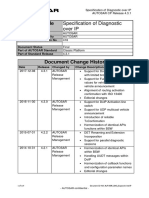
Computer network cheatsheet
Short-forms
1. OSI - Open Systems Interconnection
2. TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
3. TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
4. UDP - User Datagram Protocol
5. IP - Internet Protocol
6. NAT - Network Address Translation
7. MAC - Media Access Control
8. DNS - Domain Name System
9. DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
10. LAN - Local Area Network
11. WAN - Wide Area Network
12. MAN - Metropolitan Area Network
13. WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network
14. IPv4 - Internet Protocol version 4
15. IPv6 - Internet Protocol version 6
16. VPN - Virtual Private Network
17. ARP - Address Resolution Protocol
18. ICMP - Internet Control Message Protocol
19. QoS - Quality of Service
20. BGP - Border Gateway Protocol
21. VLAN - Virtual Local Area Network
22. SSL - Secure Sockets Layer
23. TLS - Transport Layer Security
�Questions and answers
1. OSI Model: A framework of seven layers for network interactions.
2. TCP/IP: Protocol suite for reliable data transmission and addressing.
3. TCP vs. UDP: TCP is reliable and connection-oriented; UDP is not.
4. IP Address: Unique identifier for routing data on a network.
5. Subnetting: Dividing networks into smaller subnets for efficiency.
6. NAT: Translates private IPs to a public IP for shared internet access.
7. MAC Address: Hardware identifier for network interfaces.
8. Router vs. Switch: Router connects networks; switch connects
devices within a network.
9. Firewall: Security system monitoring and controlling network traffic.
10. DNS: Translates domain names to IP addresses.
11. DHCP: Automatically assigns IP addresses on a network.
12. Network Types: LAN, WAN, MAN, WLAN for different network
scopes.
13. IPv4 vs. IPv6: IPv4 uses 32-bit; IPv6 uses 128-bit for more
addresses.
14. VPN: Creates a secure, encrypted connection over the internet.
15. Layer 3 Switch: Combines router and switch functions to manage
traffic between subnets.
16. Hub vs. Switch: Hub sends data to all devices; switch sends to
intended device only.
17. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol): Maps IP addresses to MAC
addresses in a local network.
18. Protocol: Set of rules for data communication between devices
(e.g., HTTP).
19. Port Number: Identifies specific processes/services on a network
(e.g., HTTP uses port 80).
�20. ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): Sends error messages
and operational information.
21. Public vs. Private IP: Public IP is for internet use; private IP is for
local network use.
22. Load Balancer: Distributes network traffic across multiple servers to
prevent overload.
23. QoS (Quality of Service): Prioritizes certain types of network traffic
for optimal performance.
24. Proxy Server: Intermediary between a user and the internet for
caching, filtering, and anonymity.
25. Collision Domain: Network segment where data packets can
collide.
26. Transport Layer (OSI): Ensures reliable communication, flow control,
and error correction.
27. BGP (Border Gateway Protocol): Exchanges routing information
between different networks.
28. VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network): Segments a physical network
into multiple logical networks.
29. Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast: Unicast to one, multicast to group,
broadcast to all devices.
30. Peer-to-Peer vs. Client-Server: Peer-to-peer: devices are equal;
client-server: clients request from central server.
31. Full-Duplex vs. Half-Duplex: Full-duplex: simultaneous
send/receive; half-duplex: one direction at a time.
32. DNS Cache: Stores IP addresses for domain names to speed up
website access.
33. MAC Address Table (Switch): Maps MAC addresses to ports for
data forwarding.
�34. Transport Layer Function: Ensures reliable data transfer with error
detection and flow control.
35. Transmission Media Types: Includes cables (twisted pair, coaxial,
fiber optics) and wireless (radio waves, microwaves).
36. Gateway vs. Router: Gateway connects different networks; router
forwards data within/between networks.
37. SSL/TLS: Encrypts data between client and server for secure
communication.
38. Circuit-Switched vs. Packet-Switched: Circuit-switched: dedicated
path; packet-switched: data packets transmitted independently.
39. Broadcast Storm: Excessive broadcast traffic causing network
performance issues.
40. SSL Handshake: Establishes encrypted connection between client
and server.