Lab session – 3
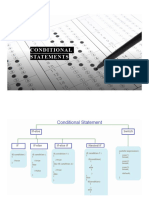
[Conditional statements]
------------------------------------------------------
1. Write a program to find the largest of three numbers without ternary operators.
[Using simple if-else statements]
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,c,L;
printf("Enter 3 integers: ");
scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c);
if (a>b)
{
L=a;
}
else
{
L=b;
}
if (L>c)
{
printf("%d is largest",L);
}
else
{
printf("%d is largest",c);
}
return 0;
}
Alternatively
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
printf("Enter 3 integers: ");
scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c);
if(a>b && a>c)
{
printf("%d is largest",a);
}
else if(b>c)
{
printf("%d is largest",b);
}
else
{
printf("%d is largest",c);
}
return 0;
}
1
�2. WAP to ask for any number and declare it as even or odd.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d",&a);
if (a%2==0) //Use of the modulo operator (%) which gives remainder after division
{
printf("Even no.");
}
else
{
printf("Odd no.");
}
return 0;
}
3. WAP to input marks of 5 subjects of a student and display the total marks scored,
percentage scored and the class of result [Use of if - else if ladder]
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,c,d,e;
float p;
printf("Enter marks (out of 100) in 5 subjects: ");
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d,&e);
printf("Total marks = %d\n",a+b+c+d+e);
printf("Percentage = %.2f%\n",p=((float)a+b+c+d+e)*100/500);
//(float)a changes ‘a’ from int to float. Now all other interactions of int
variables with ‘a’ will yield float only.
//This is called as 'Typecasting' i.e. upgrading a variable further down the
program after its initial declaration.
if (p<40)
{printf("Class: Failed");}
else if(p<60)
{printf("Class: 2nd");}
else if(p<80)
{printf("Class: 1st");}
else
{printf("Class: Distinction");}
return 0;
}
2
�4. WAP to get percentage from user and declare the class [using nested if-else
statements]
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float p;
printf("Enter percentage: ");
scanf("%f",&p);
if (p>=40)
{
if (p>=60)
{
if (p>=80)
{
printf("Distinction");
}
else
printf("1st class");
}
else
printf("2nd class");
}
else
printf("Fail");
return 0;
}
5. WAP to ask for a character from keyboard and declare if it is an alphabet or not.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a;
printf("Enter a character: ");
scanf("%c",&a);
if ((a>='a' && a<='z')||(a>='A' && a<='Z'))
printf("This is an Alphabet"); // for single statements within if-else there
is no need for {}.
else
printf("This is NOT an Alphabet");
return 0;
}
3
�ASCII table of characters for reference
6. Write a program to compute grade of students using if else ladder. The grades are
assigned as follows:
Marks Grade
Marks < 50 F
50 < Marks < 60 C
60 < Marks < 70 B
70 < Marks < 80 B+
80 < Marks < 90 A
90 < Marks < 100 A+
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float m;
flag: // returns here from goto command
printf("Enter marks: ");
scanf("%f",&m);
4
� if (m>100)
{
printf("Invalid marks. Enter <= 100.\n\n");
goto flag;
}
if (m<50)
printf("Grade: F");
else if (m<60)
printf("Grade: C");
else if (m<70)
printf("Grade: B");
else if (m<80)
printf("Grade: B+");
else if (m<90)
printf("Grade: A");
else
printf("Grade: A+");
return 0;
}
7. Write a program to check whether the entered year is leap year or not.
//To determine whether a year is a leap year, follow these steps:
//1. If the year is evenly (i.e. completely) divisible by 4, go to step 2.
Otherwise, go to step 5.
//2. If the year is evenly divisible by 100, go to step 3. Otherwise, go to step
4.
//3. If the year is evenly divisible by 400, go to step 4. Otherwise, go to step
5.
//4. The year is a leap year (it has 366 days).
//5. The year is not a leap year (it has 365 days).
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int y;
printf("Enter year: ");
scanf("%d",&y);
if(y%4==0&&y%100!=0)
printf("%d is a Leap Year",y);
else if(y%4==0&&y%100==0&&y%400==0)
printf("%d is a Leap Year",y);
else
printf("%d is a NOT a Leap Year",y);
return 0;
}
8. Write a program to find whether a character is a consonant or a vowel using Switch
– Case statement.
// Note: Switch-case statement can only be used with expressions that evaluate
to integral types. e.g. int, short, long, unsigned int, char.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
5
� char alph;
printf("Enter an alphabet: ");
scanf("%c",&alph);
switch(alph)
{
case 'a':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'e':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'i':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'o':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'u':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'A':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'E':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'I':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'O':
printf("Vowel");
break;
case 'U':
printf("Vowel");
break;
default:
printf("Consonant");
}
return 0;
}
Alternatively
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char alph;
printf("Enter Character: ");
alph = getchar();
switch(alph)
{
case 'a':
case 'A':
case 'e':
case 'E':
case 'i':
6
� case 'I':
case 'o':
case 'O':
case 'u':
case 'U': printf("Character %c is a Vowel",alph);
break;
default: printf("Character %c is a Consonant",alph);
}
return 0;
}
9. WAP to display day names from Monday to Sunday when first letter is entered by
user, using Switch - Case statement.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char day;
printf("Enter first character to display week days: ");
scanf("%c",&day);
switch(day)
{
case 'm':
printf("Monday");
break;
case 't':
printf("Tuesday");
break;
case 'w':
printf("Wednesday");
break;
case 'T':
printf("Thursday");
break;
case 'f':
printf("Friday");
break;
case 's':
printf("Saturday");
break;
case 'S':
printf("Sunday");
break;
default:
printf("Incorrect entry");
}
return 0;
}
----------------------------------X----------------------------------