0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views9 pagesPF Lab 1
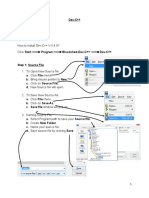
Dev-C++ is a free integrated development environment for C/C++ programming that runs on Windows. It allows users to edit, compile, link, and debug C/C++ programs. The tutorial outlines the basic steps for using Dev-C++: creating a project, writing source code, compiling and linking the code, executing the program, and debugging any errors. Key features of Dev-C++ include a source code editor, project explorer, and results window to display compilation output.
Uploaded by
shaharyarbajwa3Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views9 pagesPF Lab 1
Dev-C++ is a free integrated development environment for C/C++ programming that runs on Windows. It allows users to edit, compile, link, and debug C/C++ programs. The tutorial outlines the basic steps for using Dev-C++: creating a project, writing source code, compiling and linking the code, executing the program, and debugging any errors. Key features of Dev-C++ include a source code editor, project explorer, and results window to display compilation output.
Uploaded by
shaharyarbajwa3Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9