CS3691
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
& IOT
ASSIGNMENT 02
NAME :
ROLL NO :
YEAR & DEPT :
�1. A switch is connected to pin 1.0 and LED to pin 2.7. Write an 8051 embedded C program to
get the status of the switch and send it to LED.
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include the header file for 8051
sbit switch_pin = P1^0; // Switch connected to pin P1.0
sbit led_pin = P2^7; // LED connected to pin P2.7
void main() {
while (1) {
if (switch_pin == 0) { // Assuming switch is active low(pressed = 0)
led_pin = 0; // Turn ON LED (assuming active low)
} else {
led_pin = 1; // Turn OFF LED
}
}
}
EXPLANATION
• sbit is used to define bit-addressable pins.
• switch_pin checks the state of the switch on pin P1.0.
• If the switch is pressed (0), the LED is turned ON by writing 0 to pin P2.7.
• If the switch is not pressed (1), the LED is turned OFF by writing 1 to P2.7.
• This is written under an infinite loop while(1) to continuously check the
switch state.
2. Write an 8051 C program to send values 00-FF to port P1.
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include header for 8051
void delay() {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 255; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 100; j++); // Simple delay loop
}
void main() {
unsigned char value;
while (1) {
for (value = 0x00; value <= 0xFF; value++) {
P1 = value; // Send value to Port 1
delay(); // Wait for a short period
}
}
}
2
�EXPLANATION
• unsigned char value holds values from 0x00 to 0xFF.
• A for loop increments this value and writes it to Port P1.
• P1 = value; sends the value to port pins.
• delay() is a crude time delay to allow visible change if monitoring outputs
(e.g., via LEDs).
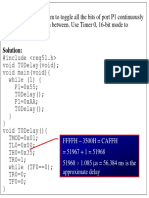
3. Write an 8051 C program to toggle all bits of P1 continuously.
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include header file for 8051
void delay() {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 255; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 127; j++); // Simple time delay
}
void main() {
while (1) {
P1 = ~P1; // Toggle all bits of Port 1
delay(); // Wait for a short time
}
}
EXPLANATION
• P1 = ~P1; uses bitwise NOT (~) to invert all bits of Port P1.
• If P1 = 0xAA (10101010), it becomes 0x55 (01010101), and vice versa.
• The loop runs forever, continuously toggling the bits.
• delay() slows down the toggling to make it visible (e.g., on LEDs).
4. Write an 8051 C program to toggle bit D0 of the port p1(P1.0) 50,000 times.
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include 8051 register definitions
sbit pin = P1^0; // Define bit D0 (P1.0)
void delay() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 100; i++); // Short delay for visibility (optional)
}
3
�void main() {
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
pin = ~pin; // Toggle P1.0
delay(); // Optional delay
}
while (1); // Stop program here
}
EXPLANATION
• sbit pin = P1^0; defines bit D0 (P1.0).
• The for loop runs 50,000 times, toggling P1.0 each time.
• pin = ~pin; inverts the current state of the pin.
• delay() is optional but useful if you want to see the toggling (e.g., on an
LED).
• After toggling 50,000 times, the program stops by entering an infinite loop.
5. Write an 8051 C program to toggle bits of P1 continuously forever with some delay.
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include 8051 header
void delay() {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 255; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 127; j++); // Simple time delay
}
void main() {
while (1) {
P1 = ~P1; // Toggle all bits of Port P1
delay(); // Wait before next toggle
}
}
EXPLANATION
• P1 = ~P1; inverts all 8 bits of Port 1 (bitwise NOT).
• The while (1) loop runs forever, continuously toggling P1.
• delay() creates a visible delay between toggles, especially useful if
connected to LEDs.
6. Write an 8051 C program to toggle bits of P1 continuously with 250ms delay.
4
�CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include header for 8051
void delay_250ms() {
unsigned int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 250; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 123; j++); // Approximate delay for 1ms × 250 = 250ms
}
void main() {
while (1) {
P1 = ~P1; // Toggle all bits of Port 1
delay_250ms(); // Wait for 250 milliseconds
}
}
EXPLANATION
• P1 = ~P1; inverts all 8 bits of Port P1.
• The delay function creates a software delay of roughly 250ms.
• This is approximate and may vary slightly depending on the crystal frequency
(usually 11.0592 MHz for 8051).
• The loop runs forever, toggling the port with each 250ms delay.
7. Write an 8051 C program to toggle bits of P0 and P2 continuously with 250ms delay.
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include 8051 header file
void delay_250ms() {
unsigned int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 250; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 123; j++); // Approximate 1ms × 250 = 250ms delay
}
void main() {
while (1) {
P0 = ~P0; // Toggle all bits of Port 0
P2 = ~P2; // Toggle all bits of Port 2
delay_250ms(); // 250ms delay
}
}
EXPLANATION
• P0 = ~P0; and P2 = ~P2; invert the current values of Port 0 and Port 2
respectively.
• The delay_250ms() function introduces a 250ms delay between each toggle.
• The loop continues forever, making the ports toggle continuously.
• Assumes standard 8051 clock (e.g., 11.0592 MHz) for approximate timing.
5
�8. LEDs are connected to bits P1 and P2. Write an 8051 C program that shows count
from 00 to FFh (0000 0000 to 1111 1111 in binary) on the LEDs.
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include 8051 header
void delay() {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 255; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 127; j++); // Approximate delay
}
void main() {
unsigned char value;
while (1) {
for (value = 0x00; value <= 0xFF; value++) {
P1 = value; // Output count to Port 1
P2 = value; // Output same count to Port 2
delay(); // Short delay to observe change
}
}
}
EXPLANATION
• P1 and P2 are both assigned the value of the counter (value).
• This shows the binary representation of the value on the LEDs connected to
both ports.
• The delay() is added so you can visually observe the counting on the LEDs.
• The count repeats from 00h to FFh continuously.
9. Write an 8051 C program to toggle bits of P0 and P2 continuously with 250ms delay.
(Use inverter operator).
CODE
#include <reg51.h> // Include 8051 header file
void delay_250ms() {
unsigned int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 250; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 123; j++); // Approximate 250ms delay
}
void main() {
P0 = 0x00; // Initialize P0
P2 = 0x00; // Initialize P2
while (1) {
P0 = ~P0; // Toggle all bits of Port 0 using inverter operator
6
� P2 = ~P2; // Toggle all bits of Port 2 using inverter operator
delay_250ms(); // 250ms delay
}
}
EXPLANATION
• ~P0 and ~P2 are bitwise NOT operations (inverters), flipping every bit of the
port value.
• The loop runs continuously to toggle bits with a 250ms delay.
• Initial values of P0 and P2 are set to 0x00 to start with all LEDs OFF (or
ON, depending on active low/high configuration).