3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
Introduction to Microcomputer Studies and Information Technology
I
Home / My courses / OCP 100 / PART 1: Microcomputer Technology/Parts / Lecture 2: Notes
Lecture 2: Notes
LECTURE TWO
HARDWARE TECHNOLOGIES
INTRODUCTION
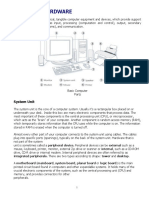
Computer hardware is the collection of physical parts both internal (HDD, motherboard) and external (computer case, monitor, keyboard,
mouse) of a computer system. Computer hardware is what you can physically touch.
In this lecture, the basic and primary computer hardware devices are discussed with focus on their use and functionalities within computer.
LECTURE OBJECTIVES
It is expected that at the completion of this lecture, you should be able to:
(i) Explain the concept of computer hardware.
(ii) List, describe and compare the functionalities of various hardware devices such as monitor, keyboard,
scanner, etc.
(iii) Describe and give examples of input devices.
(iv) Describe and give examples of output devices.
INTRODUCTION TO HARDWARE
Computer hardware is one of the major two parts of computer. It is the collection of physical parts of a computer system. This includes the
computer case, monitor, keyboard, and mouse. It also includes all the parts inside the computer case, such as the hard disk drive,
motherboard, video card, and many others. Computer hardware is what you can physically touch. Computer cannot function without
hardware. Some hardware components are easy to recognize, such as the computer case, keyboard, and monitor while some are inside the
computer case. Most of the hardware devices work either as input or output devices which are typically housed externally to the main
computer chassis.
Generally, the concept of hardware includes computer components, the physical and tangible parts of the computer, i.e., electrical, electronic
and mechanical parts which comprise a computer. Basic computer working principle is given in the Fig. 14 below:
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 1/8
�3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
Figure 14: Computer working principle
Computer working principle: data are entered into a computer via input devices, then are processed and stored in a system unit, and are
finally displayed by the output device
INPUT/OUTPUT FUNCTION
In Computing, Input/Output (I/O) refers to the communication between an information processing system such as computer and the
outside world possibly human or another information processing machine. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system, and
outputs are the signals or data sent from it. Keyboards and Mouse are considered as input devices of a computer, while Monitor and Printers
are considered output devices of a computer. Devices for communication between computers such as modems and networks cards typically
serve for both input and output. Note that the designation of a device as either input or output depends on the perspective. Mice and
keyboards take as input physical movement that the human user outputs and convert it into signals that a computer can understand. The
output from these devices is input for the computer. Similarly, printers and monitors take as input signals that a computer output. They then
convert these signals into representations that human users can see or read.
INPUT DEVICES
Input devices allow the user to enter information into the system or control its operation. Most personal computers have a mouse and
keyboard, but laptop systems typically use a touchpad insteadofamouse.Otherinputdevices include webcams, microphones, joysticks, and
image scanners.
Keyboard
Keyboard is the most commonly used input device and it is an adaptation of the typewriter. Keyboard is used for data entry and issuing
commands. They can also be wired or wireless. Computer keyboards contain several types of keys to input data and issue commands. A
keyboard has an additional numerical pad and function keys (F1 – F12). The function keys provide special functions depending on the
software you are using. A Numeric Keypad is a calculator-style set of keys for entering numbers.
Figure 15: Computer Keyboard
A QWERTY Keyboard is the standard typewriter keyboard layout, used for computer keyboards. It is the most frequently used input device
for all computers. The keyboard provides a set of alphabetic, numeric, punctuation, symbol, and control keys. Some of the major keys and
their functionalities in the keyboard include:
ENTER or RETURN - Moves the cursor down one line and to the left margin.
DEL or DELETE - Deletes the character at cursor and/or characters to the right of the cursor and all highlighted (or selected) text.
BKSP or BACKSPACE - Deletes the character to the left of cursor and all highlighted text.
SPACE BAR - Moves the cursor one space at a time to the right. SHIFT KEY - Use the shift keys to type capital letters and to type the
upper character on keys with two characters on them.
CAPS LOCK - Locks the keyboard so it types capital letters (a light goes on when caps lock is on).
TAB - Moves the cursor five spaces to the right.
ESC or ESCAPE - Cancels a menu or dialog box, a command or an operation.
ARROW KEYS - Moves the cursor around document without changing text.
FUNCTION KEYS or F KEYS - Access commands by themselves or in combination with the three command keys; CTRL, SHIFT, and ALT.
Command or Special Keys: Command keys normally do nothing on their own but work in combination with other keys. The Control key
or Ctrl is often used to access commands. It is pressed in combination with other keys, acts as a shortcut to execute commands and to
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 2/8
�3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
select commands from the drop-down menus. The Alternative key or Alt is often used to access menus. The Shift key is used to type
CAPITAL LETTERS.
NumLock – This key switches the right-hand keypad between typing numbers and being used as cursor keys.
Page Up (Pgup) and Page Down (PgDn). These keys move the cursor to the preceding screen (PgUp) or the next screen (PgDn).
ACTIVITY 1
Find out the commercial and public domain programs that are designed for typing practices. Follow step by step
typing tutorials and learn how to type and increase your typing speed.
Disks
A disk is a round plate on which data can be encoded. There are two basic types of disks: magnetic disks and optical disks. Magnetic disks
allow to record and erase data any number of times. Examples of magnetic disks are Floppy disk (diskettes), Hard disk and Flash disk. Hard
disks are placed inside the computer and they were originally called “fixed disks” or “Winchesters”.
Figure 16: Hard disk
Hard disks are measured in terms of Gigabyte (GB), Terabyte (TB), Petabyte (PB), Exabyte (EB), etc. The relationships between these units are:
1 TB = = 1000 or 1024 GB
1 PB = = 1000 or 1024 TB
1 EB = = 1000 or 1024 PB
The optical disks record data by burning microscopic holes in the surface of the disk with a laser. To read the disk, another laser beam
shines on the disk and detects the holes by changes in the reflection pattern. The optical disks come in three basic forms: CD-ROM (read-
only), WORM (write-once, read-many) and Erasable Optical Disk (EO Disk). Note that CD-ROM (Compact Disk - Read Only Memory)) and
WORM disks are not erasable while EO disks can be read to, written to, and erased just like magnetic disks. The machine that reads or writes
information to a disk is called a disk drive.
Figure 17: Optical disk
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 3/8
�3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
The CD-R Drive (Compact Disk-Recordable drive) is a type of disk drive that can create CD-ROMs and audio CDs. To create CD-ROMs and
audio CDs, you’ll need not only a CD- R drive, but also a CD-R software package. The CD-RW DISK (CD-ReWritable disk) is a type of CD disk
that enables you to write onto it in multiple sessions. One of the problems with CD-R disks is that you can only write to them once. The
capacity of the most widely available CD format is expressed either as 74 minutes or 650MB.
ACTIVITY 2
Find a new CD-R, CD-RW or DVD and copy or burn the software from the internet or other disk. Explain the
software used to perform this activity. Find-out the storage capacity of the following formatted devices: CD-R, CD-
RW, all types of DVD, floppy disks, all types of flash disks, Hard disks, etc. Why is it advisable to make a backup of
your files in these types of storage media?
Mouse
Mouse controls the pointer on your computer screen that is housed in a palm-sized case. When you move it on your desk, the
corresponding arrow, commonly known as the pointer, move on the computer screen. Use of mouse can eliminate many keyboard strokes.
The flashing bar, known as cursor, is where the work will take place on the computer screen.
To move the cursor with the mouse, place the pointer where you want the cursor to appear and click the mouse. The ordinary mouse has
two buttons: the left one is used to select objects and text and the right one is used to access menus. Sometimes a mouse comes with a
middle button or a scroll wheel between the left and right buttons.
Figure 18: Mouse
In particular, the mouse is important for Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) because you can simply point-and-click. You can never do any
harm by clicking on something with the right mouse button. The different mouse operations include:
Point - Move the mouse so that the mouse pointer rests on the required object such as icon, name of a menu, button in a dialog box,
character in a document, shape in a picture, etc.
Click - Press and release the left mouse button. Clicking selects an object, a command or a program.
Double Click - A double-click is a quick succession of two clicks in the same spot.
Drag - Dragging lets you move items around in windows or on the desktop. Point at an object, press a mouse button, hold it down, move the
mouse to a new position, then release the mouse button. (is sometimes referred to as drag-and-drop).
So, generally, a mouse is an input device that facilitates work with the graphical user interface (GUI). The mouse transmits hand movements
and the screen displays the cursor (mouse pointer) movements. They are divided into mechanical and optical (with respect to a transfer
movement), and wired and wireless (with respect to connection). Trackball, unlike a mouse, is not movable. Hand movements are transmitted
to the screen by rolling the ball which is located on the upper side of the device.
Scanners
The optical scanner resembles small photocopier and acts as input device. They operate by reading light reflected from the surface of an
object such as a photograph, figures, or printed materials such as text. The scanner is accompanied by software that allows it to have control
over the scanned image.
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 4/8
�3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
Figure 19: Scanner
Scanners allow you to transfer pictures, photographs or images to your computer. A scanner “scans” the image from the top to the bottom,
one line at a time and transfers it to the computer as a series of bits or a bitmap. With Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software you
can convert printed documents to text that can be used in your word processor. Generally, scanner is used to load data (image, text, etc.)
from the printed material into a computer. The result of scanning is an image, but with special programs, if we scan the text, we can get a
text as a result. Software used to recognize text from image is called a text recognition tool.
ACTIVITY 3
Discuss the functionalities of other input devices such as bar code readers, light pen, track ball, digital camera and
touch screens.
Other types of input devices include:
Touchpad is used for transmission of hand movement, but unlike working with a mouse, the user is the one who determines the position
of the cursor by touching the touchpad.
Lightpen enables handwriting on screen and can be used as a mouse. It requires an appropriate monitor type.
Joystick is mainly used in computer games. Unlike a mouse, it has many buttons which allow control over game objects.
Microphone is a device that converts sound into an electrical signal, which can be stored on a computer. It is mainly used for recording
sound, communication between players in online games, in combination with a web camera in video conferencing, for converting voice
into text on a computer (speech-to-text processing (e.g., textual files or emails), etc.
Webcam is a camera that stores video signal in a format appropriate for video transfer over the Internet in Realtime.
Digital camera, unlike analog, stores photographs in digital format. It can be directly connected to a computer and photographs can be
downloaded. Photograph quality is expressed in megapixels. More megapixels mean better quality of photograph; however more
memory is occupied.
OUTPUT DEVICES
Output devices display information in a human readable form. Such devices could include monitors, printers, speakers, projectors, etc.
Monitor
Monitor is an output device which shows information on the screen when you type. Monitors come in many types, sizes and different color
screens. It attaches to the video output of the computer called Video Display Unit (VDU). The common monitor interfaces are Cathode Ray
Tube (CRT) and flat screen Liquid Crystal Display (LCD).
Figure 21: Flat Panel (LCD) Monitor
Figure 20: CRT Monitor Figure 22: LCD Monitor
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 5/8
�3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
Flat panel displays are small and do not flicker, they consume very little power, so they are ideal for portable computers. In comparison with
CRT monitors, LCD monitors use less electrical energy, do not emit radiation and their price is higher, however due to smaller dimensions,
more attractive design and a good picture quality, they are pushing CRT monitors out of the market. Monitor size is expressed by the size of
screen diagonal and measured in inches (''). Picture quality is expressed with the notion of resolution, which is a number of horizontal and
vertical dots (pixels) (e.g. 1920x1080).
ACTIVITY 4
Discuss all factors that you will consider when purchasing computer monitor.
Printers
A Printer is a device designed to print your computer-generated documents onto paper. Printers vary in their quality, speed, graphics
capabilities, fonts, and even paper usage. Some printers print one character at a time; some print a line or a full page at a time. Data can be
sent to a printer through either in a serial of parallel port.
Figure 23: HP Printer Figure 24: EPSON Figure 25: CANON
The three most popular types of printers are dot matrix, ink jet (bubble jet), and laser printers. Printers are also categorized as impact and
non-impact. Impact printer produces characters by using a mechanical print-head that strikes on inked ribbon against the surface of paper
leaving an impression of the character on the paper. The dot-matrix printer is one type of the impact printers. Line printers produce output
one line at a time and can print in a range of 1,200 to 6,000 lines per minute. The most common line printer is the impact type. Non-impact
printers do not use a striking device to produce characters on paper, and because these printers do not hammer against the paper, they are
much quieter. Examples in this category include ink-jet printers, thermal printers, and laser printers.
Printers can also be distinguished between local printer (connected directly to the computer) and network printer (connected directly to
network using a network card). Dot matrix printers are the oldest, with the lowest price of print per paper, they are slow, make a lot of noise
while printing, and are mostly appropriate for printing text. Laser printers are similar to photocopy devices when it comes to technology.
They have exceptional print quality, speed and are quiet. Downsides of laser printers are their high price and high price of toners. Inkjet
printers have a high print quality (somewhat lower in comparison with laser printer), they are quiet while printing, and have low initial
investment. Ink price, especially color ink, can cost as much as the printer itself. Printing technology is based on ink dispersion from
container onto paper. Plotter is used for printing large drawings (up to A0). They are extremely expensive and used only for professional
purposes, such as in designing firms for printing technical drawings (blueprints). Thermal printer, as its name states, leaves a print on the
paper by utilizing heat. They use paper sensitive to heat, feature small dimensions; they are quiet while printing and relatively cheap. They
are usually used for printing receipts and owing to that they are called POS printer (printer of sale). Also, they are used as calculator printers
and due to their small dimensions, as portable printers.
Projectors
Projector is a device used to project a computer image or other images from independent devices, such as DVD players, Blue-ray player, etc.
onto canvas or a wall.
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 6/8
�3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
Figure 26: A projector
INPUT/OUTPUT DEVICES
Storage devices, due to necessity for writing and reading data, they are classified as input/output devices. Touch screen (i.e. monitor
sensitive to touch) is out device while displaying computer image, and at the same time input device while receiving manual orders. Other
devices which perform both I/O operations include CDs, DVDs, flash disks.
COMMON INPUT /OUTPUT PORTS
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is used to connect various devices (mouse, keyboard, USB memory). Serial port is used for example in connecting
a mouse (labeled COM1 or COM2). Parallel port is used for connecting a local printer (LPT1 or LPT2). Network port is used for connecting
computers to a network.
ACTIVITY 5
Discuss all factors that you will consider when purchasing printer.
SUMMARY
This lecture has described the hardware concepts, computer working principle and input/output function. The
functionalities of various hardware input devices (keyboard, mouse, disk, scanner, touchpad, lightpen, joystick,
microphone, webcam and digital camera) and output devices (monitor, printer, projector), and I/O devices (flash,
CD, DVD) were presented and discussed. All these make the physical part of computer.
Last modified: Thursday, 18 February 2021, 7:55 PM
◄ Lecture 1: References
Jump to...
Lecture 2: Review Questions ►
You are logged in as MADAMA STANLEY (Log out)
OCP 100
Student Manual
Click here to download a PDF file
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 7/8
�3/23/22, 9:59 AM OCP 100: Lecture 2: Notes
Instructor Manual
Click here to download a PDF file
Click here to download VIDEO to backup your course
Click here to download VIDEO to reset your course file
Click to view a video
Help
Moodle Manuals
Tutorials download
Moodle Tutorials
English (en)
English (en)
English (United States) (en_us)
Français (fr)
Kiswahili (sw)
Data retention summary
Get the mobile app
https://elms.out.ac.tz/mod/page/view.php?id=173914&forceview=1 8/8