1.
Grid-Connected Wind-Photovoltaic Cogeneration Using Back-to-Back Voltage Source Converters
Submitted by:-
17P15A0225 :- P.Thulasi prasad
16P11A0203 :- G.Indu
16P11A0207 :- K. Muni Tirumalesh
17P15A0224 :- P.Pothulaiah
under the guidance
of
MCV Suresh (Assist.professor)
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
CHADALAWADA RAMANAMMA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING , Renigunta
�Contents
Introduction
Abstract
�Abstract
In this project a new method which is simple and efficient is proposed for a gridconnected wind-
photovoltaic (PV) cogeneration system. A permanent magnet synchronous
generator-based full scale wind turbine is interfaced to the utility-grid via back-to-back (BtB)
voltage-source converters (VSCs). A PV solar generator is directly connected to the dc-link
capacitor of the BtB VSCs. No dc/dc conversion stages are required, and hence the system
efficiency is maximized. The proposed topology features an independent maximum power point
tracking for both the wind and the PV generators to maximize the extraction of the renewable
energy. The regulation of the VSCs is achieved via the vector control scheme in the rotating
reference frame. The detailed small signal models for the system components are developed to
investigate the overall stability. The influence of the utility-grid faults on the performance of the
proposed system is also evaluated. Nonlinear time-domain simulation results under different
operating conditions are presented to validate the effectiveness of the proposed topology.
�Existing Method
The combination of the grid-connected wind-PV systems has been presented. The system
comprises a Back to Back VSCs to interface the PV and wind generators to the utility-grid. On
the machine-side- VSC, the dc-link voltage is regulated to the maximum power point tracking
(MPPT) value of the PV panels by an outer loop proportional-and-integral (PI) dc voltage
controller. The reference values of the machine-side currents are calculated using the
synchronous detection method, and a hysteresis current controller is utilized for the regulation.
On the grid-side-VSC, a hysteresis grid-current controller is used to inject the total currents into
the utility-grid.
�Drawbacks:
1) The MPPT of either the PV and wind power involves the operation of both VSCs,
which in
some cases might decreases the system reliability and increases the losses.
2)If the wind velocity is lower than the cut-off speed of the wind turbine, i.e., no
wind power, the
machine-side VSC may be unable to track the solar PV MPPT dc-link voltage.
2) the currents of the machine and grid-side converters are regulated using hysteresis
controllers
resulting in a variable switching frequency and higher harmonic contents .
�Proposed Method:
This paper has presented the wind-PV cogeneration systems using vector-
controlled grid connected BtB VSCs.
The VSR at the wind generator-side is responsible for extracting the maximum
wind power following the wind speed variations.
On the utility-grid side, the roles of the VSI are to extract the maximum PV
power from the PV generator, achieve the balance between the input-output
powers across the dc-link capacitor, and to maintain a unity PCC voltage
under different modes of operation.
A small-signal stability analysis has been conducted for the entire system.
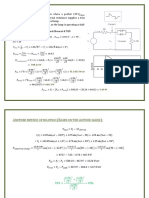
�Block Diagram
�Advantages:
1) The increased reliability and efficiency due to the combined wind and PV
generators.
2) The independent MPPT extraction as the VSR and VSI are solely responsible for
extracting
the wind and PV powers, respectively.
3) The regulation of the dc-link voltage under all operating conditions is
maintained by the VSI
and hence a better damped performance is yielded.
4) Simple system structure and controllers design.
5) Fault-ride through can be achieved using existing protection schemes
�THANK YOU