0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views23 pages(Lesson1) COMPUTERBASICS
This document provides an overview of living in the IT era, including:
- The purpose of information systems is to manage and process data using computers, which typically include people, software, hardware, procedures, and data.
- There are different types of computers like desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, as well as larger computers like supercomputers and mainframes. Hardware and software work together, with software telling hardware what to do.
- System software controls computer operations and includes the BIOS, operating system, and utilities, while application software performs specific tasks like productivity apps.
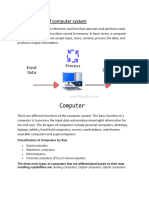
- A computer system takes inputs, processes them, and creates outputs, and includes components for input, processing, storage,
Uploaded by
rltmorenoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views23 pages(Lesson1) COMPUTERBASICS
This document provides an overview of living in the IT era, including:
- The purpose of information systems is to manage and process data using computers, which typically include people, software, hardware, procedures, and data.
- There are different types of computers like desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, as well as larger computers like supercomputers and mainframes. Hardware and software work together, with software telling hardware what to do.
- System software controls computer operations and includes the BIOS, operating system, and utilities, while application software performs specific tasks like productivity apps.
- A computer system takes inputs, processes them, and creates outputs, and includes components for input, processing, storage,
Uploaded by
rltmorenoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23