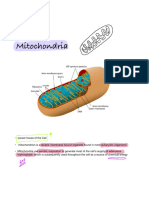
Mitochondrial Structure
Mitochondria are often called the "powerhouses of the cell" because they produce most of the
cell’s energy. Their structure is specialized for this role and includes:
1. Outer Membrane
o Smooth and surrounds the mitochondrion.
o Contains proteins called porins that allow small molecules to pass through easily.
2. Intermembrane Space
o The space between the outer and inner membranes.
o Important for the processes of cellular respiration.
3. Inner Membrane
o Folded into structures called cristae to increase surface area.
o Contains proteins for the electron transport chain and ATP synthase (the
enzyme that makes ATP).
4. Matrix
o The inner space enclosed by the inner membrane.
o Contains enzymes for the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), mitochondrial DNA, and
ribosomes.
5. Mitochondrial DNA
o Circular DNA similar to bacterial DNA.
o Allows mitochondria to make some of their own proteins.
Mitochondrial Function
The main functions of mitochondria are:
ATP Production:
o They produce ATP through aerobic respiration by breaking down glucose and
oxygen.
o Main stages: Glycolysis (in cytoplasm) → Krebs Cycle (in matrix) → Electron
Transport Chain (in inner membrane