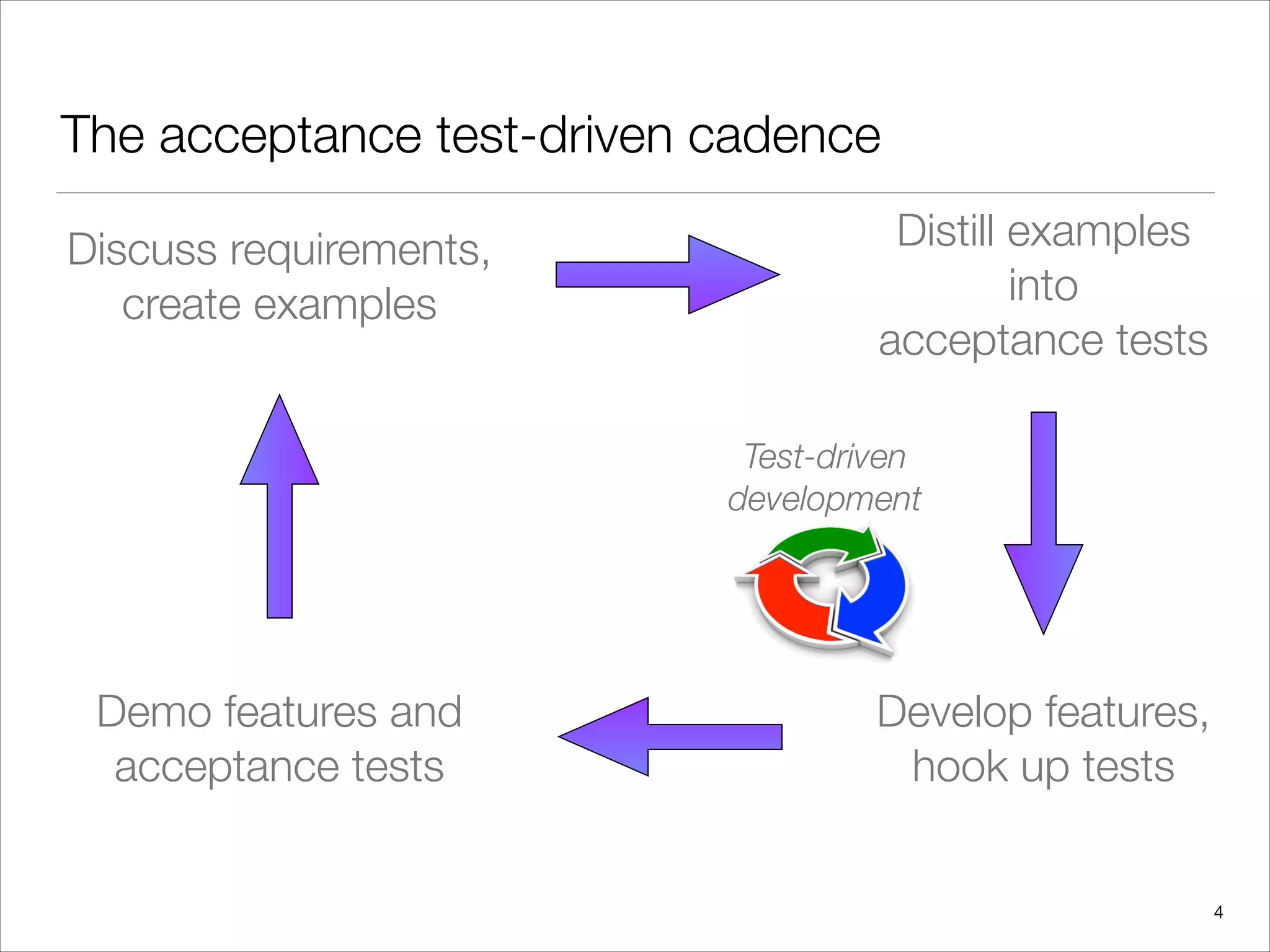
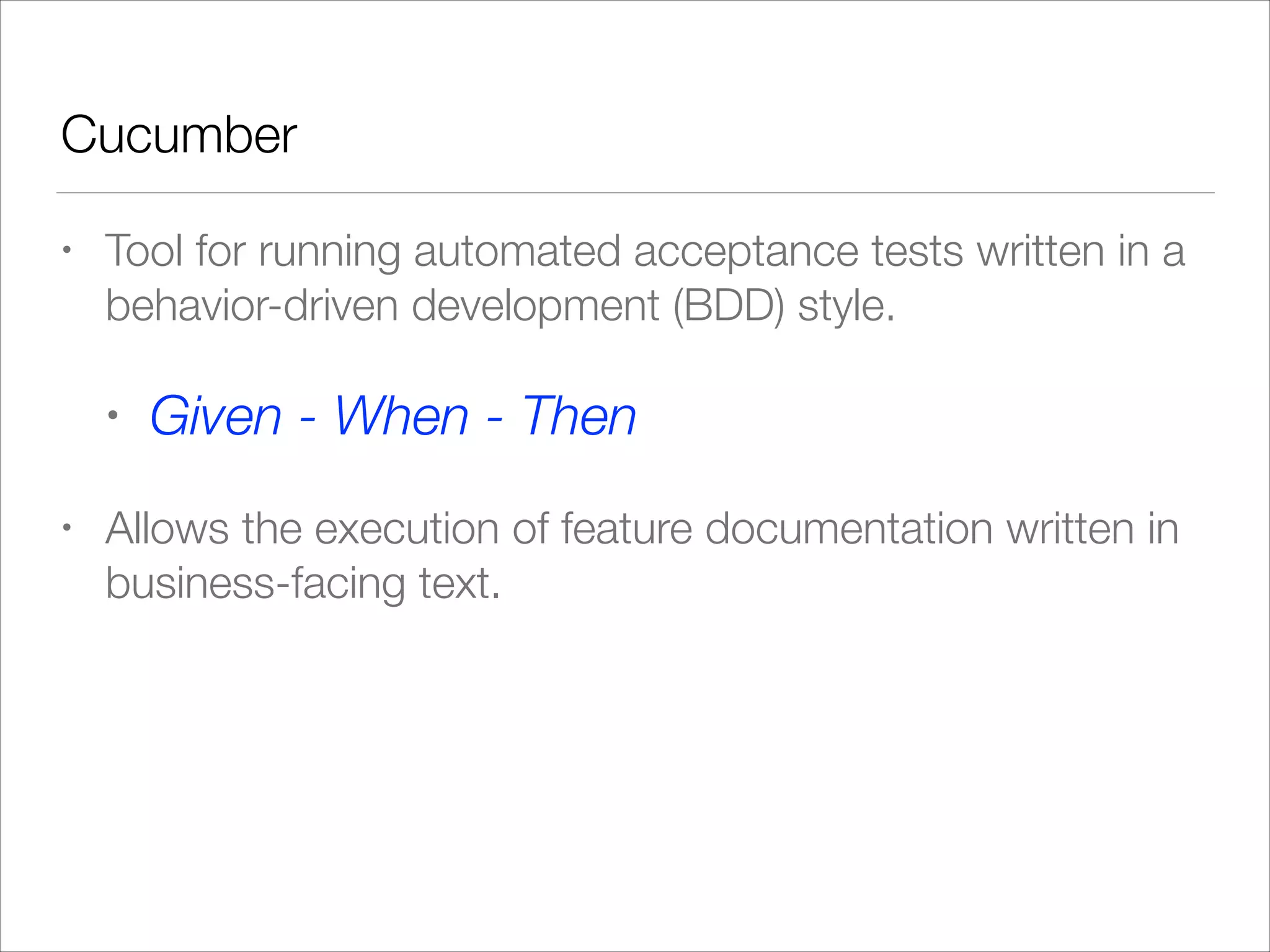
Acceptance Test-driven Development (ATDD) involves collaboratively discussing acceptance criteria and examples before development begins. These criteria and examples are then distilled into concrete acceptance tests. The team then develops software features while hooking them up to the acceptance tests. Finally, the features and successful acceptance tests are demoed. Cucumber is a tool that allows executing acceptance tests written in a behavior-driven style using a Given-When-Then format. Cucumber tests can automate interactions with a web application using tools like Selenium WebDriver.












![Cucumber step definitions
• The feature file “code-behind”.
• The executable part of Cucumber.
• Uses regular expressions to bind to feature file phrase.
When(~'^I click the "([^"]*)" navigation pill link$')
{ String navPillText ->
page.$('a', text: navPillText).click()
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acceptancetest-drivendevelopmentwithcucumber-jvm-140311214645-phpapp01/75/Acceptance-Test-driven-Development-with-Cucumber-jvm-16-2048.jpg)