0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views14 pagesC++ Lab Programs HKBK
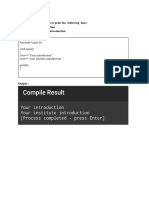
The document contains multiple C++ programs demonstrating various concepts such as sorting arrays, calculating the sum of natural numbers, swapping values using call by reference, function overloading, class inheritance, exception handling, file operations, and binary file reading/writing. Each program is presented with its respective code and comments explaining its functionality. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for learning and practicing fundamental C++ programming techniques.
Uploaded by
sameer974021Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views14 pagesC++ Lab Programs HKBK
The document contains multiple C++ programs demonstrating various concepts such as sorting arrays, calculating the sum of natural numbers, swapping values using call by reference, function overloading, class inheritance, exception handling, file operations, and binary file reading/writing. Each program is presented with its respective code and comments explaining its functionality. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for learning and practicing fundamental C++ programming techniques.
Uploaded by
sameer974021Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14