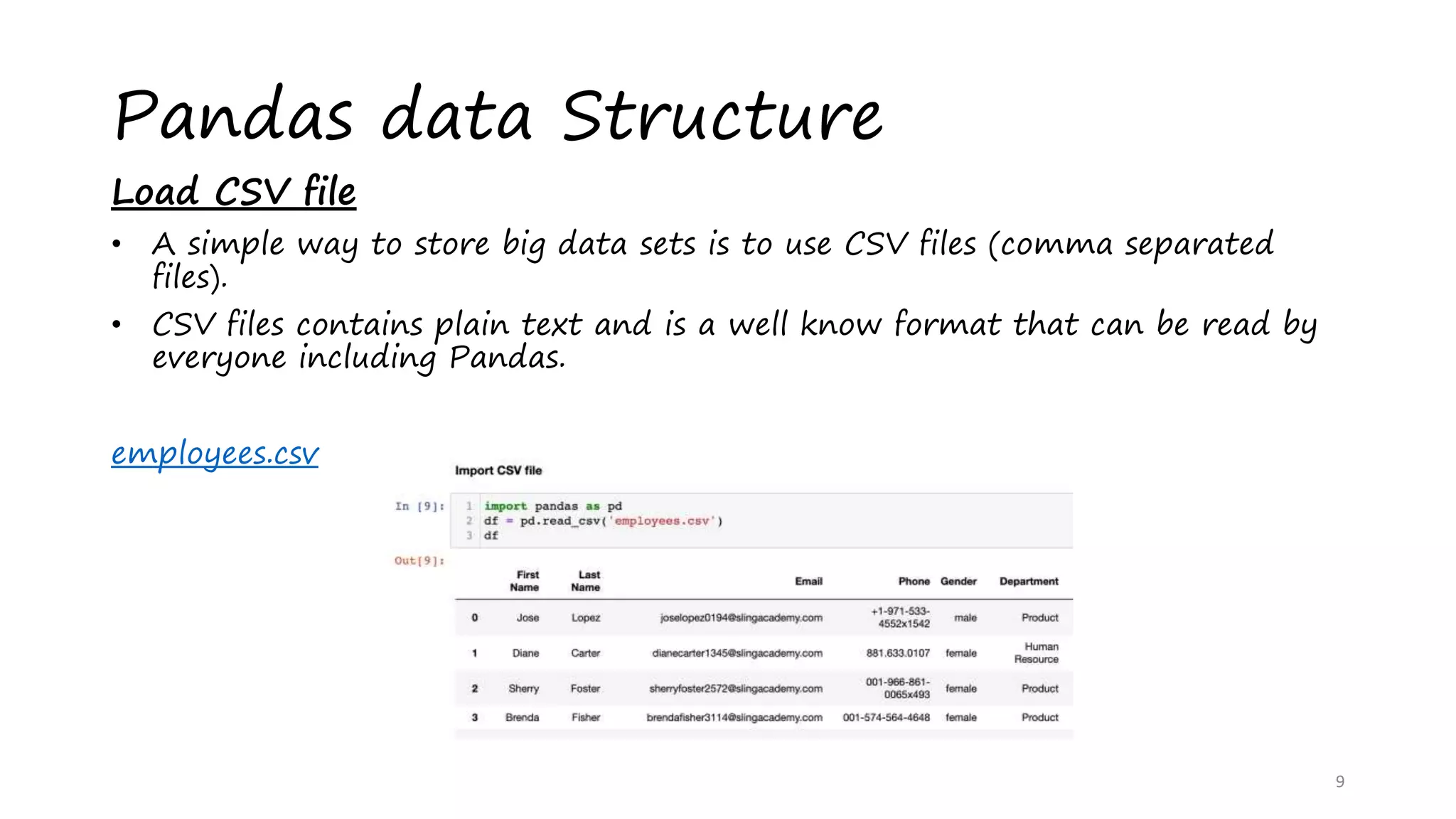
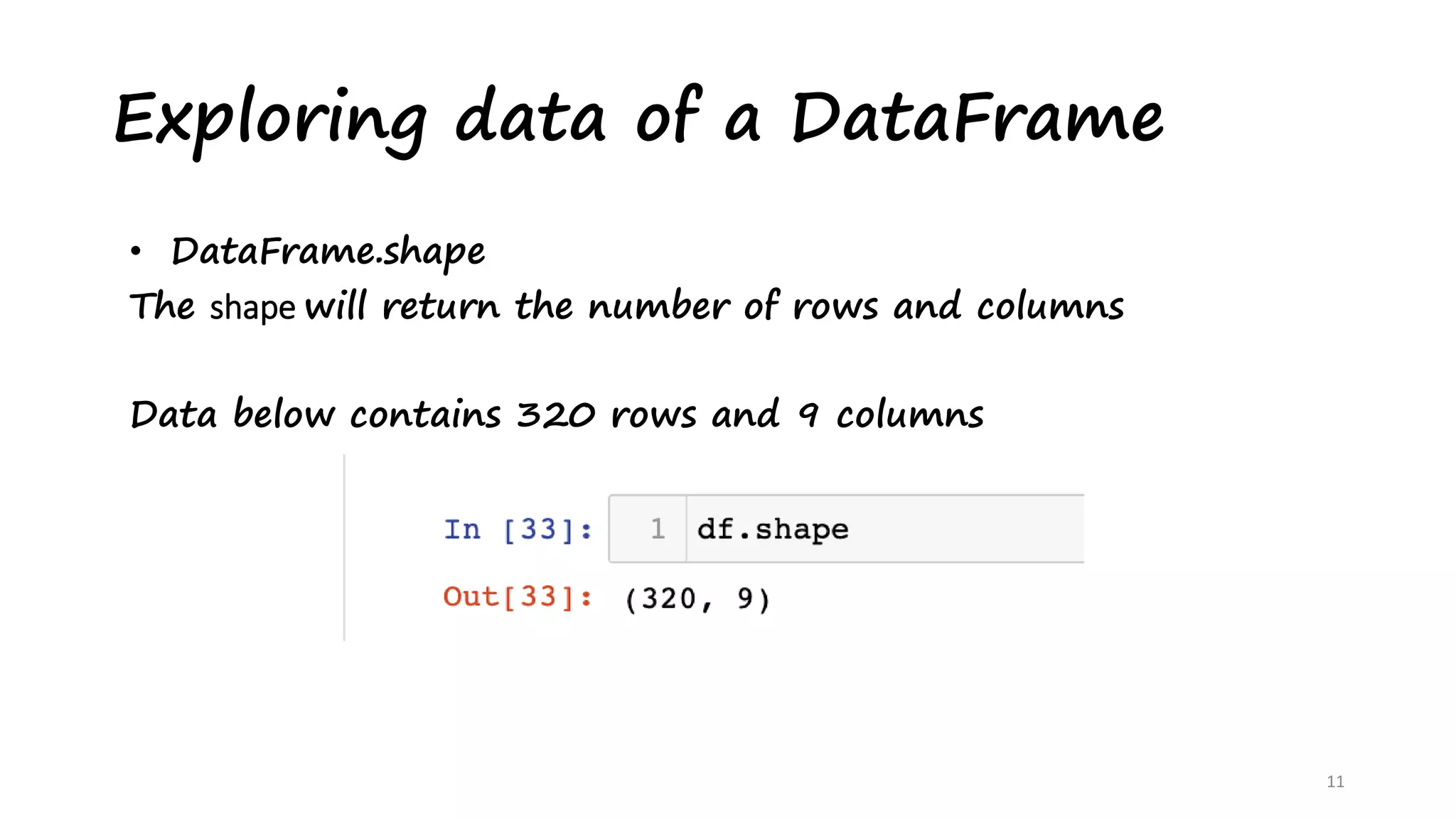
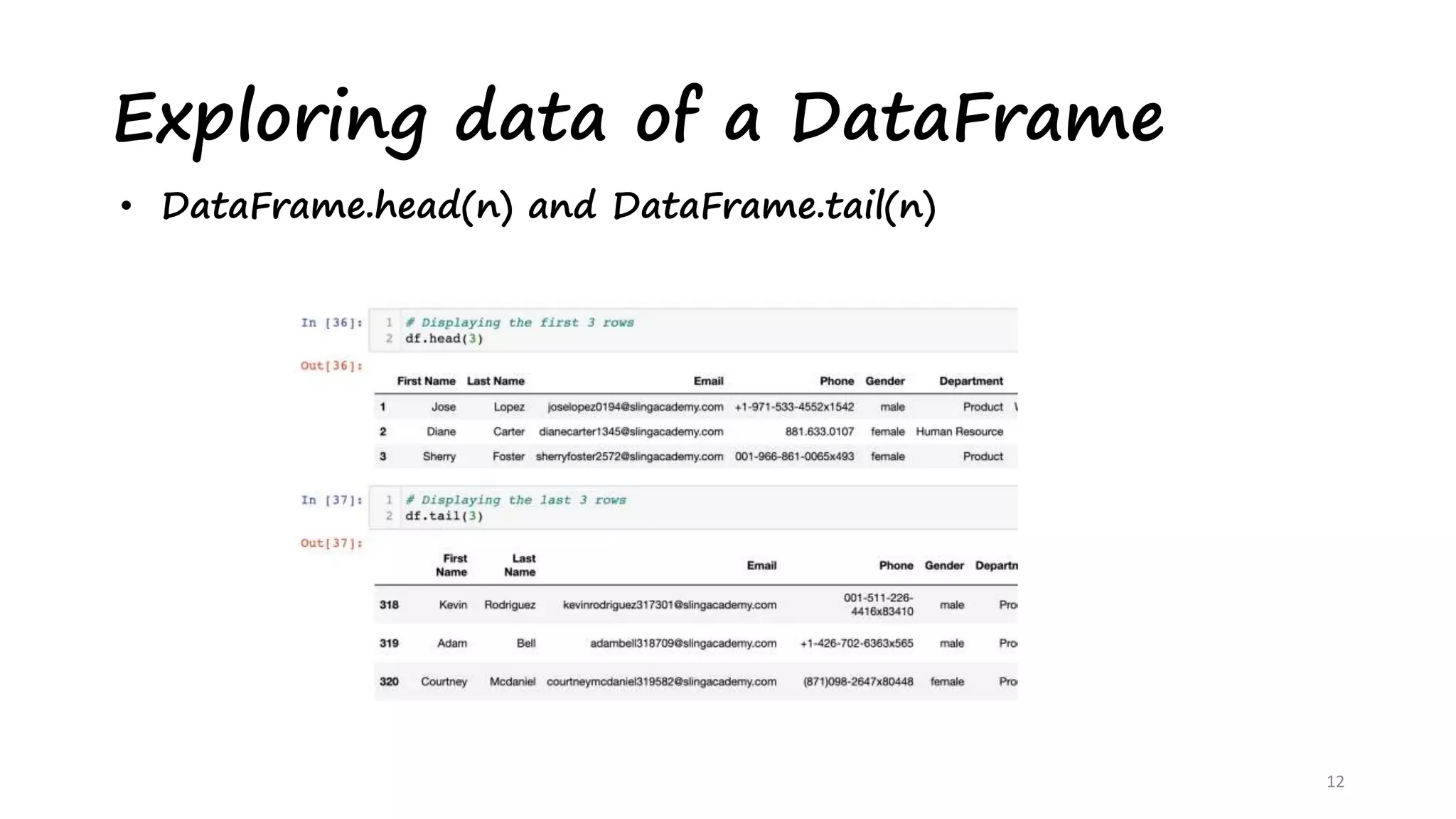
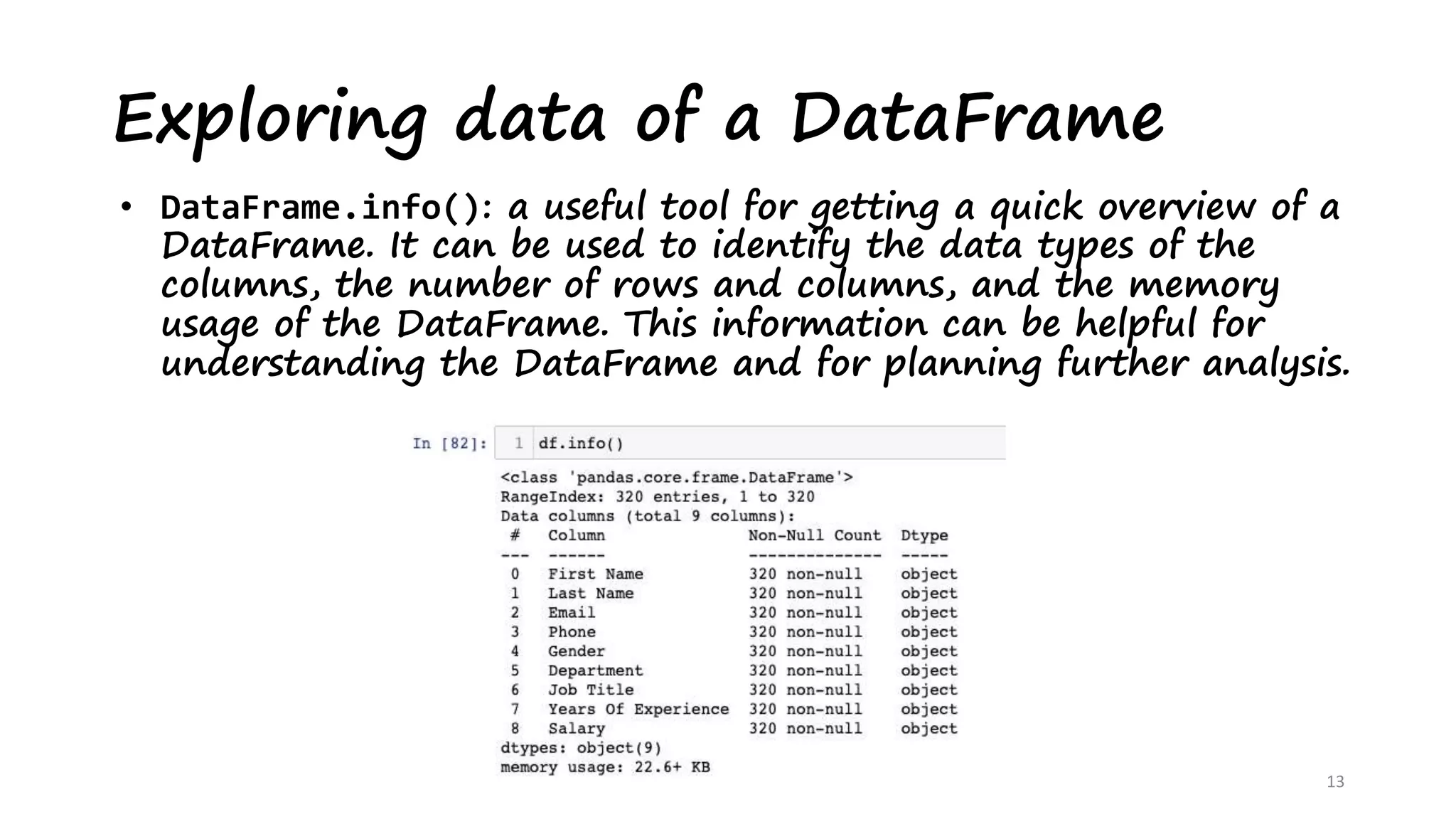
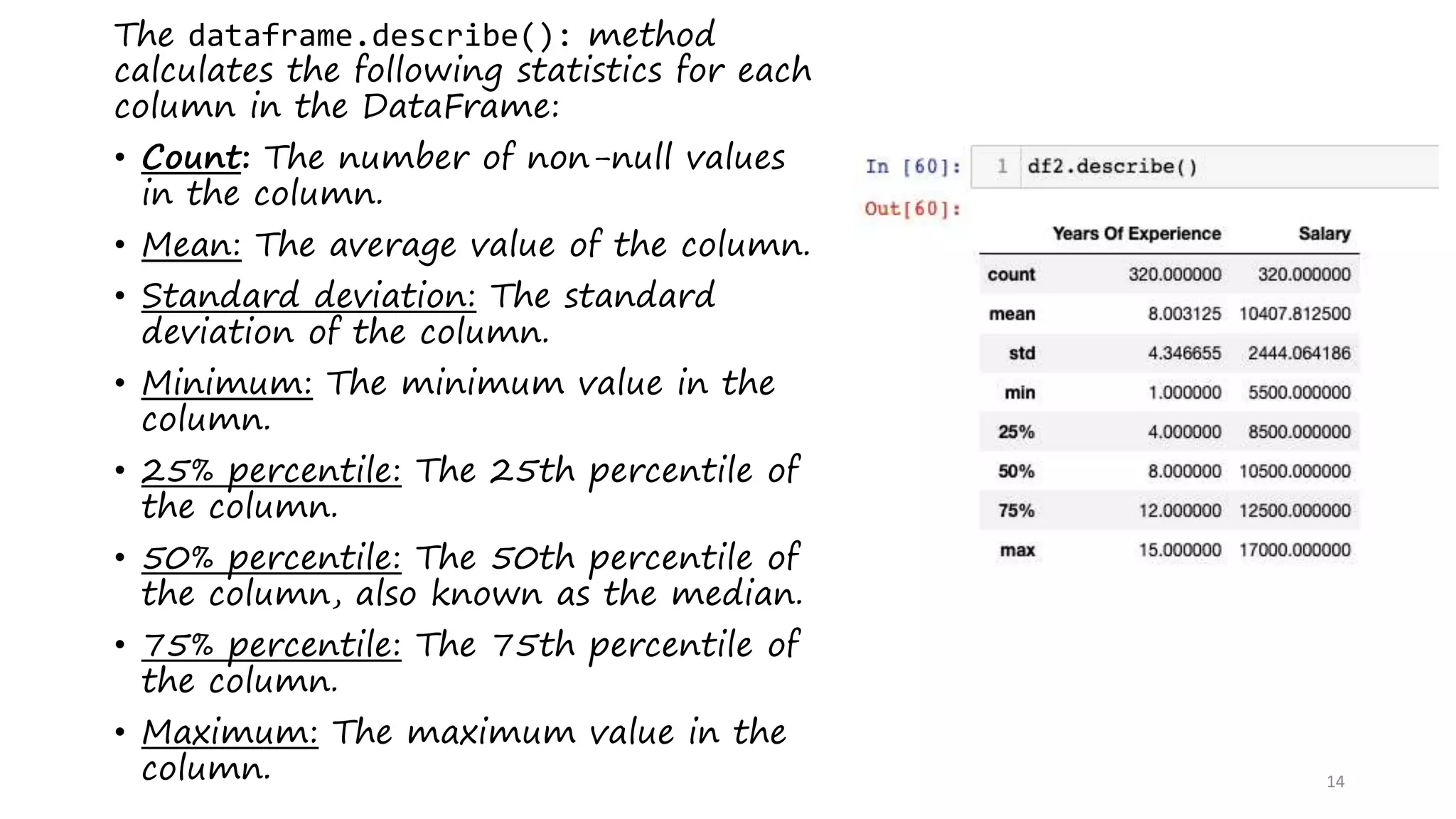
This document provides an introduction to data analysis using Pandas and NumPy. It discusses the key data structures in Pandas like Series and DataFrames, and how to load CSV files into DataFrames. It also covers common DataFrame methods for exploring data like shape, head, tail, info, and describe. The document then discusses data cleansing techniques. Finally, it introduces NumPy, describing it as a memory efficient library for scientific computing with N-dimensional arrays and various array manipulation functions.







![15
The dataframe.dtypes :method get the data
types of the columns in a DataFrame. This
method returns a Series object with the data
type of each column. The index of the Series
object is the name of the column and the
value of the Series object is the data type of
the column.
The data types that can be returned by the
dataframe.dtypes method include:
•object: strings, lists, or other non-numeric
data.
•int64: integers.
•float64: floating-point numbers.
•datetime64[ns]: dates and times.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-230713100607-abd6c2c9/75/2-Data-Preprocessing-with-Numpy-and-Pandas-pptx-15-2048.jpg)