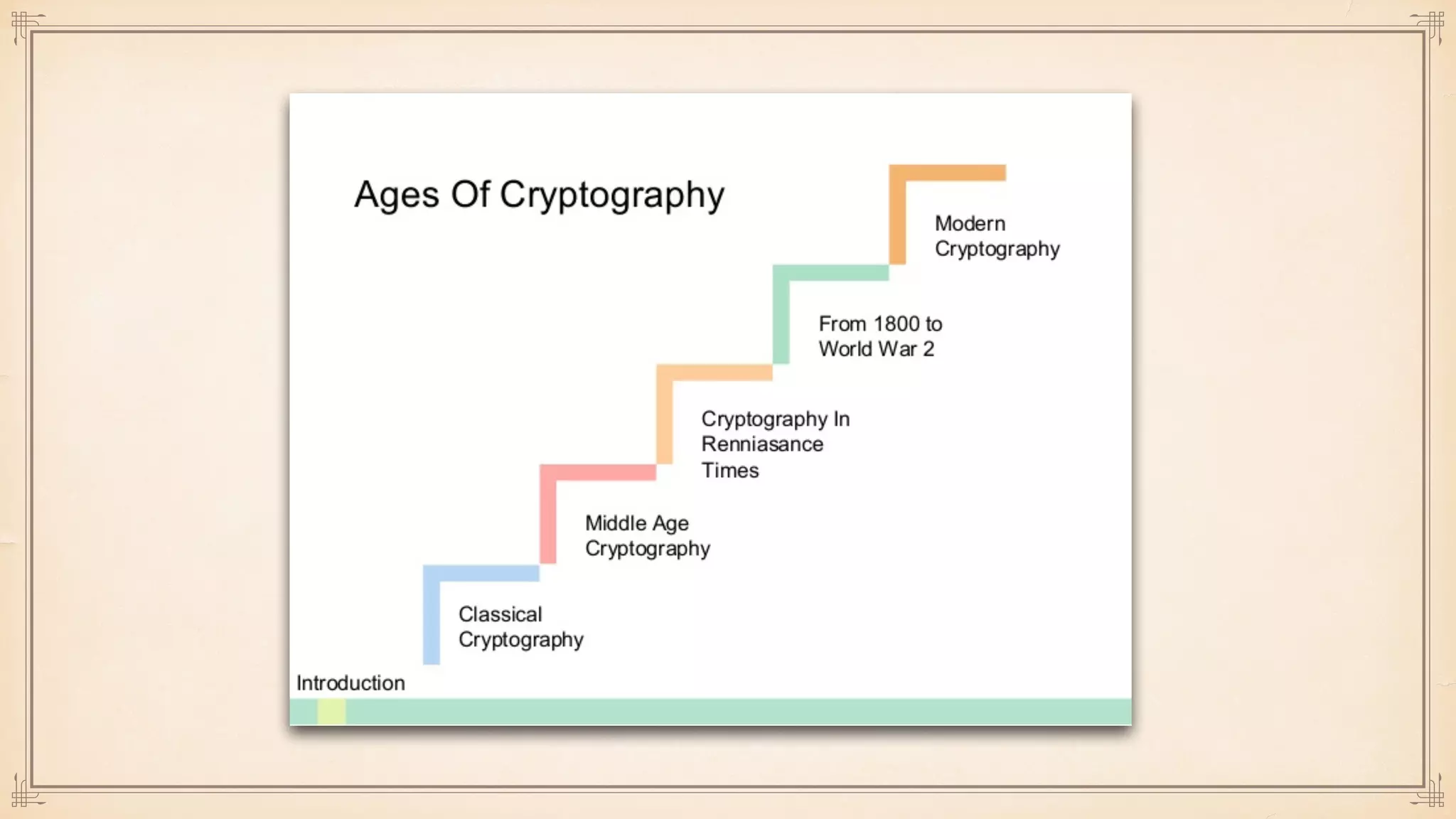
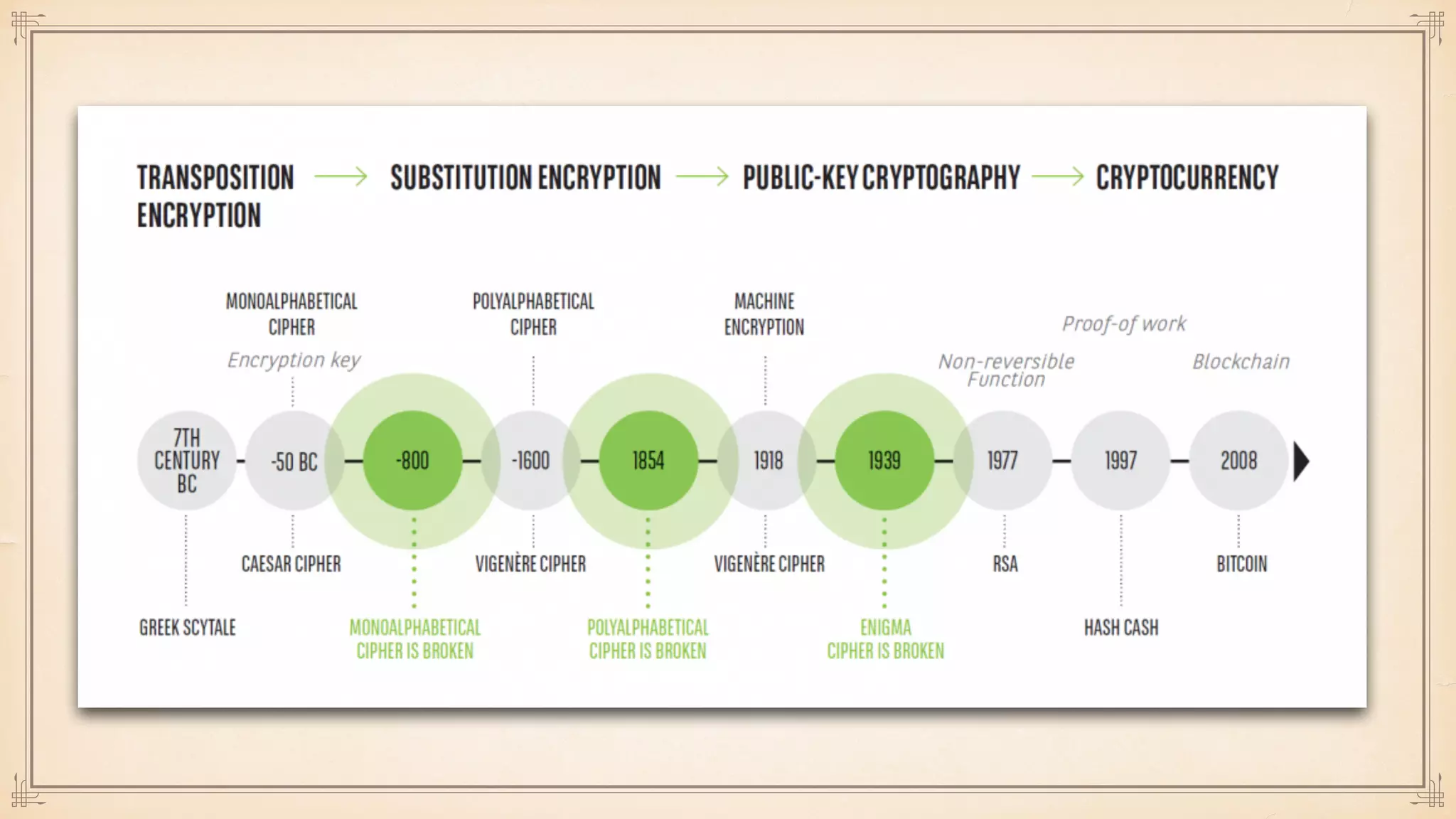
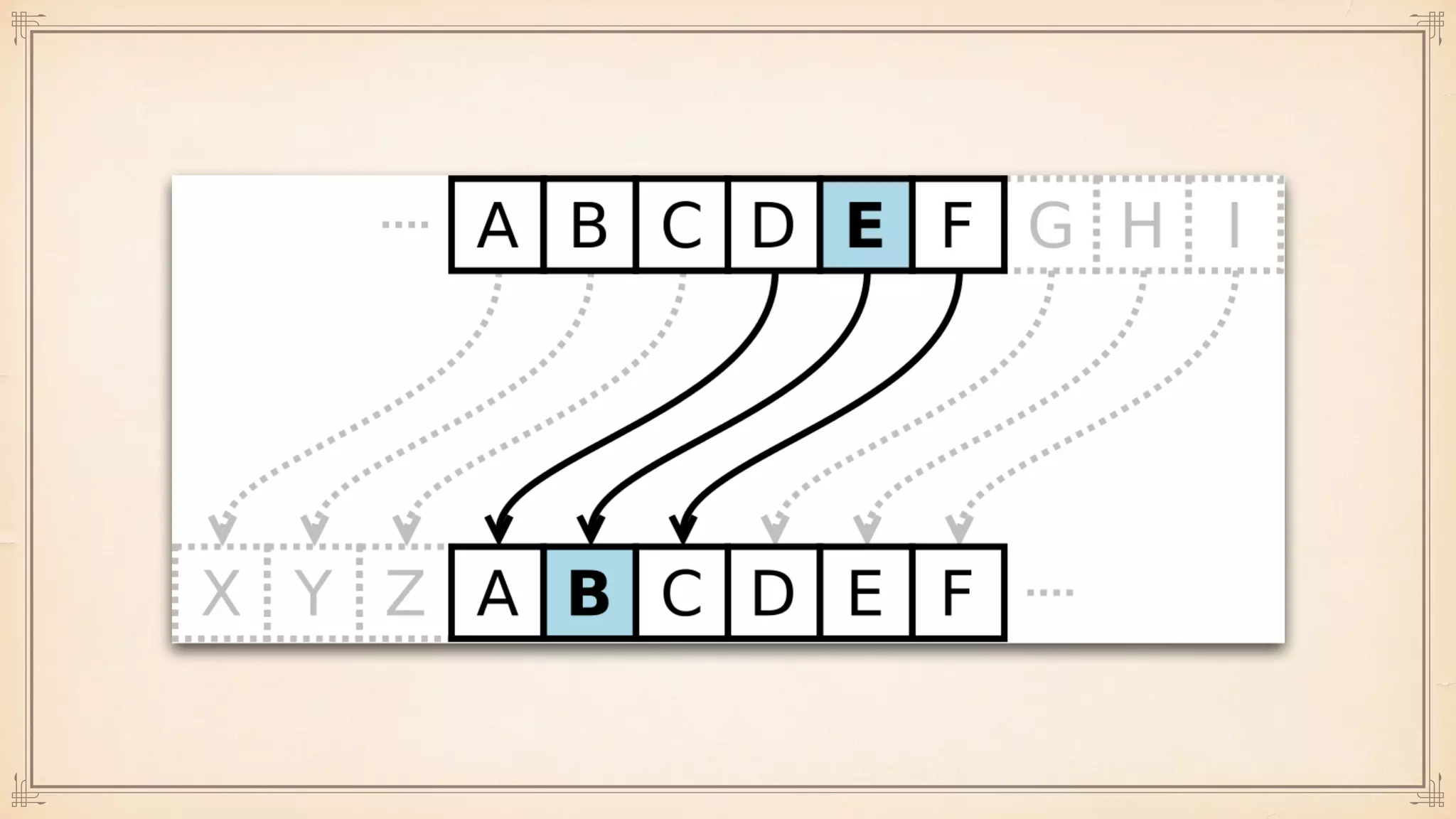
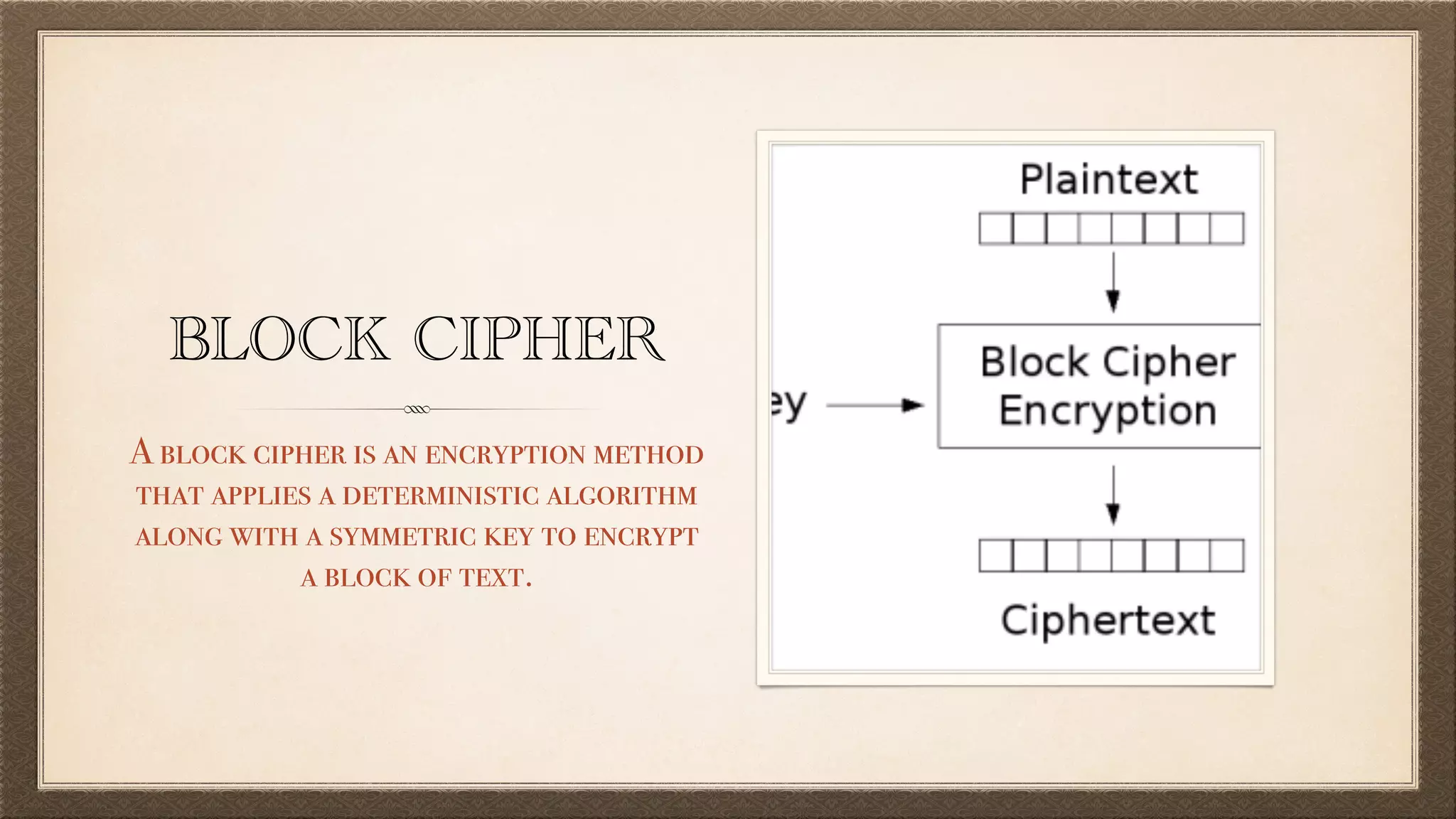
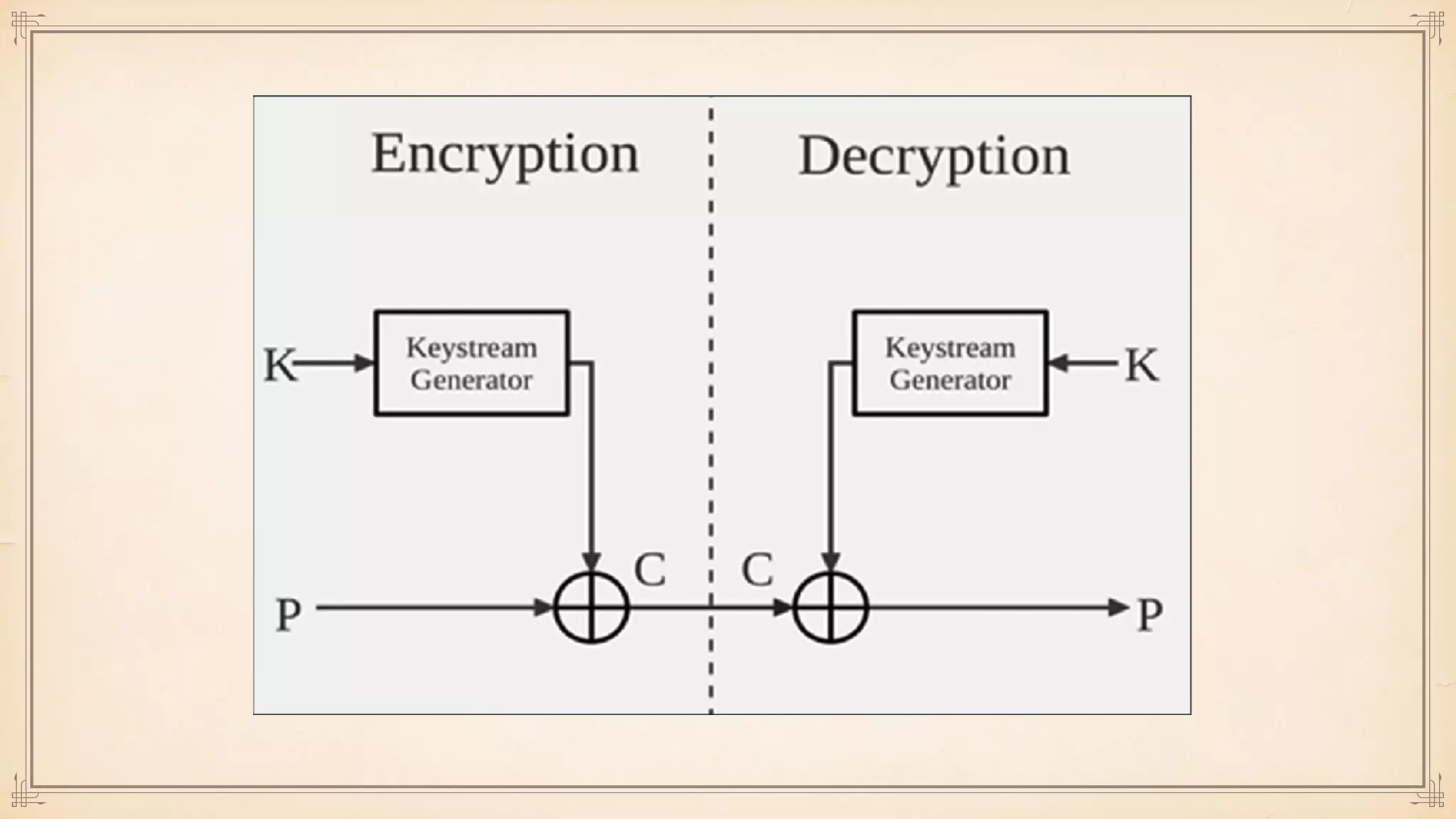
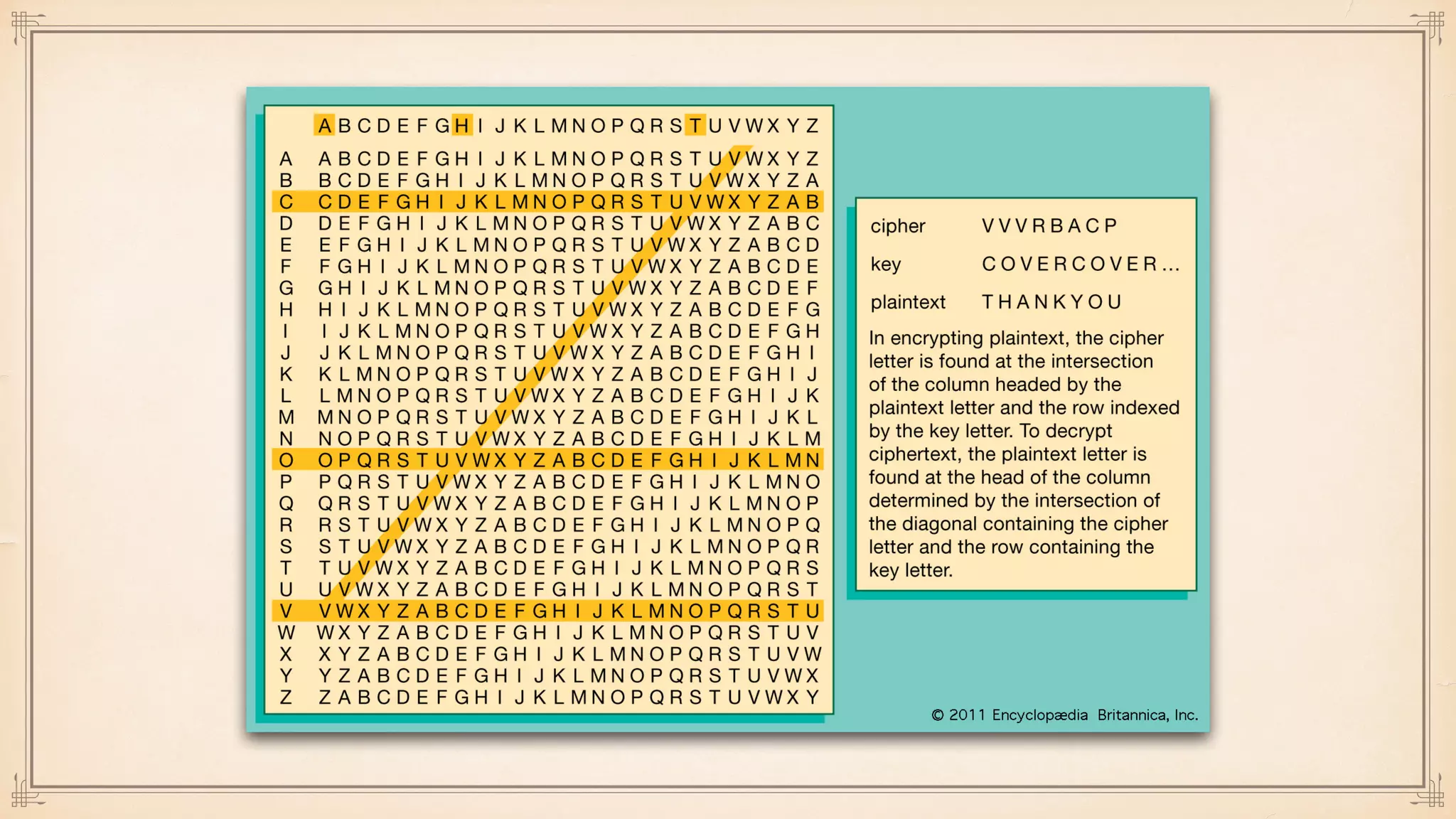
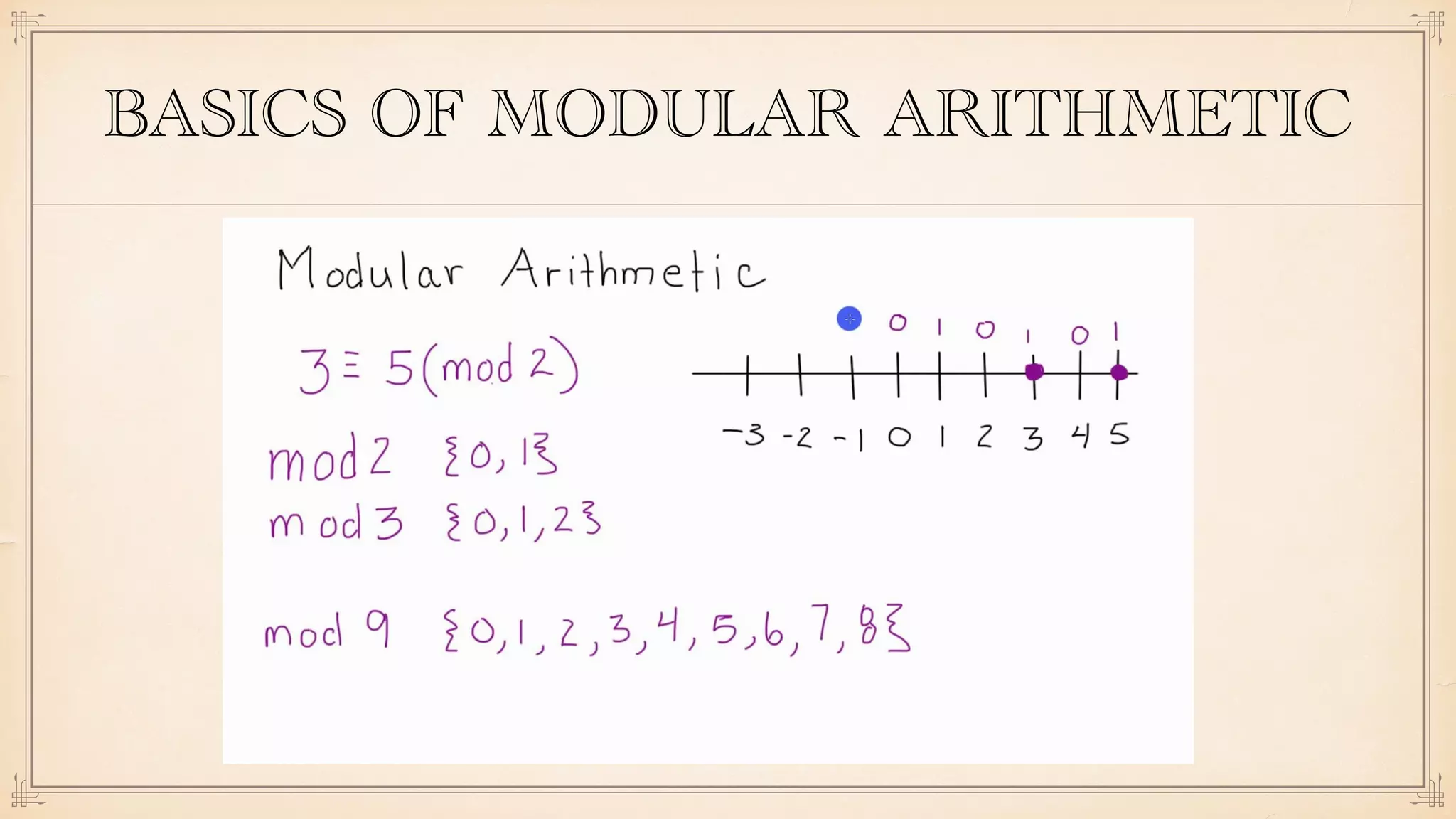
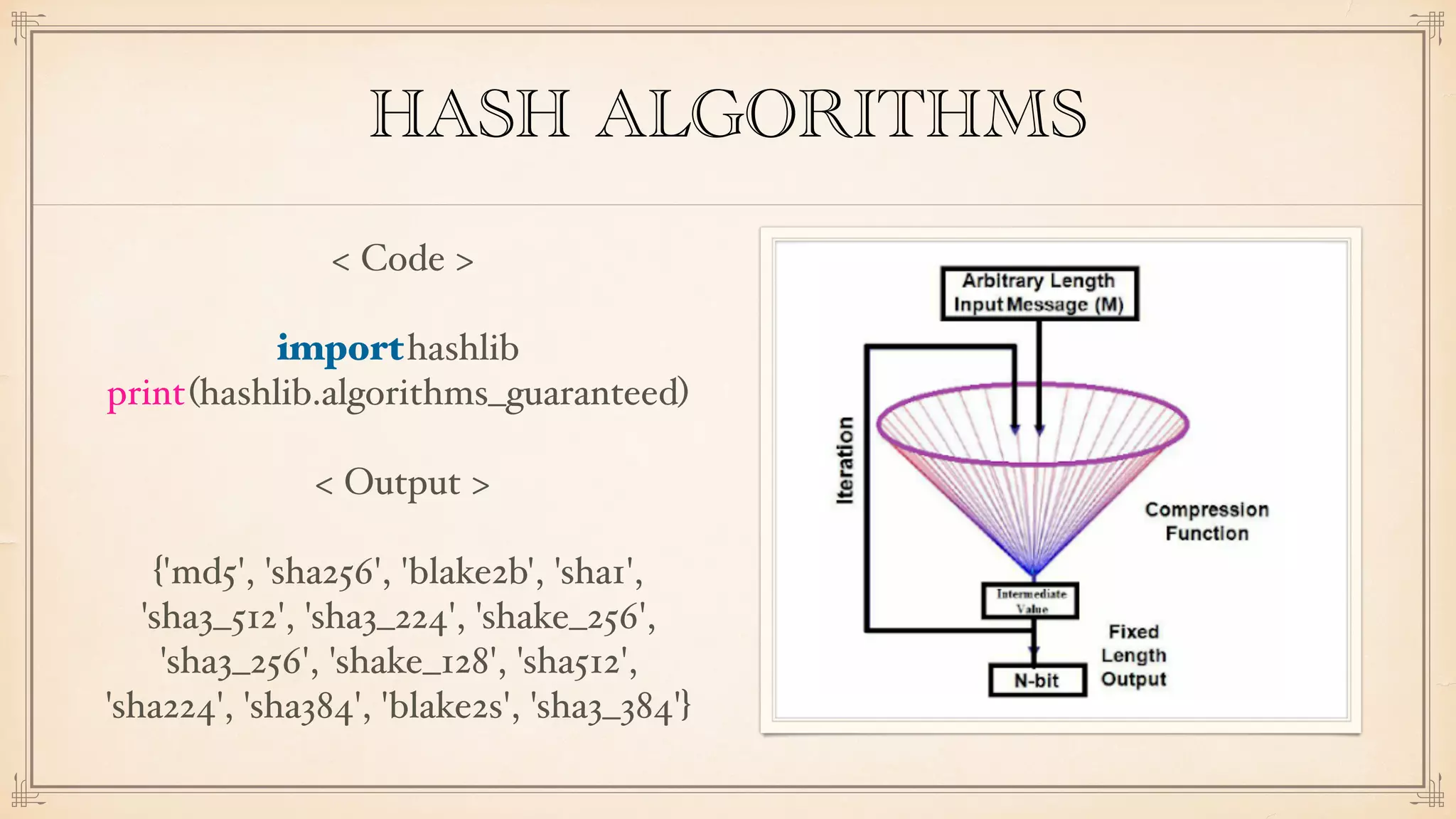
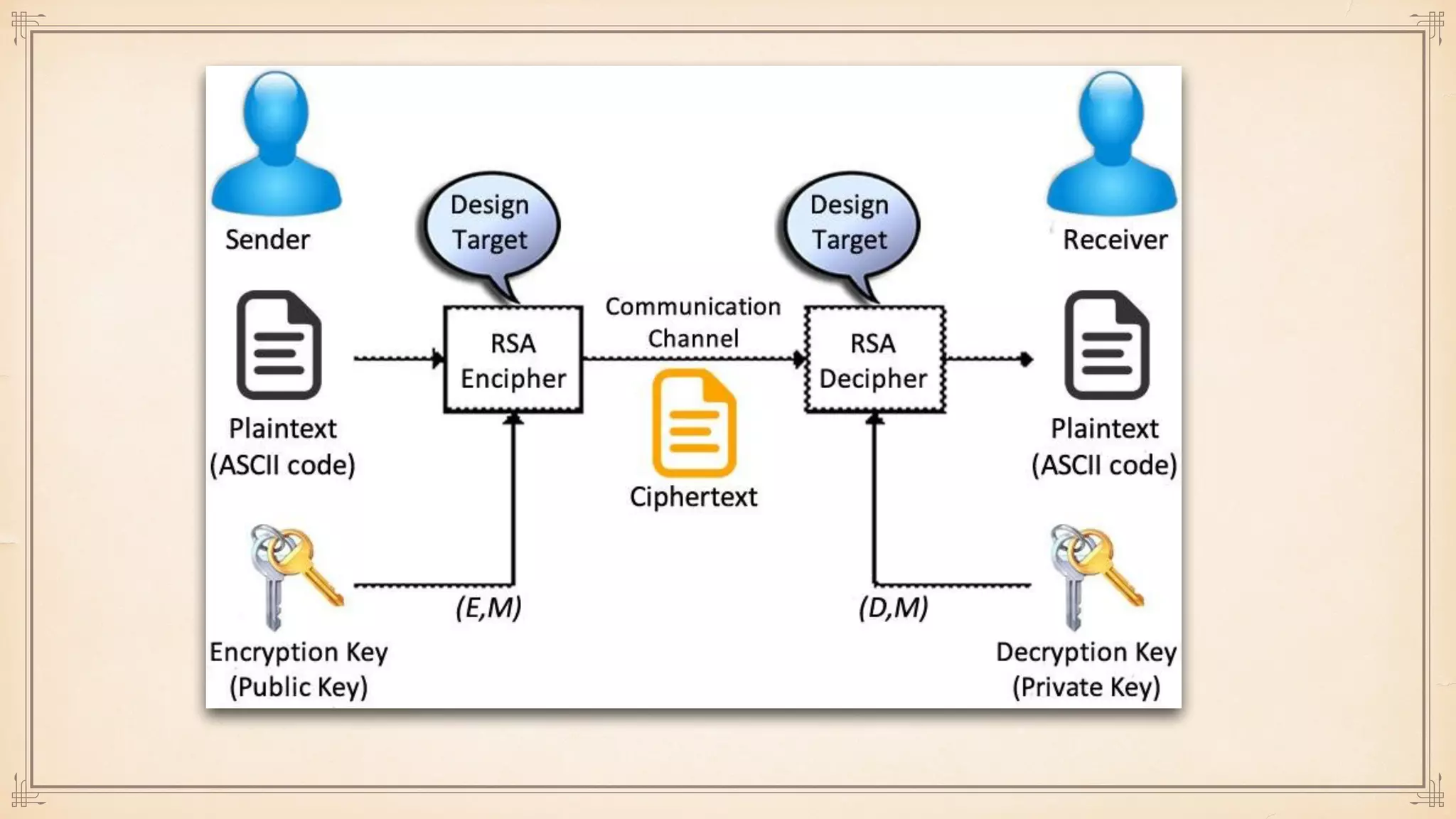
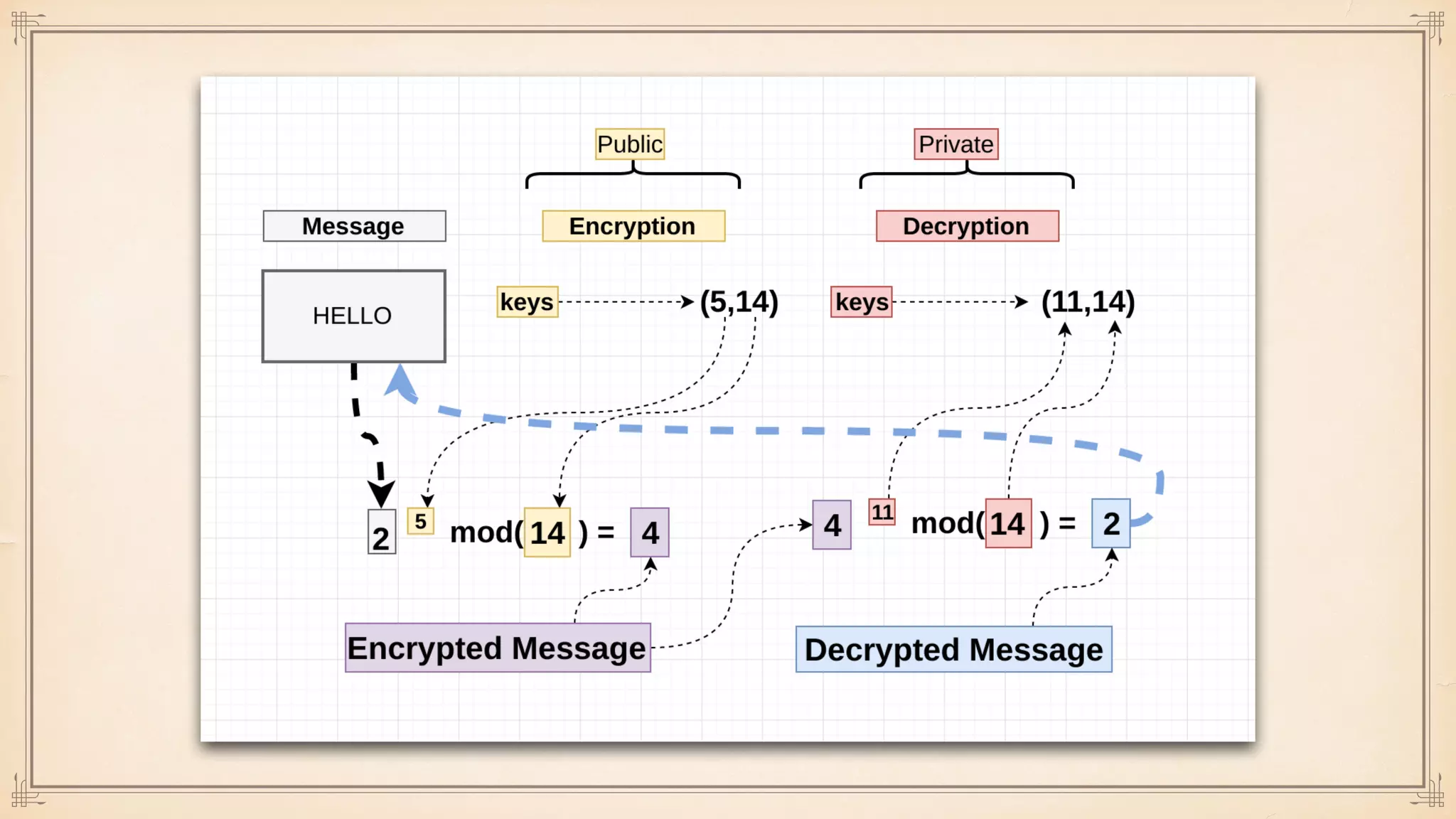
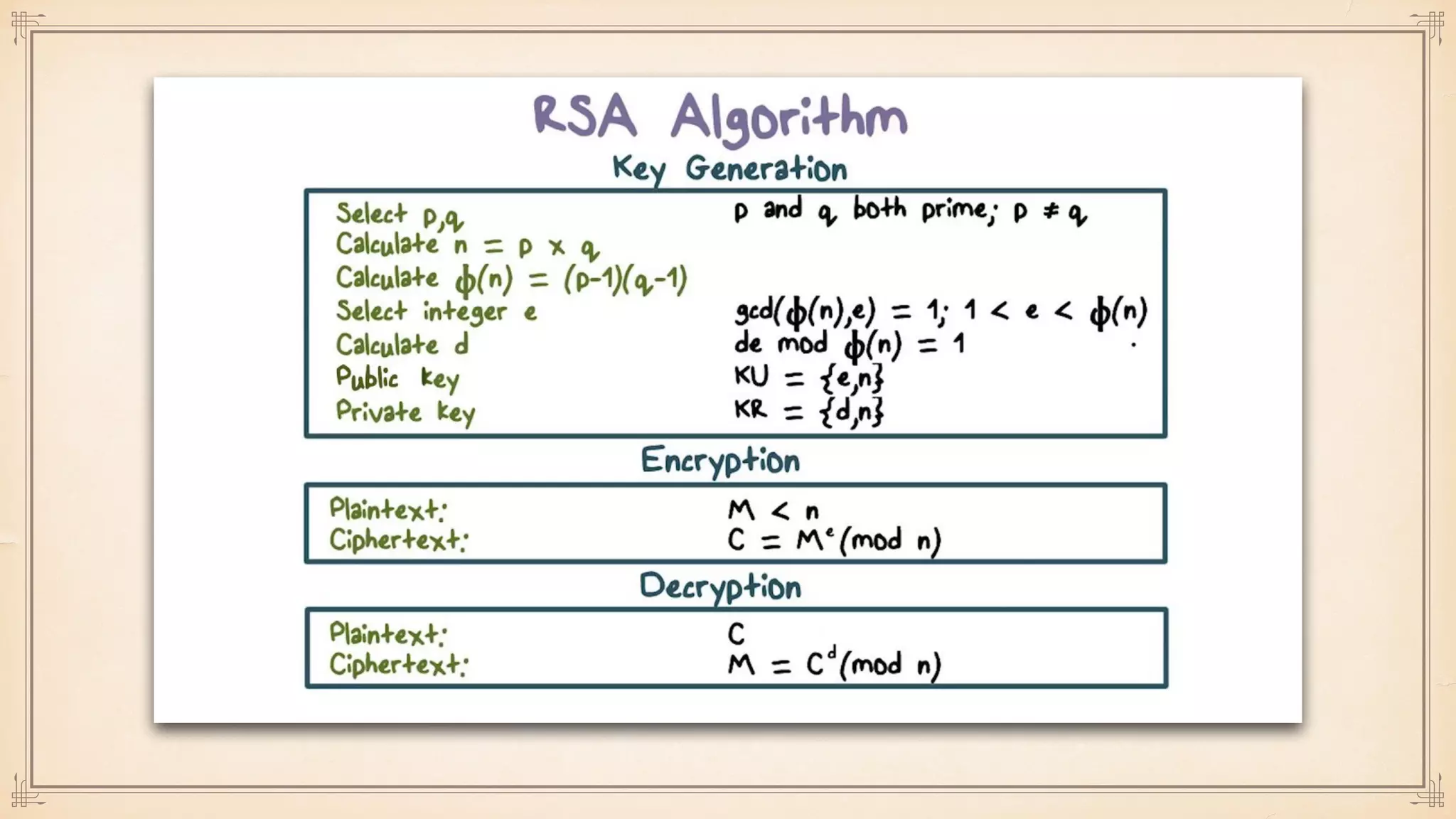
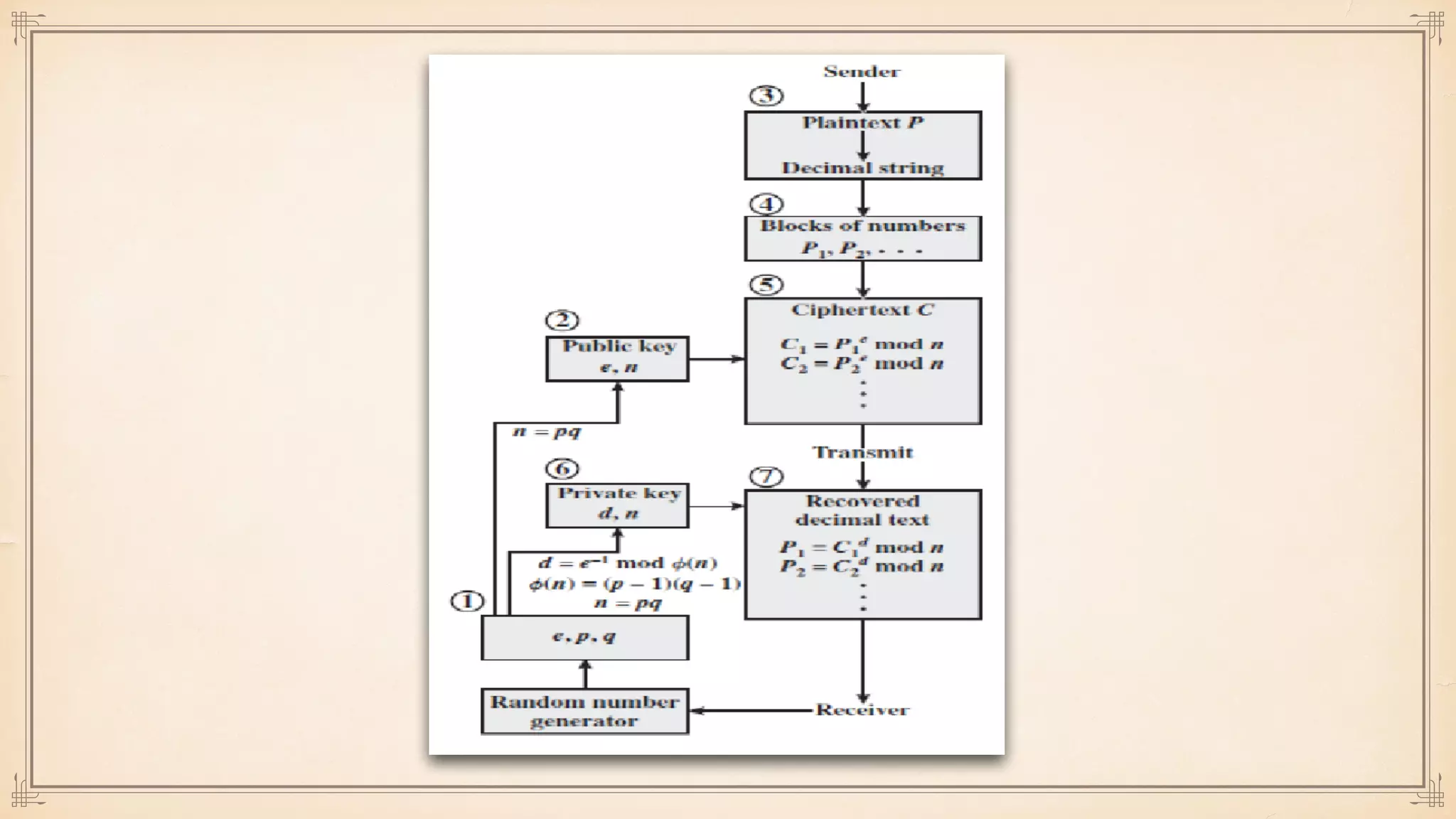
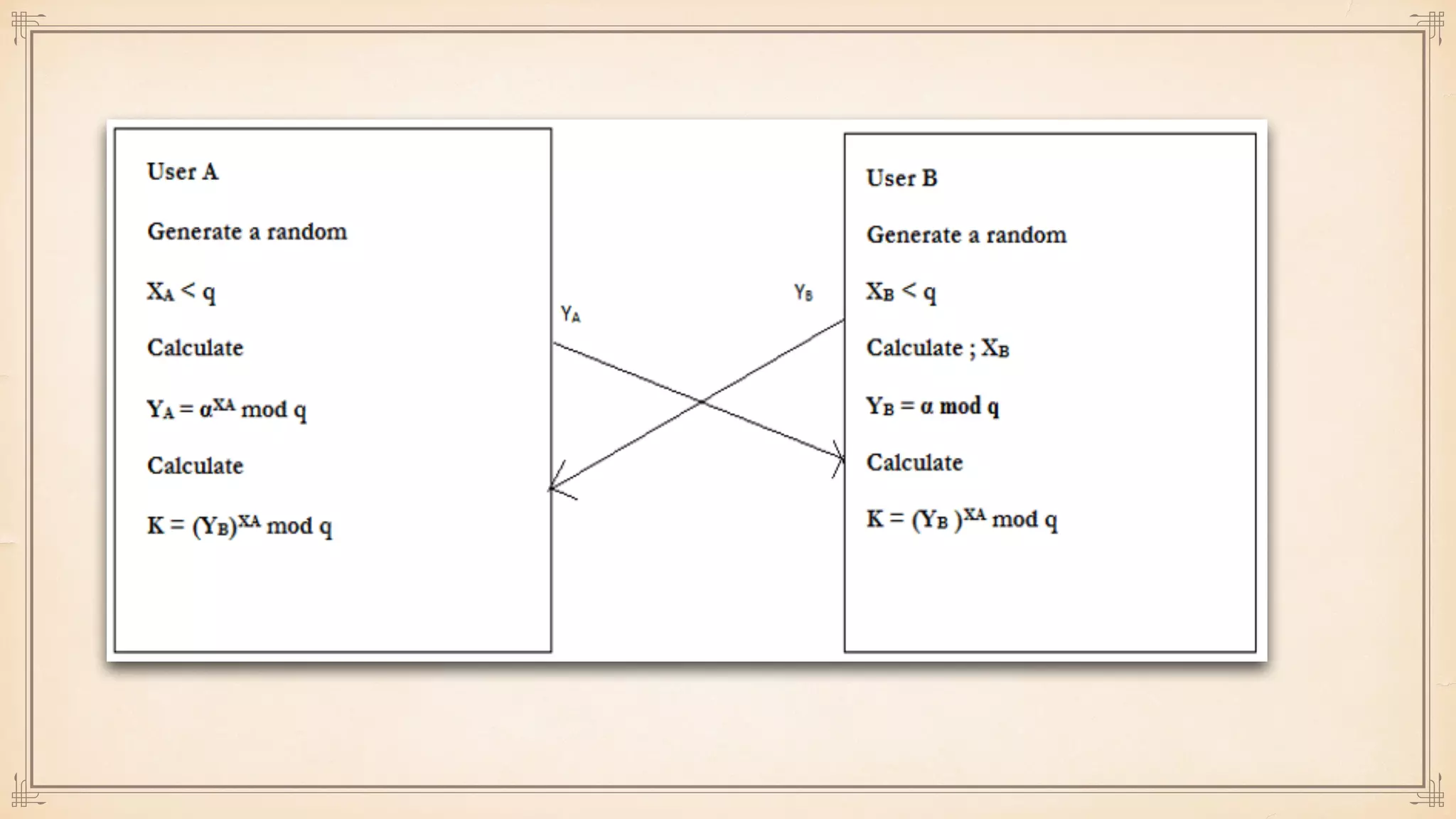
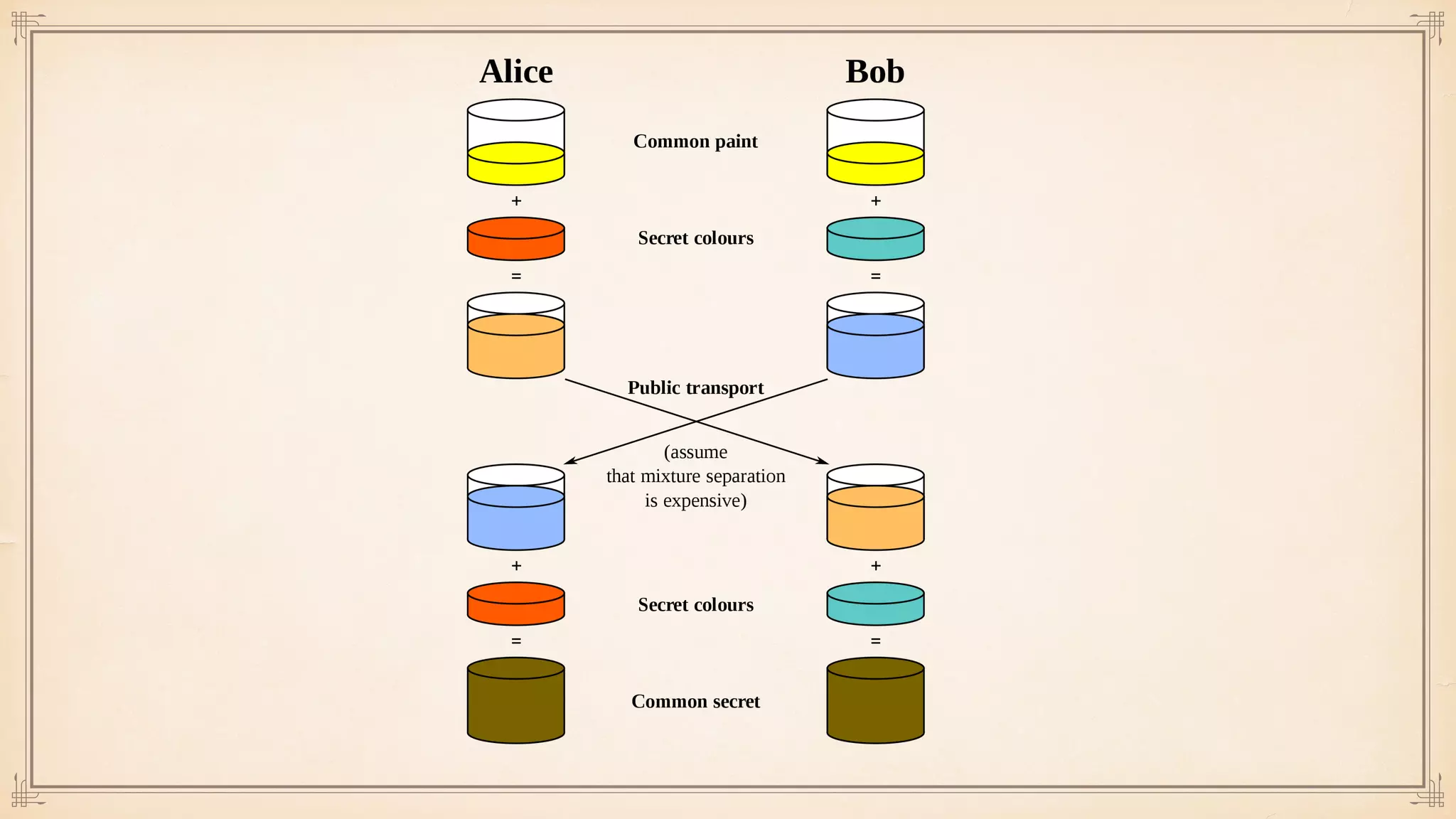
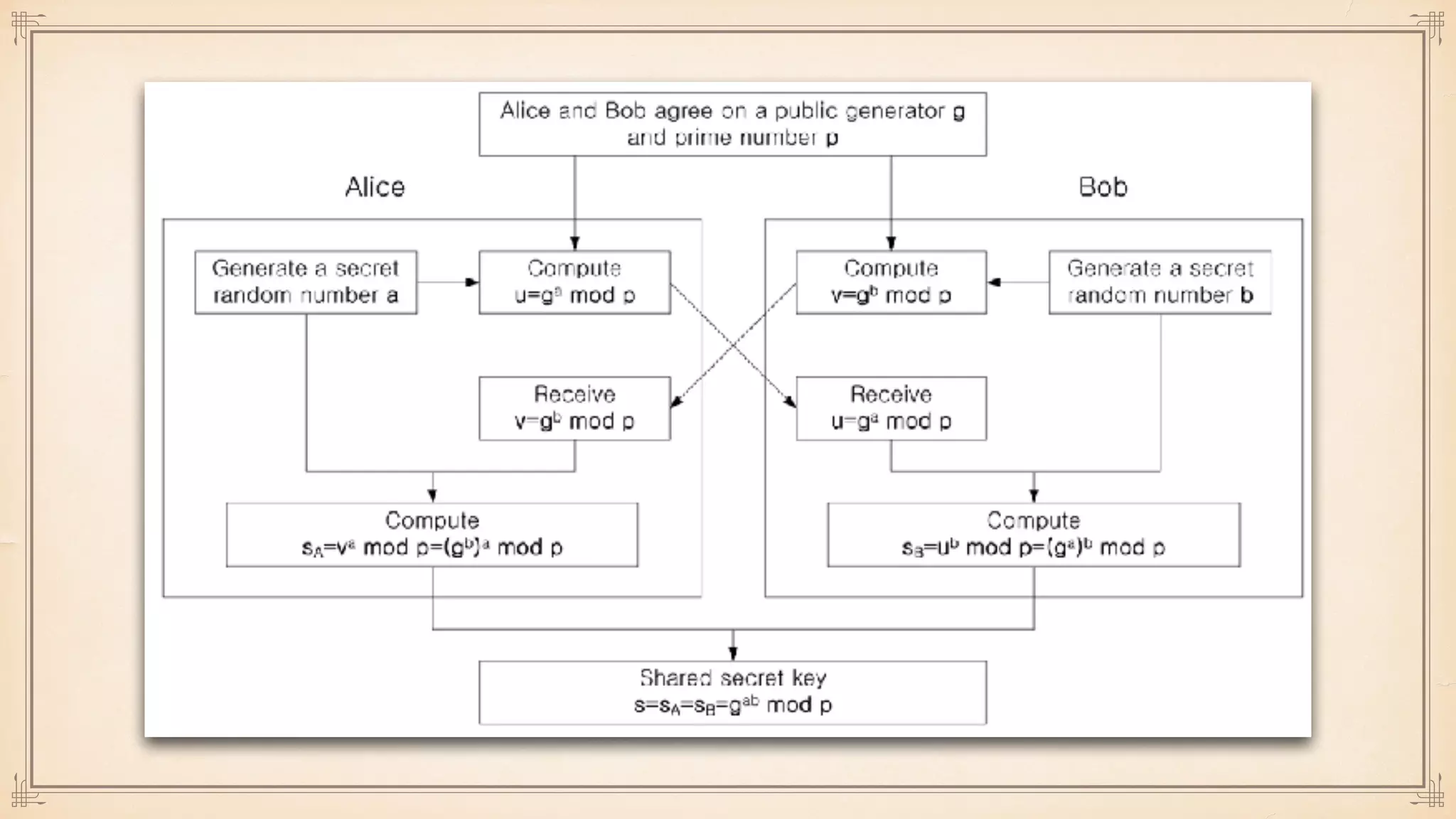
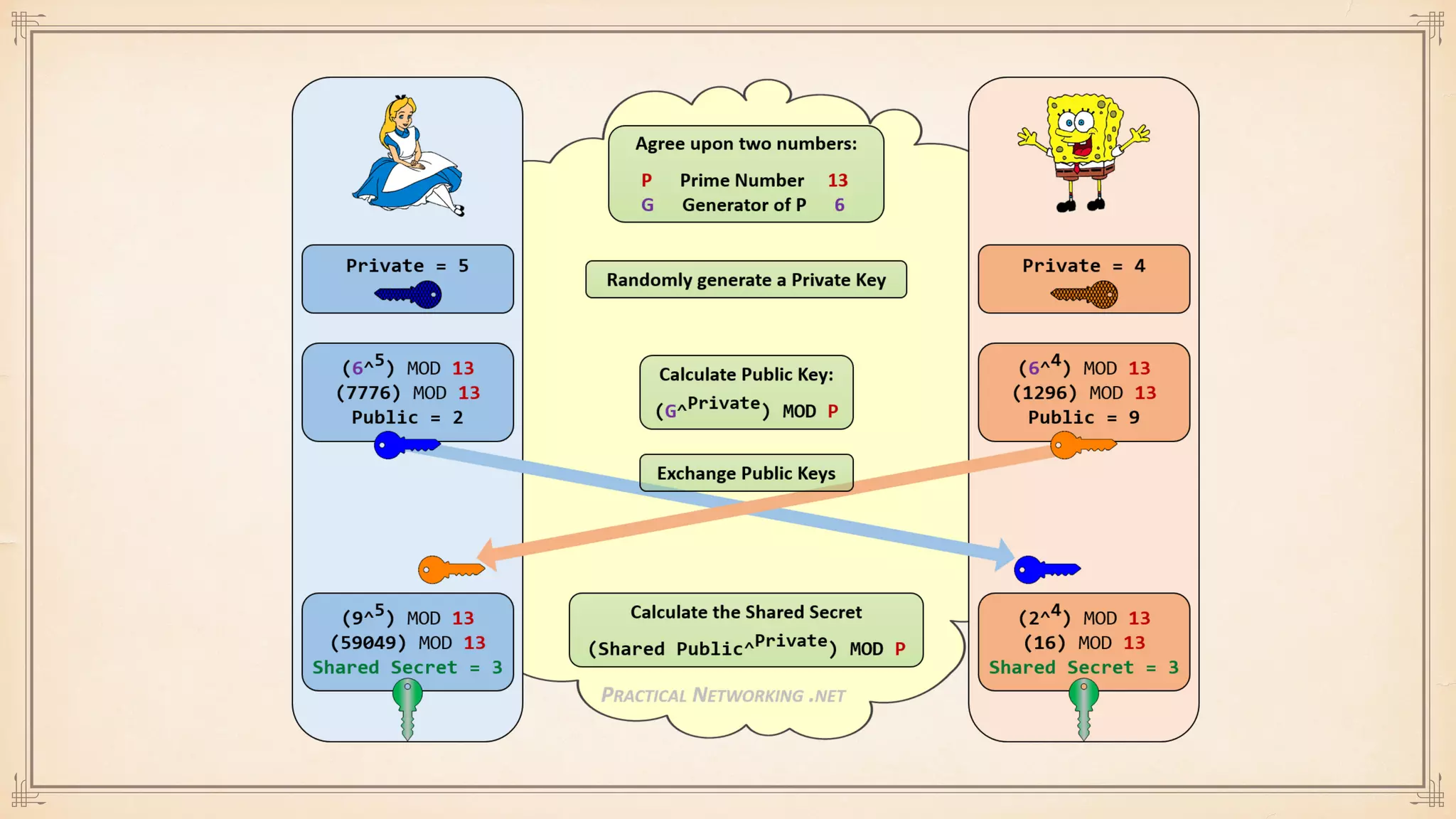
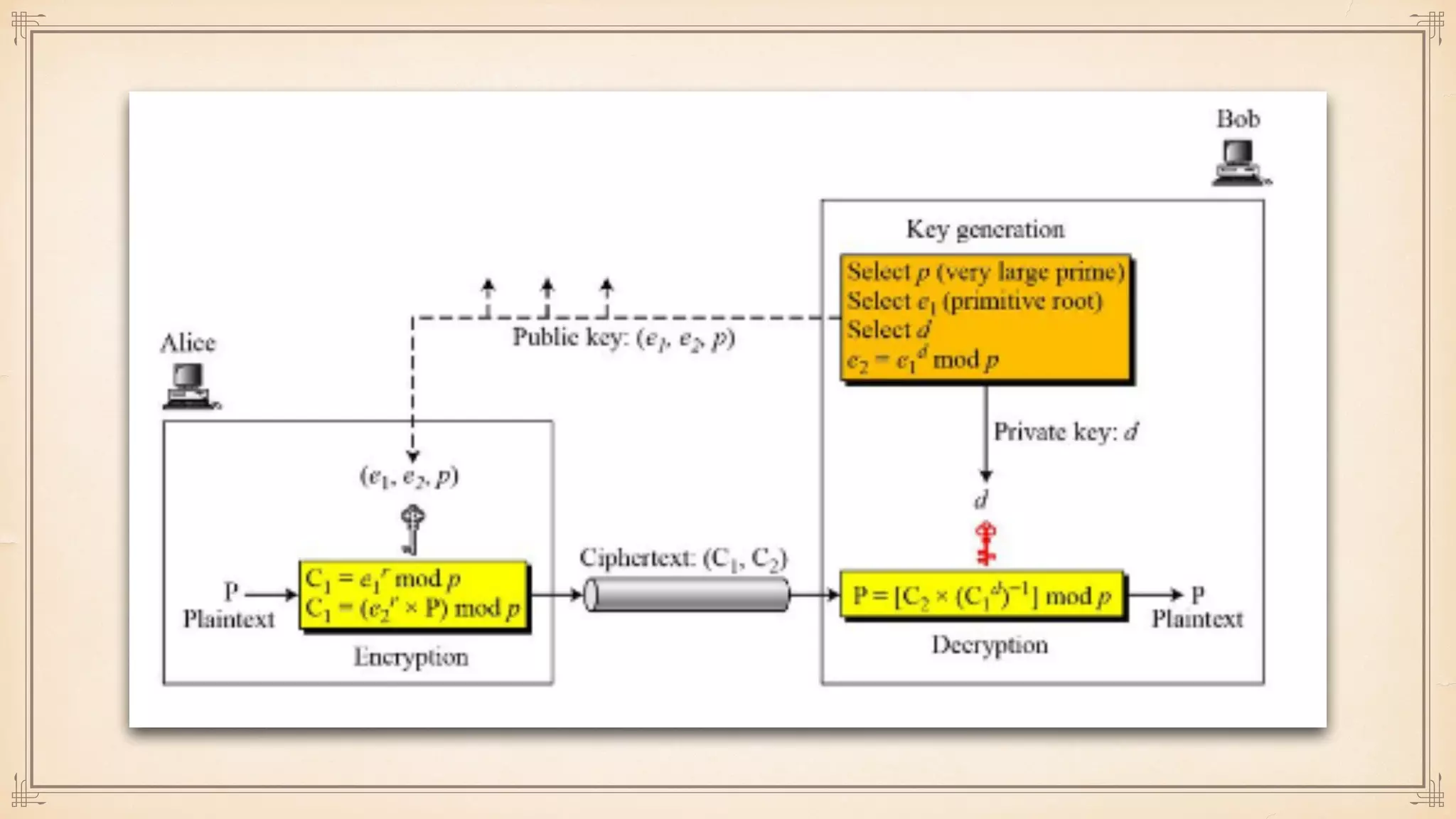
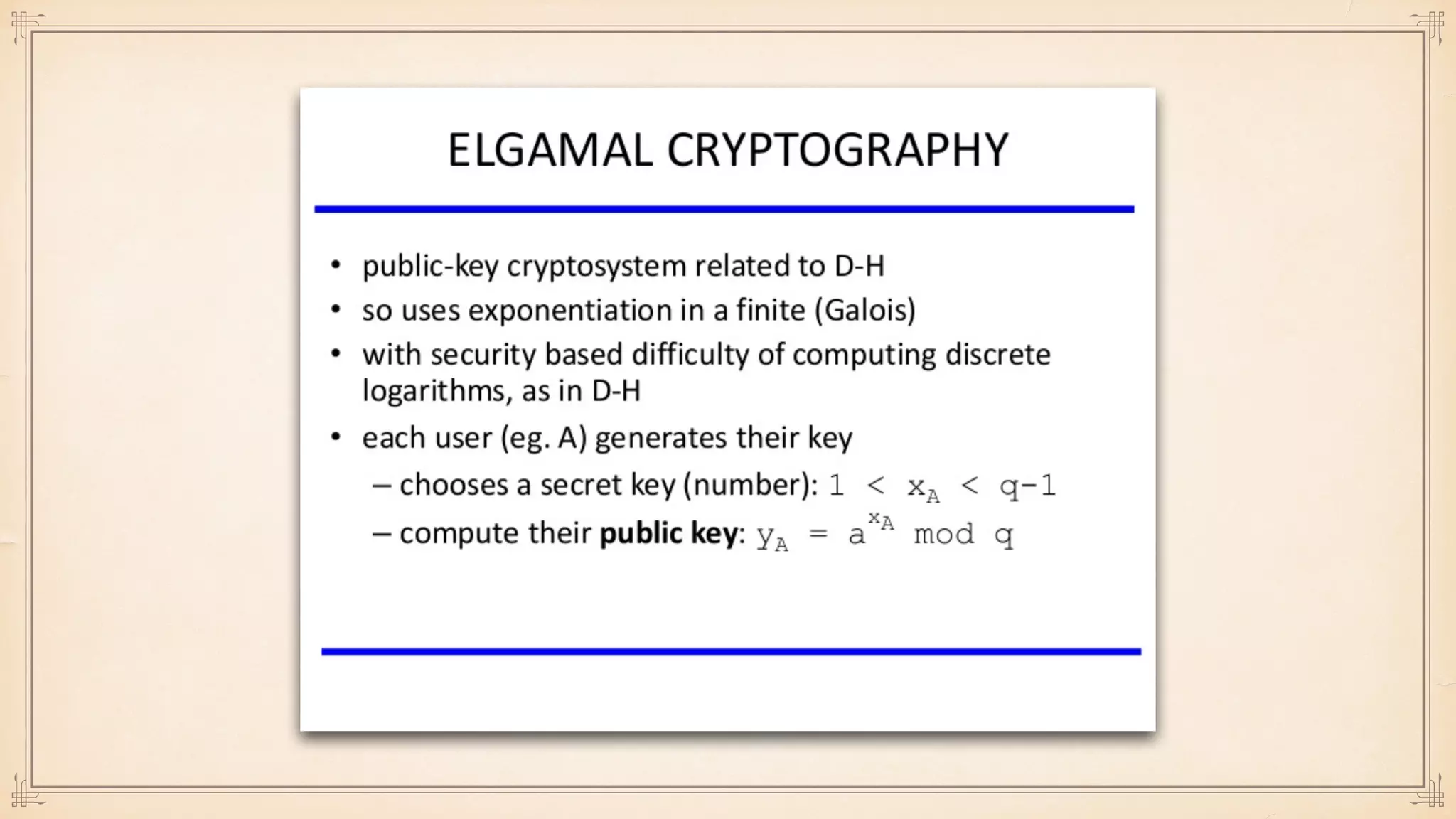
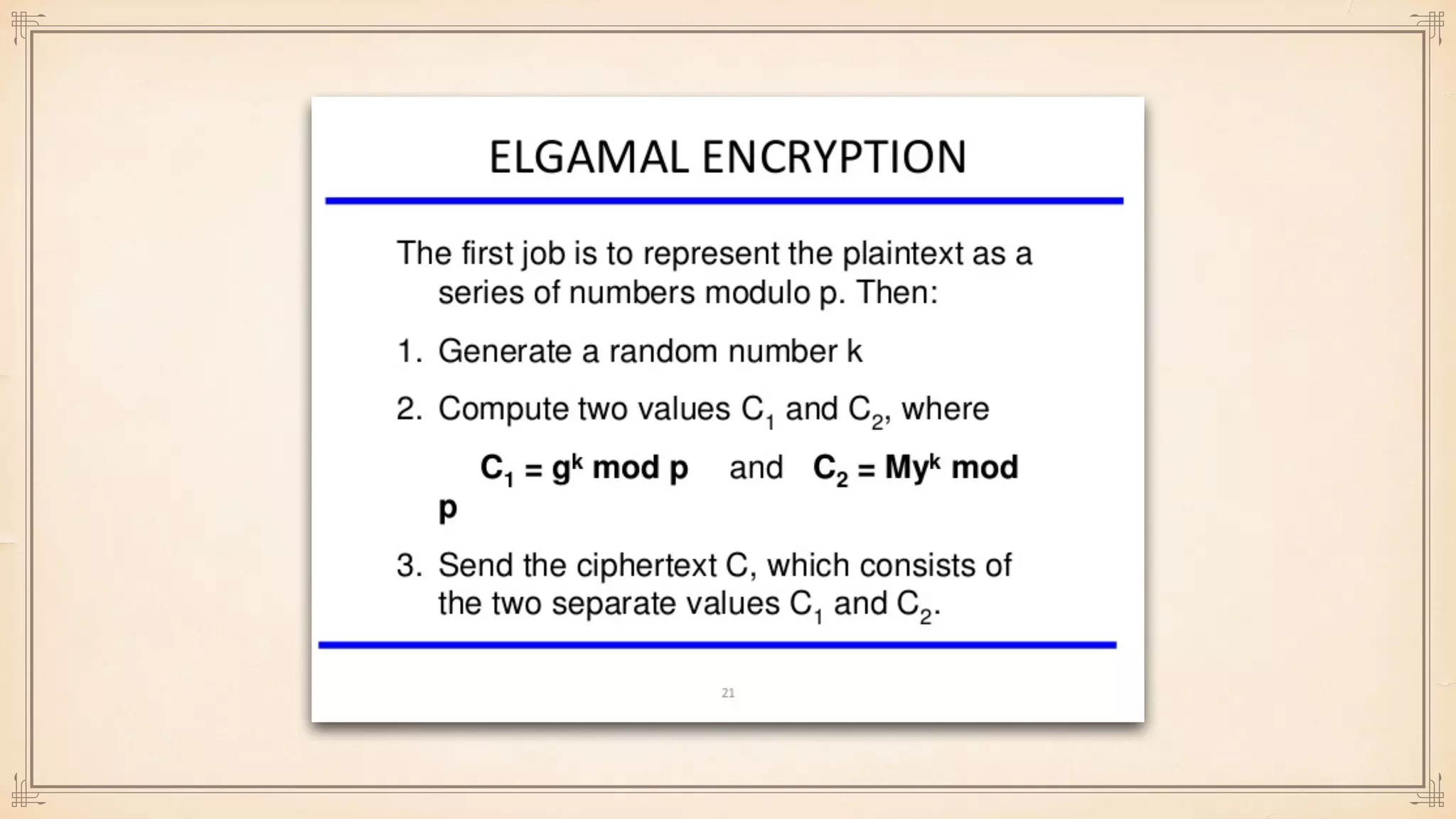
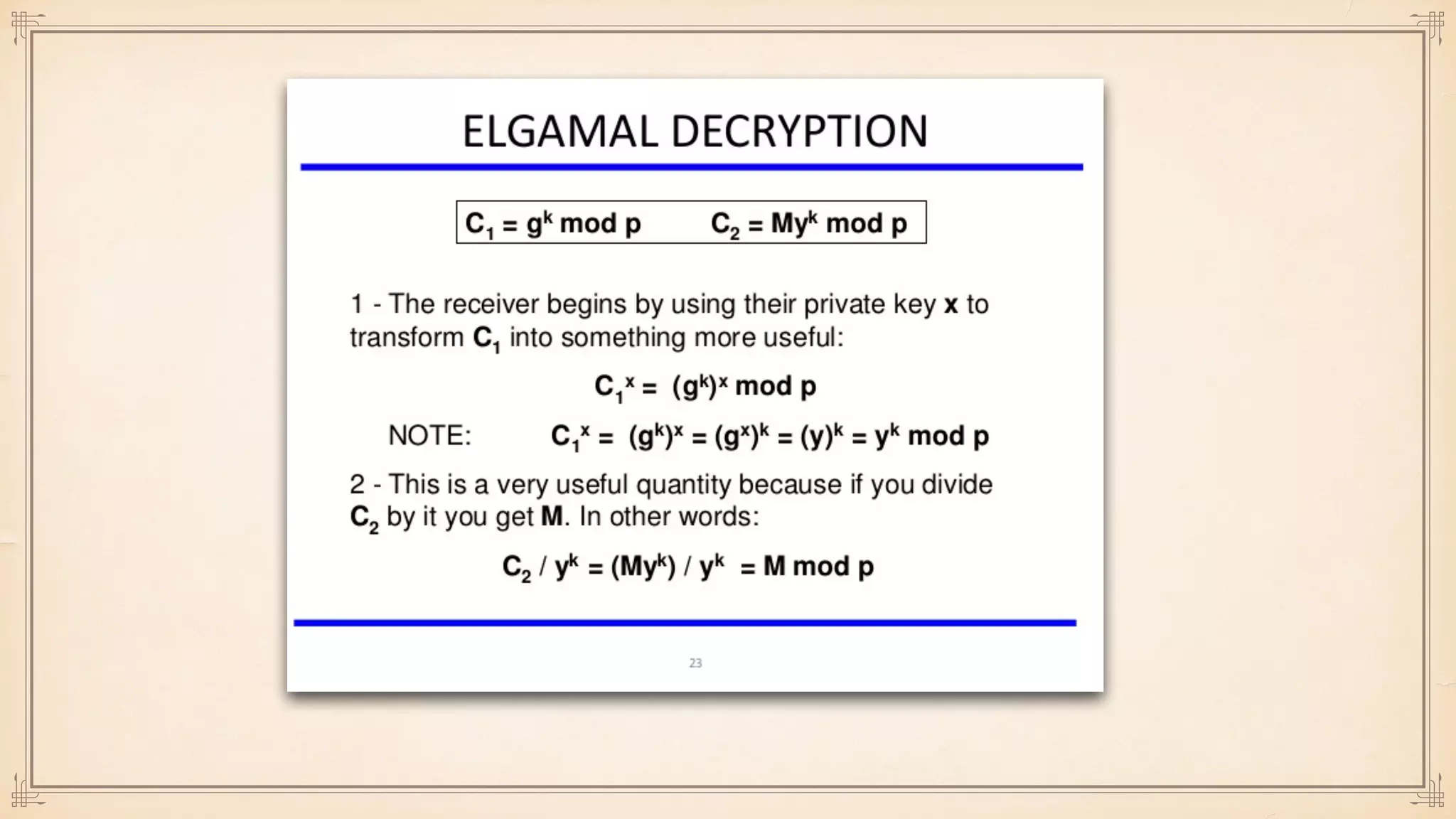
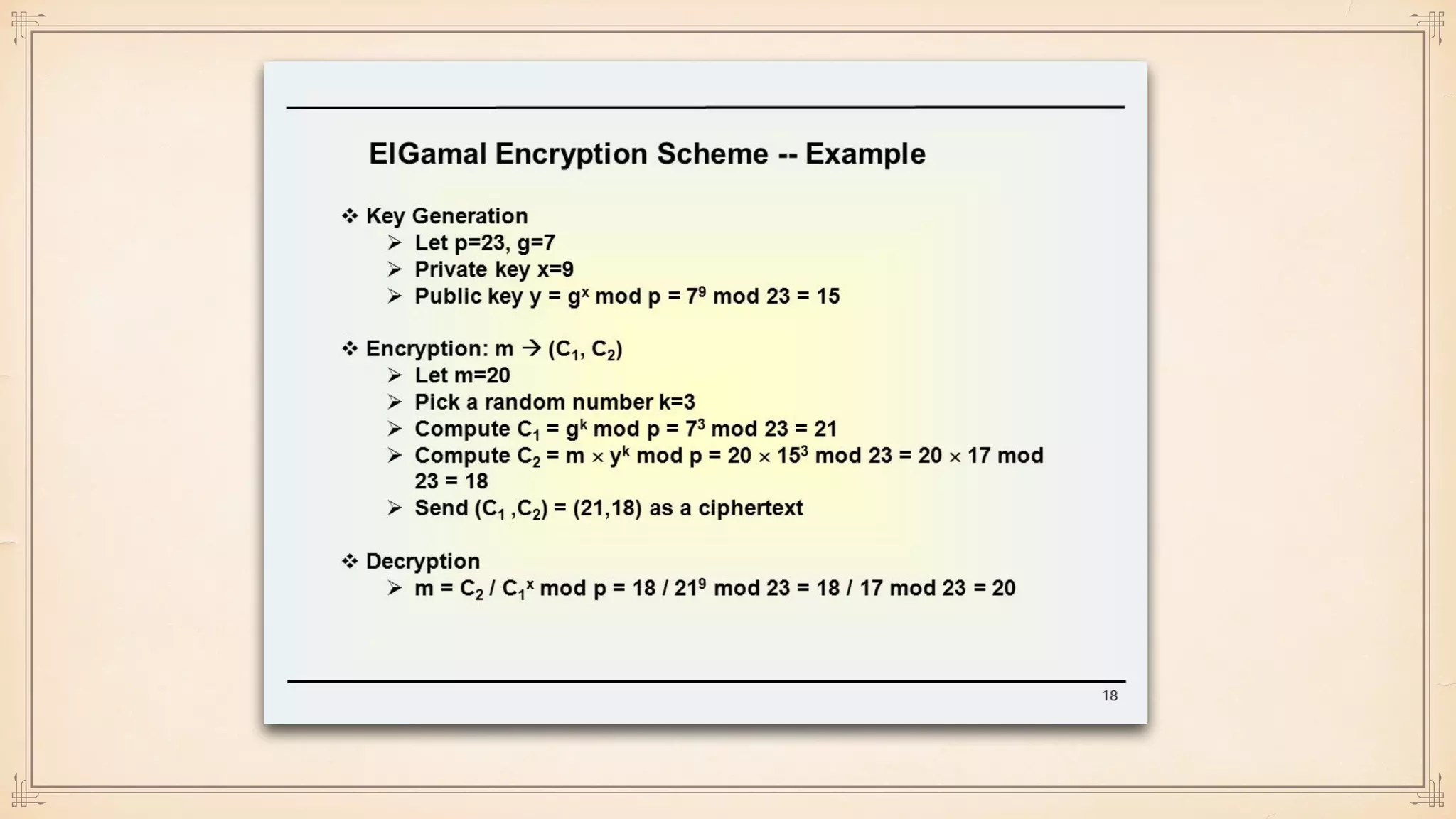
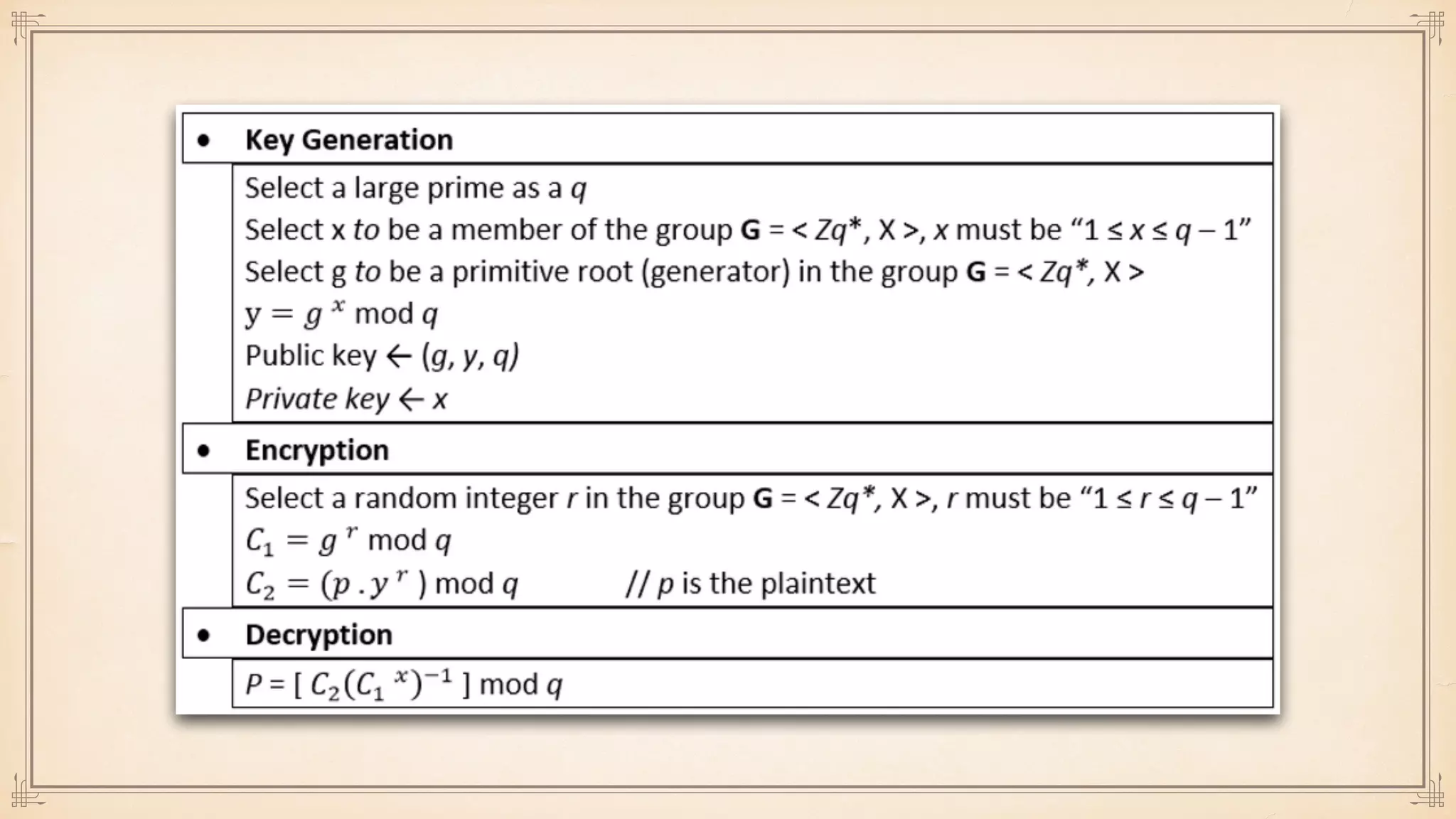
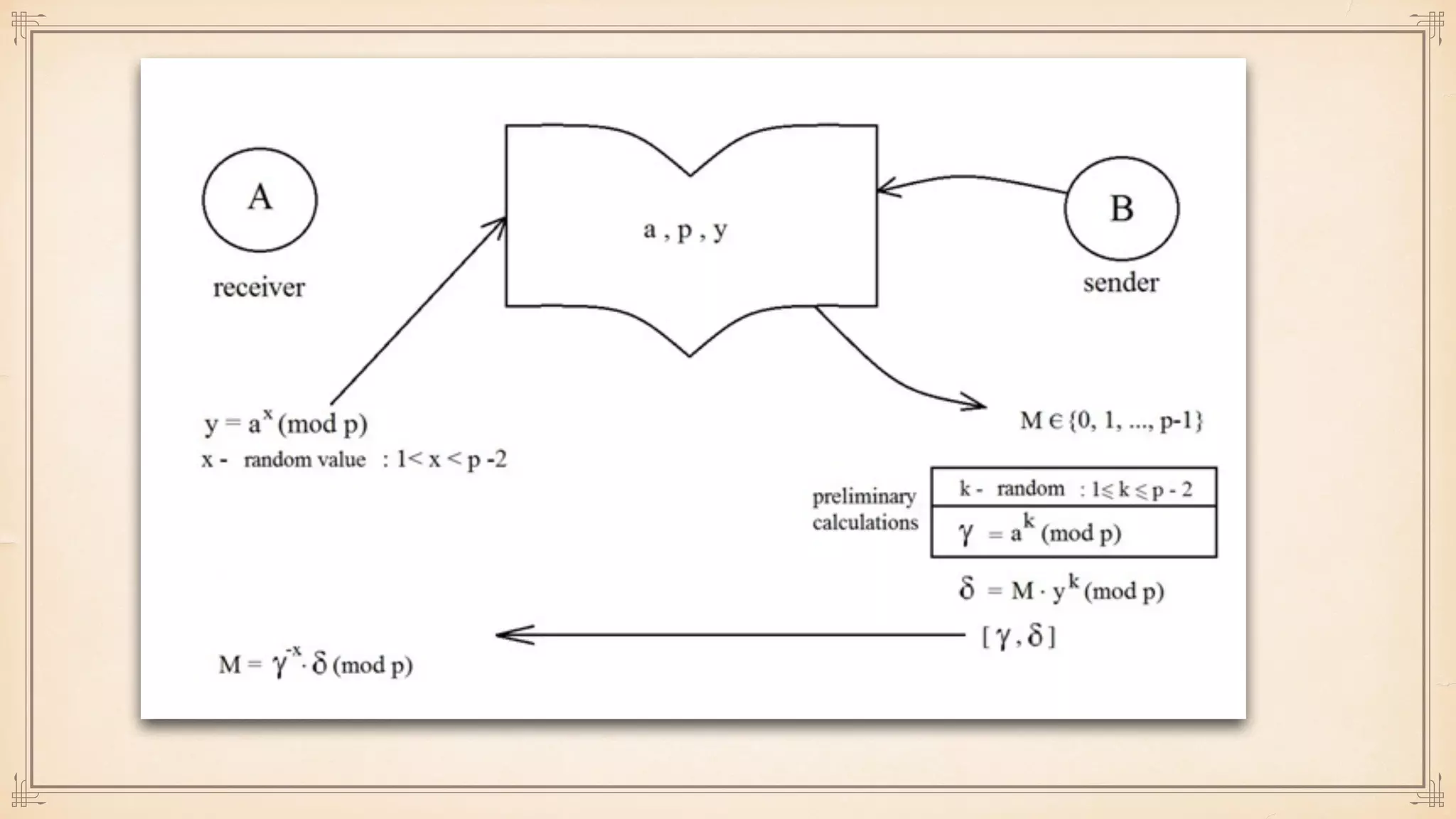
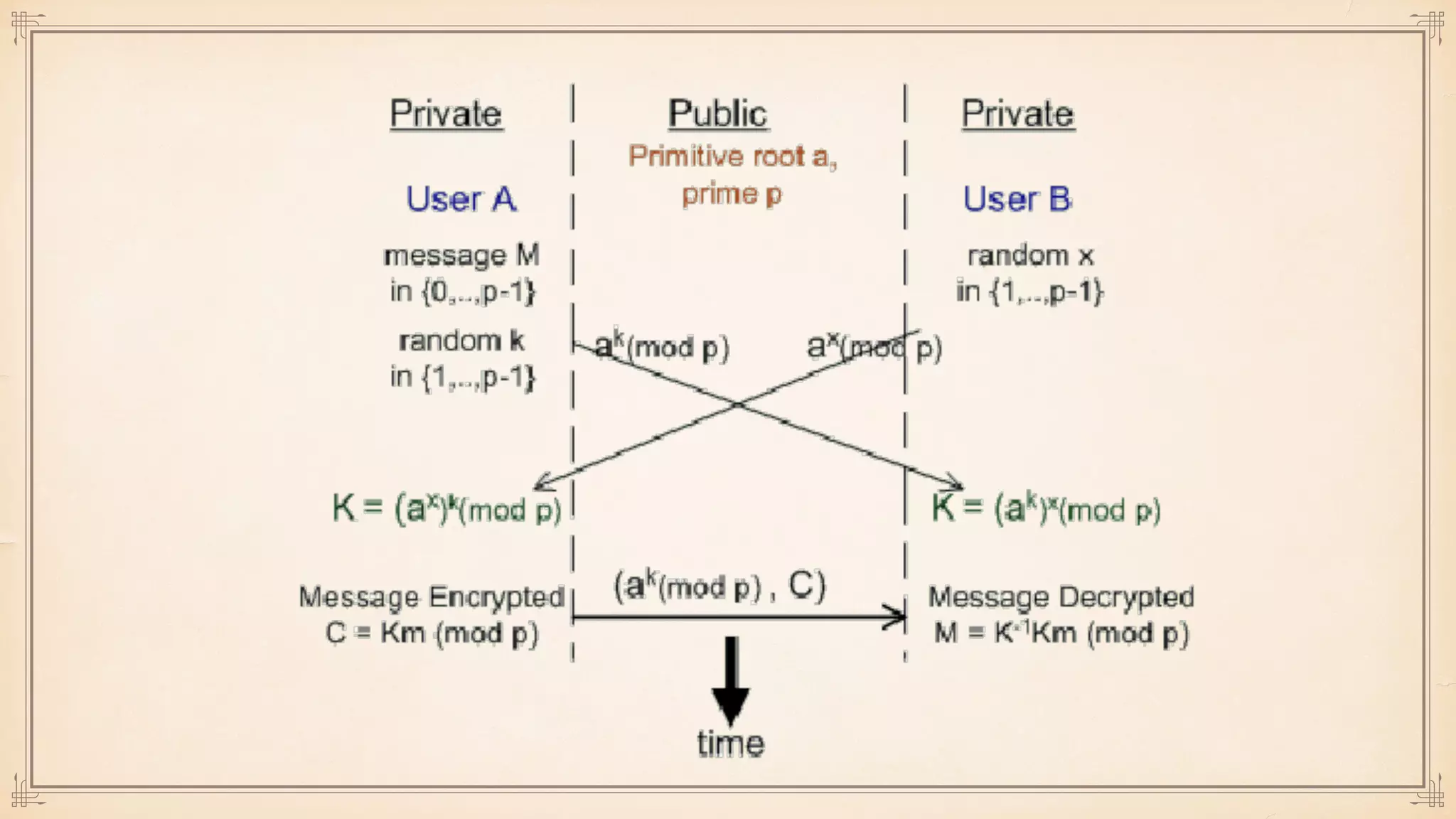
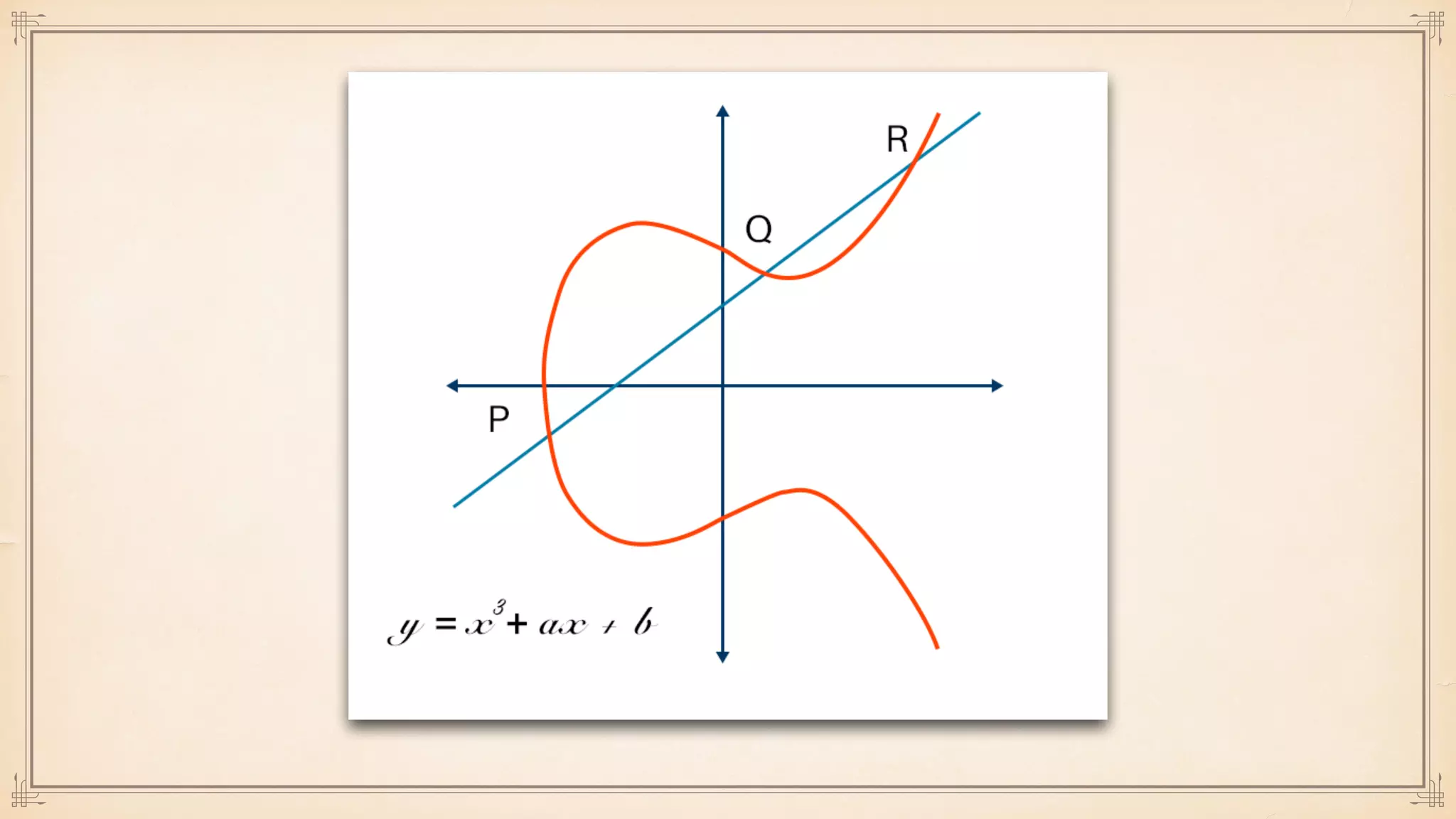
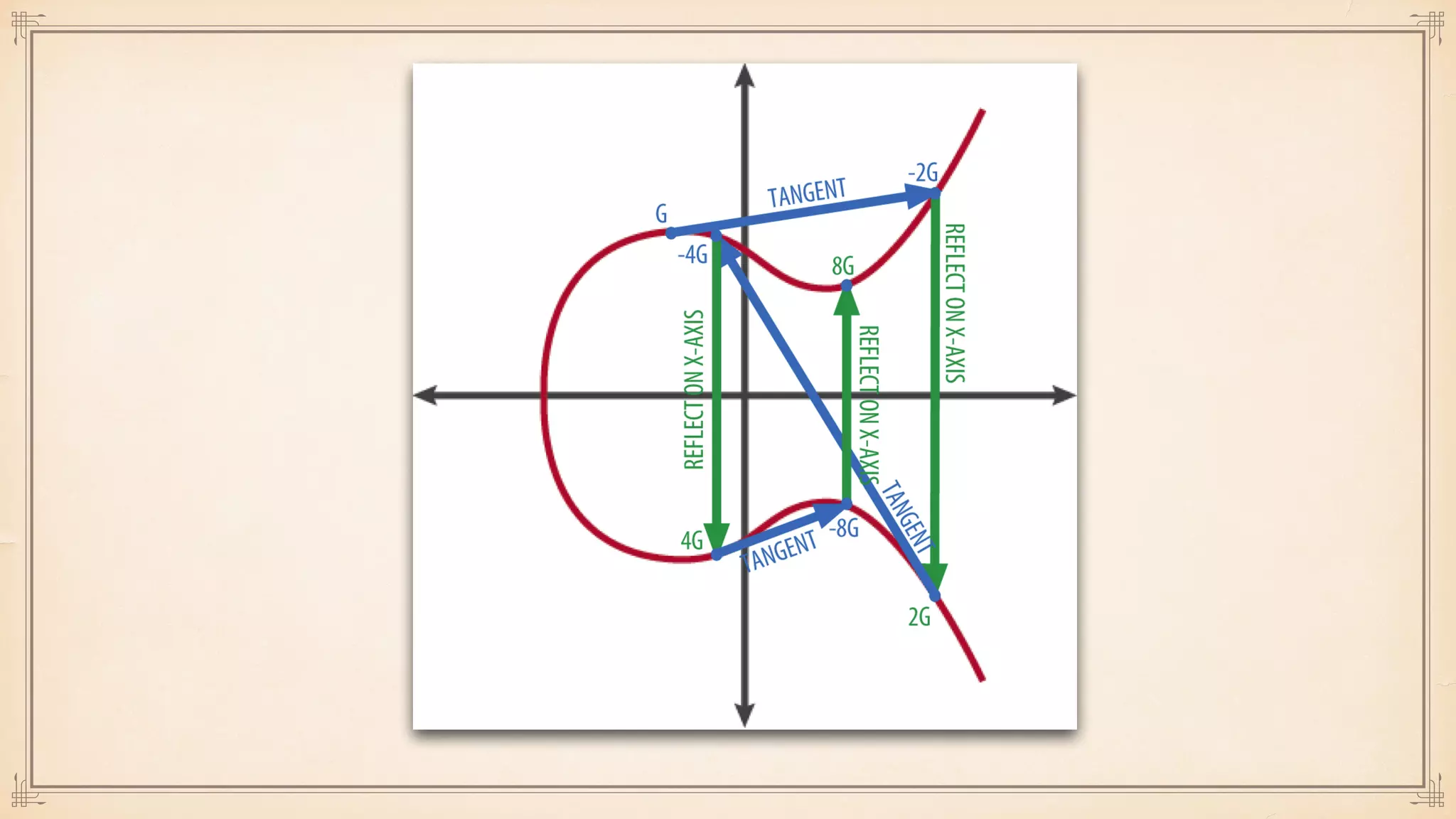
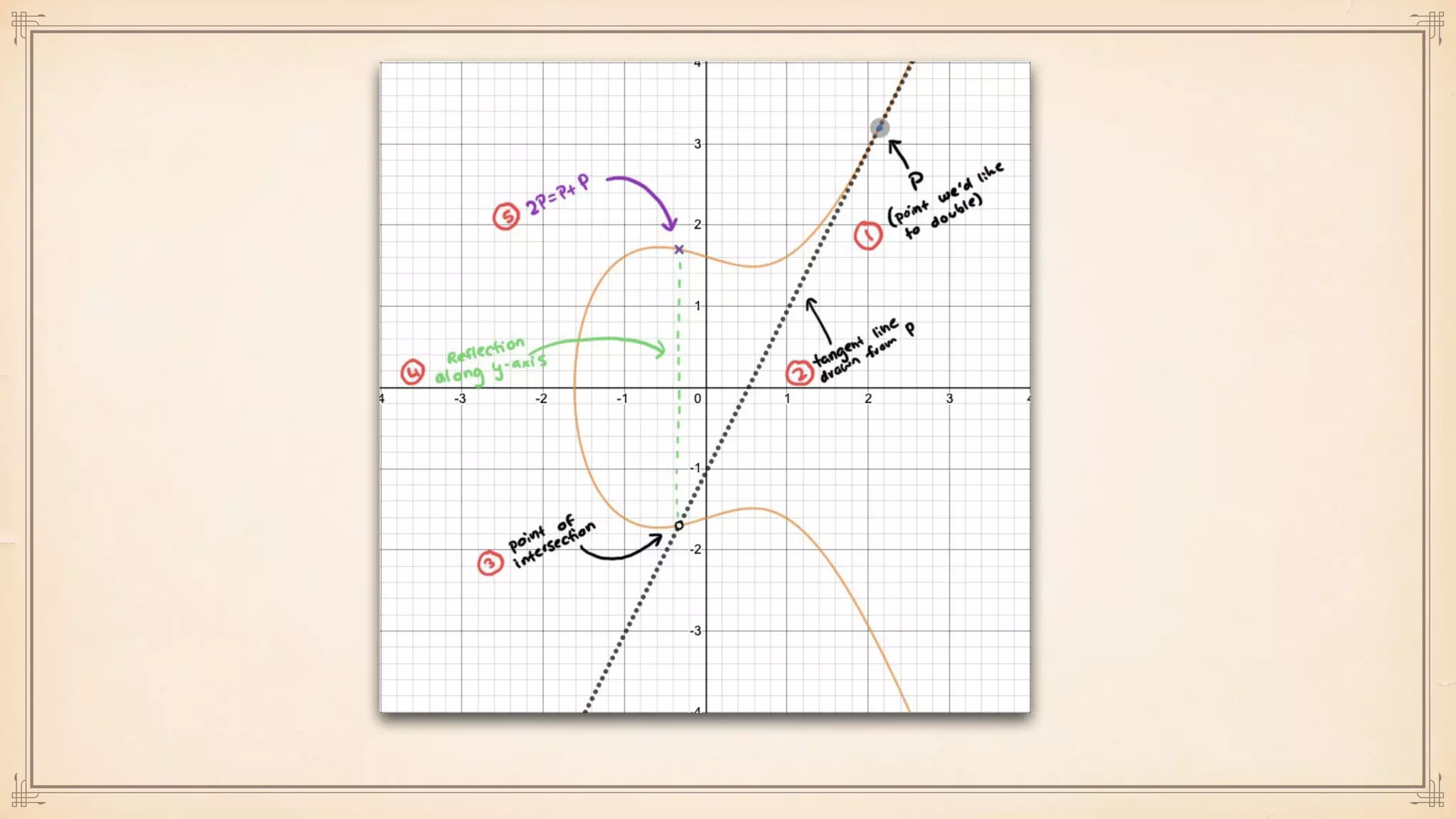
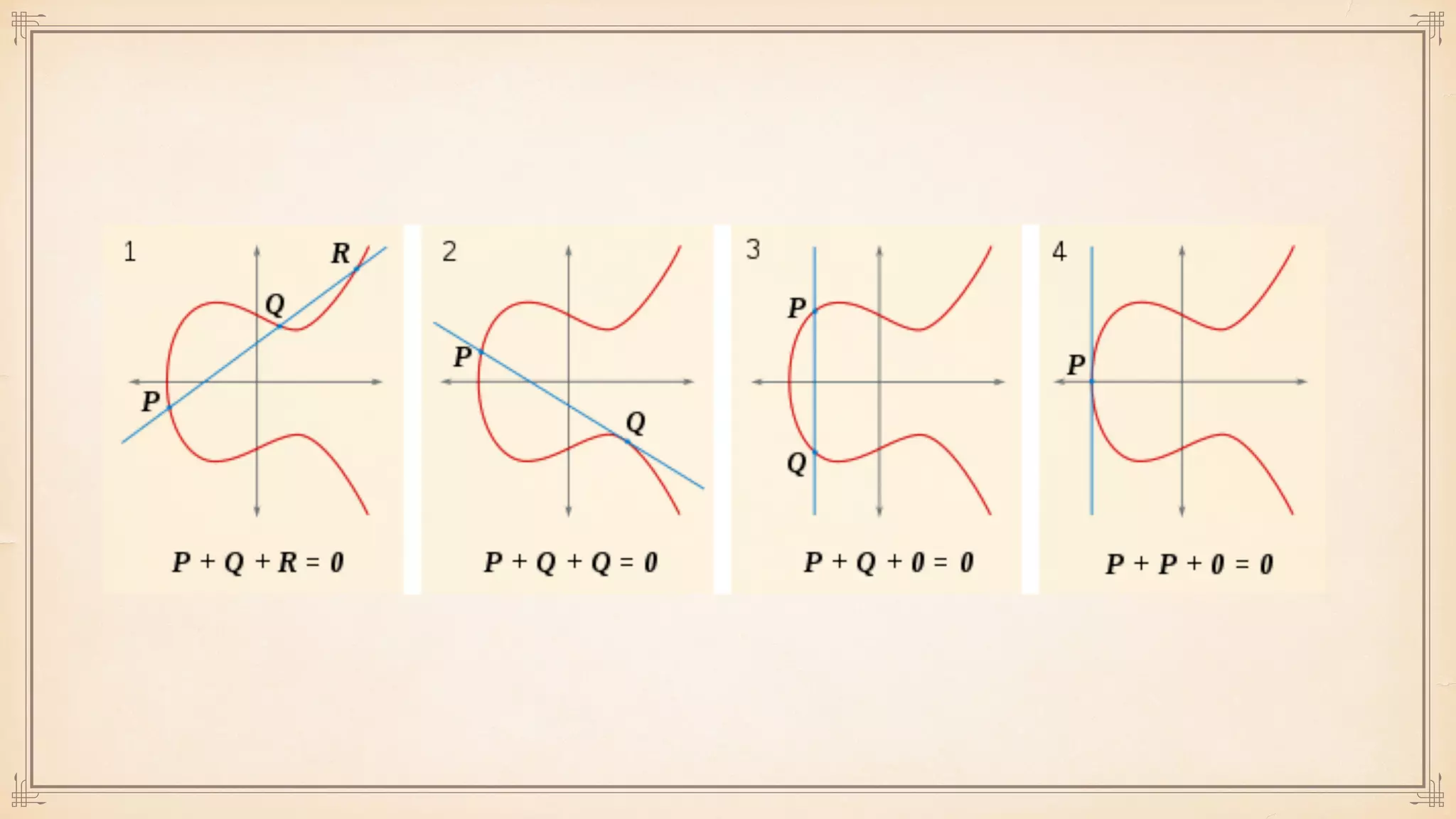
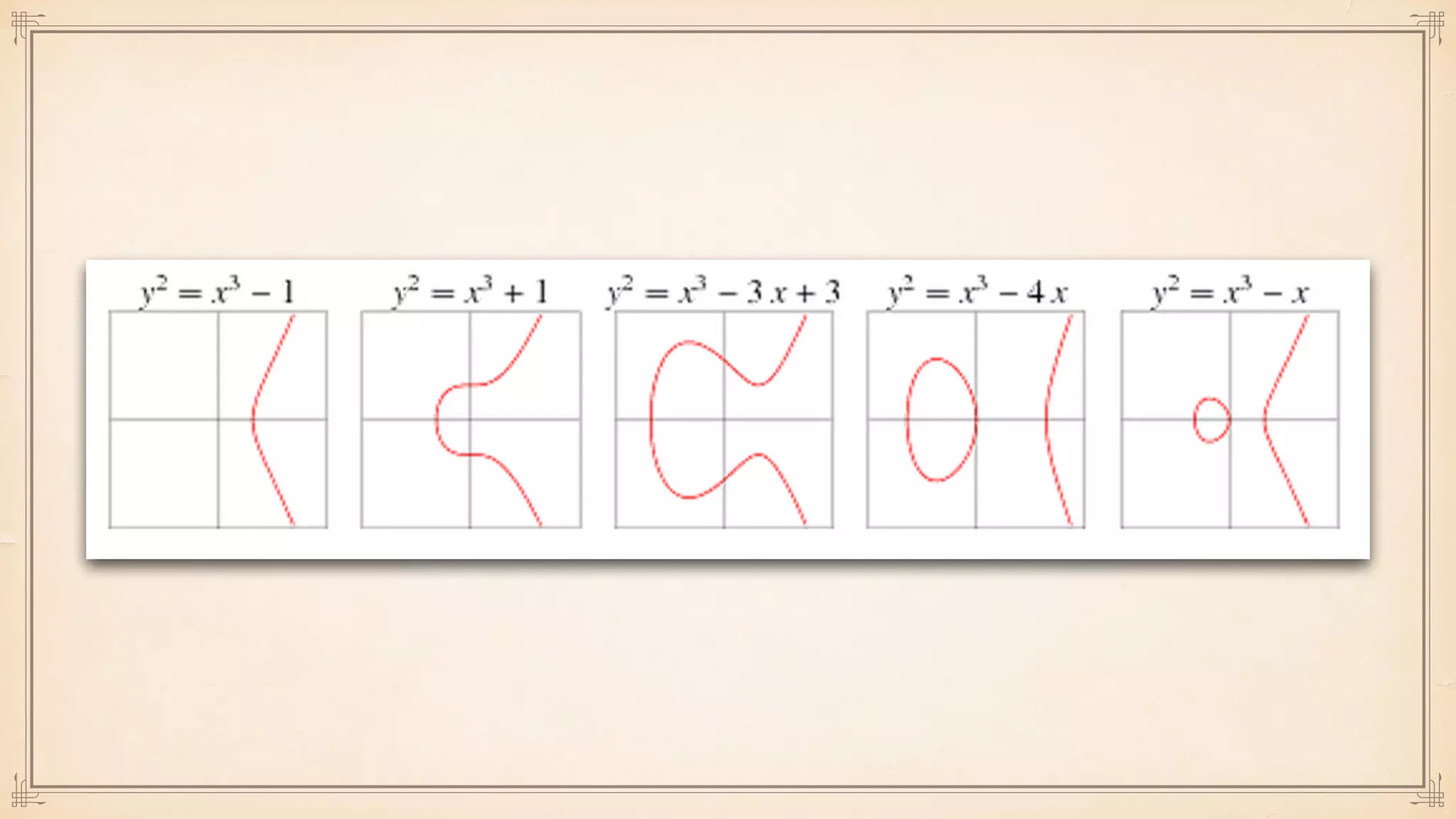
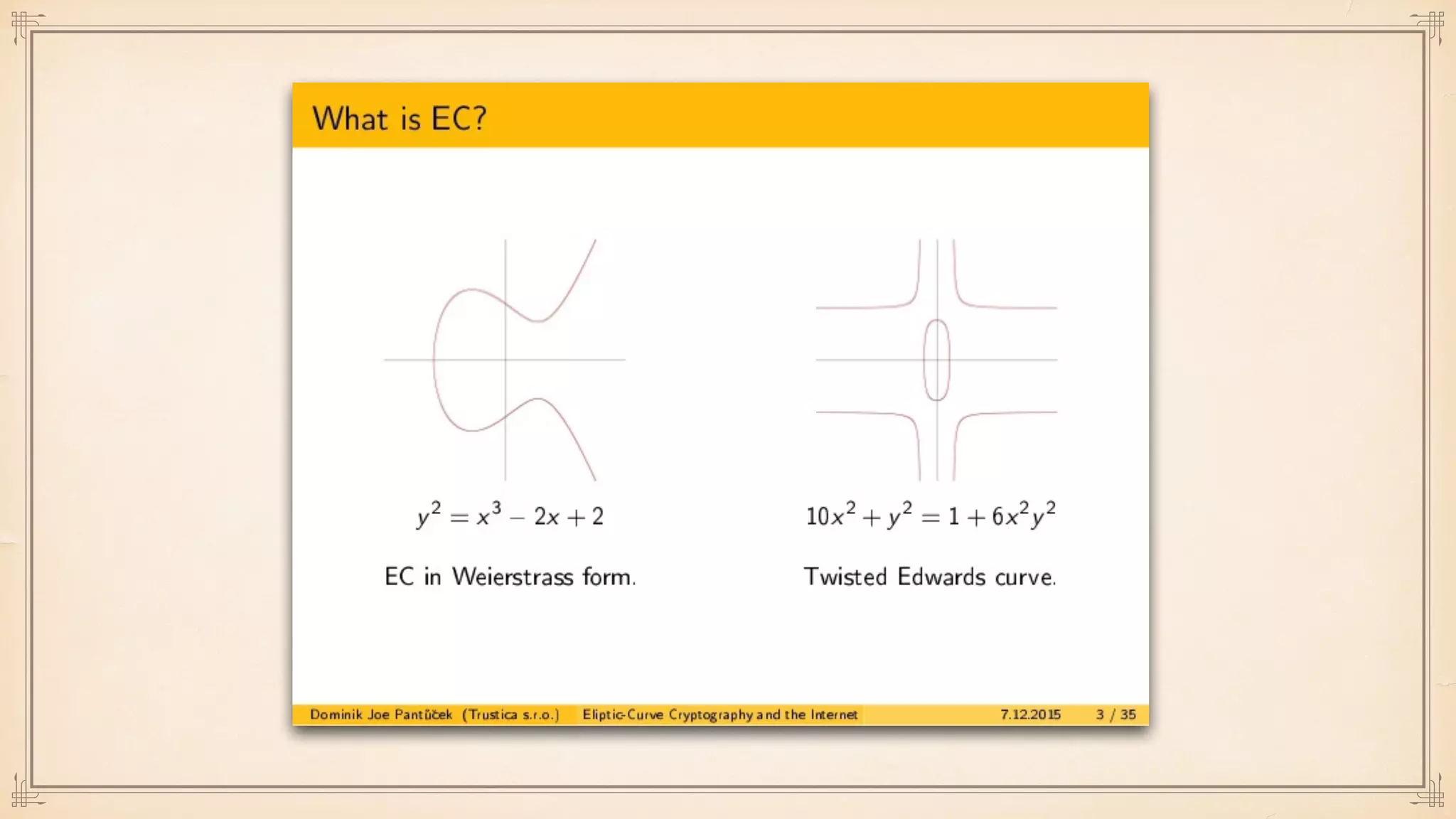
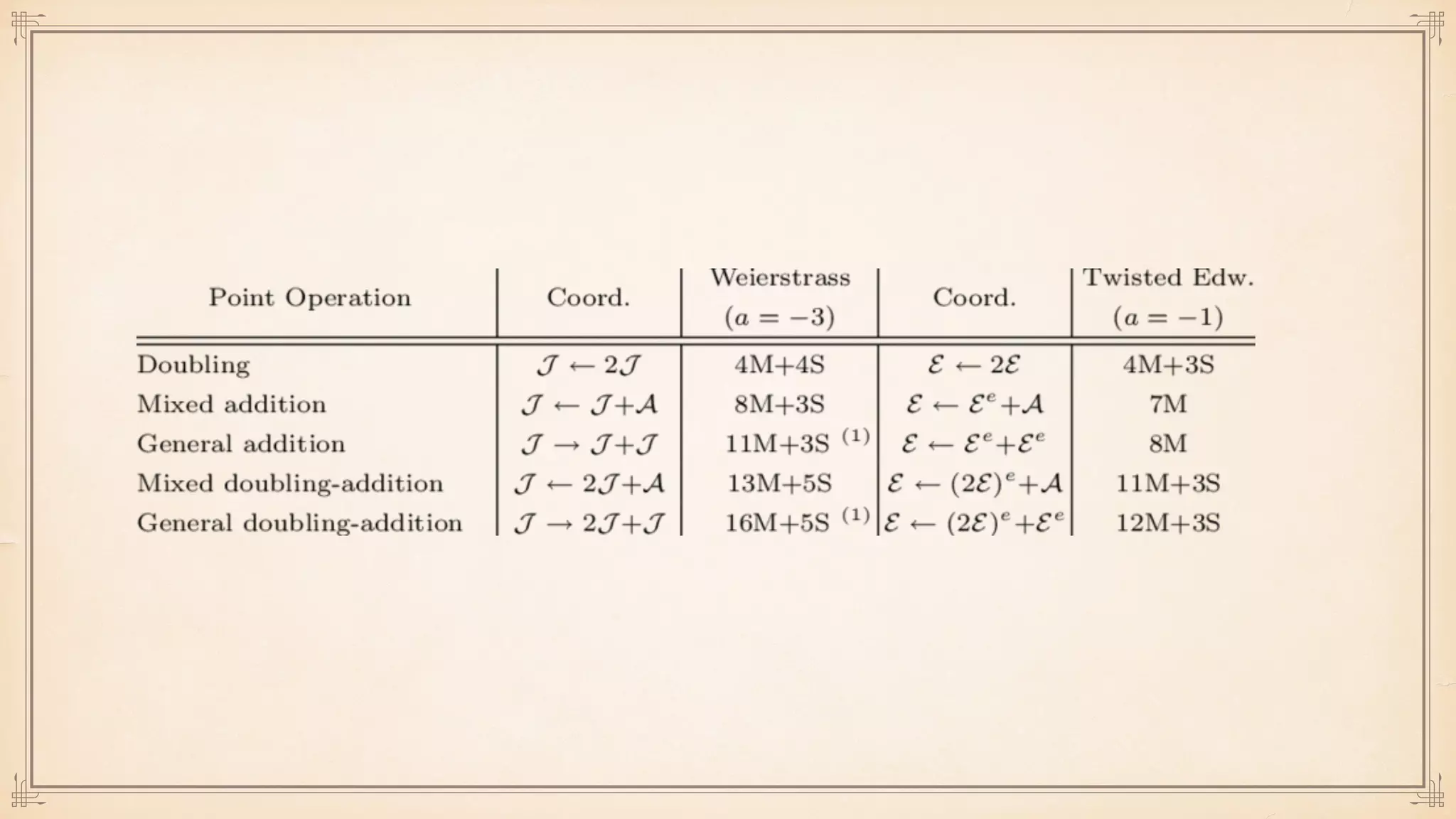
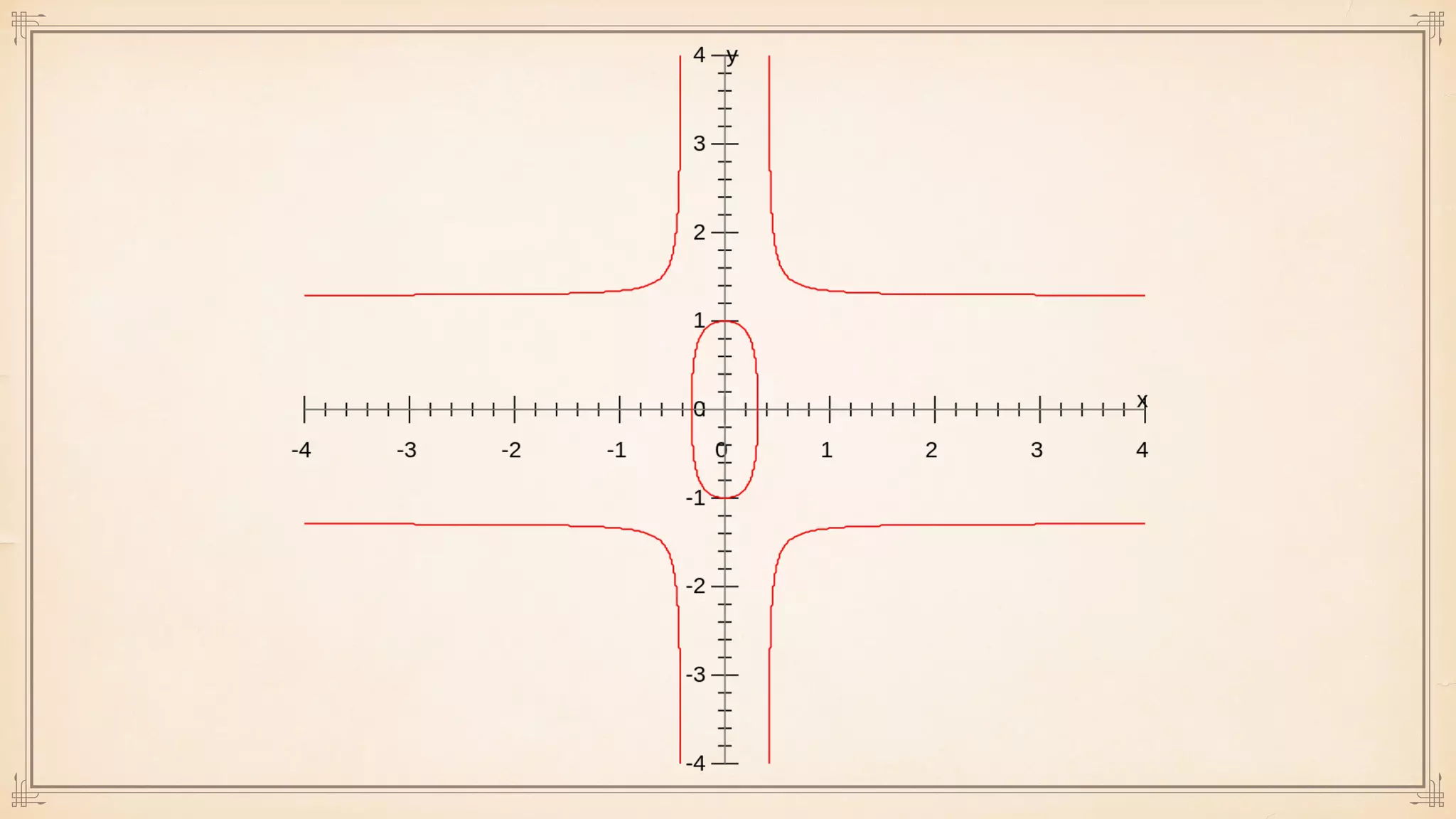
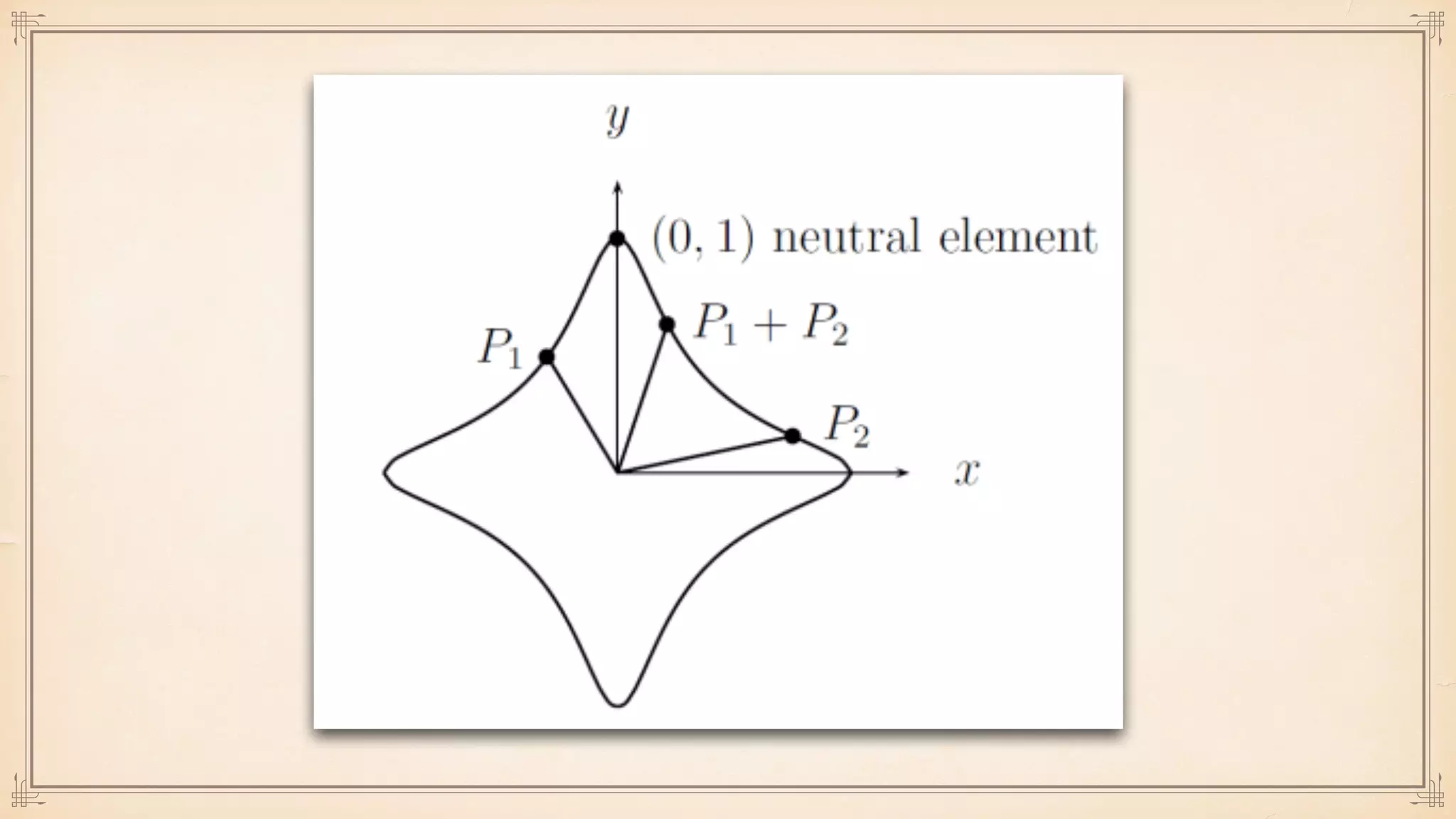
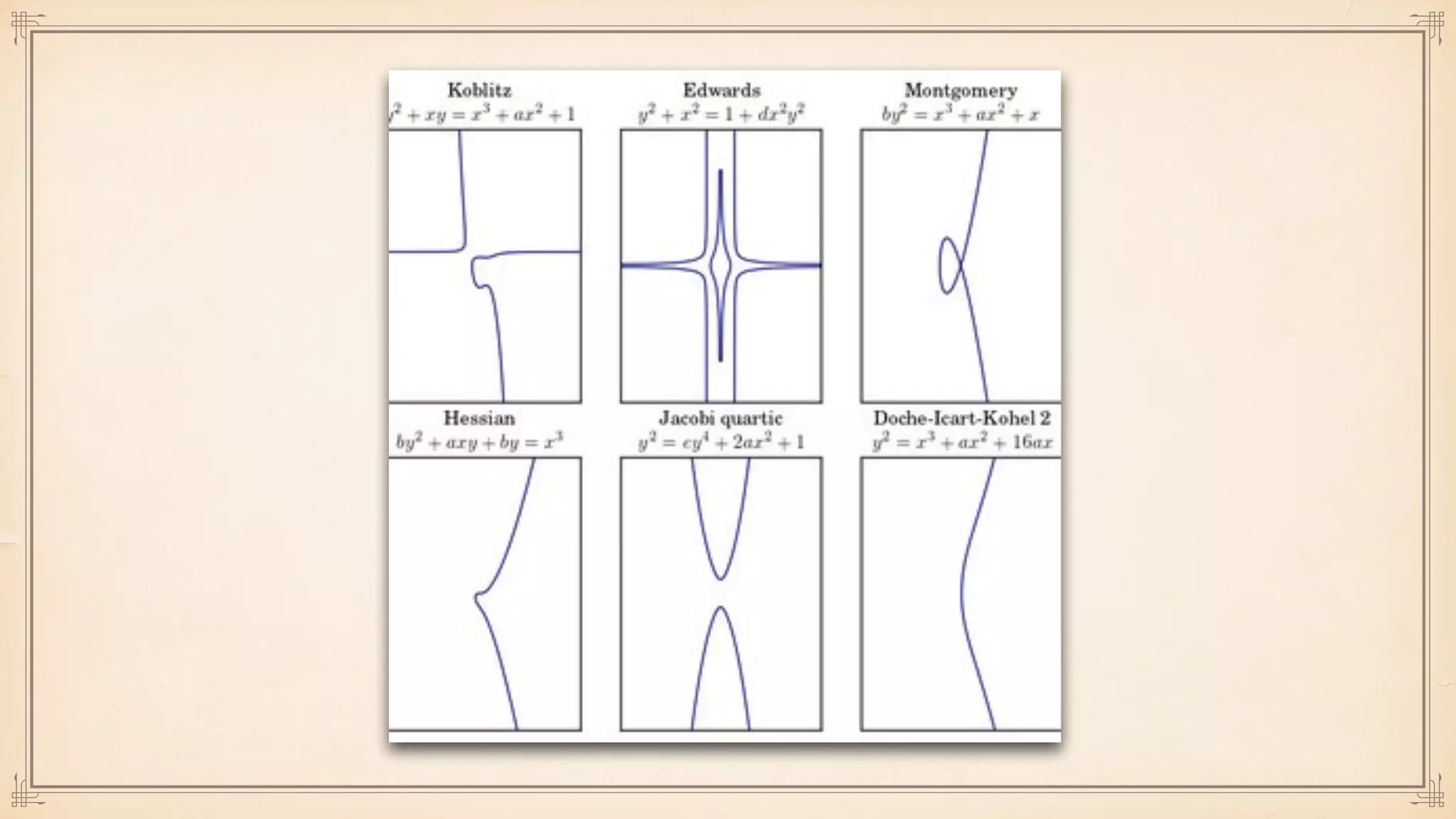
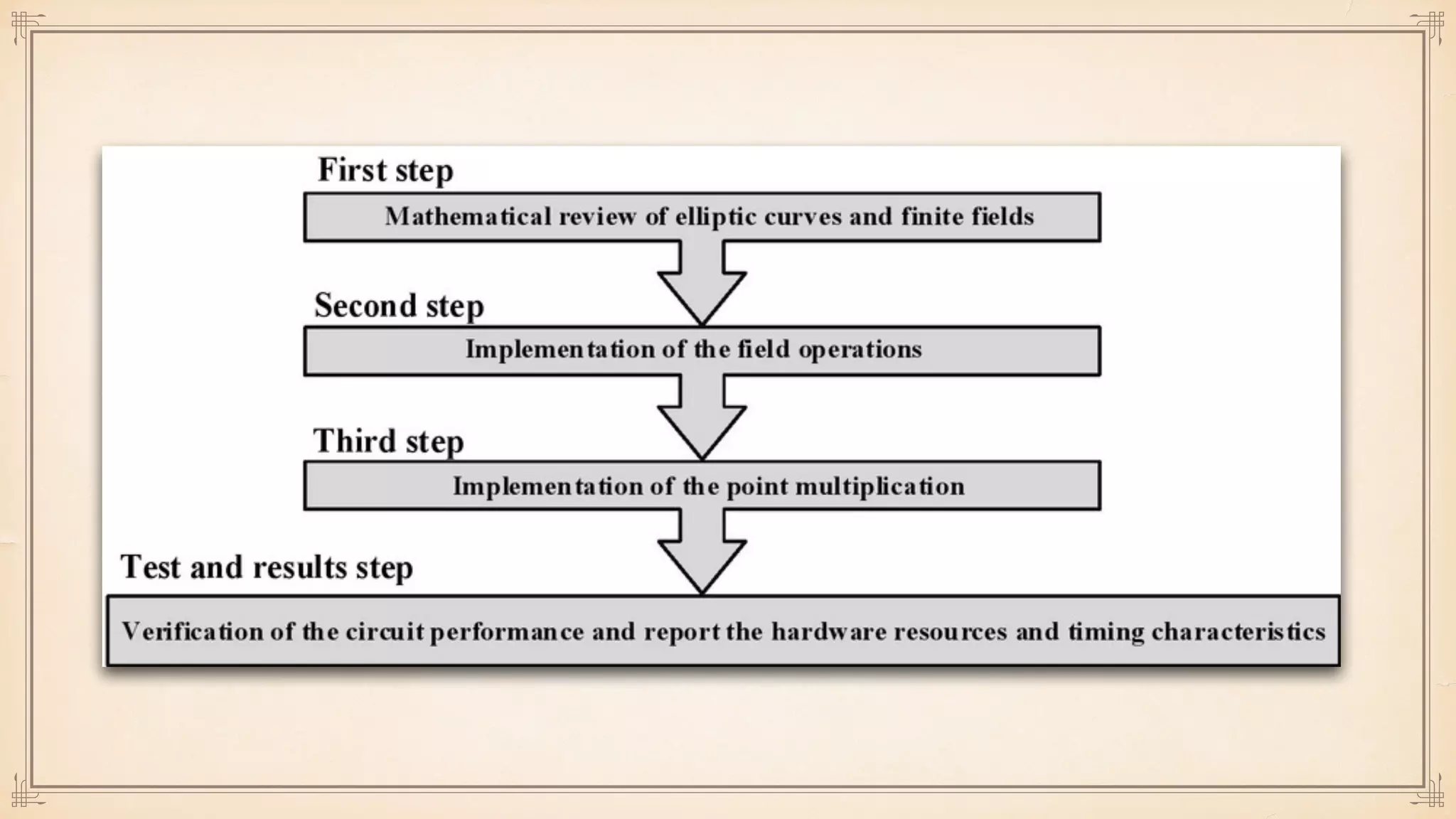
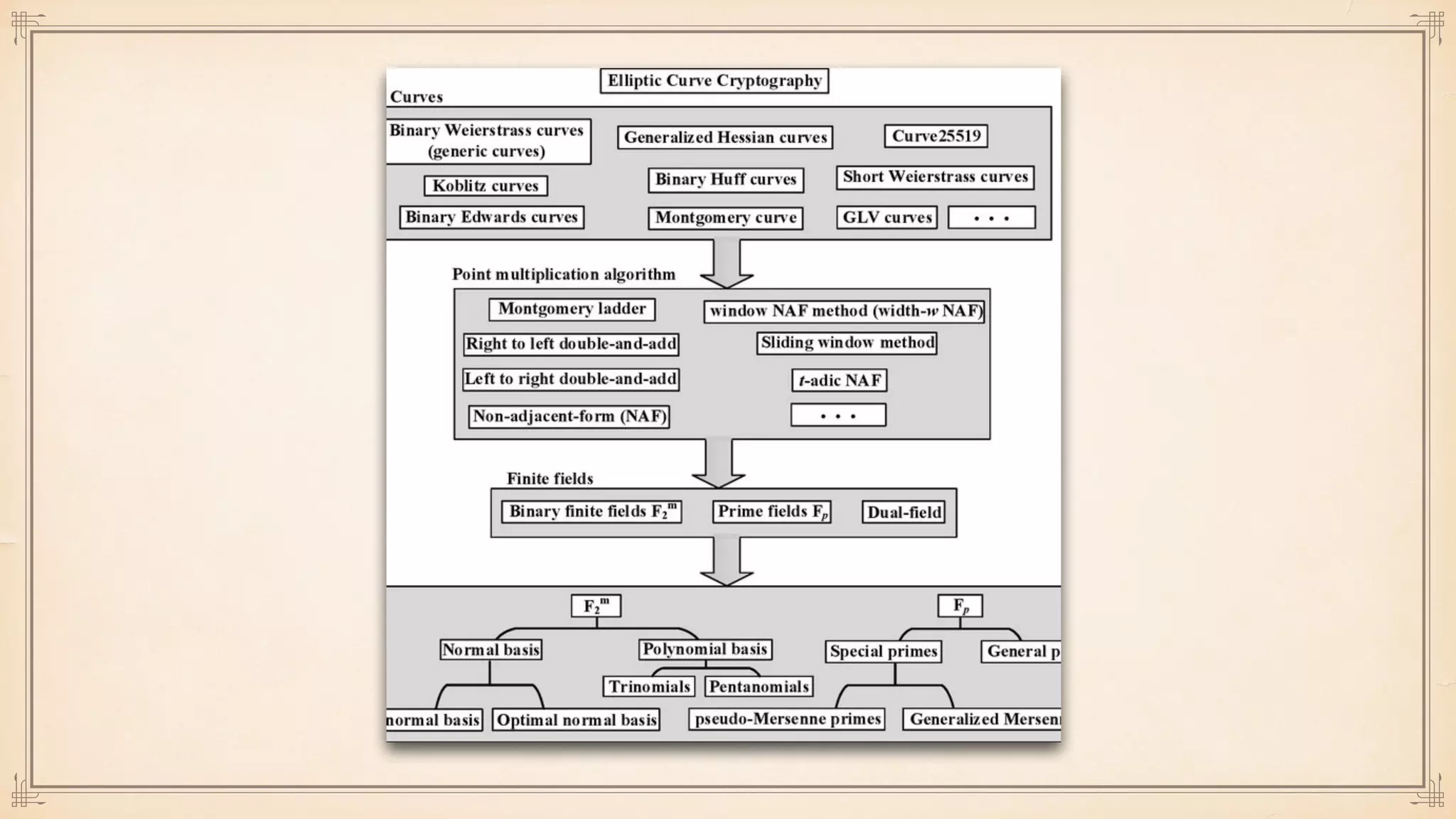
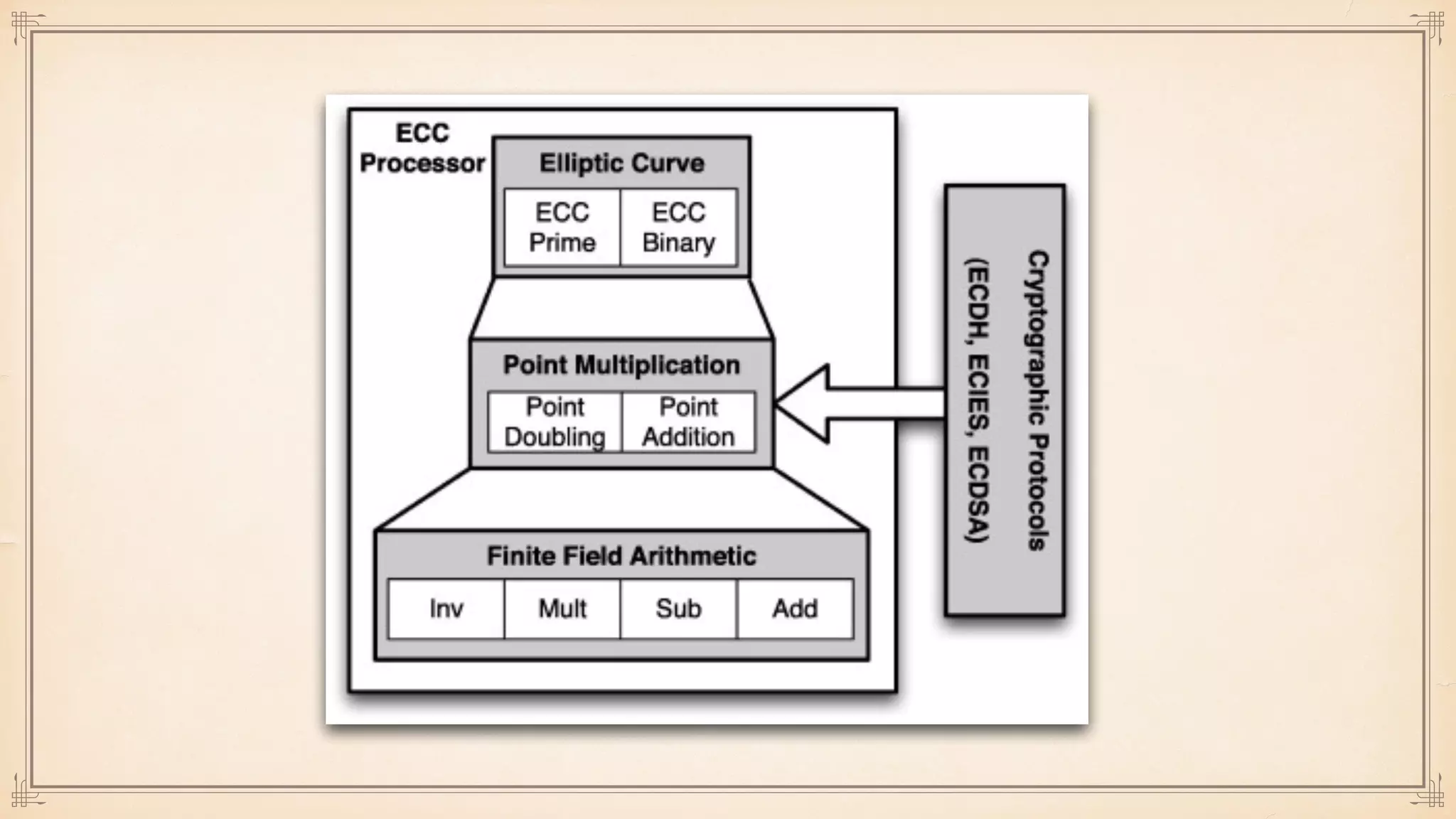
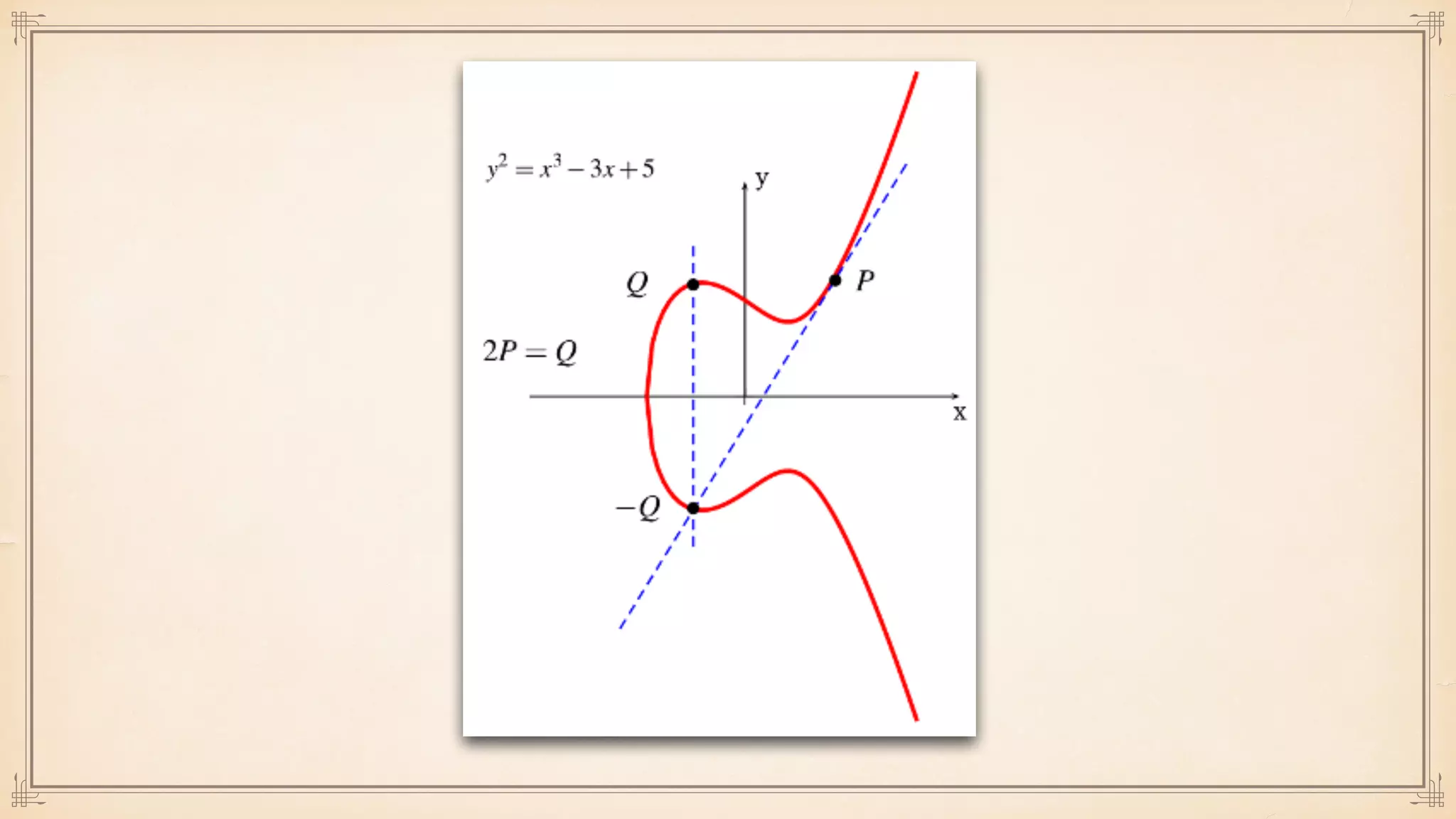
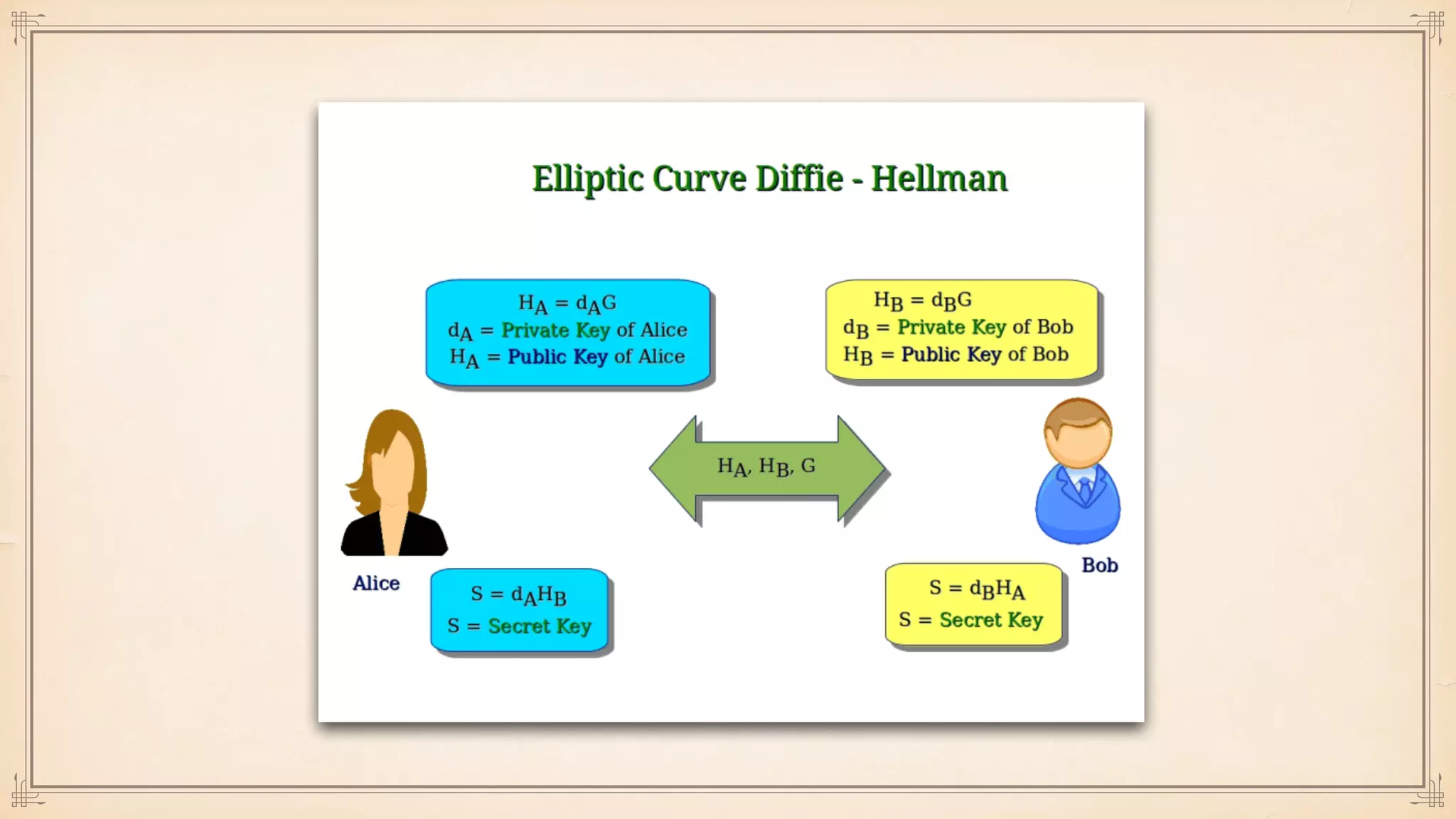
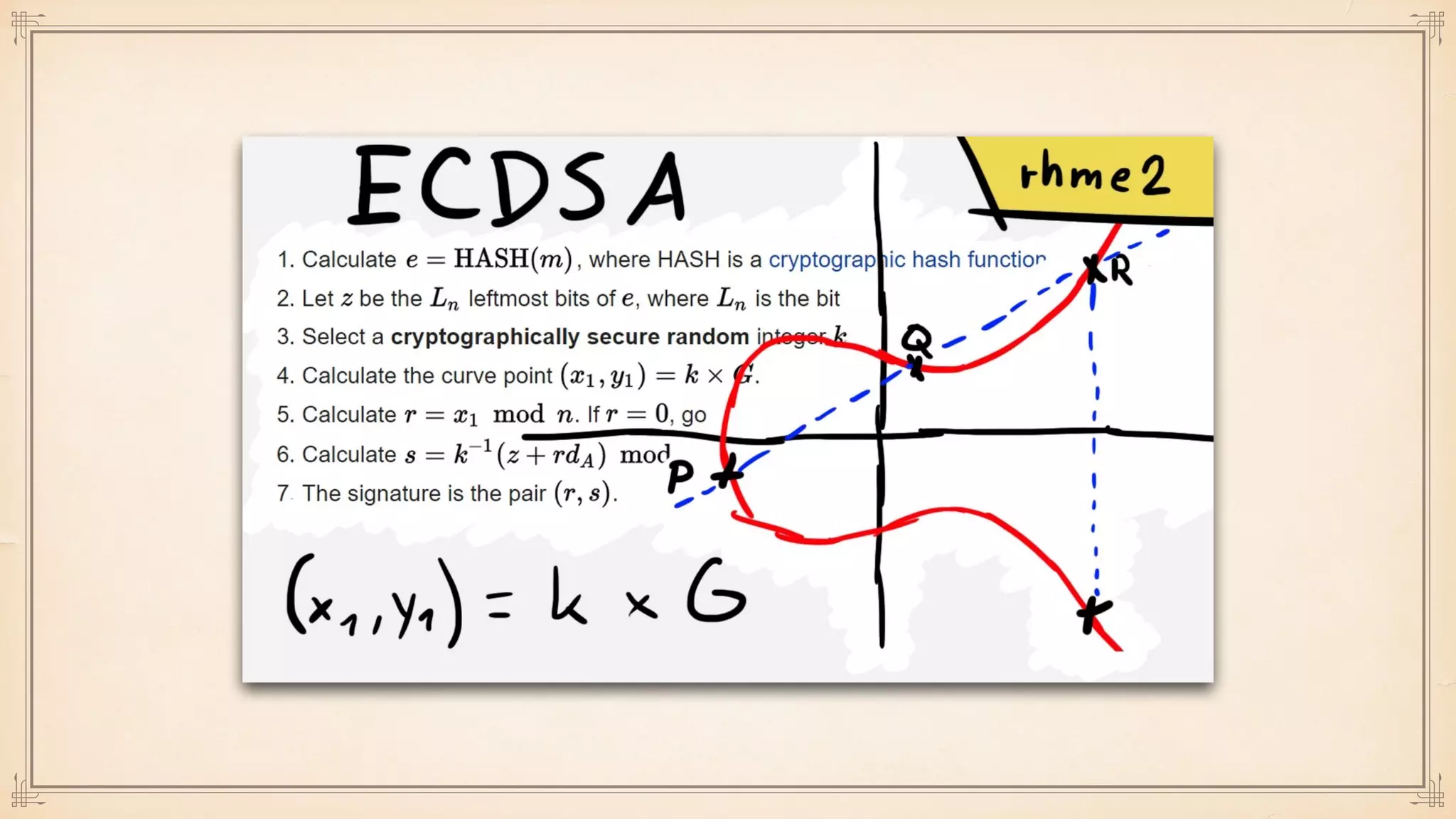
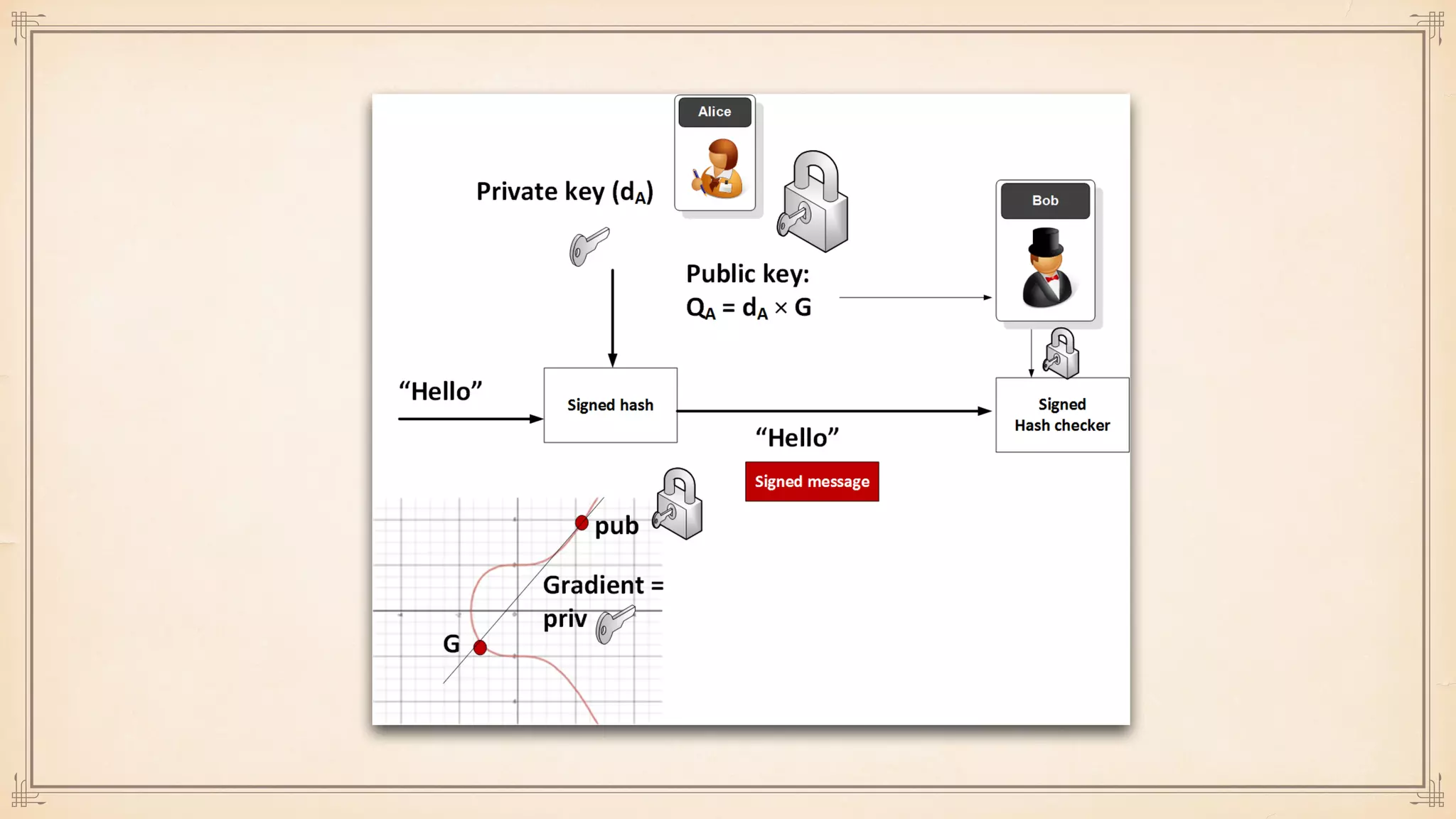
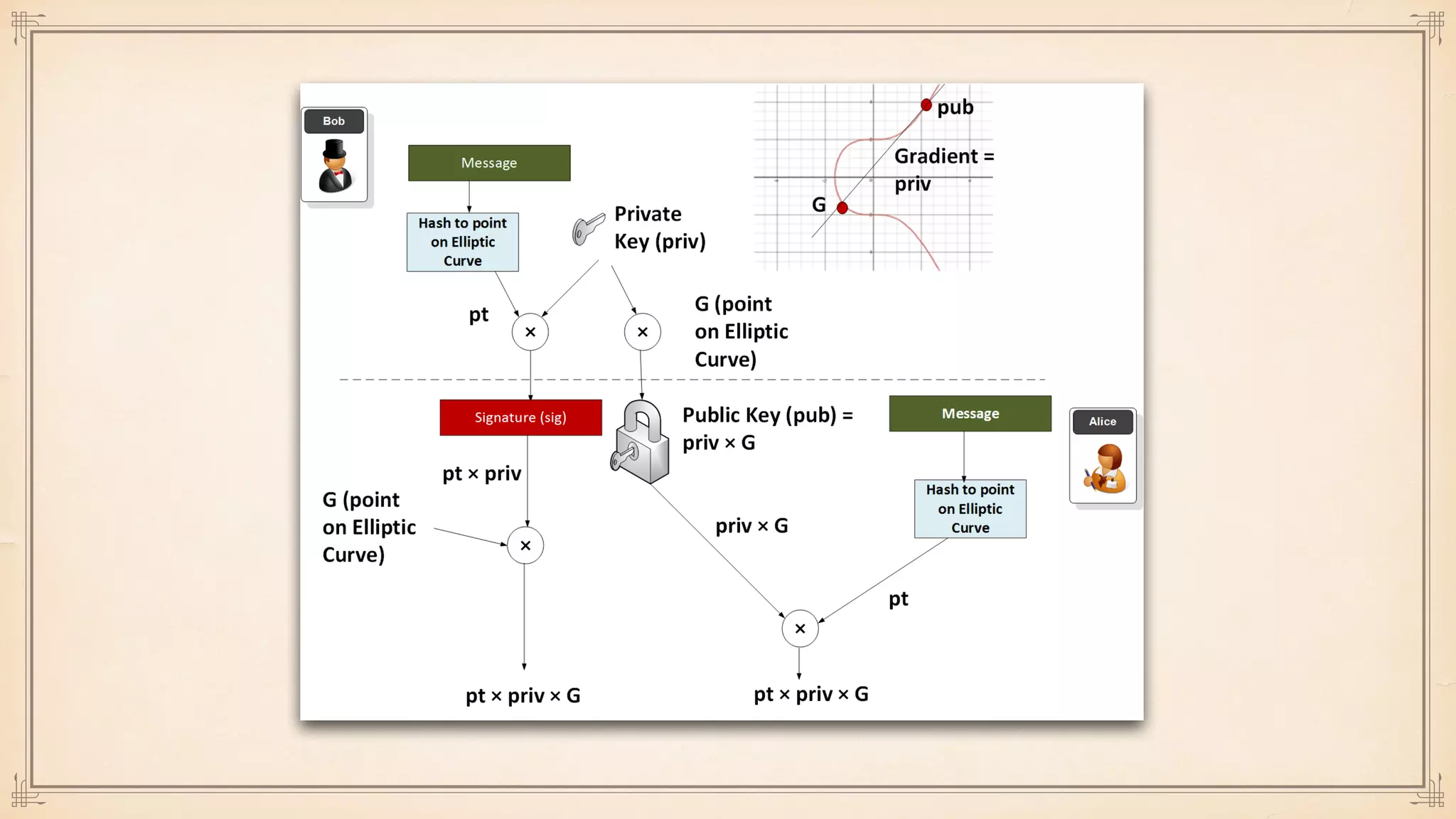
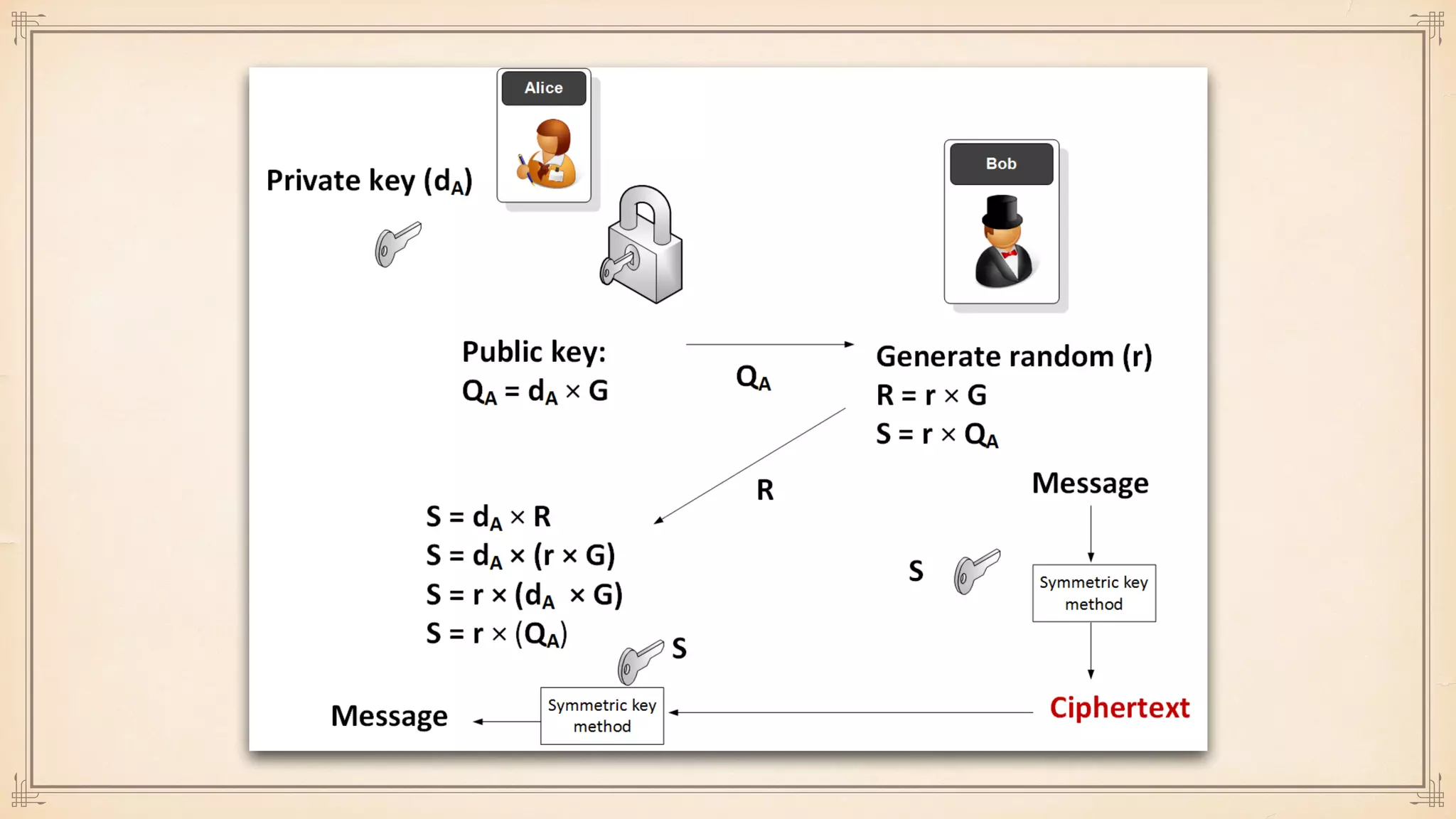
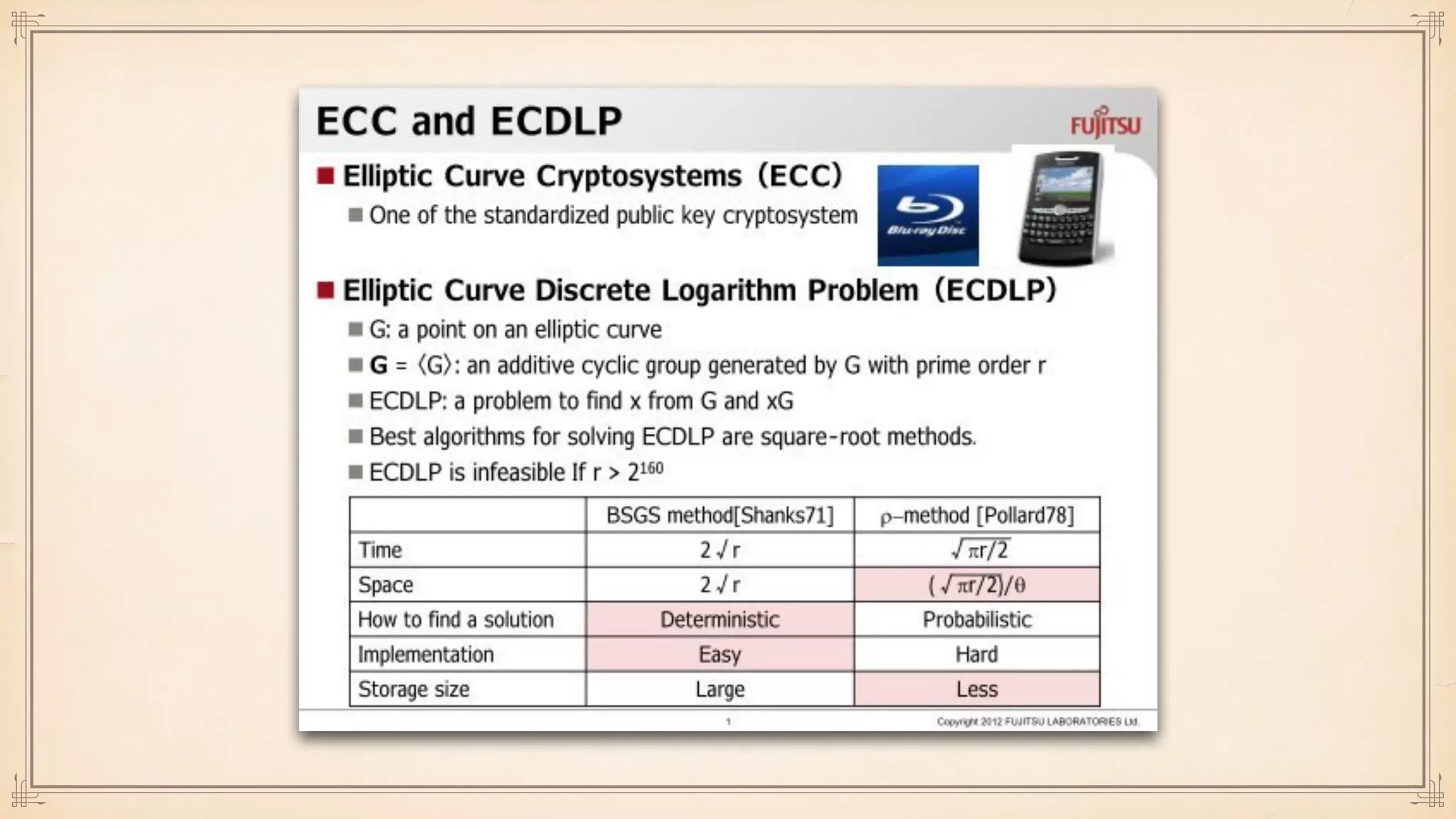
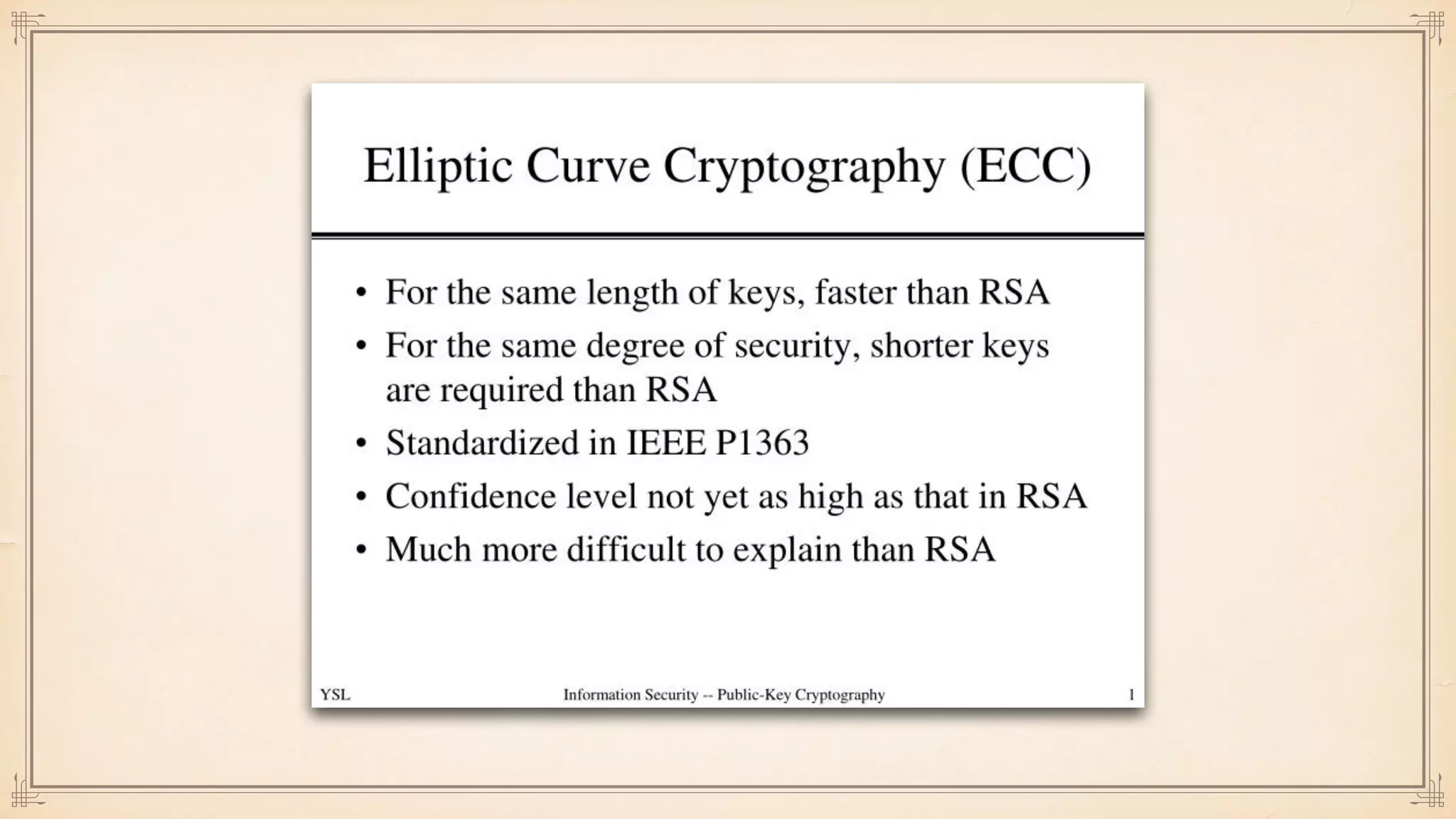
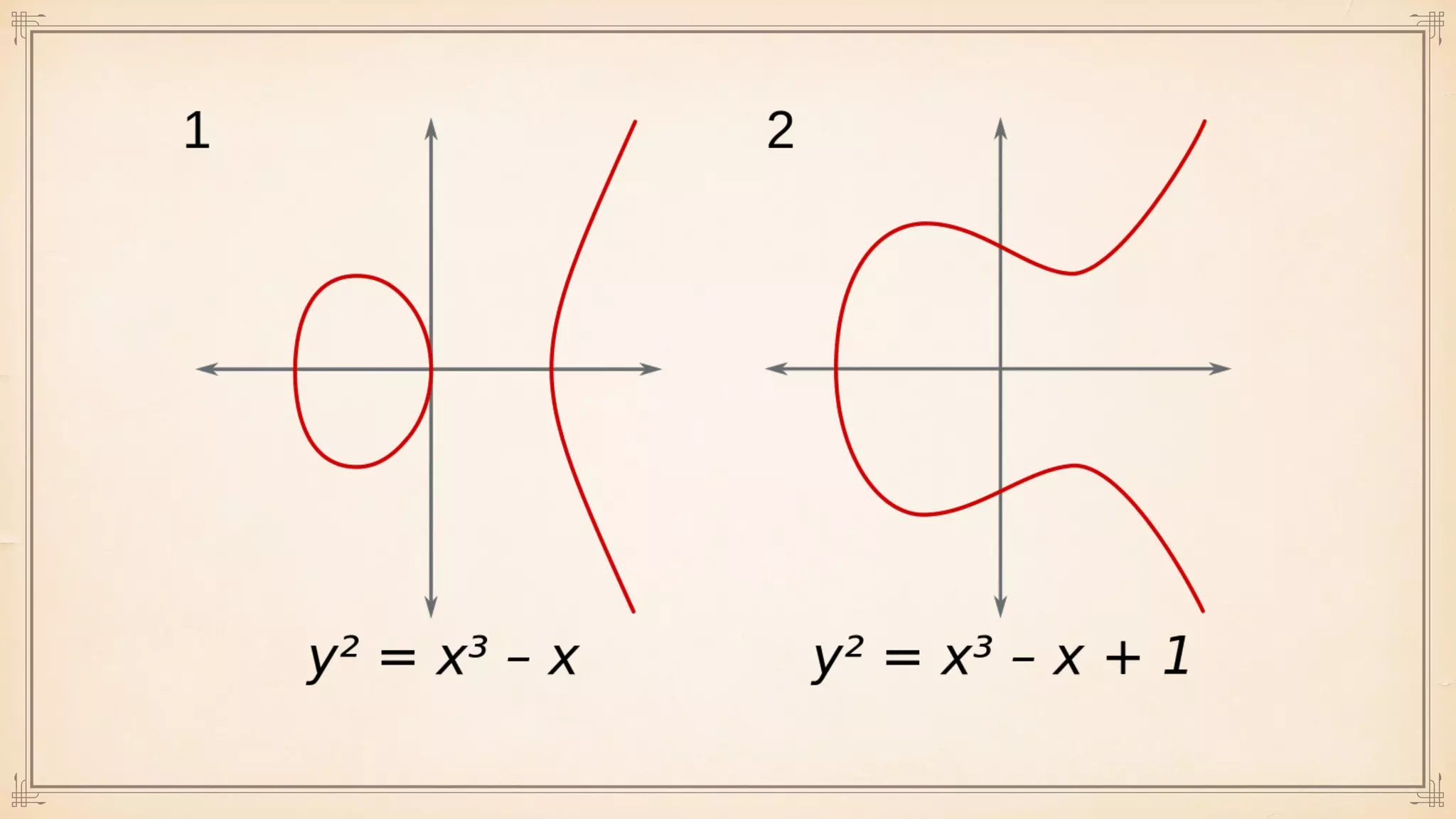The document discusses foundational and advanced concepts in applied cryptography, including various encryption methods such as symmetric and asymmetric cryptography, block and stream ciphers, and hash algorithms. It covers key historical figures and developments in cryptography, such as RSA encryption and elliptic curve cryptography, along with practical applications like multi-layer encryption and hybrid cryptography. Additionally, it provides examples of encryption techniques and their implementations.