0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesSynthesisMatrixTemplate Edited
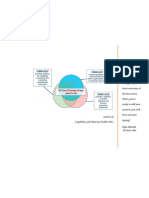
The document discusses sources related to the effects of smartphone usage on teenagers' mental health. It identifies themes across the sources, including the impacts of smartphones on adolescent mental health, smartphone addiction, and other effects of addiction such as mood disturbances, depression, reduced physical activity, and academic impacts. The document extracts evidence from the sources and organizes it into a synthesis matrix to analyze these recurring themes.
Uploaded by
gitaumary045Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesSynthesisMatrixTemplate Edited
The document discusses sources related to the effects of smartphone usage on teenagers' mental health. It identifies themes across the sources, including the impacts of smartphones on adolescent mental health, smartphone addiction, and other effects of addiction such as mood disturbances, depression, reduced physical activity, and academic impacts. The document extracts evidence from the sources and organizes it into a synthesis matrix to analyze these recurring themes.
Uploaded by
gitaumary045Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6