0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views3 pagesCommon Excel Function
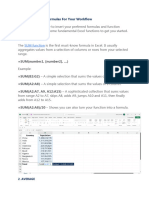
The document outlines common Excel functions categorized into eight groups: Mathematical & Statistical, Logical, Lookup & Reference, Text, Date & Time, Financial, Data Cleaning & Manipulation, and Array functions. Each function is accompanied by a brief description and an example of its usage. This serves as a quick reference guide for users to effectively utilize Excel functions.
Uploaded by
cmyuademgsljzdnnnjCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views3 pagesCommon Excel Function
The document outlines common Excel functions categorized into eight groups: Mathematical & Statistical, Logical, Lookup & Reference, Text, Date & Time, Financial, Data Cleaning & Manipulation, and Array functions. Each function is accompanied by a brief description and an example of its usage. This serves as a quick reference guide for users to effectively utilize Excel functions.
Uploaded by
cmyuademgsljzdnnnjCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3