0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views18 pagesLab Results Vlsi
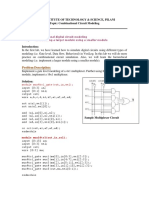
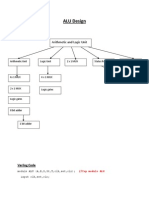
The document describes the Verilog code implementation and simulation of various digital logic circuits including logic gates, adders, decoders, encoders, multiplexers, converters and flip-flops. Code examples are provided for different modeling styles along with test benches and simulation waveforms to verify the circuit outputs.
Uploaded by
pankaj rangareeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views18 pagesLab Results Vlsi
The document describes the Verilog code implementation and simulation of various digital logic circuits including logic gates, adders, decoders, encoders, multiplexers, converters and flip-flops. Code examples are provided for different modeling styles along with test benches and simulation waveforms to verify the circuit outputs.
Uploaded by
pankaj rangareeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18