0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views8 pagesNotes
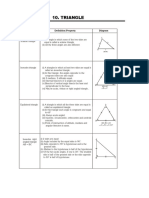
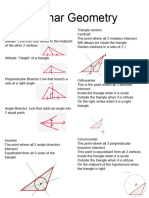
The document provides definitions and classifications of geometric shapes including points, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and polygons. It details types of triangles based on sides and angles, as well as properties of various quadrilaterals. Additionally, it distinguishes between regular and irregular polygons based on the equality of their sides and angles.
Uploaded by
saumyatanna1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views8 pagesNotes
The document provides definitions and classifications of geometric shapes including points, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and polygons. It details types of triangles based on sides and angles, as well as properties of various quadrilaterals. Additionally, it distinguishes between regular and irregular polygons based on the equality of their sides and angles.
Uploaded by
saumyatanna1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8