0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesLECTURE 4 Programming
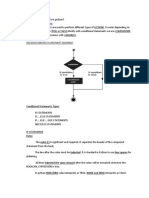
This lecture covers the basics of programming in Python, focusing on indentation, control structures, and selection statements. It explains how to use if, if-else, if-elif-else, and nested if statements, along with boolean expressions and operators for condition checking. Additionally, it discusses compound conditions and string checks that can be used in conditional statements.
Uploaded by
Gelo MarananCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesLECTURE 4 Programming
This lecture covers the basics of programming in Python, focusing on indentation, control structures, and selection statements. It explains how to use if, if-else, if-elif-else, and nested if statements, along with boolean expressions and operators for condition checking. Additionally, it discusses compound conditions and string checks that can be used in conditional statements.
Uploaded by
Gelo MarananCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4