none
2 BOOL 1 Module removed
3 BOOL 1 Communication with module not o.k.
4 BOOL 1 Module in slot, communication o.k.
5 BOOL 1 Operating voltage too low, no RDY
6 BOOL 1 Module error, ERR
7...8 BOOL 0 none
9 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z2 0
10 BOOL 1 1-signal at input d2 1
11 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z4 2
12 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z6 3
13 BOOL 1 1-signal at input d6 4
14 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z8 5
15 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z10 6
16 BOOL 1 1-signal at input d10 7
17 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z12 8
18 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z14 9
19 BOOL 1 1-signal at input d14 10
20 BOOL 1 1-signal at input z16 11
21...40 BOOL 0 none
41 BOOL 1 1-signal at output z22 Y1 24
42 BOOL 1 1-signal at output z18 DF1 25
43 BOOL 1 1-signal at output d22 Y2 26
44 BOOL 1 1-signal at output d18 DF2 27
45 BOOL 1 1-signal at output z24 Y3 28
46 BOOL 1 1-signal at output z20 DF3 29
47 BOOL 1 1-signal at output d24 Y4 30
48 BOOL 1 1-signal at output d20 DF4 31
Value: 0 always has the contrary meaning
H: hexadecimal value
absolute address: A = p ∗ 256 + rel. address
absolute event no.: E = (p - 1) ∗ 32 + rel. event no.
p = module location no. in the subrack
2/4
�42 500 (0128)
Reading of all variables
Function code 3, 84 words
since address 2000 H, 3000 H or 4000 H
Word 0 (16 bit) Word 1 (16 bit) Word 2 (16 bit) Word 3 (16 bit)
Rel. address 0 8 . . . . . . 1 24 . . . . . . 17 16 . . . . . . 9 40 . . . . . . 33 32 . . . . . . 25 48 . . . . . . 41
Data Mod. type Mod. state Inputs Inputs none none none Outputs
For a faultless data transfer all 84 words must be read. With that all the
variables of the modules of one subrack are transferred. For module loca-
tions not in use the values 0 are transferred.
3/4
�42 500 (0128)
Communication via Profibus-DP
Reading of variables
Relative addresses type WORD and type BYTE
WORD Bit BYTE Bit Value Meaning
0...7 0 0...7 45 H Module type 42 500
8 0 0 none
9 1 1 Module removed
10 2 1 Communication with module not o.k.
0 11 1 3 1 Module in slot, communication o.k.
12 4 1 Operating voltage too low, no RDY
13 5 1 Module error, ERR
14 6 0 none
15 7 0 none
0 0 1 1-signal at input z2
1 1 1 1-signal at input d2
2 2 1 1-signal at input z4
3 2 3 1 1-signal at input z6
4 4 1 1-signal at input d6
5 5 1 1-signal at input z8
1 6 6 1 1-signal at input z10
7 7 1 1-signal at input d10
8 0 1 1-signal at input z12
9 1 1 1-signal at input z14
10 3 2 1 1-signal at input d14
11 3 1 1-signal at input z16
12...15 4...7 0 none
2 4...5 0 none
0 0 1 1-signal at output z22 Y1
1 1 1 1-signal at output z18 DF1
2 2 1 1-signal at output d22 Y2
3 6 3 1 1-signal at output d18 DF2
3 4 4 1 1-signal at output z24 Y3
5 5 1 1-signal at output z20 DF3
6 6 1 1-signal at output d24 Y4
7 7 1 1-signal at output d20 DF4
8...15 7 0...7 0 keine
Value: 0 always has the contrary meaning
H: hexadecimal value
absolute address WORD: W = 4 ∗ (p - 1) + rel. address
absolute address BYTE: B = 8 ∗ (p - 1) + rel. address
p = module location no. in the subrack
4/4